Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
- Influence of silver nanoparticles on resin-dentin bond strength durability in a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive system
- Zahra Jowkar, Fereshteh Shafiei, Elham Asadmanesh, Fatemeh Koohpeima
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e13. Published online March 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of dentin pretreatment with silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and chlorhexidine (CHX) on the microshear bond strength (µSBS) durability of different adhesives to dentin.
Materials and Methods Occlusal surfaces of 120 human molars were ground to expose flat dentin surfaces. The specimens were randomly assigned to six groups (
n = 20). Three groups (A, B, and C) were bonded with Adper Single Bond 2 (SB) and the other groups (D, E, and F) were bonded with Clearfil SE Bond (SEB). Dentin was pretreated with CHX in groups B and E, and with SNPs in groups C and F. The specimens were restored with Z250 composite. Half of the bonded surfaces in each group underwent µSBS testing after 24 hours and the other half was tested after 6 months of water storage.Results SNP application was associated with a higher µSBS than was observed in the CHX and control groups for SEB after 24 hours (
p < 0.05). A significantly lower µSBS was observed when no dentin pretreatment was applied compared to dentin pretreatment with CHX and SNPs for SB after 24 hours (p < 0.05). The µSBS values of the 6-month specimens were significantly lower than those obtained from the 24-hour specimens for all groups (p < 0.05). This decrease was much more pronounced when both adhesives were used without any dentin pretreatment (p < 0.05).Conclusions SNPs and CHX reduced the degradation of resin-dentin bonds over a 6-month period for both adhesive systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Nanoparticle-enhanced dental adhesives: improving dentin bond strength through multifunctional nanotechnology
Suleiman Ibrahim Mohammad, Asokan Vasudevan, Lashin Saad Ali, Wenchang Chen
The Journal of Adhesion.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer: An In Vitro Study
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Dalal AlDabeeb
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(21): 9817. CrossRef - Performance of self-etching adhesives on caries-affected primary dentin treated with glutaraldehyde or silver diamine fluoride
Marcelly Tupan Christoffoli Wolowski, Andressa Mioto Stabile Grenier, Victória Alícia de Oliveira, Caroline Anselmi, Mariana Sversut Gibin, Lidiane Vizioli de Castro-Hoshino, Francielle Sato, Cristina Perez, Régis Henke Scheffel, Josimeri Hebling, Mauro L
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 150: 106293. CrossRef - The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles on Dentinal Tubule Penetration of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealer
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Amal Almohaimede, Nourah Alkhayatt, Shahad Alsulaiman, Salma Alohali
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11639. CrossRef - Effect of silver diamine fluoride on the longevity of the bonding properties to caries-affected dentine
LP Muniz, M Wendlinger, GD Cochinski, PHA Moreira, AFM Cardenas, TS Carvalho, AD Loguercio, A Reis, FSF Siqueira
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 143: 104897. CrossRef - Evaluation of Chitosan-Oleuropein Nanoparticles on the Durability of Dentin Bonding
Shuya Zhao, Yunyang Zhang, Yun Chen, Xianghui Xing, Yu Wang, Guofeng Wu
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2023; Volume 17: 167. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on the resin-dentin bond strength and antibacterial activity of a self-etch adhesive system
Jia Wang, Wei Jiang, Jingping Liang, Shujun Ran
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(6): 1363.e1. CrossRef - Marginal Integrity of Composite Restoration with and without Surface Pretreatment by Gold and Silver Nanoparticles vs Chlorhexidine: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Aya AEM Nemt-Allah, Shereen H Ibrahim, Amira F El-Zoghby
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1087. CrossRef - Effect of Cavity Disinfectants on Dentin Bond Strength and Clinical Success of Composite Restorations—A Systematic Review of In Vitro, In Situ and Clinical Studies
Ana Coelho, Inês Amaro, Beatriz Rascão, Inês Marcelino, Anabela Paula, José Saraiva, Gianrico Spagnuolo, Manuel Marques Ferreira, Carlos Miguel Marto, Eunice Carrilho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 22(1): 353. CrossRef
- An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
- 1,537 View
- 13 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Critical evaluation of fracture strength testing for endodontically treated teeth: a finite element analysis study
- Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Oğuz Eraslan, Sema Belli
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e15. Published online April 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
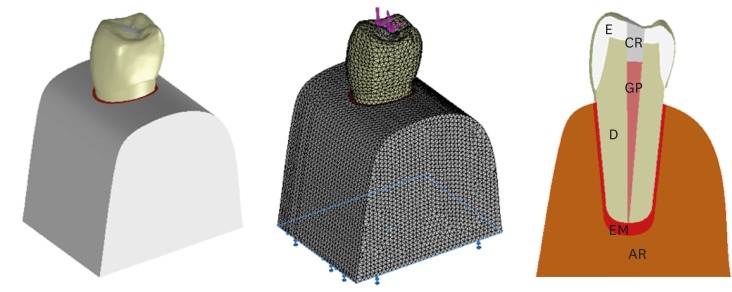
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate whether the diameter and direction of the plunger and simulation of the periodontal ligament (PDL) affected the stress distribution in endodontically treated premolars.
Methods A fracture strength test was simulated via finite element analysis. A base model was set up, and the following parameters were modified: plunger diameter (3 mm vs. 6 mm), plunger direction (vertical vs. 135° angular to the central fossa), and PDL simulation. The analysis was conducted using the CosmosWorks structural analysis program, and the results are presented in terms of von Mises stresses.
