-
Revitalization of necrotic mature permanent incisors with apical periodontitis: a case report
-
Emre Nagas, M. Ozgur Uyanik, Zafer C. Cehreli
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e31. Published online July 5, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e31
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
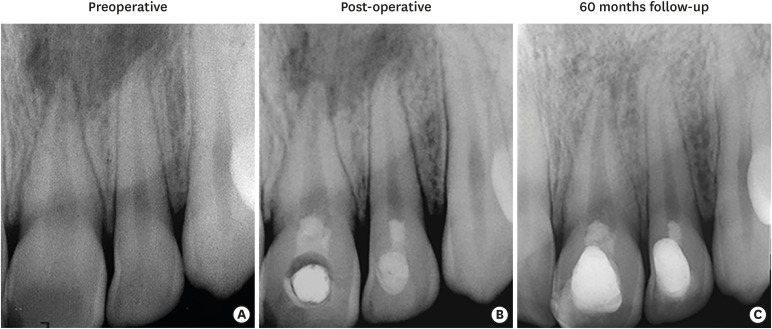
Despite considerable focus on the regenerative endodontic treatment of immature teeth with necrotic infected pulps and apical periodontitis, little data exist with regard to its possible implementation in necrotic permanent teeth with complete apical and radicular development. The present report describes the procedures and outcome of a regenerative endodontic treatment approach in 2 previously-traumatized incisors with closed apex with apical periodontitis. A 2-visit treatment procedure was employed. At initial visit, the root canals were copiously irrigated, followed by placement of a triple antibiotic paste containing ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and clindamycin into the root canals. After 4 weeks, the antibiotic paste was removed, and apical bleeding was initiated with size 10 hand files beyond the apices. The root canals were coronally sealed with mineral trioxide aggregate, and the access cavities were restored with bonded resin composite. At post-operative 60 months, both teeth were remained asymptomatic, with the recall radiographs showing complete resolution of apical radiolucency and reestablishment of periradicular tissues. In both teeth, the dimensions of root space remained unchanged as verified by image analysis. The revitalization protocol utilizing root canal disinfection and induced apical bleeding in necrotic, closed-apex incisors may offer a clinically acceptable alternative to conventional root canal treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Regenerative potential of concentrated growth factor compared to platelet-rich fibrin in treatment of necrotic mature teeth: a randomized clinical trial
Taghreed Salah, Wael Hussein, Heba Abdelkafy
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Pulp Revascularization in the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis in Mature Necrotic Teeth: An Umbrella Review
Wanderson Limeira de Sousa Barbosa, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Márcia Valente de Brito Dantas, Rômulo Dias Jesuino, João Marcos da Costa Ribeiro, Walbert A. Vieira, Felipe de Souza Matos
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 495. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of non-surgical retreatment of mature maxillary incisors using two regenerative endodontic techniques in adolescents: a 24-month randomized clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Sherif Shafik EL Bahnasy, Yassmin Mohamed ElMakawi, Mohammed Turky, Eman Farouk Ahmed, Norhan Khaled Omar Wahba
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of chitosan medicaments loaded with green-synthesized silver nanoparticles on basic fibroblast growth factor release from infected dentin
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Zehra Gun Gok, Nebahat Aytuna Cerci, Eray Ceylanoglu, Bengisu Ozturk, Ozum Hekim Harput, Sevda Durust Baris, Filiz Kiper, Ali Erdemir
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revolutionizing Endodontics: Innovative Approaches for Treating Mature Teeth With Closed Apices and Apical Lesions: A Report of Two Cases
Claudia Brizuela, Gastón Meza, Maroun Khoury
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 596. CrossRef - Current Aspects of Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review
A. V. Mitronin, K. A. Archakov, D. A. Ostanina, Yu. A. Mitronin, T. V. Khizrieva
Endodontics Today.2024; 21(4): 287. CrossRef - Correlation between pulp sensibility and magnetic resonance signal intensity following regenerative endodontic procedures in mature necrotic teeth- a retrospective cohort study
Noha Mohamed El-Kateb, Amr Mohamed Abdallah, Rania Noaman ElBackly
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of periapical lesion size on healing outcome following regenerative endodontic procedures: a clinical investigation
Noha Mohamed El Kateb, Mahmoud Mostafa Fata
Oral Radiology.2022; 38(4): 480. CrossRef - Do alternative scaffolds used in regenerative endodontics promote better root development than that achieved with blood clots?
