Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 30(6); 2005 > Article
- Original Article Coincidence between radiographs and clearing samples on the root canal systems of single rooted premolars
- Ho-Keel Hwang, Ho-Min Kang, Kang Seo
-
2005;30(6):-469.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.461
Published online: November 30, 2005
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Ho-Keel Hwang. Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, 375 Seosuk-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju, Korea, 501-759. Tel: 82-62-220-3846, Fax: 82-62-232-9064, rootcanal@hanmail.net
• Received: June 26, 2005 • Revised: August 25, 2005 • Accepted: September 1, 2005
Copyright © 2005 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 805 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
The aim of this study was to compare the root canal systems of maxillary and mandibular premolars that had a single root using radiographs and clearing samples. 142 single rooted premolars were selected and mesio-distal and bucco-lingual views were radiographed using intra-oral dental standard films. Four equally trained examiners classify the root canal types from the developed radiographs. After opening the tooth for access, it was stored in 5% NaOCl to dissolve the pulp tissue. Indian ink was then injected into the pulp cavity to stain the pulp tissue. It was cleared in methyl salicylate after being decalcified with 5% nitric acid for 48 hours, and the root canal type was evaluated at a magnification of × 20 using a stereomicroscope.The results are as follows;There were statistically significant differences between the radiographs and clearing samples of the root canal types among examiners (p < 0.05). There might be differences in the root canal types among examiners when the same radiograph is used. Therefore, considering the difficulty in estimating the root canal types, clinicians need to be careful when interpreting radiographs before root canal therapy.
- 1. Weine FS. Endodontic Therapy. 1982;3rd ed. Mosby; 210-211.
- 2. Ingle JI, Bakland LK. Endodontics. 2002;5th ed. BC Decker Inc; 405-408.
- 3. Lim SS. Clinical Endodontics. 1999;2nd ed. Dental & Medical Publishing Co; 42-76.
- 4. Cohen S, Burns RC. Pathways of the pulp. 2002;8th ed. St. Louis: CV Mosby; 194-209.
- 5. Hession RW. Endodontic morphology, II. A radiographic analysis. Oral Surg. 1977;44: 610-620.PubMed
- 6. Pineda F, Kuttler Y. Mesiodistal and buccolingual roentgenographic investigation of 7,275 root canals. Oral Surg. 1972;33: 101-110.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Pineda F. Roentgenographic investigations of the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar. Oral Surg. 1973;36: 253-260.PubMed
- 8. Slowey RR. Radigoraphic aids in the detection of extra root canals. Oral Surg. 1974;37: 762-772.PubMed
- 9. Green D. Double canals in single roots. Oral Surg. 1973;35: 689-696.PubMed
- 10. Hsu YY, Kim S. The receted root surface: The issue of canal isthmus. Dent Clin North Am. 1997;41: 529-540.PubMed
- 11. Weller RN, Niemczyk SP, Kim S. Incidence and position of the canal isthmus. Part 1. Mesiobuccal oot of the maxillary first molar. J Endod. 1995;21: 380-383.PubMed