Results The smaller plunger increased the stresses at the contact area of the crown, but the plunger diameter had no effect on the stress distribution within the root. An angular plunger direction increased stresses within the root, as well as at the buccal cusp of the crown, compared with the vertical direction. Simulation of the PDL caused higher stress accumulation, especially in the cervical region of the root.
Conclusions The plunger diameter had no effect on the stress distribution in the roots, whereas the plunger direction and PDL simulation did affect the stress distribution. More stringent standards can be established by taking such parameters into account when performing fracture testing in future studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Access cavity in endodontics: Balancing precision, preservation, and clinical needs
Dina Abdellatif, Ismail Davut Capar, De Fontaine Sarah, Alfredo Iandolo, Christophe Meyer, Davide Mancino
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 573. CrossRef - Assessment of Stress Distribution with 3 Taper Design Preparation of Root Canal Using Finite Element Analysis
Tejasree Rathod, G. Durgabhavani, Pudu Tirupathi, Nusrath Parveen, Yelloji Paramesh, Prabhakar Dharavattu
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S112. CrossRef - The impact of the filling technique with two sealers in bulk or associated with gutta-percha on the fatigue behavior and failure patterns of endodontically treated teeth
Isabella Marian Lena, Luiza Colpo Chiaratti, Rafaela Oliveira Pilecco, Renan Vaz Machry, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Renata Dornelles Morgental
PeerJ.2024; 12: e18221. CrossRef - Stronger than Ever: Multifilament Fiberglass Posts Boost Maxillary Premolar Fracture Resistance
Naji Kharouf, Eugenio Pedullà, Gianluca Plotino, Hamdi Jmal, Mohammed-El-Habib Alloui, Philippine Simonis, Patrice Laquerriere, Valentina Macaluso, Dina Abdellatif, Raphaël Richert, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2975. CrossRef - Neural network approach to evaluate the physical properties of dentin
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Ali Mohammad Saghiri, Elham Samadi, Devyani Nath, Julia Vakhnovetsky, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2023; 111(1): 68. CrossRef - Modelling and evaluating periodontal ligament mechanical behaviour and properties: A scoping review of current approaches and limitations
Enaiyat Ghani Ovy, Dan L. Romanyk, Carlos Flores Mir, Lindsey Westover
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2022; 25(2): 199. CrossRef - FEAr no more! Finite element analysis in orthodontics
Shilpa Chawla, Shailesh Deshmukh
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2022; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - Influence of Methodological Variables on Fracture Strength Tests Results of Premolars with Different Number of Residual Walls. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Carlo Gaeta, Crystal Marruganti, Emanuele Mignosa, Giovanni Franciosi, Edoardo Ferrari, Simone Grandini
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 146. CrossRef
- Access cavity in endodontics: Balancing precision, preservation, and clinical needs
- 2,480 View
- 44 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Fused roots of maxillary molars: characterization and prevalence in a Latin American sub-population: a cone beam computed tomography study
- Maytté Marcano-Caldera, Jose Luis Mejia-Cardona, María del Pilar Blanco-Uribe, Elena Carolina Chaverra-Mesa, Didier Rodríguez-Lezama, Jose Hernán Parra-Sánchez
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e16. Published online April 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
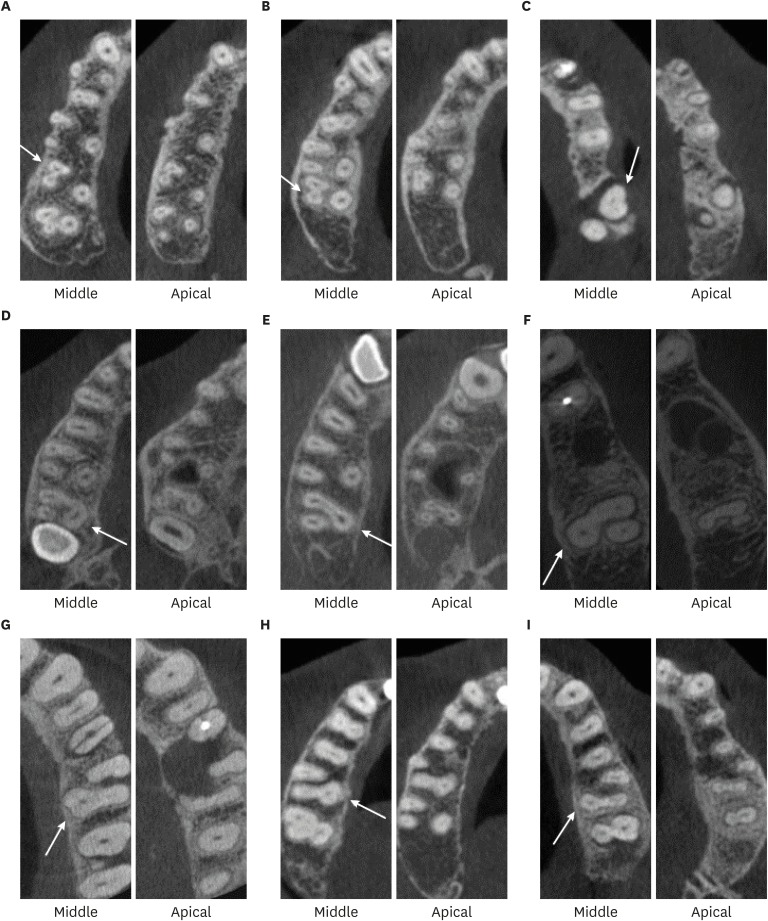
ePub Objectives The upper molars generally have three roots; therefore, different combinations of fusion can occur, increasing the possibility of finding more complex root canal systems. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and characterization of fused roots in first and second maxillary molars using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in a Colombian population.