Letícia de Araújo, Taynara Santos Goulart, Ana Clara Kuerten Gil, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Daniela de Rossi Figueiredo, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 22. CrossRef - Endodontic Regenerative Procedures in Necrotic Adult Teeth
Sara Garrido-Parada, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Nancy Feijoo-Pato, José Gaviño-Orduña, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(9): 4212. CrossRef - Combined conventional and regenerative treatment in molars with coexistent closed and open apices: A case series
Zafer C. Cehreli, Gizem Erbas Unverdi, Pinar Eymirli, Irem Mergen, Ezgihan Arslan, Gulce Esenturk
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 197. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Procedures for the Treatment of Necrotic Mature Teeth with Apical Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Antonios Glynis, Federico Foschi, Ismini Kefalou, Despina Koletsi, Giorgos N. Tzanetakis
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 873. CrossRef - Different Approaches to the Regeneration of Dental Tissues in Regenerative Endodontics
Anna M. Krupińska, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Tomasz Staniowski
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1699. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Intracanal Regenerated Tissues after Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Mature Teeth Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Noha Mohamed El-Kateb, Rania Noaman El-Backly, Wessam Mohamed Amin, Amr Mohamed Abdalla
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(5): 563. CrossRef
-
1,928
View
-
23
Download
-
14
Crossref
-
Calcium hydroxide dressing residues after different removal techniques affect the accuracy of Root-ZX apex locator
-
Emel Uzunoglu, Ayhan Eymirli, Mehmet Özgür Uyanik, Semra Çalt, Emre Nagas
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):44-49. Published online November 5, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.44
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study compared the ability of several techniques to remove calcium hydroxide (CH) from the root canal and determined the influence of CH residues on the accuracy of the electronic apex locator. Materials and MethodsRoot canals of 90 human maxillary lateral incisors with confirmed true working length (TWL) were prepared and filled with CH. The teeth were randomly assigned to one of the experimental groups according to the CH removal technique (n = 14): 0.9% saline; 0.9% saline + master apical file (MAF); 17% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA); 17% EDTA + MAF; 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); 5.25% NaOCl + MAF. Six teeth were used as negative control. After CH removal, the electronic working length was measured using Root-ZX (Morita Corp.) and compared with TWL to evaluate Root-ZX accuracy. All specimens were sectioned longitudinally, and the area of remaining CH (CH) and total canal area were measured using imaging software. ResultsThe EDTA + MAF and NaOCl + MAF groups showed better CH removal than other groups (p < 0.05). Root-ZX reliability to prevent overestimated working length to be > 85% within a tolerance of ± 1.0 mm (p < 0.05). There was strong negative correlation between amount of CH residues and EAL accuracy (r = -0.800 for ± 0.5 mm; r = -0.940 for ± 1.0 mm). ConclusionsThe mechanical instrumentation improves the CH removal of irrigation solutions although none of the techniques removed the dressing completely. Residues of CH medication in root canals affected the accuracy of Root-ZX adversely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of the Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Residues Including Different Vehicles on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators
Simay Koç, Damla Erkal, Dide Tekinarslan, Kürs¸at Er
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluation of heated sodium hypochlorite’s effect on the accuracy of contemporary electronic apex locators: an in vitro study
İkbal Sena Çelebi Keskin, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing the accuracy of electronic apex locators: A scoping review
Shayan Golkar, Abbasali Khademi, Amin Saatchi, Amir Ghorani, Pedram Iranmanesh
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a new irrigation solution -RISA- on removing calcium hydroxide from artificial standardized grooves in root canals - an in vitro study
İpek Eraslan Akyüz, Salih Düzgün, Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the accuracy of electronic apex locators and cone-beam computed tomography in detection of root canal perforation and working length during endodontic retreatment
Simay Koç, Hatice Harorlı, Alper Kuştarcı
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Intracanal Medicaments on the Measurement Accuracy of Four Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study
Hamza Cudal, Tuğrul Aslan, Bertan Kesim
Meandros Medical and Dental Journal.2023; 24(3): 215. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Apical Patency, Coronal Preflaring and Calcium Hydroxide on the Accuracy of Root ZX Apex Locator for Working Length Determination: An In Vitro Study
Mostafa Godiny, Reza Hatam, Roya Safari-Faramani, Atefeh Khavid, Mohammad Reza Rezaei
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(1): 38. CrossRef - Endodontic cement penetration after removal of calcium hydroxide dressing using XP-endo finisher
Alyssa Sales dos Santos, Maria Aparecida Barbosa de Sá, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Martinho Campolina Rebello Horta, Frank Ferreira Silveira, Eduardo Nunes
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of glycolic acid for the removal of calcium hydroxide from simulated internal Resorption cavities
Cangül Keskin, Ali Keleş, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(7): 4407. CrossRef - Accuracy of electronic apex locator in the presence of different irrigating solutions
Padmanabh Jha, Vineeta Nikhil, Shalya Raj, Rohit Ravinder, Preeti Mishra
Endodontology.2021; 33(4): 232. CrossRef - Farklı Kanal İçi Ortamların Apeks Bulucuların Doğruluğu Üzerine Etkisi
Asena OKUR, Tuğrul ASLAN, Burak SAĞSEN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 859. CrossRef - Evaluation of the accuracy of different apex locators in determiningthe working length during root canal retreatment
Pelin Tufenkci, Aylin Kalaycı
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 125. CrossRef - Influence of calcium hydroxide residues after using different irrigants on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators: An in vitro study
NooshinSadat Shojaee, Zahra Zaeri, MohammadMehdi Shokouhi, Fereshteh Sobhnamayan, Alireza Adl
Dental Research Journal.2020; 17(1): 48. CrossRef - The Effect of Calcium Hydroxide and File Sızes on the Accuracy of the Electronic Apex Locator in Simulated Immature Teeth
Leyla AYRANCİ, Ahmet ÇETİNKAYA, Serkan ÖZKAN
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2019; 5(3): 273. CrossRef - The Effect of File Size and Type and Irrigation Solutions on the Accuracy of Electronic Apex Locators: AnIn VitroStudy on Canine Teeth
Maciej Janeczek, Piotr Kosior, Dagmara Piesiak-Pańczyszyn, Krzysztof Dudek, Aleksander Chrószcz, Agnieszka Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz, Małgorzata Kowalczyk-Zając, Aleksandra Gabren-Syller, Karol Kirstein, Aleksandra Skalec, Ewelina Bryła, Maciej Dobrzyński
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
-
1,256
View
-
7
Download
-
16
Crossref
|