Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of whitening mouth rinses formulated with mushroom residues and their effect on enamel’s physical properties
- Julliana Andrade da Silva, Dayse Alexia de Carvalho de Brito, Débora Alves Nunes Leite Lima, Juliano Lemos Bicas, Gislaine Ricci Leonardi
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e27. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
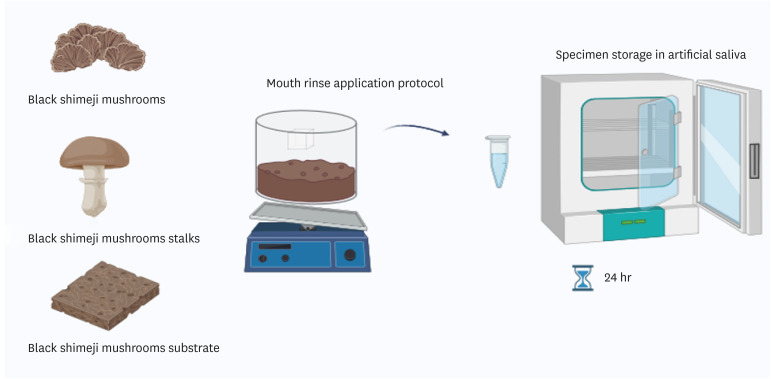
ePub Objectives This study aimed to develop whitening mouth rinses formulated with industrial mushrooms and compare them with over-the-counter whitening mouth rinses.
Materials and Methods Formulations with black shimeji mushrooms, mushroom substrates, and mushroom stalks were developed. Bovine enamel/dentin samples were divided into 7 groups (
n = 10): Colgate Luminous White, Listerine Whitening Extreme (LWE), Listerine Cool Mint (LC), mushroom extract rinse (MEC), mushroom substrate rinse (MSB), mushroom stalk rinse (MTC), and artificial saliva. Samples were stained with black tea for 6 days, and then were immersed in 100 mL of each mouth rinse twice daily for 14 days. Color parameters (CIELAB [ΔE*], CIEDE2000 [ΔE00], whiteness index for dentistry [ΔWID]) and microhardness (Knoop hardness number [KHN]) were analyzed at T1 (initial), T2 (24 hours), and T3 (7 days). Mouth rinse pH was measured, and enamel was examined using a scanning electron microscope. Data were analyzed using generalized linear models, and KHN with the generalized linear mixed model for repeated measures (p ≤ 0.05).Results ΔE* was higher in LW and MSB groups. No significant differences were found for ΔE00 (
p = 0.0982) and ΔWID (p = 0.2536). Experimental mouth rinses did not promote enamel whitening based on ΔE00 and ΔWID. LWE and LC reduced KHN and had a more acidic pH, while MEC had higher KHN at T2. MEC, MSB, and MTC had alkaline pH, not altering the tooth surface.Conclusions Black shimeji mushrooms are promising for mouth rinse development due to their alkaline pH and non-altering effect on surface microhardness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of cytotoxicity and bleaching efficacy of gels with calcium polyphosphate and violet LED
Larissa de Jesus Gomes, Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Mariangela Ivette Guanipa Ortiz, Klaus Rischka, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa, Débora Alves Nunes Leite Lima
Brazilian Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of cytotoxicity and bleaching efficacy of gels with calcium polyphosphate and violet LED
- 1,866 View
- 84 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Evaluation of at-home bleaching protocol with application on different surfaces: bleaching efficacy and hydrogen peroxide permeability
- Heloisa Forville, Michael Willian Favoreto, Michel Wendlinger, Roberta Micheten Dias, Christiane Philippini Ferreira Borges, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e33. Published online October 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
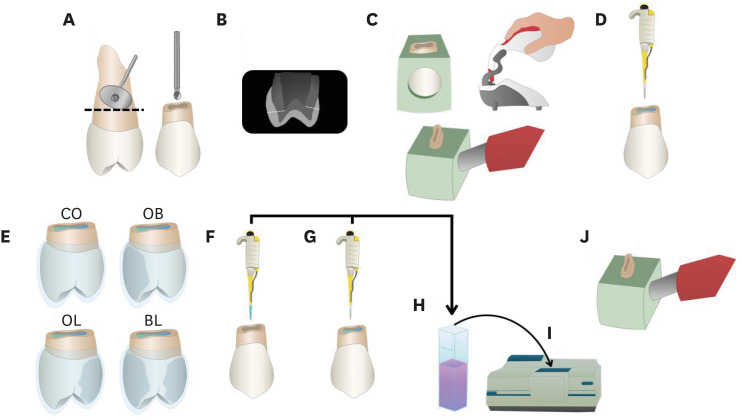
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the bleaching efficacy and hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber by the at-home bleaching gel in protocols applied on different dental surfaces.