Materials and Methods A total of 1274 teeth were evaluated, of which 534 were maxillary first molars and 740 were maxillary second molars. Axial sections were made at the cervical, middle, and apical levels to determine the prevalence of root fusion and the types of fusion.
Results Overall, 43% of the molars (
n = 551) presented some type of fused root. Root fusion was present in 23.4% of the maxillary first molars. The most frequent type of fused root was type 3 (distobuccal-palatal; DB-P) (58.9%). Root fusion was observed in 57.6% of the maxillary second molars, and the most prevalent type of fused root was type 6 (cone-shaped) (45.2%). Of the maxillary molars, 12.5% were classified as C-shaped.Conclusion Within the limitations of this study, there was a high prevalence of fused roots in maxillary molars in the Colombian population, mainly in the maxillary second molars. In first molars, the most common type of fused root was type 3 (DB-P) and in second molars, the most common type was type 6 (cone-shaped). Additionally, molars with root fusion presented variation at different levels of the radicular portion, with implications for treatment quality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intentional Tooth Replantation: Current Evidence and Future Research Directions for Case Selection, Extraction Approaches, and Post-Operative Management
Rahul Minesh Shah, Thomas Manders, Georgios Romanos
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(1): 59. CrossRef - Management of a rare bilateral maxillary first molar with six canals using a cone-beam computed tomography: Report of two cases
Aishwarya D. Jain, Nimisha Chinmay Shah, Abhya Jain, Shreya S. Volety
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 186. CrossRef - Assessment of root and root canal morphology in maxillary molars with fused roots using Cone Beam Computer Tomography (CBCT) in a Sri Lankan population
Ruvienath Daham Weerasinghe Rajapaksa, Manil Christopher Nishan Fonseka, Ruwan Duminda Jayasinghe, Rasika Manori Jayasinghe
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(6): 1297. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of root and canal morphology of maxillary molars in a Chinese kazakh population
Shuchun Yang, Chenye Li, Hui Shi, Ming Liu, Xu Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Twisted Tale of Dilacerated Fused Roots Mimicking Radicular Dens Invaginatus
Rashmi D Sathe, Preeti P. Nair, Richa Bajpai, Bidushi Mishra
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2025; 17(2): 214. CrossRef - Exploring the sex-associated differences in molars fused roots
Maria Eduarda Nunis Locks, Erika Calvano Küchler, Leonardo Santos Antunes, Alice Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Natanael Henrique Ribeiro Mattos, Camila Paiva Perin, Paulo Henrique Condeixa França, Peter Proff, Christian Kirschneck, Flares Baratto-Filho
Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger.2024; 254: 152245. CrossRef - Cone beam computed tomography analysis of the root and canal morphology of the maxillary second molars in a Syrian subpopulation
Safaa Allawi, Mouhammad Al-Tayyan, Hassan Achour, Eyad Al-Toutangy, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of root fusion in canine maxillary second molar teeth using cone-beam computed tomography
Kristin Linder, Scott MacGee, Loren Schultz
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentine thickness in maxillary fused molars depends on the fusion type: An ex vivo micro‐computed tomography study
Cangül Keskin, Defne Toplu, Ali Keleş
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(5): 637. CrossRef - Root and canal-specific features of maxillary first molars with fused roots
Katarina Beljic-Ivanovic, Branislav Karadzic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2022; 79(11): 1092. CrossRef - Micro-CT Analysis of the Root Canal Configuration of Maxillary Second Molars with Fusion
Cangül KESKİN, Özgür ÖZDEMİR, Ali KELEŞ
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(Suppl 1): 25. CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Root and Canal Morphology of Fused and Separate Rooted Maxillary Molar Teeth in Turkish Population
H Aydin
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2021; 24(3): 435. CrossRef - Investigating prevalence of dental anomalies in Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia through digital orthopantomogram
Jehan ALHumaid, Maryam Buholayka, Arishiya Thapasum, Muhanad Alhareky, Maha Abdelsalam, Amr Bughsan
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(5): 2900. CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars—A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence studies using cone beam computed tomography
Jorge N.R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 113: 104589. CrossRef
- Intentional Tooth Replantation: Current Evidence and Future Research Directions for Case Selection, Extraction Approaches, and Post-Operative Management
- 1,954 View
- 14 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Effects of the cathepsin K inhibitor with mineral trioxide aggregate cements on osteoclastic activity
- Hee-Sun Kim, Soojung Kim, Hyunjung Ko, Minju Song, Miri Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e17. Published online April 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
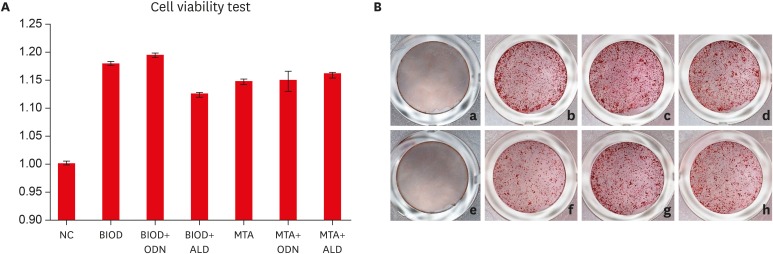
ePub Objectives Root resorption is an unexpected complication after replantation procedures. Combining anti-osteoclastic medicaments with retrograde root filling materials may avert this resorptive activity. The purpose of this study was to assess effects of a cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cements on osteoclastic activity.
