Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 29(6); 2004 > Article
- Original Article Cytotoxicity of resin-based root canal sealer, adseal
- Hee-Jung Kim, Seung-Ho Baek, Woo-Cheol Lee, Han-Soo Park, Kwang-Shik Bae
-
2004;29(6):-503.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.498
Published online: November 30, 2004
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Kwang-Shik Bae. Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, 28 Yoengun-dong, Chongro-gu, Seoul, Korea, 110-749. Tel: 82-2-2072-2650, Fax: 82-2-2072-3859, baeks@plaza.snu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2004 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,311 Views
- 7 Download
- 6 Crossref
Abstract
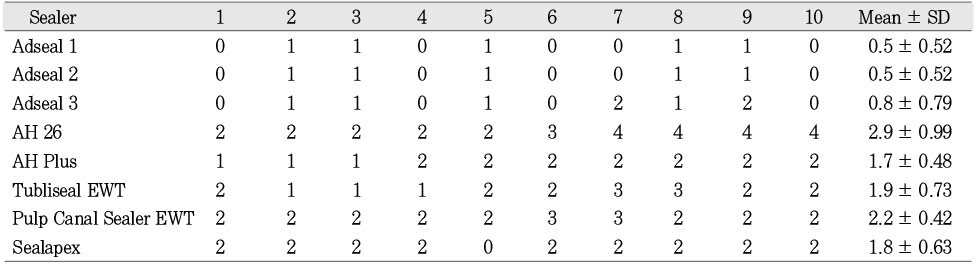
- The properties of ideal root canal sealers include the ability of sealing the total root canal system and no toxic effects to periradicular tissues. Cytotoxicity test using cell culture is a common screening method for evaluation of the biocompatibility of root canal sealers. The purpose of this study was to investigate the cytotoxic effect of newly developed resin-based sealer (Adseal 1, 2, and 3) comparing with those commercial resin-based sealers (AH26 and AH Plus), ZOE-based sealers (Tubliseal EWT, Pulp Canal Sealer EWT) and calcium hydroxide based sealer (Sealapex). An indirect contact test of cytotoxicity by agar diffusion was performed according to the international standard ISO 10993-5. L929 fibroblast cells were incubated at 37℃ in humidified 5% CO2-containing air atmosphere. The freshly mixed test materials were inserted into glass rings of internal diameter 5 mm and height 5 mm placed on the agar. After the 24 hrs incubation period, the decolorization zones around the test materials were assessed using an inverted microscope with a calibrated screen. A Decolorization Index was determined for each specimen. Adseal 1, 2, and 3 did not exert any cytotoxic effects, whereas AH26, AH Plus, Tubliseal EWT, Pulp Canal Sealer EWT, and Sealapex produced mild cytotoxicity.
- 1. Grossman LI, Olivet S, Del-Rio CE. Endodontic Practice. 1998;11th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Fabiger.
- 2. Geurtsen W, Leyhausen G. Biological aspects of root canal filling materials - histocompatibility, cytotoxicity, and mutgenicity. Clin Oral Investig. 1997;1: 5-11.PubMed
- 3. Wayman BE, Murata SM, Almeida RJ, Fowler CB. A bacterial and histological evaluation of 58 periapical lesions. J Endod. 1992;18: 152-158.PubMed
- 4. Cohen BI, Pagnillo MK, Musikant BL, Deutsch AS. Evaluation of the release of formaldehyde for three endodontic filing materials. Oral Health. 1998;88: 37-39.
- 5. Spangberg L, Barbosa SV, Lavigne GD. AH26 releases formaldehyde. J Endod. 1993;19: 596-598.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Cohen BI, Pagnillo MK, Musikant BL, Deutsch AS. An in vitro study of the cytotoxicity of two root canal sealers. J Endod. 2000;26: 228-229.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Schmalz G. Concepts in biocompatibility testing of dental restorative materials. Clin Oral Investig. 1997;1: 154-162.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Beltes P, Koulaouzidou E, Kotoula V, Kortsaris AH. In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxicity of calcium hydroxide-based root canal sealers. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1995;11: 245-249.ArticlePubMed
- 9. The Internatnal Organization for Standardization. ISO 10993-5. Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 5. Tests for cytotoxicity: in vitro method.
