-
The effectiveness of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e37. Published online June 18, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
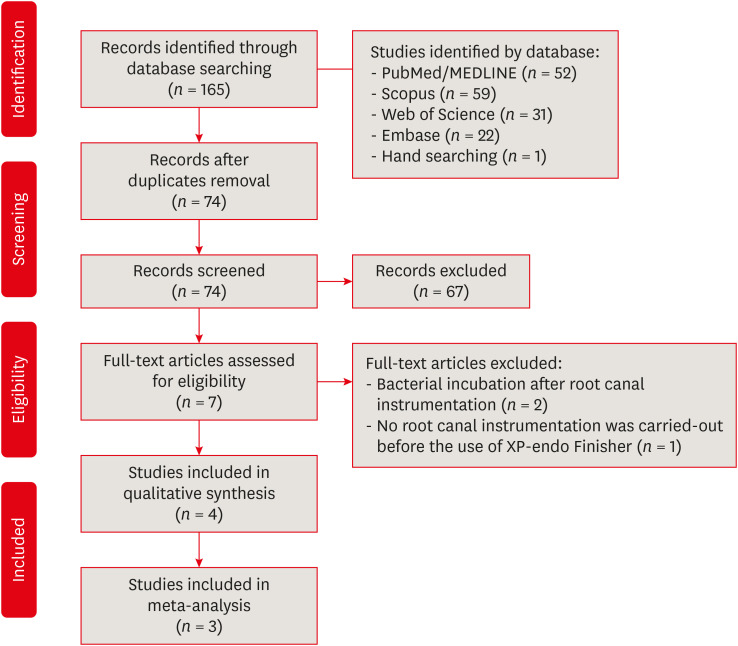
This systematic review evaluated the efficacy of the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content reduction in the root canal system. Materials and MethodsIn-vitro studies evaluating the use of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria content were searched in four databases in July 2020. Two authors independently screened the studies for eligibility. Data were extracted, and risk of bias was assessed. Data were meta-analyzed by using random-effects model to compare the effect of the supplementary use (experimental) or not (control) of the XP-endo Finisher on bacteria counting reduction, and results from different endodontic protocols were combined. Four studies met the inclusion criteria while 1 study was excluded from the meta-analysis due to its high risk of bias and outlier data. The 3 studies that made it to the meta-analysis had an unclear risk of bias for at least one criterion. ResultsNo heterogeneity was observed among the results of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The study excluded from the meta-analysis assessing the bacteria counting deep in the dentin demonstrated further bacteria reduction upon the use of the XP-endo Finisher. ConclusionsThis systematic review found no evidence supporting the supplementary use of the XP-endo Finisher on further bacteria counting the reduction in the root canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP‐Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
Sarah M. Alkahtany, Rana Alfadhel, Aseel AlOmair, Sarah Bin Durayhim, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact XP-endo finisher on the 1-year follow-up success of posterior root canal treatments: a randomized clinical trial
Ludmila Smith de Jesus Oliveira, Fabricio Eneas Diniz de Figueiredo, Janaina Araújo Dantas, Maria Amália Gonzaga Ribeiro, Carlos Estrela, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(12): 7595. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of modern irrigants activation techniques in the process of mechanical root canal system treatment (Literature review)
Anatoliy Potapchuk, Vasyl Almashi, Arsenii Horzov, Victor Buleza
InterConf.2023; (34(159)): 200. CrossRef - Methodological quality assessment criteria for the evaluation of laboratory‐based studies included in systematic reviews within the specialty of Endodontology: A development protocol
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul V. Abbott, Christos Boutsioukis, Henry F. Duncan, Clovis M. Faggion, Anil Kishen, Peter E. Murray, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(4): 326. CrossRef
-
287
View
-
10
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
Color assessment of resin composite by using cellphone images compared with a spectrophotometer
-
Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Rafael Ratto Moraes, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e23. Published online April 5, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e23
