Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
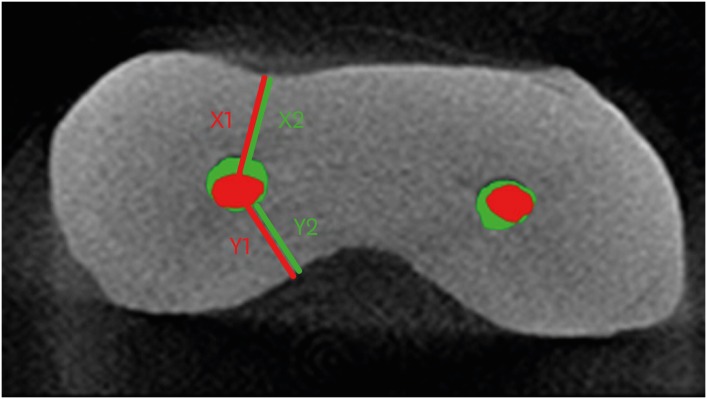
- Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
- Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare root canal volume change and canal transportation by Vortex Blue (VB; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties), ProTaper Next (PTN; Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Universal (PTU; Dentsply Maillefer) nickel-titanium rotary files in curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty canals with 20°–45° of curvature from extracted human molars were used. Root canal instrumentation was performed with VB, PTN, and PTU files up to #30.06, X3, and F3, respectively. Changes in root canal volume before and after the instrumentation, and the amount and direction of canal transportation at 1, 3, and 5 mm from the root apex were measured by using micro-computed tomography. Data of canal volume change were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test, while data of amount and direction of transportation were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney
U test.Results There were no significant differences among 3 groups in terms of canal volume change (
p > 0.05). For the amount of transportation, PTN showed significantly less transportation than PTU at 3 mm level (p = 0.005). VB files showed no significant difference in canal transportation at all 3 levels with either PTN or PTU files. Also, VB files showed unique inward transportation tendency in the apical area.Conclusions Other than PTN produced less amount of transportation than PTU at 3 mm level, all 3 file systems showed similar level of canal volume change and transportation, and VB file system could prepare the curved canals without significant shaping errors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
Yaprak Cesur, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Ahmet Serper, Mert Ocak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of Vortex Blue and TruNatomyTM Ni-Ti Rotary Systems
Batool Alghamdi, Mey Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman, Lina Bahanan, Ali Alrahlah, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Sarah Bukhari, Mohammed Howait, Loai Alsofi
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 980. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of nickel titanium rotary instruments on canal transportation and centering ability in curved canals by using cone beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Krishnaveni Krishnaveni, Nikitha Kalla, Nagalakshmi Reddy, Sharvanan Udayar
Journal of Dental Specialities.2023; 11(2): 105. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - A Comparison of Canal Width Changes in Simulated Curved Canals prepared with Profile and Protaper Rotary Systems
Aisha Faisal, Huma Farid, Robia Ghafoor
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 55. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Respect of the Root Canal Trajectory by Rotary Niti Instruments (Protaper®Universal): Retrospective Radiographic Study
Salma El Abbassi, Sanaa Chala, Majid Sakout, Faïza Abdallaoui
Integrative Journal of Medical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
- 1,820 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Rheological characterization of composites using a vertical oscillation rheometer
- In-Bog Lee, Byung-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Sang-Tag Lee, Chung-Moon Um
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(6):489-497. Published online November 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.489
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective The purpose of this study was to investigate the viscoelastic properties related to handling characteristics of composite resins.
Methods A custom designed vertical oscillation rheometer (VOR) was used for rheological measurements of composites. The VOR consists of three parts: (1) a measuring unit, (2) a deformation induction unit and (3) a force detecting unit. Two medium viscous composites, Z100 and Z250 and two packable composites, P60 and SureFil were tested. The viscoelastic material function, including complex modulus
E * and phase angle δ, were measured. A dynamic oscillatory test was used to evaluate the storage modulus (E '), loss modulus (E ") and loss tangent (tanδ) of the composites as a function of frequency (ω) from 0.1 to 20 Hz at 23℃.Results The
E ' andE " increased with increasing frequency and showed differences in magnitude between brands. TheE *s of composites at ω = 2 Hz, normalized to that of Z100, were 2.16 (Z250), 4.80 (P60) and 25.21 (SureFil). The magnitudes and patterns of the change of tanδ of composites with increasing frequency were significantly different between brands. The relationships between the complex modulusE *, the phase angle δ and the frequency ω were represented by frequency domain phasor form,E * (ω) =E *eiδ =E *∠δ.Conclusions The viscoelasticity of composites that influences handling characteristics is significant different between brands. The VOR is a relatively simple device for dynamic, mechanical analysis of high viscous dental composites. The locus of frequency domain phasor plots in a complex plane is a valuable method of representing the viscoelastic properties of composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of instrument compliance on the polymerization shrinkage stress measurements of dental resin composites
Deog-Gyu Seo, Sun-Hong Min, In-Bog Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 145. CrossRef
- Effect of instrument compliance on the polymerization shrinkage stress measurements of dental resin composites
- 1,418 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