Methods MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured for biocompatibility analyses. RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in the presence of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B and lipopolysaccharide, followed by treatment with Biodentine (BIOD) or ProRoot MTA with or without medicaments (Odanacatib [ODN], a cathepsin inhibitor and alendronate, a bisphosphonate). After drug treatment, the cell counting kit-8 assay and Alizarin red staining were performed to evaluate biocompatibility in MC3T3-E1 cells. Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed in RAW 264.7 cells to determine the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's
post hoc test (p < 0.05).Results Biocompatibility results showed that there were no significant differences among any of the groups. RAW 264.7 cells treated with BIOD and ODN showed the lowest levels of TNF-α and PGE2. Treatments with BIOD + ODN were more potent suppressors of inflammatory cytokine expression (
p < 0.05).Conclusion The cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cement inhibits osteoclastic activity. This may have clinical application in preventing inflammatory root resorption in replanted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Root-filling materials for endodontic surgery: biological and clinical aspects
Andreas Koutroulis, Vasileios Kapralos, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2024; 11: 115. CrossRef - Effect of intra‐alveolar delivery of Frondoside A on inflammatory response of delayed tooth replantation
Lan Herr, Ju Ri Ye, Sang Wook Kang, Sang Tae Ro, Yong Kwon Chae, Ko Eun Lee, Mi Sun Kim, Myeong Kwan Jih, Chunui Lee, Sung Chul Choi, Ok Hyung Nam
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(2): 178. CrossRef - Bone-targeting PLGA derived lipid drug delivery system ameliorates bone loss in osteoporotic ovariectomized rats
Youyun Zeng, Yiding Shen, Shuyi Wu, Lei Cai, Zhen Wang, Kexin Cai, Jiating Shen, Kendrick Hii Ru Yie, Hualin Zhang, Lihua Xu, Jinsong Liu
Materials & Design.2022; 221: 110967. CrossRef
- Root-filling materials for endodontic surgery: biological and clinical aspects
- 1,552 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomographic study of remaining filling materials of two bioceramic sealers and epoxy resin sealer after retreatment
- KyungJae Kim, Da Vin Kim, Sin-Young Kim, SungEun Yang
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e18. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This study evaluated the presence of residual root canal filling material after retreatment using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
Materials and Methods Extracted human teeth (single- and double-rooted,
n = 21/each; C-shaped,n = 15) were prepared with ProFile and randomly assigned to three subgroups for obturation with gutta-percha and three different sealers (EndoSeal MTA, EndoSequence BC sealer, and AH Plus). After 10 days, the filling material was removed and the root canals were instrumented one size up from the previous master apical file size. The teeth were scanned using micro-CT before and after retreatment. The percentage of remaining filling material after retreatment was calculated at the coronal, middle, and apical thirds. Data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-WhitneyU test with Bonferronipost hoc correction.Results The tested sealers showed no significant differences in the percentage of remaining filling material in single- and double-rooted teeth, although EndoSeal MTA showed the highest value in C-shaped roots (
p < 0.05). The percentage of remaining filling material of AH Plus and EndoSeal MTA was significantly higher in C-shaped roots than in single- or double-roots (p < 0.05), while that of BC sealer was similar across all root types. EndoSeal MTA showed the highest values at the apical thirds of single- and double-roots (p < 0.05); otherwise, no significant differences were observed among the coronal, middle, and apical thirds.Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, a large amount of EndoSeal MTA remained after retreatment, especially in C-shaped root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a deep neural network and empirical model for predicting local gas holdup profiles in bubble columns
Sebastián Uribe, Ahmed Alalou, Mario E. Cordero, Muthanna Al‐Dahhan
The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 103(6): 2918. CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparison of Epoxy Resin Sealer Removal During Endodontic Retreatment
Prashant A Bondarde, Aditi S Patkar, Aishwarya R Pawar, Rukmini Pande, Akshata Deshpande, Rachana S Agrawal, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(3): e25. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength of two endodontic sealers in retreated canals using different solvents
Sara Gamal Ghanem, Walaa M. Ghoneim, Ahmed H. Labib
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(3): 504. CrossRef - Assessing Volume of Two Sealers’ Remnants after Reinstrumentation Using 3D Imaging Technology: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Khalel Mutaz Dawod, Raghad Abdulrazzaq Al-Hashimi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(8): 743. CrossRef - Removal efficacy of two different root canal sealers in retrograde cavities: a micro-CT study