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
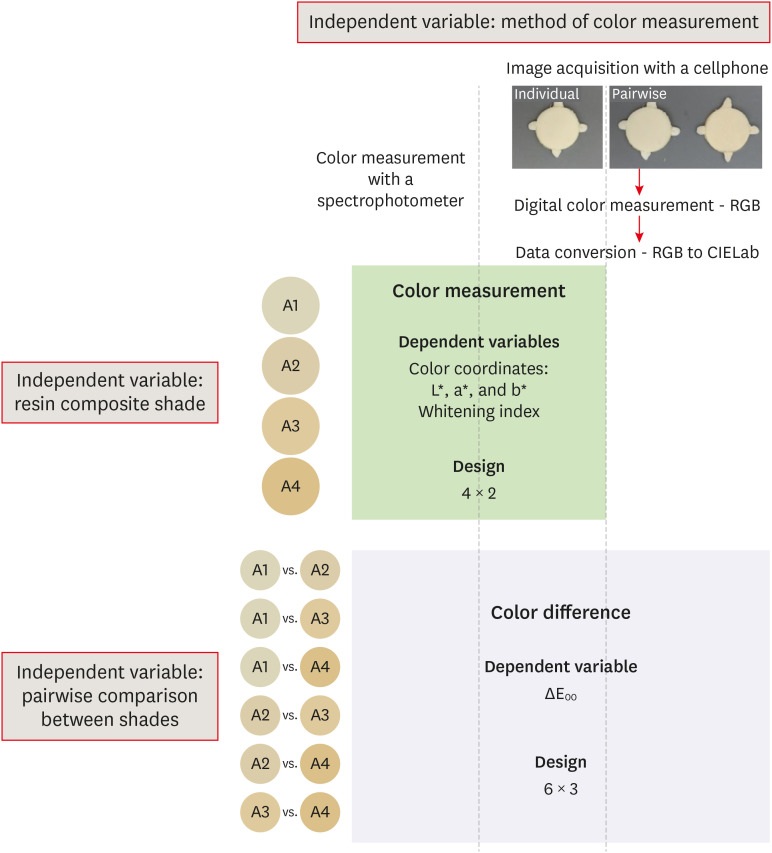
This study assessed the reliability of digital color measurements using images of resin composite specimens captured with a cellphone. Materials and MethodsThe reference color of cylindrical specimens built-up with the use of resin composite (shades A1, A2, A3, and A4) was measured with a portable spectrophotometer (CIELab). Images of the specimens were obtained individually or pairwise (compared shades in the same photograph) under standardized parameters. The color of the specimens was measured in the images using RGB system and converted to CIELab system using image processing software. Whiteness index (WID) and color differences (ΔE00) were calculated for each color measurement method. For the cellphone, the ΔE00 was calculated between the pairs of shades in separate images and in the same image. Data were analyzed using 2-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (α = 0.05). Linear regression models were used to predict the reference ΔE00 values of those calculated using color measured in the images. ResultsImages captured with the cellphone resulted in different WID values from the spectrophotometer only for shades A3 and A4. No difference to the reference ΔE00 was observed when individual images were used. In general, a similar ranking of ΔE00 among resin composite shades was observed for all methods. Stronger correlation coefficients with the reference ΔE00 were observed using individual than pairwise images. ConclusionsThis study showed that the use of cellphone images to measure the color difference seems to be a feasible alternative providing outcomes similar to those obtained with the spectrophotometer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of color stability in single-shade composite resins using spectrophotometer and cross-polarized mobile photography
Hatice Tepe, Ozge Celiksoz, Batu Can Yaman
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How the Translucency and Color Stability of Single-Shade Universal Resin Composites Are Affected by Coffee?
Büşra Özdemir, Betül Kübra Kurucu Karadeniz, Seyit Bilal Özdemir, Ömer Akbulut
Current Research in Dental Sciences.2024; 34(4): 270. CrossRef - Color Image Expression through CIE L*a*b* System in Foods
Hyun-Woong Choi, Seong-Eun Park, Hong-Seok Son
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(2): 223. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of VITA Shade Guide and Various Composite Shades Using Spectrophotometer, Digital Single-lens Reflex, and Cellphone: An In Vitro Study
Aman Verma, Sonali Taneja, Surabhi Ghosh
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 803. CrossRef - Comparison of instrumental methods for color change assessment of Giomer resins
Luiza de Almeida Queiroz Ferreira, Rogéli Tibúrcio Ribeiro da Cunha Peixoto, Cláudia Silami de Magalhães, Tassiana Melo Sá, Monica Yamauti, Francisca Daniele Moreira Jardilino
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
383
View
-
7
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
|