Materials and Methods Forty premolars were randomly into 4 groups: control group no bleaching, only application on the buccal surface (OB), only application on the lingual surface (OL) and application in buccal and lingual surfaces, simultaneously (BL). At-home bleaching gel (White Class 7.5%) was used for the procedure. The bleaching efficacy was evaluated with a digital spectrophotometer (color change in CIELAB [Δ
E ab] and CIEDE 2000 [ΔE 00] systems and Whitening Index for Dentistry [ΔWID]). The hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber (µg/mL) was assessed using UV-Vis spectrophotometry and data were analyzed for a 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).Results All groups submitted to bleaching procedure showed bleaching efficacy when measured with Δ
E ab and ΔE 00 (p > 0.05). Therefore, when analyzed by ΔWID, a higher bleaching efficacy were observed for the application on the groups OB and BL (p = 0.00003). Similar hydrogen peroxide permeability was found in the pulp chambers of the teeth undergoing different protocols (p > 0.05).Conclusions The application of bleaching gel exclusively on the OB is sufficient to achieve bleaching efficacy, when compared to BL. Although the OL protocol demonstrated lower bleaching efficacy based on the ΔWID values, it may still be of interest and relevant in certain clinical scenarios based on individual needs, requiring clinical trials to better understand its specificities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of whitening pens on hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber, color change and surface morphology
Laryssa Mylenna Madruga Barbosa, Gabrielle Gomes Centenaro, Deisy Cristina Ferreira Cordeiro, Maria Alice de Matos Rodrigues, Letícia Condolo, Michael Willian Favoreto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 154: 105595. CrossRef - Evaluation of bleaching efficiency of carbamide peroxide applied on different dental surfaces: An in vitro study
R. Gokulnath, R. S. Mohan Kumar, A. Jayasenthil, R. Anjana, G. Sree Vidya
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 366. CrossRef - Characterization and effects on enamel of low-concentration bleaching gels containing hyaluronic acid, NF_TiO2 nanoparticles and irradiated with violet LED light
Marcos Roberto Lima Benati, Matheus Kury, Priscila Borges Gobbo de Melo, Iago César Ribeiro Teles Matos, Roberta Tarkany Basting, Rosanna Tarkany Basting, Fernando Luis Esteban Florez, Vanessa Cavalli
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of bleaching on white spot lesions: hydrogen peroxide permeability and color alteration
Laryssa Mylenna Madruga Barbosa, Bruno Baracco, Taynara S. Carneiro, Michael Willian Favoreto, Michel Wendlinger, Daniel Jiménez-Díez, Laura Ceballos, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of a buccal and lingual at‐home bleaching protocol—A randomized, split‐mouth, single‐blind controlled trial
Heloisa Forville, Laís Giacomini Bernardi, Michael Willian Favoreto, Felipe Coppla, Taynara de Souza Carneiro, Fabiana Madalozzo Coppla, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(9): 1301. CrossRef - REANATOMIZAÇÃO DE DENTE CONOIDE ASSOCIADA A ESTÉTICA VERMELHA: RELATO DE CASO
Ana Karolayne Sousa de Morais, Daniele Fernanda Sousa Barros, Daniel Messias Limeira, Rhana Leticia de Oliveira Faria, Roberta Furtado Carvalho, Sandna Nolêto de Araújo, Laura Barbosa Santos Di Milhomem
Revista Contemporânea.2024; 4(10): e6299. CrossRef - Effect of the reduction in the exposure time to at-home bleaching gel on color change and tooth sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Priscila Borges Gobbo de Melo, Letícia Vasconcelos Silva Souza, Lucianne Cople Maia, Guido Artemio Marañón-Vásquez, Matheus Kury, Vanessa Cavalli
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of whitening pens on hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber, color change and surface morphology
- 4,188 View
- 79 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a bleaching agent on properties of commercial glass-ionomer cements
- Fernanda Lúcia Lago de Camargo, Ailla Carla Lancellotti, Adriano Fonseca de Lima, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo Martins, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e32. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of a bleaching agent on the composition, mechanical properties, and surface topography of 6 conventional glass-ionomer cements (GICs) and one resin-modified GIC.