Özge Başar, Ahter Şanal Çıkman, Cangül Keskin
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the retreatability of bioceramic root canal sealers with various formulations in simulated grooves
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Abdulaziz Bakhsh, Hakan Arslan
PeerJ.2025; 13: e20398. CrossRef - Correlation of Bond Strength and Dentinal Tubule Penetration Evaluation of Four Different Endodontic Sealers: AH Plus, MTA Fillapex, Endoseal MTA, and Endoseal TCS (Maruchi): An In Vitro Study
Arezoo Mirzaei Sadeghloo, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Akam Saeidi, Elham Mahmoudi, Murilo Baena Lopes
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Root canal cleanliness and debris extrusion following retreatment of thermoplastic injection technique and bioceramic-based root canal sealer
Deniz Bender, Mert Ocak, Emel Uzunoğlu Özyürek
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Different Obturation Techniques Using Different Root Canal Sealers on the Residual Filling Material After Retreatment Procedures
M Sarı, K Yılmaz
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(2): 174. CrossRef - Effect of Different Obturation Techniques on the Amount of Debris Extrusion During Endodontic Retreatment Using XP Endo Retreatment Set Files (In vitro Study)
Pawan Mohamad Amin, Hawzhen Mohammed Saeed
Sulaimani Dental Journal.2023; 10: 49. CrossRef - The efficiency of different irrigation activation techniques in the removal of calcium silicate‐based endodontic sealer from artificially created groove
Meltem Sümbüllü, Afzal Ali, Mine Büker, Hakan Arslan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 238. CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser and ultrasonic‐activated irrigation in retreatment of gutta percha and bioceramic sealer: An in vitro study
Rahaf A. Almohareb, Reem M. Barakat, Noor Aljarallah, Halah Mudhish, Amjaad Almutairi, Fahda N. Algahtani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(2): 318. CrossRef - Efficiency of the new reciprocating and rotary systems with or without ultrasonics in removing root-canals filling with calcium silicate-based sealer (MTA)
Ahmad A. Madarati, Aya M. N. Sammani, Ahmad A. Alnazzawi, Ali Alrahlah
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Retreatability of calcium silicate‐based root canal sealer using reciprocating instrumentation with different irrigation activation techniques in single‐rooted canals
Daniele Angerame, Matteo De Biasi, Davide Porrelli, Lorenzo Bevilacqua, Riccardo Zanin, Matteo Olivi, Vassilios Kaitsas, Giovanni Olivi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(3): 415. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Efficacy of Er:YAG Laser-Activated Shock Wave-Enhanced Emission Photoacoustic Streaming Compared to Ultrasonically Activated Irrigation and Needle Irrigation in the Removal of Bioceramic Filling Remnants from Oval Root Canals—An Ex Vivo Study
Gabrijela Kapetanović Petričević, Marko Katić, Valentina Brzović Rajić, Ivica Anić, Ivona Bago
Bioengineering.2022; 9(12): 820. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of retreatability of a bioceramic and resin sealer using cone-beam computed tomography analysis
Sumit Sharma, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara, Harika Lakshmisetty, G. Bharath
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 173. CrossRef - Positive and negative properties of four endodontic sealant groups: a systematic review
E. V. Chestnyh, I. O. Larichkin, M. V. Iusufova, D. I. Oreshkina, E. I. Oreshkina, V. S. Minakova, S. V. Plekhanova
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2021; 28(3): 130. CrossRef - Retrievability of bioceramic-based sealers in comparison with epoxy resin-based sealer assessed using microcomputed tomography: A systematic review of laboratory-based studies
Buvaneshwari Arul, Aswathi Varghese, Anisha Mishra, Subashini Elango, Sairathna Padmanaban, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 421. CrossRef - Micro CT pilot evaluation of removability of two endodontic sealers
David Colmenar, Tenzin Tamula, Qiang Zhu, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2021; 63(4): 306. CrossRef - Comparison of Obturation Quality between Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers and Resin-Based Sealers for Endodontic Re-treatment
Hye-Ryeon Jin, Young-Eun Jang, Yemi Kim
Materials.2021; 15(1): 72. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Retreatment efficacy of hydraulic calcium silicate sealers used in single cone obturation
M. Garrib, J. Camilleri
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 98: 103370. CrossRef
- Development of a deep neural network and empirical model for predicting local gas holdup profiles in bubble columns
- 2,406 View
- 31 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of ProTaper Gold and EdgeEvolve files in canals with single- and double-curvature
- Wafaa A. Khalil, Zuhair S. Natto
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e19. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
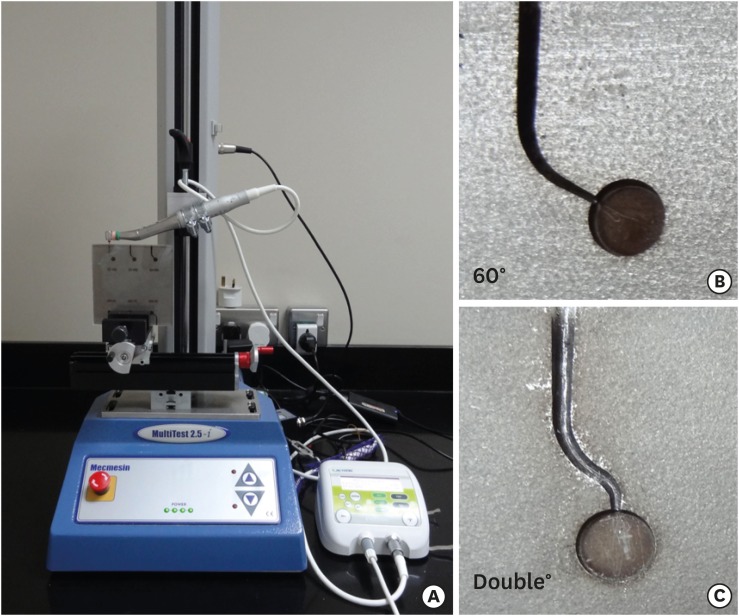
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of EdgeEvolve (EdgeEndo) and ProTaper Gold (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties) nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files.
