-
Can silver diamine fluoride or silver nanoparticle-based anticaries agents to affect enamel bond strength?
-
Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Yana Cosendey Toledo de Mello Peixoto, Omar Geha, Flaviana Alves Dias, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e7. Published online January 12, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
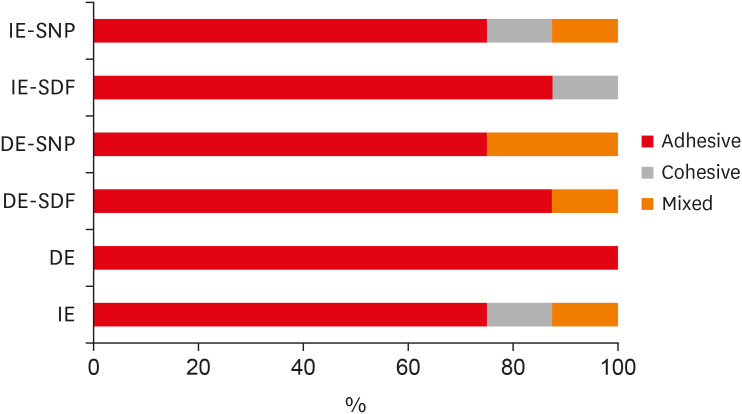
The aim of the current study is to investigate the effect of different anticaries agents, such as experimental agents based on silver nanoparticles (SNPs) and silver diamine fluoride (SDF), on the micro-shear bond strength (μ-SBS) of composite resin applied to intact enamel (IE) or demineralized enamel (DE). Materials and MethodsSixty dental enamel fragments were collected from human third molars and categorized into 6 groups (n = 10): positive control (IE), negative control (DE), IE + SDF, DE + SDF, IE + SNP and DE + SNP. Samples from DE, DE + SDF and DE + SNP groups were subjected to pH cycling; superficial microhardness test was performed to confirm demineralization. Resin composite build-ups were applied to the samples (0.75-mm diameter and 1-mm height) after the treatments (except for IE and DE groups); μ-SBS was also evaluated. Samples were analyzed under a stereomicroscope at 40× magnification to identify failure patterns. Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey's and Dunnett's tests (p < 0.05). ResultsThere was no significant difference among the IE, IE + SNP, DE + SDF, and DE + SNP groups. The IE + SDF and DE groups recorded the highest and the lowest μ-SBS values, respectively. Adhesive-type failures were the most frequent for all treatments. ConclusionsAnticaries agents did not have a negative effect on the μ-SBS of composite resin when it was used on IE or DE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of Incorporating Nanoparticles to Adhesive Resin on the Demineralization of Enamel: A Systematic Review
Naif Almosa
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(3): 89. CrossRef - Preventing white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets: efficacy of pre-reacted glass-ionomer barrier coat versus silver diamine fluoride: an in vitro study
Enas A. Elshenawy, Safa B. Alawy, Wafaa Yahia Alghonemy, Ahmed Ibrahime El dosoky
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Status of Silver Nanoparticles for Dental Applications
Yanyan Guo, Xiaomei Hou, Sanjun Fan, Chanyuan Jin
Inorganics.2025; 13(5): 168. CrossRef - The use of silver diamine fluoride to prevent/treat enamel carious lesions: a narrative review
Rasha N. AlSheikh
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17897. CrossRef - Phosphoric Acid Etch Partially Restores the Initial Bond Strength of Composite to Silver Diamine Fluoride–Treated Enamel Using Universal Adhesives
Zaher Jabbour, Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Reuben Kim
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(7): 161. CrossRef - Efficacy of Nano Silver Fluoride and/or Diode Laser In Enhancing Enamel Anticariogenicity around orthodontic brackets
Aya Anwar Alsherif, Mohamed Ali Farag, Mai Badreldin Helal
BDJ Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Amelioration Strategies for Silver Diamine Fluoride: Moving from Black to White
Amjad Almuqrin, Inder Preet Kaur, Laurence J. Walsh, Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne, Sobia Zafar
Antibiotics.2023; 12(2): 298. CrossRef - The Effect of Loading Time on Color Stability of Various Restorative Materials Bonded to Silver Diamine Fluoride-Treated Demineralized Dentin
Mohammed M Aldosari, Fares S Al-Sehaibany
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2022; Volume 14: 123. CrossRef - In vitro study of the effect of nanosilver fluoride on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and demineralization of enamel
Mariam H. El-Toukhy, Eman M. El-Shourbagy, Neveen M. Fakhry
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(4): 281. CrossRef
