Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 33(2); 2008 > Article
- Original Article A comparative study on radiopacity of canal filling and retrograde root-end filling materials
- Yong-Sang Kim, Seo-Kyong Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
-
2008;33(2):-114.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.2.107
Published online: March 31, 2008
Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, DSRI, Chonnam National University, BK21, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Won-Mann Oh. Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, 8 Hak-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-757, Korea. Tel: 82-62-220-4431, Fax: 82-62-225-8387, wmoh@chonnam.ac.kr
Copyright © 2008 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,266 Views
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
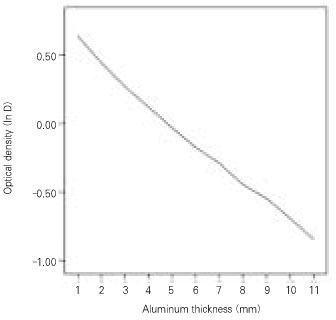
This study was performed to assess the radiopacity of a variety of canal filling and retrograde root-end filling materials according to the specification concerning root canal obturation materials.Ten materials including Gutta-percha pellets, amalgam, Fuji II LC, Dyract® AP, Super EBA®, IRM®, AH 26®, Sealapex™, Tubli-Seal™ and dentin were evaluated in this study. In the first part, densitometric reading of an each step of aluminum step wedge on occlusal film were performed at 60 kVp (0.2, 0.3, 0.4 s), 70 kVp (0.2, 0.3, 0.33 s) to decide appropriate voltage and exposure time. In the second part, ten specimens which are 5 mm in diameter and 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 mm in thickness, were fabricated from each material studied. The specimens were radiographed simultaneously with an aluminum step wedge under decided condition (60 kVp, 0.2 s). The mean radiographic density values of the materials were transformed into radiopacity expressed equivalent thickness of aluminum (mm Al).The following results were obtained.
Among the various conditions including 0.2 s, 0.3 s, 0.4 s at 60 kVp and 0.2 s, 0.3 s, 0.33 s at 70 kVp, the appropriate voltage and exposure time that meet the requirement of density from 0.5 to 2.0 was 0.2 s at 60 kVp.
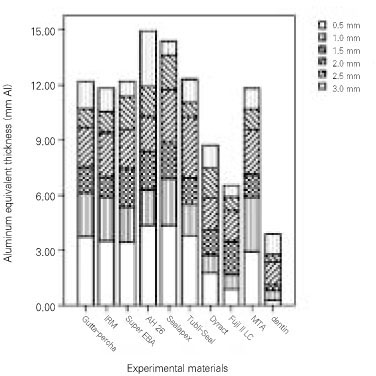
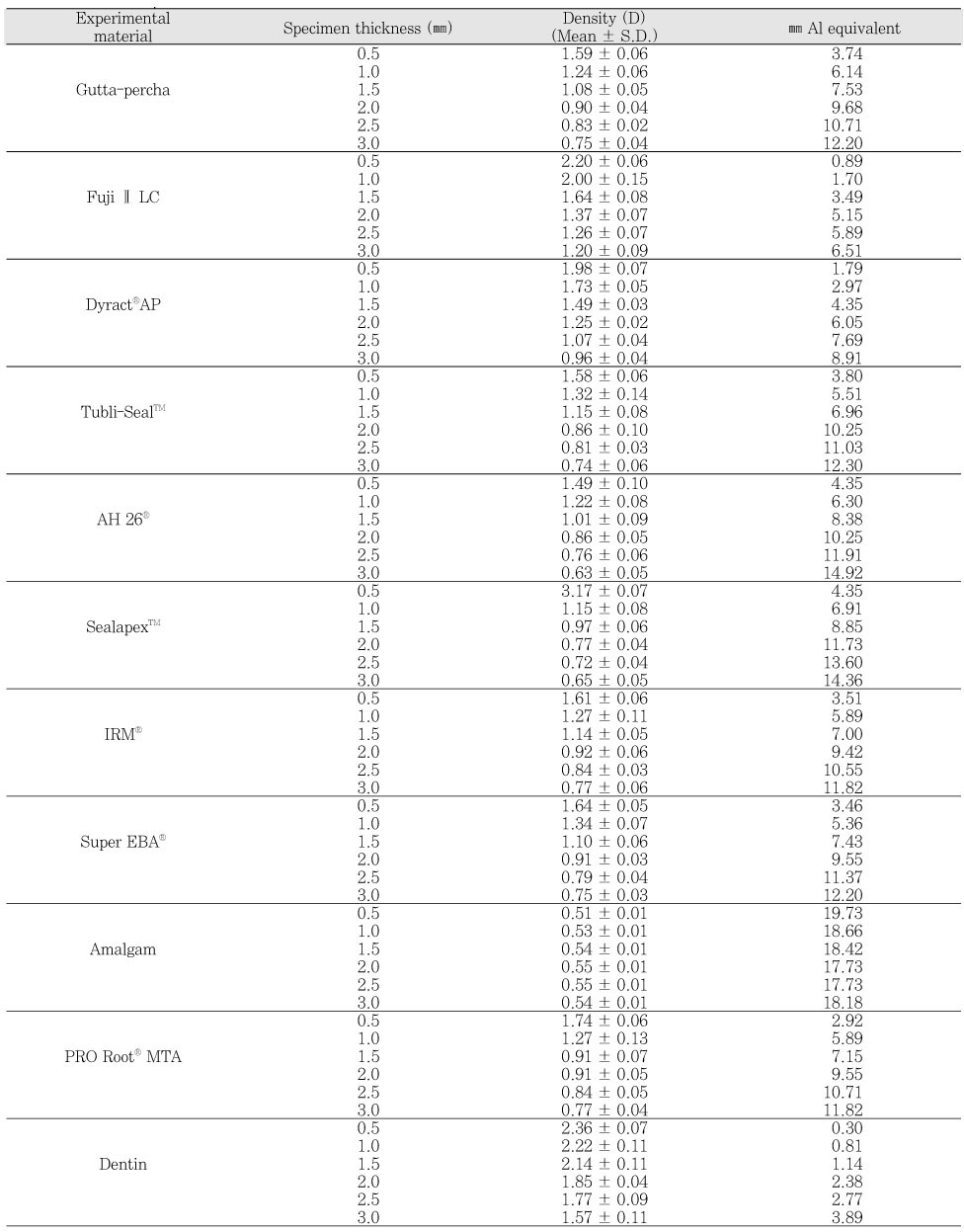
All of the materials in this study had greater radiopacity than the minimun level recommended by ISO No. 4049 standards.