Materials and Methods The instruments (
n = 15/each) were tested for cyclic fatigue in single- (60° curvature, 5-mm radius) and double-curved (coronal curvature 60°, 5-mm radius, and apical curvature of 30° and 2-mm radius) artificial canals. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated. The bending resistance of both files were tested using a universal testing machine where the files were bent until reach 45°. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray energy-dispersive spectrometric analysis were used for imaging the fractured segments, while the atomic force microscope was used to quantify the surface roughness average (Ra).Results EdgeEvolve files exhibited higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in single- and double-curved canals (
p < 0.05) and both files were more resistant to cyclic fatigue in single-curved canals than double-curved canals (p < 0.05). EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly more flexibility than did ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05). Both files had approximately similar Ni and Ti contents (p > 0.05). EdgeEvolve files showed significantly lower Ra values than ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitation of this study, EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in both single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
Mert Unal, Elif Bahar Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2026; 89(1): 87. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of alterations in surface topographies of three different rotary files after root canal preparation with different irrigating solutions: Atomic force microscopic study
PremSai Parepalli, TB. V G. Raju, PKrishna Prasad, GowtamDev Dondapati, VenkataSrija Kintada, Alekhya Mediboyina
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 299. CrossRef - Assessment of surface topographic changes of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic file at repeated usage: An in vitro study
E. Viswas, VSS Krishna, E. Sridevi, A. J. Sai Sankar, K. Siva Sankar, B. Nagesh
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 149. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Influence of nickel-titanium rotary systems with varying cross-sectional, pitch, and rotational speed on deflection and cyclic fatigue: a finite element analysis study
Wignyo Hadriyanto, Lukita Wardani, Christina Nugrohowati, Ananto Alhasyimi, Rachmat Sriwijaya, Margareta Rinastiti, Widowati Siswomihardjo, Gunadi, T. Yamada, A.A.C. Pramana, Y. Ophinni, A. Gusnanto, W.A. Kusuma, J. Yunus, Afiahayati, R. Dharmastiti, T.
BIO Web of Conferences.2021; 41: 05005. CrossRef - Can the Separated Instrument be Removed From the Root Canal System out by Magnetism? A Hypothesis
Mohammad Daryaeian, Sanjay Miglani, AbdolMahmood Davarpanah, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Mohsen Ramazani
Dental Hypotheses.2019; 10(4): 108. CrossRef - Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis
Raymond Scott, Ana Arias, José C. Macorra, Sanjay Govindjee, Ove A. Peters
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(3): 400. CrossRef
- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,546 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

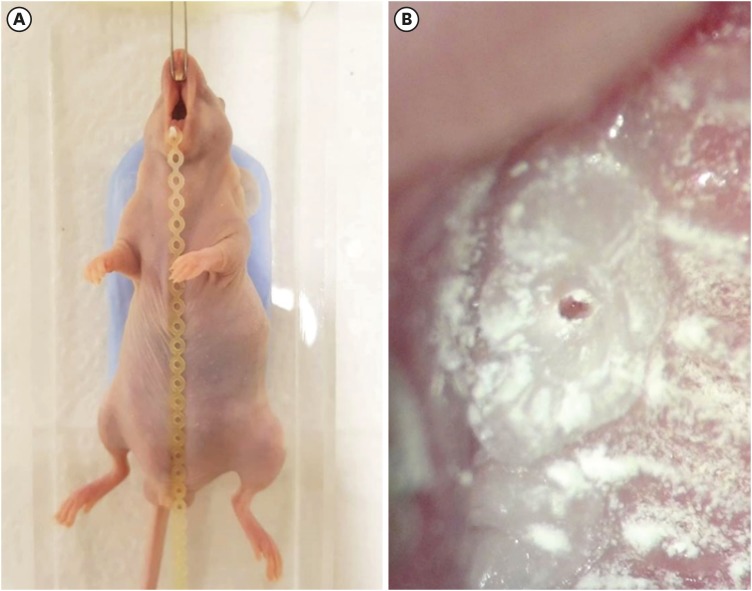
- Development of a mouse model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research: a preliminary study
- Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Han-Sung Jung, Sun-Young Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e20. Published online May 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To achieve pulp-dentin complex regeneration with tissue engineering, treatment efficacies and safeties should be evaluated using
in vivo orthotopic transplantation in a sufficient number of animals. Mice have been a species of choice in which to study stem cell biology in mammals. However, most pulp-dentin complex regeneration studies have used large animals because the mouse tooth is too small. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the utility of the mouse tooth as a transplantation model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research.Materials and Methods Experiments were performed using 7-week-old male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice; a total of 35 mice had their pulp exposed, and 5 mice each were sacrificed at 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, 12 and 14 days after pulp exposure. After decalcification in 5% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, the samples were embedded and cut with a microtome and then stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were observed under a high-magnification light microscope.
Results Until 1 week postoperatively, the tissue below the pulp chamber orifice appeared normal. The remaining coronal portion of the pulp tissue was inflammatory and necrotic. After 1 week postoperatively, inflammation and necrosis were apparent in the root canals inferior to the orifices. The specimens obtained after experimental day 14 showed necrosis of all tissue in the root canals.
Conclusions This study could provide opportunities for researchers performing
in vivo orthotopic transplantation experiments with mice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
Iago Ramirez, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula-Silva, Aline Aparecida Ferraresi Tiballi, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Christie Ramos Andrade Leite-Panissi, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 177: 106320. CrossRef - PRIASE 2021 guidelines for reporting animal studies in Endodontology: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, A. Kishen, P. E. Murray, M. H. Nekoofar, J. A. P. de Figueiredo, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, A. Jakovljevic, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(6): 858. CrossRef
- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
- 1,766 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

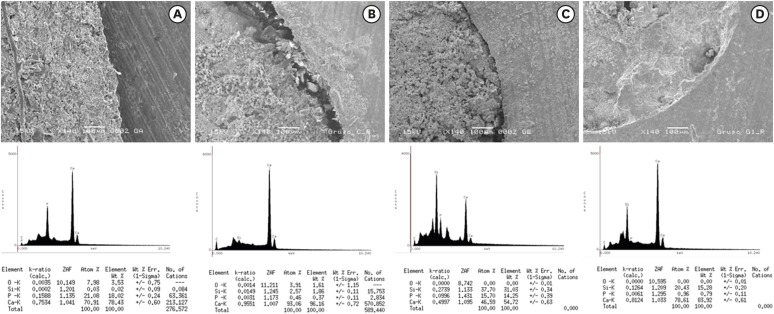
- Effect of intracanal medications on the interfacial properties of reparative cements
- Andrea Cardoso Pereira, Mariana Valerio Pallone, Marina Angélica Marciano, Karine Laura Cortellazzi, Marcos Frozoni, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Adriana de Jesus Soares
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e21. Published online May 9, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effect of calcium hydroxide with 2% chlorhexidine gel (HCX) or distilled water (HCA) compared to triple antibiotic paste (TAP) on push-out bond strength and the cement/dentin interface in canals sealed with White MTA Angelus (WMTA) or Biodentine (BD).
