Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 30(6); 2005 > Article
- Original Article Effect of increasing application time of single bottle adhesives to microtensile bond strength of dried dentin
- Hak-Geun Kim, Dong-Jun Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Wonmann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
2005;30(6):-441.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.435
Published online: November 30, 2005
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Korea.
- Corresponding author: In-Nam Hwang. Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, 8 Hak-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju, South Korea, 501-757. Tel: 82-62-220-4443, Fax: 82-62-225-8387, hinso@jnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2005 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 848 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
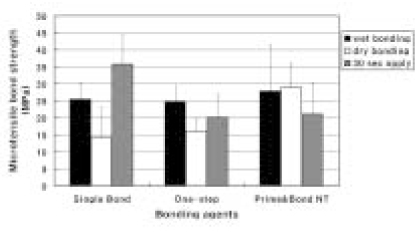
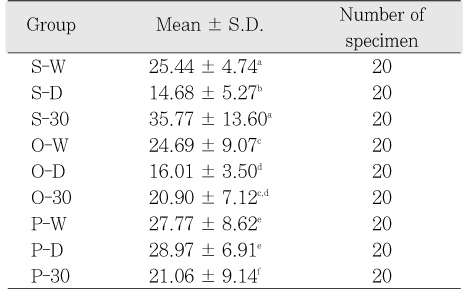
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of increasing application time of single bottle adhesives (SBA) to microtensile bond strength (MTBS) of dried dentin. To expose the superficial dentin surfaces, human molars were sectioned perpendicular to the long axis of tooth. 32% phosphoric acid gels were applied for 15s and rinsed. The teeth were randomly assigned to 3 groups ; S group (Single Bond), O group (One-Step), P group (Prime & Bond NT). Each group was divided to 3 subgroups (W: dentin wipe with wet gauge and light cured immediately, D: dentin dried for 30s and light cured immediately, 30: dentin dried for 30s and light cured after applying SBA for 30s). Composite resin was built up on the dentin surface and sectioned to obtain 20 specimens with 1 mm2 cross sectional area and the MTBS was measured.For Single Bond, the mean MTBS of S-W and S-30 group were higher than that of S-D group statistically (P < 0.05). For One-Step, the mean MTBS of O-D group was statistically lower than that of O-W group (P < 0.05). For Prime & Bond NT, the mean MTBS of P-30 group was statistically lower than that of P-D group (P < 0.05).
- 1. Gwinnett AJ. Moist versus dry dentin: its effect on shear bond strength. Am J Dent. 1992;5: 127-129.PubMed
- 2. Kanca J 3rd. Resin bonding to wet substrate. I. Bonding to dentin. Quintessence Int. 1992;23(1):39-41.PubMed
- 3. Pashley DH, Bernard C, Hidehiko S, Horner JA. Permeability of dentin to adhesive agents. Quintessence Int. 1993;24: 618-631.PubMed
- 4. Kanca J. Effect of drying on bonding strength. J Dent Res. 1991;70: 304. (abstract 1029).
- 5. Tay FR, Gwinnett JA, Stephen HY, Wei SHY. Micromorphological spectrum from overdrying to overwetting acid-conditioned dentin in water-free acetone-based, single-bottle primer/adhesives. Dent Mater. 1996;12: 236-244.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Van Meerbeek VB, Yoshida Y, Lambrechts G, Vanherle G, Duke ES, Eick JD, Robinson SJ. A TEM study of two water-based adhesive systems bonded to dry and wet dentin. J Dent Res. 1998;77(1):50-59.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Perdigão J, Frankenberger R. Effect of solvent and re-wetting time on dentin adhesion. Quintessence Int. 2001;32(5):385-390.PubMed
- 8. Perdigão J, Swift EJ, Heymann HO, Malek MA. Effect of a re-wetting agent on performance of acetone based dentin adhesives. Am J Dent. 1998;11: 207-213.PubMed
- 9. Gwinnett AJ. Dentin Bond strength after air drying and rewetting. Am J Dent. 1994;7(3):144-148.PubMed
- 10. Tay FR, Gwinnett AJ, Wei SHY. Ultrastructure of the resin-dentin interface following reversible and irreversible re-wetting. Am J Dent. 1997;10: 77-82.PubMed
- 11. Ritter AV, Heymann HO, Swift JR, Perdigao J, Rosa BT. Effects of different re-wetting techniques on dentin sheer bond strengths. J Esth Rest Dent. 2000;12(2):85-96.