- 12. Kartal N, Ozcelik B, Cimilli H. Root canal morphology of maxillary premolars. J Endod. 1998;24: 417-419.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Robertson D, Leeb IJ, McKee M, Brewer E. A clearing technique for the study of root canal systems. J Endod. 1980;6: 421-424.PubMed
- 14. Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg. 1984;58: 589-599.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Vertucci F, Seelig A, Gillis R. Root canal morphology of the human maxillary second premolar. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974;38: 456-464.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Gilles J, Reader A. An SEM investigation of the mesiolingual canal in human maxillary first and second molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990;70: 638-643.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Baumann MA, Doll GM. Spatial reproduction of the root canal system by magnetic resonance microscopy. J Endod. 1997;23: 49-51.PubMed
- 18. Goldman M, Pearson AH, Darzenta ND. Endodontic success-Who's reading the radiograph? Oral Surg. 1972;33: 432-437.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Gelfand M, Sunderman EJ, Goldman M. Reliability of radiographical interpretations. J Endod. 1983;9: 71-75.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Zakariasen KL, Scott DA, Jensen JR. Endodontic recall radiographs: How reliable is our interpretation of endodontic success or failure and what factors affect our reliability? Oral Surg. 1984;57: 343-347.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Senia ES, Marshall FJ, Rosen S. The solvent action of sodium hypochlorite on pulp tissue of extracted teeth. Oral Surg. 1971;31: 96-103.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Pollard BK, Weller RN, Kulid JC. Standardized technique for linear dye leakage studies: Immediate versus delayed immersion times. Int Endod J. 1990;23: 250-253.PubMed
- 23. Tamse A, Katz A, Kablan F. Comparison of apical leakage shown by four different dyes with two evaluating methods. Int Endod J. 1998;31: 333-337.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Friedman S, Lustman J, Shaharabany V. Treatment results of apical surgery in premolar and molar teeth. J Endod. 1991;17: 30-33.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Omer OE, Al Shalabi RM, Jennings M, Glennon J, Claffey NM. A comparison between clearing and radiographic techniques in the study of the root-canal anatomy of maxillary first and second molars. Int Endod J. 2004;37: 291-296.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Coincidence between radiographs and clearing samples on the root canal systems of single rooted premolars
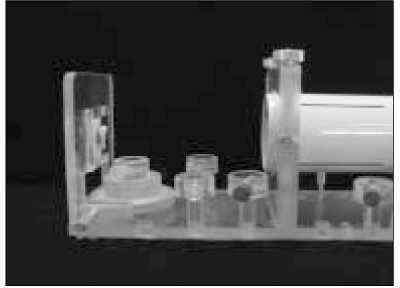
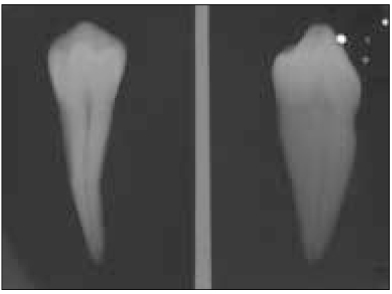
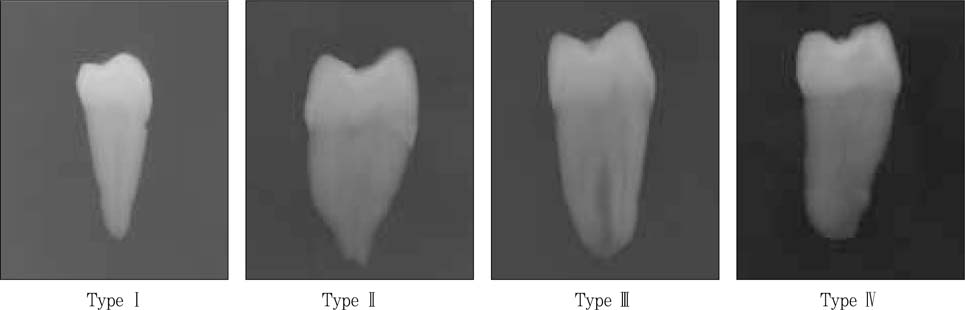
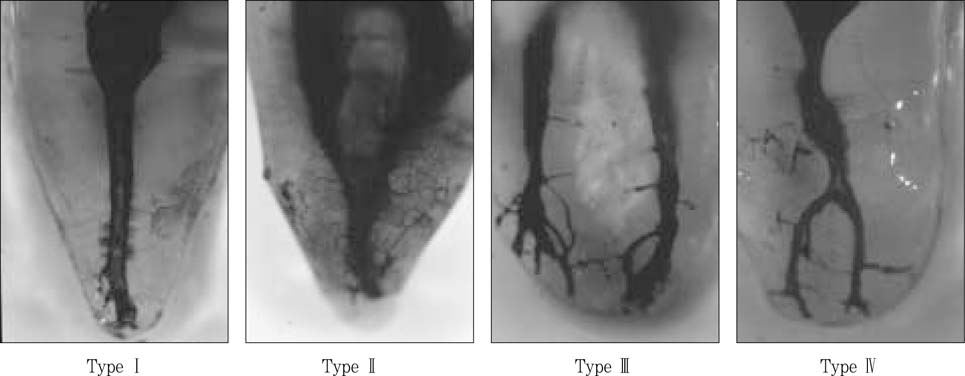
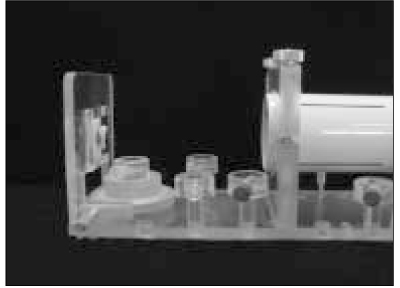
Figure 1
A paralleling device.
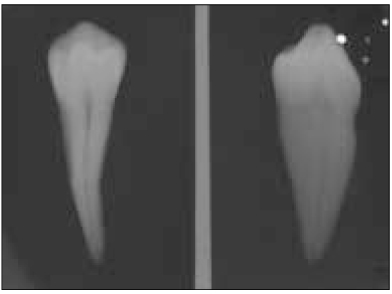
Figure 2
A double exposed radiograph.
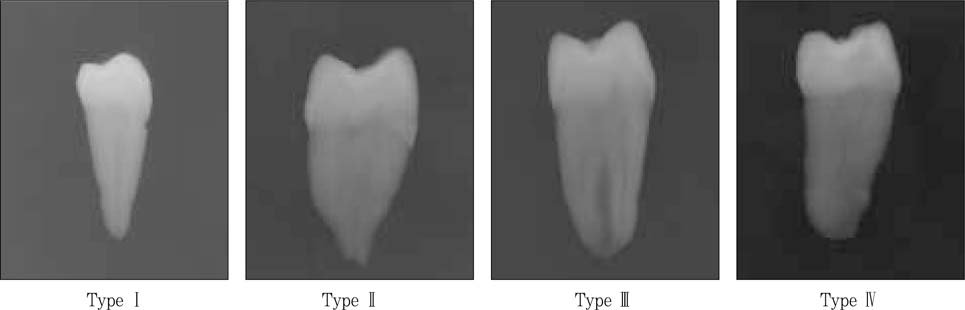
Figure 3
Classification of root canal types on radiographs.
