-
Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
-
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):286-289. Published online September 2, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.286
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
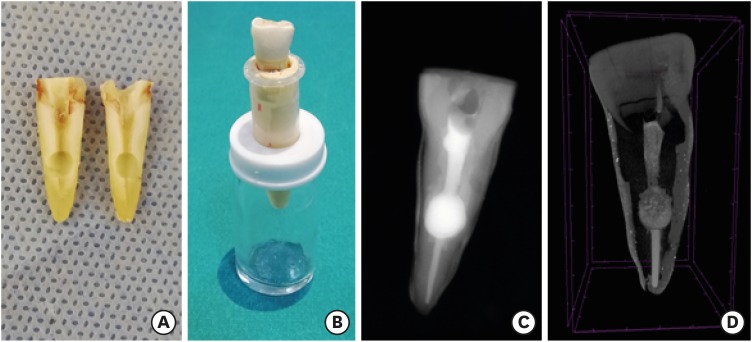
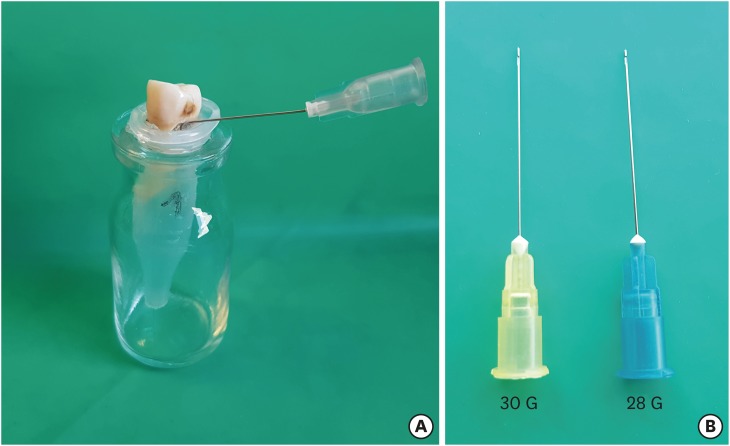
The aim was to evaluate dentinal crack formation after root canal preparation with ProTaper Next system (PTN) with and without a glide path. Materials and MethodsForty-five mesial roots of mandibular first molars were selected. Fifteen teeth were left unprepared and served as controls. The experimental groups consist of mesiobuccal and mesiolingual root canals of remaining 30 teeth, which were divided into 2 groups (n = 15): Group PG/PTN, glide path was created with ProGlider (PG) and then canals were shaped with PTN system; Group PTN, glide path was not prepared and canals were shaped with PTN system only. All roots were sectioned perpendicular to the long axis at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 mm from the apex, and the sections were observed under a stereomicroscope. The presence/absence of cracks was recorded. Data were analyzed with chi-square tests with Yates correction. ResultsThere were no significant differences in crack formation between the PTN with and without glide path preparation. The incidence of cracks observed in PG/PTN and PTN groups was 17.8% and 28.9%, respectively. ConclusionsThe creation of a glide path with ProGlider before ProTaper Next rotary system did not influence dentinal crack formation in root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of the Recent, Fifth-generation ProTaper Next and Revo-S NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files Using Three-dimensional Imaging: An Imaging-based Study
Prajna Pattanaik, Akilan Balasubramanian, P. Veeralakshmi, Gautam Singh, Vandana Sadananda, Hina Ahmed, J. Suresh Babu, C. Swarnalatha, Abhishek Singh Nayyar
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Microscopic Assessment of Dentinal Defects Induced by ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and Hyflex Electric Discharge Machining Rotary File Systems – An in vitro Study
Takhellambam Premlata Devi, Amandeep Kaur, Shamurailatpam Priyadarshini, B. S. Deepak, Sumita Banerjee, Ng Sanjeeta
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 230. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef
-
190
View
-
2
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Effects of dentin moisture on the push-out bond strength of a fiber post luted with different self-adhesive resin cements
-
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu, Zeliha Yılmaz
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):234-240. Published online November 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.234
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the effects of intraradicular moisture on the pushout bond strength of a fibre post luted with several self-adhesive resin cements. Materials and MethodsEndodontically treated root canals were treated with one of three luting cements: (1) RelyX U100, (2) Clearfil SA, and (3) G-Cem. Roots were then divided into four subgroups according to the moisture condition tested: (I) dry: excess water removed with paper points followed by dehydration with 95% ethanol, (II) normal moisture: canals blot-dried with paper points until appearing dry, (III) moist: canals dried by low vacuum using a Luer adapter, and (IV) wet: canals remained totally flooded. Two 1-mm-thick slices were obtained from each root sample and