- 12. Marshall GW, Watanabe LG, Wu-Magidi IL. AFM study of drying and rehydration of etched dentin. J Dent Res. 1996;75: 390.
- 13. Perdigão J, Van Meerbeek VB, Lopes MM, Ambrose WW. The effect of a re-wetting agent on dentin bonding. Dent Mater. 1999;15: 282-295.PubMed
- 14. Nakabayashi N, Kojima K, Masuhara E. The promotion of adhesion by infiltration of monomers into tooth substrates. J Biomed Mater Res. 1982;16: 265-273.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Gallo JR 3rd, Henderson M, Burgess JO. Shear bond strength to moist and dry dentin of four dentin bonding systems. Am J Dent. 13(5):267-270.PubMed
- 16. Gwinnett AJ. Dentin bond strength after air drying and rewetting. Am J Dent. 1994;7(3):144-148.PubMed
- 17. Nakajima M, Kanemura N, Pereira PN, Tagami J, Pashley DH. Comparative microtensile bond strength and SEM analysys of bonding to wet and dry dentin. Am J Dent. 2000;13: 324-328.PubMed
- 18. Reis A, Loguercio AD, Azevedo CLN, Cavalho RM, Singer JM, Grand RHM. Moisture spectrum of demineralized dentin for different solvent-based adhesive system. J Adhes Dent. 2003;5: 183-192.PubMed
- 19. Kanca J 3rd. Effect of resin primer solvents and surface wetness on resin composite bond strength to dentin. Am J Dent. 1992;5: 213-215.PubMed
- 20. Jacobsen T, Soderhold KJ. Some effects of water on dentin bonding. Dent Mater. 1995;11: 132-136.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations

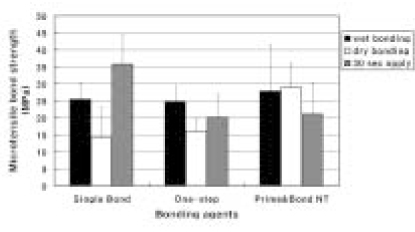
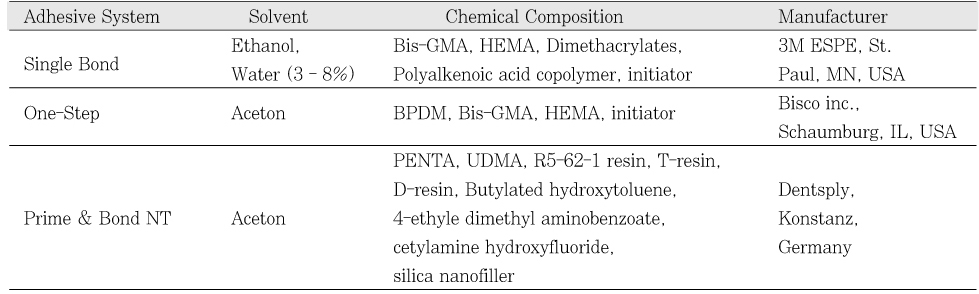
Figure 1
Adhesive systems used in this study
Bis-GMA = bis-phenol-A-diglycidyl methacrylate,
HEMA = 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate,
BPDM = biphenyl dimethacrylate,
PENTA = dipentaerythritol pentacrylate phosphorous acid ester,
UDMA = urethane dimethacrylate.
Microtensile bond strength (MPa) of each group
Superscripts of the same letter indicate values of no statistical significant difference (p > 0.05).
Bis-GMA = bis-phenol-A-diglycidyl methacrylate, HEMA = 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, BPDM = biphenyl dimethacrylate, PENTA = dipentaerythritol pentacrylate phosphorous acid ester, UDMA = urethane dimethacrylate.
Superscripts of the same letter indicate values of no statistical significant difference (p > 0.05).

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