Most of the materials had greater radiopacity than 3 mm Al requirement of ANSI/ADA specification No. 57 (2000) and ISO No. 6876 (2001) standards except for Fuji II LC and Dyract.
It suggests that all experimental canal filling and retrograde root-end filling materials have a sufficient radiopacity that meet the requirement concerning root canal obturation materials except for Fuji II LC and Dyract.
- 1. Seltzer S, Bender IB, Smith J, Freedman I, Nazimov H. Endodontic failures. An analysis based on clinical roentgenographic and histologic findings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1967;23: 517-530.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Gutmann JL, Harrison JW. Surgical Endodontics. 1994;St. Louis, MO: IEA Inc..
- 3. Eliasson ST, Haasken B. Radiopacity of impression materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1979;47: 485-491.ArticlePubMed
- 4. American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association (ANSI/ADA). Specification No. 57: endodontic sealing materials. 1999;2nd draft. Chicago: American Dental Association; (revision).
- 5. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 2001;Geneva, Switzerland: Dental Root Canal Sealing Materials; 6876.
- 6. Tagger M, Katz A. A standard for radiopacity of root-end (retrograde) filling materials is urgently needed. Int Endod J. 2004;37: 260-264.ArticlePubMed
- 7. ISO : DP 4049 Dental resin based restorative materials. International standards organization (draft proposal) Clause. 1985;6: 10.
- 8. Grossman LI, Oliet S, Del-Rio CE. Endodontic practice. 1988;Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.
- 9. Orlay HG. Overfilling in root canal treatment. Two accidents with N2. Br Dent J. 1966;120: 376.PubMed
- 10. Abou-Tabl ZM, Tidy DC, Combe EC. Radiopacity of composite restorative materials. Br Dent J. 1979;147: 187-188.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Beyer-Olsen EM, Ørstavik D. Radiopacity of root canal sealers. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981;51: 320-328.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Kaffe I, Littner MM, Tagger M, Tamse A. Is the radiopacity standard for gutta-percha sufficient in clinical use? J Endod. 1983;9: 58-59.PubMed
- 13. Bae KS, Eom JM. A Study on the Radiopacity of Root Canal Sealers. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1993;18: 133-143.