- 10. Mohammad AR, Mincer HH, Younis O, Dillingham E, Siskin M. Cytotoxicity evaluation of root canal sealers by the tissue culture--agar overlay technique. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1978;45: 768-773.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Briseno BM, Willershausen B. Root canal sealer cytotoxicity on human gingival fibroblasts. 1. Zinc oxide-eugenol-based sealers. J Endod. 1990;16: 383-386.PubMed
- 12. Lindqvist L, Otteskog P. Eugenol: liberation from dental materials and effect on human diploid fibroblast cells. Scand J Dent Res. 1980;88: 552-556.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Meryon SD, Johnson SG, Smith AJ. Eugenol release and the cytotoxicity of different zinc oxide-eugenol combination. J Dent. 1988;16: 66-70.PubMed
- 14. Meryon SD, Jakeman KJ. The effects in vitro of zinc released from dental restorative materials. Int Endod J. 1985;18: 191-198.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Gordon TM, Ranly DM, Boyan BD. The effects of calcium hydroxide on bovine pulp tissue: variations in pH and calcium concentration. J Endod. 1985;11: 156-160.PubMed
- 16. Huang FM, Tai KW, Chou MY, Chang YC. Cytotoxicity of resin-, zinc oxide-eugenol-, and calcium hydroxide-based root canal sealers on human periodontal ligament cells and permanent V79 cells. Int Endod J. 2002;35: 153-158.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Leonardo RT, Consolaro A, Carlos IZ, Leonardo MR. Evaluation of cell culture cytotoxicity of five root canal sealers. J Endod. 2000;26: 328-330.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Briseno BM, Willershausen B. Root canal sealer cytotoxicity on human gingival fibroblasts. Part II. Silicone- and resin-based sealers. J Endod. 1991;17: 537-540.PubMed
- 19. Cohen BI, Pagnillo MK, Musikant BL, Deutsch AS. The evaluation of apical leakage for three endodontic fill systems. Gen Dent. 1998;46: 618-623.PubMed
- 20. Leyhausen G, Heil J, Reifferscheid G, Waldmann P, Geurtsen W. Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of the epoxy resin-based root canal sealer AH Plus. J Endod. 1999;25: 109-113.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Koulaouzidou EA, Papazisis KT, Beltes P, Geromichalos GD, Kortsaris AH. Cytotoxicity of three resin-based root canal sealers: an in vitro evaluation. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1998;14: 182-185.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Huang TH, Lii CK, Chou MY, Kao CT. Lactate dehydrogenase leakage of hepatocytes with AH26 and AH Plus sealer treatments. J Endod. 2000;26: 509-511.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Kim YB, Baek SH, Bae KS. In vivo study on the biocompatibility of new resin-based root canal sealers. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2002;27: 122-134.Article
- 24. Park SY, Lee WC, Lim SS. Cytotoxicity and antibacterial property of new resin-based sealer. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2003;28: 162-168.Article
- 25. Chohayeb AA, Chow LC, Tsaknis PJ. Evaluation of calcium phosphate as a root canal sealer-filler material. J Endod. 1987;13: 384-387.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Sugawara A, Nishiyama M, Kusama K, Moro I, Nishimura S, Kudo I, Chow LC, Takagi S. Histopathological reactions of calcium phosphate cement. Dent Mater J. 1992;11: 11-16.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure 1
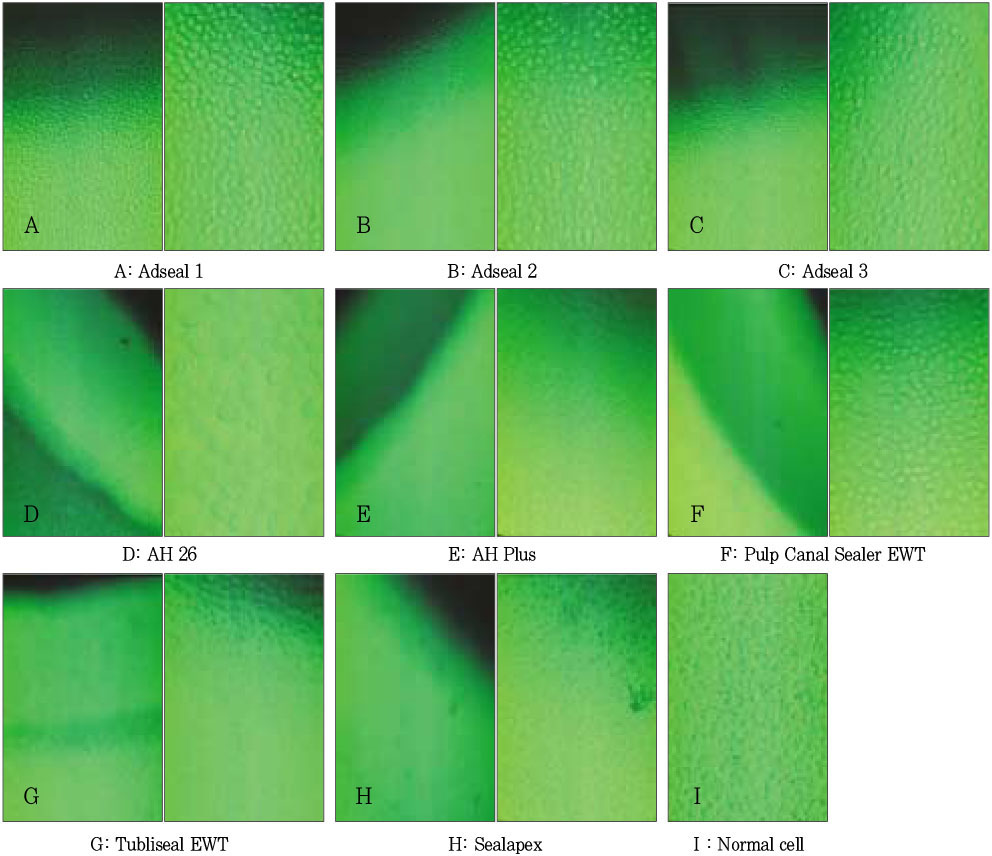
Decolorization zone and cell appearance by agar diffusion test (inverted microscope, left: × 200, right: × 400). Each sealer has two pictures. The left sides show the decolorization zone except Adseal 1, 2, and 3. Adseal 1, 2, and 3 show normal cell morphology and cell density.

Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Cytotoxicity and subcutaneous tissue response of beta RCS in comparison with ADSeal and AH plus endodontic sealers: in vitro/in vivo study
Mehdi Dastorani, Mohammad Reza Babaie, Babak Farzaneh, Atousa Haghdoost
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytotoxicity Comparison of Sure-seal root and Adseal Sealers on mouse fibroblast Cells:Invitro study
Azam haddadikohsar, Mohammad shokrzade, Marjan Fallah, Fatemeh Shakeri
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 46. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers before and after Setting Procedures
Mijoo Kim, Marc Hayashi, Bo Yu, Thomas K. Lee, Reuben H. Kim, Deuk-won Jo
Life.2022; 12(6): 847. CrossRef - Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Four Different Root Canal Sealers in Osteoblastic Cell Line MC3T3-El
Nu-Ri Jun, Sun-Kyung Lee, Sang-Im Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(4): 243. CrossRef
Cytotoxicity of resin-based root canal sealer, adseal
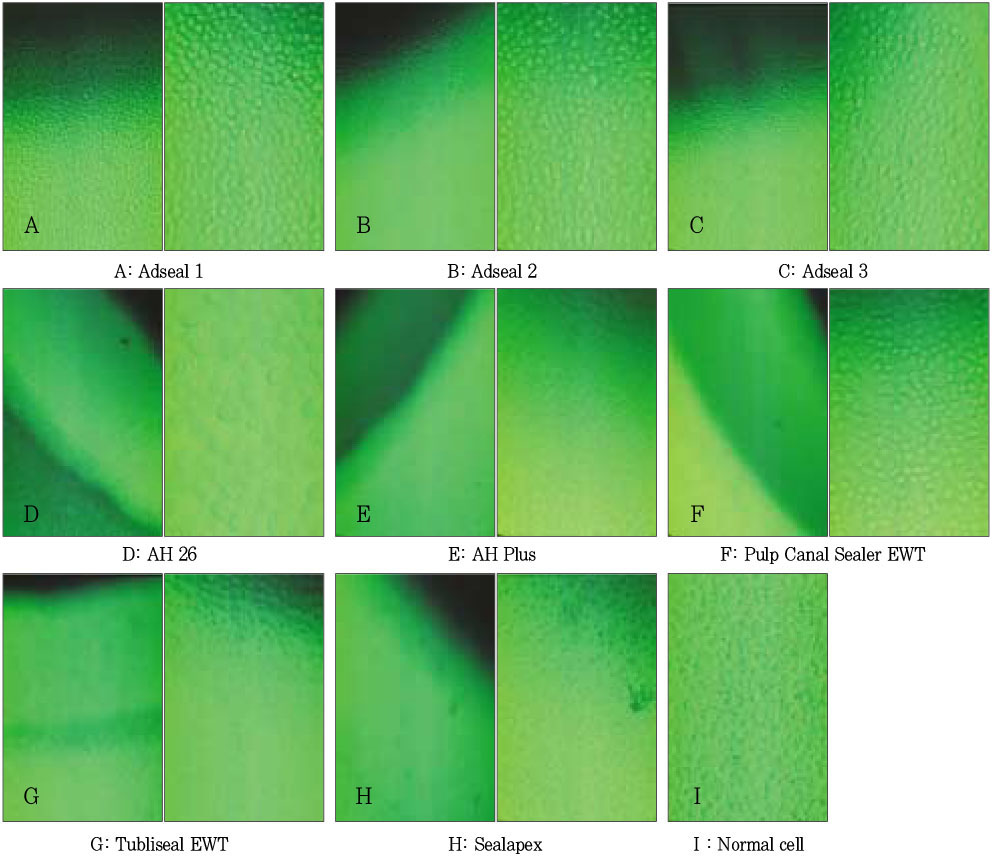
Figure 1
Decolorization zone and cell appearance by agar diffusion test (inverted microscope, left: × 200, right: × 400). Each sealer has two pictures. The left sides show the decolorization zone except Adseal 1, 2, and 3. Adseal 1, 2, and 3 show normal cell morphology and cell density.