Materials and Methods For 3 days, the specimens were subjected to three 20-minute applications of a 37% H2O2-based bleaching agent and evaluated for water uptake (WTK), weight loss (WL), compressive strength (CS), and Knoop hardness number (KHN). Changes in surface topography and chemical element distribution were also analyzed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. For statistical evaluation, the Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon paired tests (
α = 0.05) were used to evaluate WTK and WL. CS specimens were subjected to 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05), and KH was evaluated by one-way ANOVA, the Holm-Sidakpost hoc test (α = 0.05), and thet -test for independent samples (α = 0.05).Results The bleaching agent increased the WTK of Maxxion R, but did not affect the WL of any GICs. It had various effects on the CS, KHN, surface topography, and the chemical element distribution of the GICs.
Conclusions The bleaching agent with 37% H2O2 affected the mechanical and surface properties of GICs. The extent of the changes seemed to be dependent on exposure time and cement composition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multidisciplinary conservative management of a severely discolored nonvital tooth
Álvaro Ferrando Cascales, Francesc Abella Sans, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, José Amengual Lorenzo
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(4): 941. CrossRef - The effects of bleaching products on the color stability of ion-releasing restoratives
Jian Sheng Lee, Noor Azlin Yahya, Azwatee Abdul Aziz, Adrian U-Jin Yap
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Exploration of Interaction Mechanisms of Intracoronal Bleaching on the Compressive Strength of Conventional and Calcium Silicate–Based Self‐Adhesive Resins and Their Bonding to Composite Resin Restorative Material
Fereshteh Shafiei, Paria Dehghanian, Shadi Tivay, Yasamin Ghahramani, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharama, E. Terrer
EMC - Odontologie.2023; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Home and In-Office Bleaching on Microhardness and Color of Different CAD/CAM Ceramic Materials
Ruwaida Z. Alshali, Mohammed A. Alqahtani
Materials.2022; 15(17): 5948. CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharama, E. Terrer
EMC - Médecine buccale.2022; 15(4): 1. CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharam, E. Terrer
EMC - Orthopédie dentofaciale.2022; 34(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Glass Polyalkenoate Cements: An In Vivo Pilot Study Using a Sheep Model
Leyla Hasandoost, Daniella Marx, Paul Zalzal, Oleg Safir, Mark Hurtig, Cina Mehrvar, Stephen D. Waldman, Marcello Papini, Mark R. Towler
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2021; 12(3): 44. CrossRef - The Effect of Simulated Field Storage Conditions on Dental Restorative Materials for Military Field Use
David J Lemon, Wen Chen, Trevor Smith, April A Ford, Steven X Moffett, Jeffrey T Hoyle, Nicholas J Hamlin, Yoon Y Hwang
Military Medicine.2020; 185(5-6): e831. CrossRef
- Multidisciplinary conservative management of a severely discolored nonvital tooth
- 1,646 View
- 5 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
- Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(2):95-102. Published online March 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.2.095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of light energy on the tooth whitening effect of bleaching agent in vitro. Extracted human mandibular molars were sectioned to 2 fragments(mesial, distal) and lingual portions of crown were used in this study. All specimens were stained using a red wine for 24 hours and immersed in artificial saliva. Specimens divided into four groups, group 1 and 2 light-activated by LumaCool (LED, LumaLite, Inc., Spring Valley, USA), group 3 and 4 light-activated by FlipoWhite2 (Plasma acr lamp, Lokki, Australia). Group 1 and 3 bleached with LumaWhite(LumaLite, Inc., Spring Valley, USA), group 2 and 4 bleached with Polaoffice(SDI, Victoria, Australia). Bleaching treatment performed during 10 minutes every 24 hours and repeated 6 times. During bleaching treatment , distal fragments was light-activated(L) but mesial fragments was not(NL). Shade assessment employed before and after bleaching treatment using spectrophotometer. The results of the change in shade was compared and analysed between NL and L by using paired-sample T test with 95% level of confidence.