Materials and Methods A total of 70 extracted human lower premolars were endodontically prepared and randomly divided into 4 groups according to the intracanal medication, as follows: group 1, HCX; group 2, TAP; group 3, HCA; and group 4, control (without intracanal medication). After 7 days, the medications were removed and the cervical third of the specimens was sectioned into five 1-mm sections. The sections were then sealed with WMTA or BD as a reparative material. After 7 days in 100% humidity, a push-out bond strength test was performed. Elemental analysis was performed at the interface, using energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The data were statistically analyzed using analysis of variance and the Tukey test (
p < 0.05).Results BD presented a higher bond strength than WMTA (
p < 0.05). BD or WMTA in canals treated with calcium hydroxide intracanal medications had the highest bond strength values, with a statistically significant difference compared to TAP in the WMTA group (p < 0.05). There were small amounts of phosphorus in samples exposed to triple antibiotic paste, regardless of the coronal sealing.Conclusions The use of intracanal medications did not affect the bond strength of WMTA and BD, except when TAP was used with WMTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic treatment of teeth with a wide apical opening – a clinical case
V. A. Popov, E. S. Pestova, S. A. Anisimova
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(2): 282. CrossRef - Effects of calcium hydroxide intracanal medicament on push‐out bond strength of endodontic sealers: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Mohammed Nasser Alhajj, Fadhilah Daud, Sadeq Ali Al‐Maweri, Yanti Johari, Zuryati Ab‐Ghani, Mariatti Jaafar, Yoshihito Naito, Widyasri Prananingrum, Zaihan Ariffin
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(8): 1166. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Novel Tool for Apical Plug Formation during Apexification of Immature Teeth
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Line Droubi, Saleh Alkurdi, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Nada Bshara, Thuraya Lazkani, Chaza Kouchaji, Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Ziad D. Baghdadi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5304. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric analysis of internal bleaching of traumatized teeth with coronal discoloration following regenerative endodontic procedures
Jaqueline Lazzari, Walbert Vieira, Vanessa Pecorari, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Adriana De-Jesus-Soares
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Do intracanal medications used in regenerative endodontics affect the bond strength of powder-to-liquid and ready-to-use cervical sealing materials?
MarinaCarvalho Prado, Kevillin Martiniano, AndreaCardoso Pereira, KarineL Cortellazzi, MarinaA Marciano, Gabriel Abuna, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 464. CrossRef
- Endodontic treatment of teeth with a wide apical opening – a clinical case
- 1,541 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref

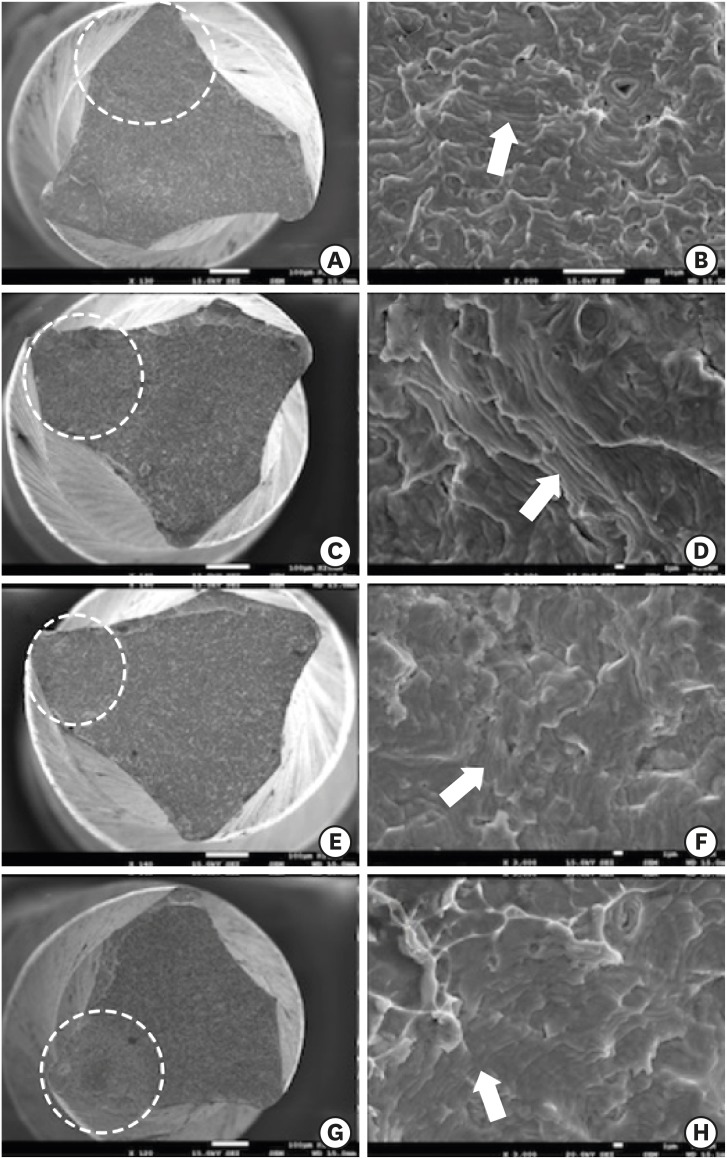
- Effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne nickel-titanium files
- Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e22. Published online May 9, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider nickel-titanium (NiTi) files on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne NiTi files.