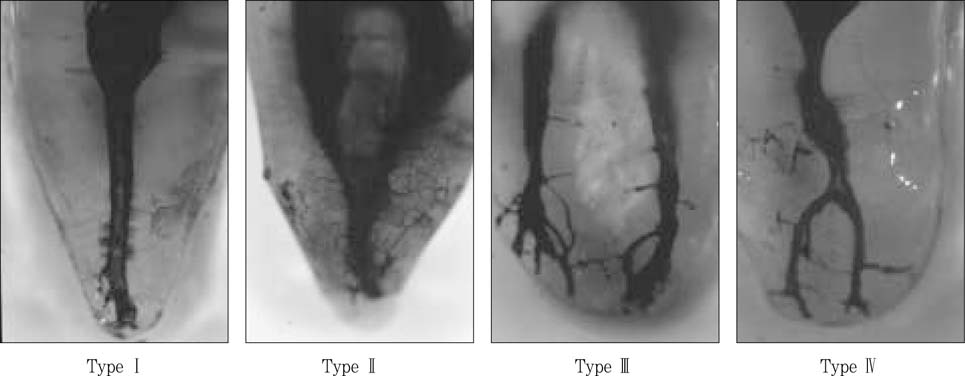
Figure 4
Classification of root canal types on clearing samples.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Coincidence between radiographs and clearing samples on the root canal systems of single rooted premolars
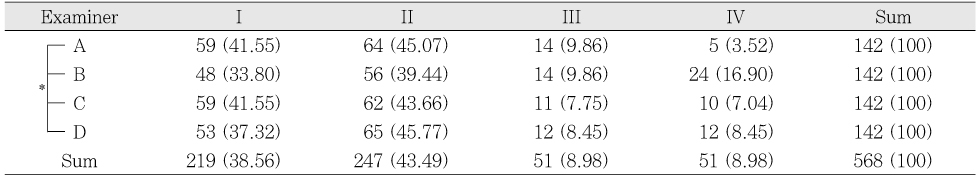
Root canal types by interpreted radiographs (%)
*: Significantly different at p < 0.05 (χ2 test)
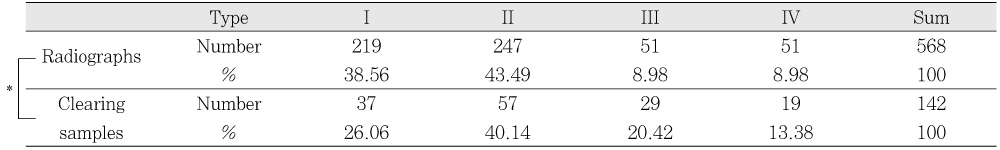
A comparison of root canal types between radiographs and clearing samples
*: Significantly different at p < 0.05 (χ2 test)
Coincidence of root canal types between radiographs and clearing samples (%)
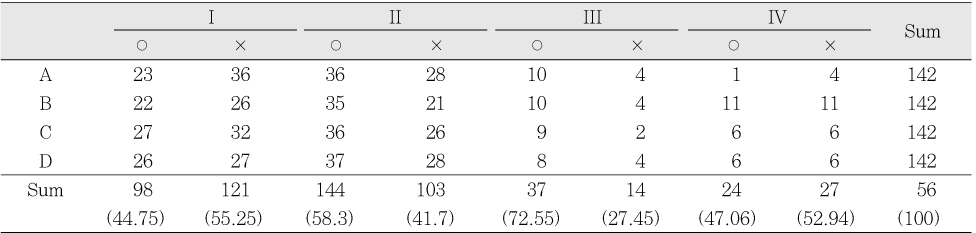
Coincidence according to the root canal types (%)
○: Correct, ×: Incorrect
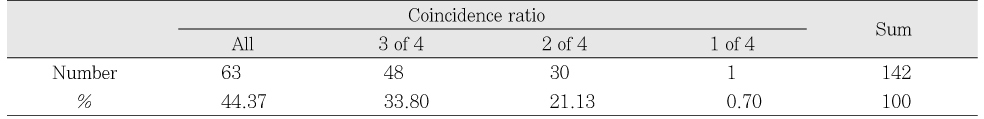
Coincidence ratio among examiners
Table 1
Root canal types by interpreted radiographs (%)
*: Significantly different at p < 0.05 (χ2 test)
Table 2
A comparison of root canal types between radiographs and clearing samples
*: Significantly different at p < 0.05 (χ2 test)
Table 3
Coincidence of root canal types between radiographs and clearing samples (%)
Table 4
Coincidence according to the root canal types (%)
○: Correct, ×: Incorrect
Table 5
Coincidence ratio among examiners

 KACD
KACD

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