bond strength was measured using a push-out test setup. The data were analysed using a two-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni post hoc test with p = 0.05. ResultsStatistical analysis demonstrated that moisture levels had a significant effect on the bond strength of luting cements (p < 0.05), with the exception of G-Cem. RelyX U100 displayed the highest bond strength under moist conditions (III). Clearfil SA had the highest bond strength under normal moisture conditions (II). Statistical ranking of bond strength values was as follows: RelyX U100 > Clearfil SA > G-Cem. ConclusionsThe degree of residual moisture significantly affected the adhesion of luting cements to radicular dentine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Dentin bond strength of resin luting agents under a simulated intra-oral environment
Takashi Washino, Hanemi Tsuruta, Masaomi Ikeda, Michael F. Burrow, Toru Nikaido
Asian Pacific Journal of Dentistry.2024; 24(2): 13. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of dentin moisture on the adhesive properties of luting fiber posts using adhesive strategies
Renata Terumi JITUMORI, Rafaela Caroline RODRIGUES, Alessandra REIS, João Carlos GOMES, Giovana Mongruel GOMES
Brazilian Oral Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of different intraradicular chemical pretreatments on the bond strength of adhesive interface between dentine and fiber post cements: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Ana Luiza Barbosa Jurema, Ayla Macyelle de Oliveira Correia, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SELF ADEZİV REZİN SİMANLAR / SELF ADHESIVE RESIN CEMENTS
Kübra AMAÇ, Engin ESENTÜRK, Bilge TURHAN BAL
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Postspace pretreatment with 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7% maleic acid, and 1% phytic acid on bond strength of fiber posts luted with a self-adhesive resin cement
PriyaC Yadav, Ramya Raghu, Ashish Shetty, Subhashini Rajasekhara
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(6): 558. CrossRef - Development and characterization of biological bovine dentin posts
Alice Gonçalves Penelas, Eduardo Moreira da Silva, Laiza Tatiana Poskus, Amanda Cypriano Alves, Isis Ingrid Nogueira Simões, Viviane Hass, José Guilherme Antunes Guimarães
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 92: 197. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of time and concentration of sodium hypochlorite on the bond strength of glass fibre post
Beau Knight, Robert M. Love, Roy George
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(3): 267. CrossRef - Test methods for bond strength of glass fiber posts to dentin: A review
F. C. Dos Santos, M. D. Banea, H. L. Carlo, S. De Barros
The Journal of Adhesion.2017; 93(1-2): 159. CrossRef - Is the bonding of self-adhesive cement sensitive to root region and curing mode?
Thaynara Faelly BOING, Giovana Mongruel GOMES, João Carlos GOMES, Alessandra REIS, Osnara Maria Mongruel GOMES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(1): 2. CrossRef - A Twofold Comparison between Dual Cure Resin Modified Cement and Glass Ionomer Cement for Orthodontic Band Cementation
Hanaa El Attar, Omnia Elhiny, Ghada Salem, Ahmed Abdelrahman, Mazen Attia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2016; 4(4): 695. CrossRef - Shear bond strengths of various self-adhesive resin cements between bovine dentin and 4 types of adherends
Ah-Jin Kim, Da-Ryeong Park, Seunghan Oh, Ji-Myung Bae
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(4): 365. CrossRef
-
216
View
-
1
Download
-
13
Crossref
|