Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of ProTaper Gold and EdgeEvolve files in canals with single- and double-curvature
- Wafaa A. Khalil, Zuhair S. Natto
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e19. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e19
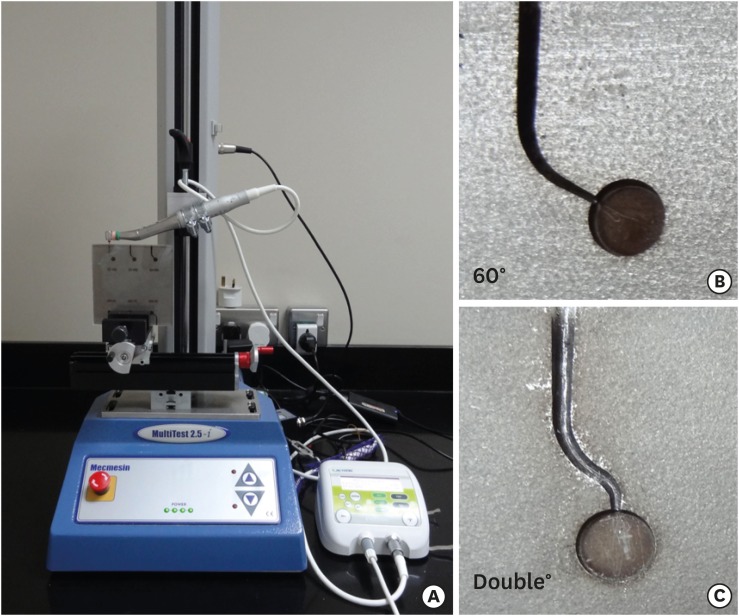
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cyclic fatigue, bending resistance, and surface roughness of EdgeEvolve (EdgeEndo) and ProTaper Gold (Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties) nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary files.
Materials and Methods The instruments (
n = 15/each) were tested for cyclic fatigue in single- (60° curvature, 5-mm radius) and double-curved (coronal curvature 60°, 5-mm radius, and apical curvature of 30° and 2-mm radius) artificial canals. The number of cycles to fracture was calculated. The bending resistance of both files were tested using a universal testing machine where the files were bent until reach 45°. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray energy-dispersive spectrometric analysis were used for imaging the fractured segments, while the atomic force microscope was used to quantify the surface roughness average (Ra).Results EdgeEvolve files exhibited higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in single- and double-curved canals (
p < 0.05) and both files were more resistant to cyclic fatigue in single-curved canals than double-curved canals (p < 0.05). EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly more flexibility than did ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05). Both files had approximately similar Ni and Ti contents (p > 0.05). EdgeEvolve files showed significantly lower Ra values than ProTaper Gold files (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitation of this study, EdgeEvolve files exhibited significantly higher cyclic fatigue resistance than ProTaper Gold files in both single- and double-curved canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
Mert Unal, Elif Bahar Cakici
Microscopy Research and Technique.2026; 89(1): 87. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of alterations in surface topographies of three different rotary files after root canal preparation with different irrigating solutions: Atomic force microscopic study
PremSai Parepalli, TB. V G. Raju, PKrishna Prasad, GowtamDev Dondapati, VenkataSrija Kintada, Alekhya Mediboyina
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 299. CrossRef - Assessment of surface topographic changes of nickel–titanium rotary endodontic file at repeated usage: An in vitro study
E. Viswas, VSS Krishna, E. Sridevi, A. J. Sai Sankar, K. Siva Sankar, B. Nagesh
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 149. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Surface Roughness of Rotary NiTi Instruments after Simulated Clinical Use in Curved Root Canals – An Atomic Force Microscopy Study
Raksha Bhat, Arjun Kini, Preethesh Shetty, Payalben Kansara, Bapanaiah Penugonda
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - Influence of nickel-titanium rotary systems with varying cross-sectional, pitch, and rotational speed on deflection and cyclic fatigue: a finite element analysis study
Wignyo Hadriyanto, Lukita Wardani, Christina Nugrohowati, Ananto Alhasyimi, Rachmat Sriwijaya, Margareta Rinastiti, Widowati Siswomihardjo, Gunadi, T. Yamada, A.A.C. Pramana, Y. Ophinni, A. Gusnanto, W.A. Kusuma, J. Yunus, Afiahayati, R. Dharmastiti, T.
BIO Web of Conferences.2021; 41: 05005. CrossRef - Can the Separated Instrument be Removed From the Root Canal System out by Magnetism? A Hypothesis
Mohammad Daryaeian, Sanjay Miglani, AbdolMahmood Davarpanah, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Mohsen Ramazani
Dental Hypotheses.2019; 10(4): 108. CrossRef - Resistance to cyclic fatigue of reciprocating instruments determined at body temperature and phase transformation analysis
Raymond Scott, Ana Arias, José C. Macorra, Sanjay Govindjee, Ove A. Peters
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(3): 400. CrossRef
- Comparison of Design, Cyclic Fatigue Resistance, and Metallurgical Properties of Original, Replica‐Like, and Counterfeit Nickel‐Titanium Files
- 1,551 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The effect of reinforcing methods on fracture strength of composite inlay bridge
- Chang-Won Byun, Sang-Hyuk Park, Sang-Jin Park, Kyoung-Kyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(2):111-120. Published online March 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.2.111
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effects of surface treatment and composition of reinforcement material on fracture strength of fiber reinforced composite inlay bridges.
The materials used for this study were I-beam, U-beam TESCERA ATL system and ONE STEP(Bisco, IL, USA). Two kinds of surface treatments were used; the silane and the sandblast. The specimens were divided into 11 groups through the composition of reinforcing materials and the surface treatments.
On the dentiform, supposing the missing of Maxillary second pre-molar and indirect composite inlay bridge cavities on adjacent first pre-molar disto-occlusal cavity, first molar mesio-occlusal cavity was prepared with conventional high-speed inlay bur.The reinforcing materials were placed on the proximal box space and build up the composite inlay bridge consequently. After the curing, specimen was set on the testing die with ZPC. Flexural force was applied with universal testing machine (EZ-tester; Shimadzu, Japan). at a cross-head speed of 1 mm/min until initial crack occurred. The data wasanalyzed using one-way ANOVA/Scheffes' post-hoc test at 95% significance level.
Groups using I-beam showed the highest fracture strengths (p < 0.05) and there were no significant differences between each surface treatment (p > 0.05). Most of the specimens in groups that used reinforcing material showed delamination.
The use of I-beam represented highest fracture strengths (p < 0.05).
In groups only using silane as a surface treatment showed highest fracture strength, but there were no significant differences between other surface treatments (p > 0.05).
The reinforcing materials affect the fracture strength and pattern of composites inlay bridge.
The holes at the U-beam did not increase the fracture strength of composites inlay bridge.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Esthetic rehabilitation of single anterior edentulous space using fiber-reinforced composite
Hyeon Kim, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon Lee, Jeong-Won Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 220. CrossRef
- Esthetic rehabilitation of single anterior edentulous space using fiber-reinforced composite
- 1,193 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