Materials and Methods Forty-four WaveOne Primary files were used and divided into four groups (
n = 11). In the first group (0 WaveOne), the WaveOne Primary files served as a control group and were not used on acrylic blocks. In the 1 WaveOne Group, acrylic blocks were prepared using only WaveOne Primary files, and in the PF+WaveOne group and PG+WaveOne groups, acrylic blocks were first prepared with PathFile or ProGlider NiTi files, respectively, followed by the use of WaveOne Primary files. All the WaveOne Primary files were then subjected to cyclic fatigue testing. The number of cycles to failure was calculated and the data were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey honest significant difference multiple-comparison test at a 5% significance level.Results The highest number of cycles to failure was found in the control group, and the lowest numbers were found in the 1 WaveOne group and the PF+WaveOne group. Significant differences were found among the 1 WaveOne, PF+WaveOne, and control groups (
p < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were found between the PG+WaveOne group and the other three groups (p > 0.05).Conclusion Glide path preparation with NiTi rotary files did not affect the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne Primary files used on acrylic blocks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of glide path instruments in cyclic fatigue resistance of reciprocating instruments after three uses
André Schroder Scherer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, José Roberto Vanni
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(2): 27. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Evaluation of Cyclic Fatigue of Hyflex EDM, Twisted Files, and ProTaper Gold Manufactured with Different Processes: An In Vitro Study
Pooja D. Khandagale, Prashant P. Shetty, Saleem D. Makandar, Pradeep A. Bapna, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Pietro Messina, Giuseppe Alessandro Scardina, Antonino Lo Giudice
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
- 1,730 View
- 10 Download
- 6 Crossref

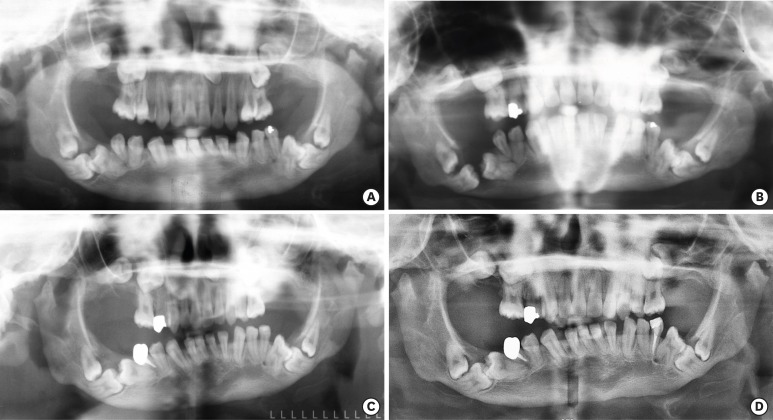
- Oral manifestation and root canal therapy of the patient with mucopolysaccharidosis
- Ji-Hye Yoon, Hyo-Il Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e14. Published online April 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency in enzymes that participate in the degradation of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) such as heparin sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Left untreated, patients show progressive mental and physical deterioration due to deposition of GAGs in organs. Death often occurs due to cardiac or respiratory failure before patients reach their early twenties. MPS has several oral and dental manifestations. An enlarged head, short neck, and open mouth associated with a large tongue are major characteristics of MPS patients. Dental complications can be severe, including unerupted dentition, dentigerous cyst-like follicles, malocclusions, condylar defects, and gingival hyperplasia. A 21-year-old female patient with MPS was described in this article, with special emphasis on oral manifestations and dental treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric Interventions in a Sanfilippo Syndrome Patient Under General Anesthesia: A Case Report
Ahmad Al Malak, Hassan Issawi, Mohammad Hassoun, Mohammad Al Halabi, Darko Macan
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioural disorders and sleep problems in Sanfilippo syndrome: overlaps with some other conditions and importance indications
Karolina Wiśniewska, Jakub Wolski, Paulina Anikiej-Wiczenbach, Magdalena Żabińska, Grzegorz Węgrzyn, Karolina Pierzynowska
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.2025; 34(6): 1795. CrossRef - Hurler syndrome: Oral and radiographic findings of a rare clinical case
W. Kabbassi, H. Hessissen, J. Hammouti
Medical Reports.2025; 14: 100325. CrossRef - Sanfilippo syndrome: consensus guidelines for clinical care
Nicole Muschol, Roberto Giugliani, Simon A. Jones, Joseph Muenzer, Nicholas J. C. Smith, Chester B. Whitley, Megan Donnell, Elise Drake, Kristina Elvidge, Lisa Melton, Cara O’Neill
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Manifestaciones bucales de pacientes con mucopolisacaridosis. Serie de casos
Andrea Verónica Ríos, Mariana Llorensi
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Pediatric Interventions in a Sanfilippo Syndrome Patient Under General Anesthesia: A Case Report
- 1,632 View
- 7 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KACD
KACD



 First
First Prev
Prev