- 14. Torabinejad M, Higa RK, McKendry DJ, Pitt Ford TR. Dye leakage of four root end filling materials : effects of blood contamination. J Endod. 1994;20: 159-163.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Bates CF. Carnes DL, del Rio CE. Longitudinal sealing ability of mineral Trioxide Aggregates as a root end filling material. J Endod. 1996;22: 575-578.PubMed
- 16. Dorn SO, Gartner AH. Retrograde filling materials : A retrospective success failure study of amalgam, EBA, and IRM. J Endod. 1990;16: 391-393.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Yaccino JM, Walker WA III, Carnes DL Jr, Schindler WG. Longitudinal microleakage evaluation of Super-EBA as a root end sealing material. J Endod. 1999;25: 552-554.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Dammaschke T, Gerth HU, Zuchner H, Schafer E. Chemical and physical surface and bulk material characterization of white ProRoot MTA and two Portland cements. Dent Mater. 2005;21: 731-738.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Chong BS, Pitt Ford TR, Watson TF. Light-cured glass ionomer cement as a retrograde root seal. Int Endod J. 1993;26: 218-224.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Aoyagi Y, Takahashi H, Iwasaki N, Honda E, Kurabayashi T. Radiopacity of experimental composite resins containing radiopaque materials. Dent Mater J. 2005;24: 315-320.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Limkangwalmongkol S, Abbott PV, Sandler AB, Apical dye. Apical dye penetration with four root canal sealers and guttapercha using longitudinal sectioning. J Endod. 1992;18: 535.PubMed
- 22. Kim CK, Ryu HW, Chang HS, Lee BD, Min KS, Hong CU. Evaluation of the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of resinous root canal sealers. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007;32: 419-425.Article
- 23. Holland R, de Souza V. Ability of a new calcium hydroxide root canal filling material to induce hard tissue formation. J Endod. 1985;11: 535-543.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Tanomaru-Filho M, Jorge EG, Tanomaru JM, Gonçalves M. Evaluation of the radiopacity of calcium hydroxideand glass-ionomer-based root canal sealers. Int Endod J. 2007;41: 50-53.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Shah PM, Chong BS, Sidhu SK, Ford TR. Radiopacity of potential root-end filling materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996;81: 476-479.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Russin TP, Zardiackas LD, Reader A, Menke RA. Apical seals obtained with laterally condensed chloroform softened gutta-percha and laterally condensed gutta-percha and Grossmans sealer. J Endod. 1980;6: 678-682.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Katz A, Kaffe I, Littner M, Tagger M, Tamse A. Densitometric measurement of radiopacity of guttapercha cones and root dentin. J Endod. 1990;16: 211-213.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Orfali S, Lilley JD, Molokhia A. The radiopacity of some endodontic sealer cements. J Dent Res. 1987;66: 876.
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

- Evaluation of prognosis related to compliance with supportive periodontal treatment in patients with chronic periodontitis: a clinical retrospective study
Jong-Bin Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Dae-Yeob Kim, Eun-Kyoung Pang
Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science.2019; 49(2): 76. CrossRef
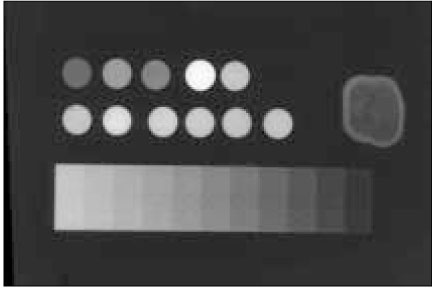
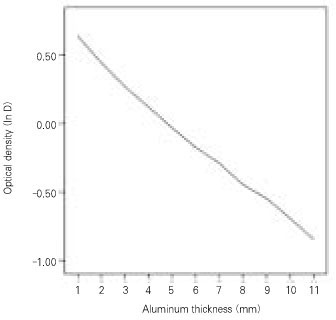
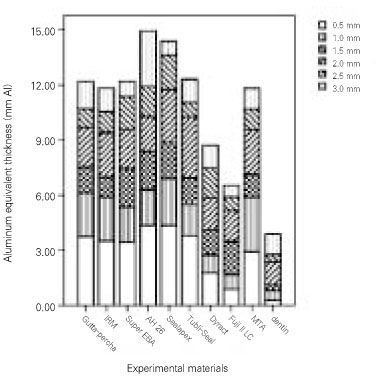
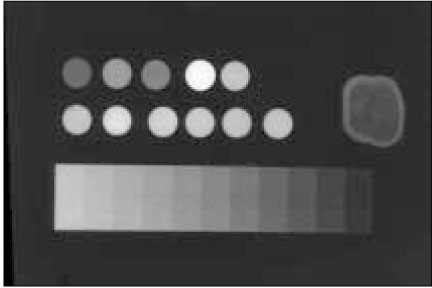
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Mean values and standard deviations of the radiopacity values in terms of equivalent thickness of aluminum for the experimental materials

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