-
1,406
View
-
22
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
9
Crossref
-
Evaluation of the effects of whitening mouth rinses combined with conventional tooth bleaching treatments
-
Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Omar Geha, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e6. Published online January 30, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e6
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
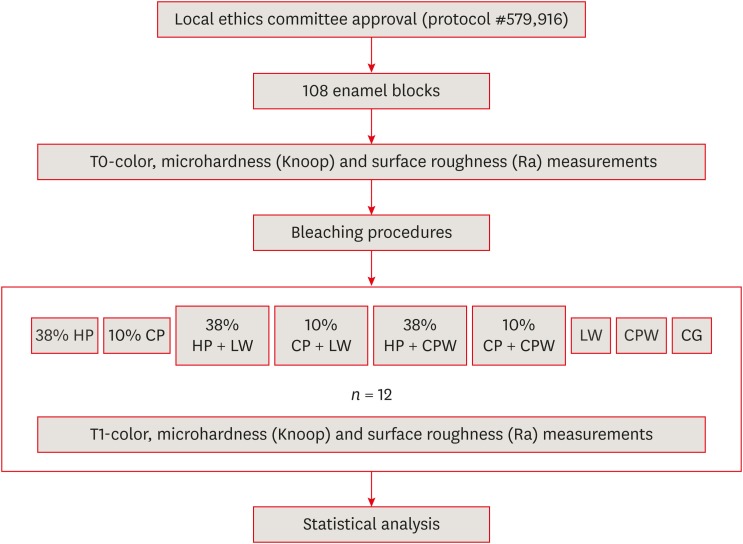
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of whitening mouth rinses alone and in combination with conventional whitening treatments on color, microhardness, and surface roughness changes in enamel specimens. Materials and MethodsA total of 108 enamel specimens were collected from human third molars and divided into 9 groups (n = 12): 38% hydrogen peroxide (HP), 10% carbamide peroxide (CP), 38% HP + Listerine Whitening (LW), 10% CP + LW, 38% HP + Colgate Plax Whitening (CPW), 10% CP + CPW, LW, CPW, and the control group (CG). The initial color of the specimens was measured, followed by microhardness and roughness tests. Next, the samples were bleached, and their color, microhardness, and roughness were assessed. Data were analyzed through 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA; microhardness and roughness) and 1-way ANOVA (color change), followed by the Tukey post hoc test. The Dunnett test was used to compare the roughness and microhardness data of the CG to those of the treated groups. ResultsStatistically significant color change was observed in all groups compared to the CG. All groups, except the LW group, showed statistically significant decreases in microhardness. Roughness showed a statistically significant increase after the treatments, except for the 38% HP group. ConclusionsWhitening mouth rinses led to a whitening effect when they were used after conventional treatments; however, this process caused major changes on the surface of the enamel specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Which Whitening Mouthwash With Different Ingredients Is More Effective on Color and Bond Strength of Enamel?
Elif Varli Tekingur, Fatih Bedir, Muhammet Karadas, Rahime Zeynep Erdem
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 960. CrossRef - Do Different Tooth Bleaching–Remineralizing Regimens Affect the Bleaching Effectiveness and Enamel Microhardness In Vitro?
Hamideh Sadat Mohammadipour, Parnian Shokrollahi, Sima Gholami, Hosein Bagheri, Fatemeh Namdar, Salehe Sekandari, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrogen peroxide versus charcoal-based whitening mouthwashes on color, surface roughness, and color stability of enamel
Mayada S. Sultan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of online marketplace-sourced over-the-counter tooth whitening products on the colour, microhardness, and surface topography of enamel: an in vitro study
Radhika Agarwal, Nikki Vasani, Urmila Sachin Mense, Niharika Prasad, Aditya Shetty, Srikant Natarajan, Arindam Dutta, Manuel S. Thomas
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Whitening Mouthwashes on Color Change and Enamel Mineralization: An In Vitro Study
Rosa Josefina Roncal Espinoza, José Alberto Castañeda Vía, Alexandra Mena-Serrano, Lidia Yileng Tay
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 739. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Over-the-Counter Whitening Products on Dental Tissues
Maiara Rodrigues de Freitas, Marynara Mathias de Carvalho, Priscila Christiane Suzy Liporoni, Ana Clara Borges Fort, Rodrigo de Morais e Moura, Rayssa Ferreira Zanatta
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Renklendirilmiş kompozit rezinin renk değişimine ve yüzey pürüzlülüğüne beyazlatıcı ağız gargarasının etkisi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Tuğba TUNCDEMIR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2020; 7(3): 435. CrossRef
-
1,241
View
-
13
Download
-
7
Crossref
|