Figure 1
Cytotoxicity of resin-based root canal sealer, adseal
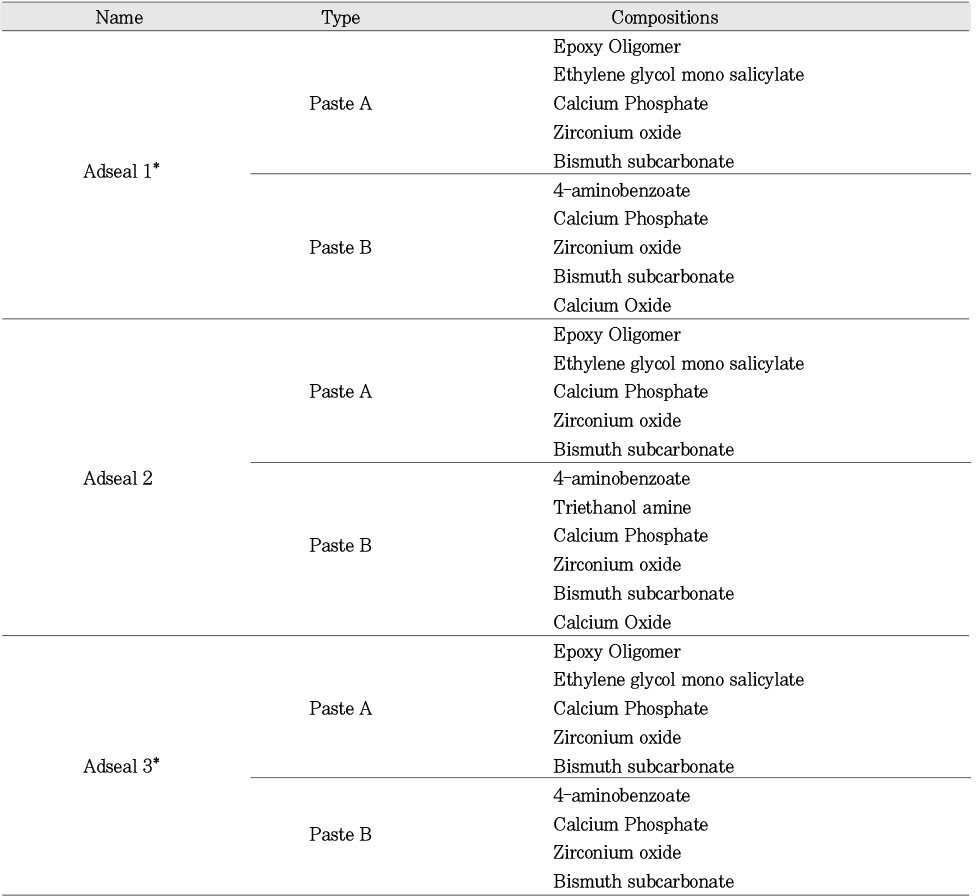
Compositions of Adseal 1, 2, and 3
*Adseal 1 and Adseal 3 have same ingredients but they are different in the ratio of ingredients.
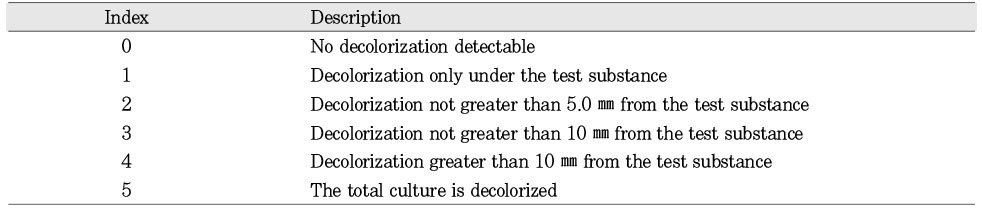
Criteria for scoring of decolorization index
Decolorization index of experimental sealers (agar diffusion test)
Table 1
Compositions of Adseal 1, 2, and 3
*Adseal 1 and Adseal 3 have same ingredients but they are different in the ratio of ingredients.
Table 2
Criteria for scoring of decolorization index
Table 3
Decolorization index of experimental sealers (agar diffusion test)

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