There were no significant differences between NL and L with a few exceptions. In group 2, a* value more change in L, in group 3, b* value more change in L, in group 4, a* value less change in L. After bleaching, L* value and ΔE increased in all groups and the value of a* and b* decreased in all groups.
Within the limitation of this test conditions, the results of this study indicate that the light energy has no obvious improving impact on the tooth whitening effect of a bleaching agent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Tooth-whitening Apparatus
Young-Jin Lee, Jong-Hoo Paik, Jeong-Bae Lee, Seung-Jae Choi
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2013; 14(5): 268. CrossRef - Clinical assessment of whitening efficacy and safety of in-office tooth whitening system containing 15% hydrogen peroxide with or without light activation
Young-Suk Noh, Young-Jee Rho, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hyang-Ok Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Hyun-Jeong Kweon, Yeun Kim, Seong-Yeon Park, Hee-Young Yoon, Jung-Hyun Lee, Chan-Hee Lee, So-Ram Oh, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(4): 306. CrossRef
- Development of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Tooth-whitening Apparatus
- 1,335 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
The effects of tooth bleaching agents on microhardness of enamel
in situ - Yoon-Woo Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(6):470-476. Published online November 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.6.470
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The objective of this
in situ study was to evaluate the effects of whitening strip (Claren, LG Household & Health Care Ltd, 2.6% hydrogen peroxide) and gel (Opalescence, Ultradent, 10% carbamide peroxide) on microhardness of enamel in comparison with untreated control. Extracted twenty human upper incisors were disinfected, cleaned, and labial side of each incisor sectioned into 3 fragments by 2 × 2 mm size. After sectioning, labial sides of fragments were flattened and fixed to orthodontic bracket using flowable composite resin. Specimens prepared from each tooth were attached to the labial side of upper incisors of twenty volunteers one by one and treated by three different methods: (1) untreated control (2) treated with whitening strip for 14 days (3) treated with whitening gel for 14 days.Microhardness (Microhardness tester, Zwick) of each specimen was measured at the baseline of pre-treatment, immediate after bleaching treatment, 14 days after bleaching treatment and Knoop Hardness Number was determined. Microhardness changes of experimental groups were compared.
The results show that tooth whitening strip and gel used in this study does not effect the micro-hardness of enamel during bleaching procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Damage and Bleaching Effect according to the Application Type of Home Tooth Bleaching Applicants
Na-Yeoun Tak, Do-Seon Lim, Hee-Jung Lim, Im-Hee Jung
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2020; 20(4): 252. CrossRef - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef
- Surface Damage and Bleaching Effect according to the Application Type of Home Tooth Bleaching Applicants
- 3,006 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


