Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Pattern of endodontic instrument separation and factors affecting its retrieval: a 10-year retrospective observational study in a postgraduate institute
- Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Aswathi Varghese, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Srinivasan Narasimhan
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e7. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
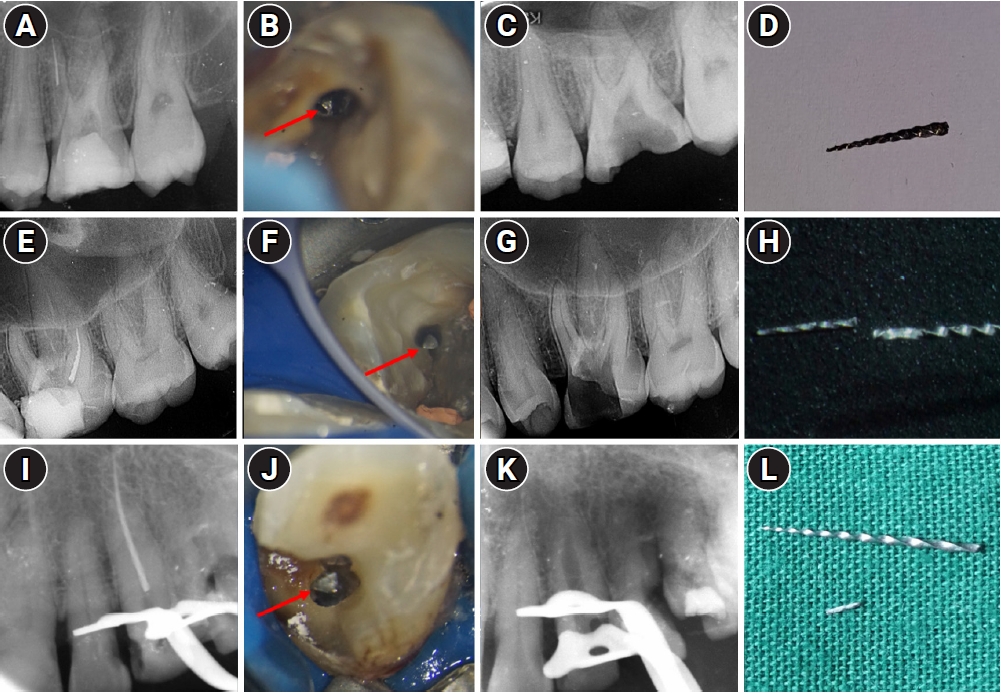
This study aimed to assess the pattern of endodontic instrument separation, their retrievability, and factors affecting its retrieval, in a postgraduate institute.
Methods
Cases referred for the management of separated endodontic instruments (SEI) from 2013 to 2023 were considered for this study. Data related to demographics, tooth type, file type, and retrieval were documented in an Excel sheet. Eight prognostic factors assumed to influence the retrieval were analyzed in this study. The secondary aim was to compare the pattern of SEI and retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. Retrieval was attempted by a senior endodontist under the dental operating microscope. Various ultrasonic tips and a Broken Tool Removal loop system were used during retrieval. Simple descriptive statistics were performed. Binomial logistic regression was done to identify the effect of the eight prognostic factors on the retrieval outcome.
Results
A total of 190 SEI was reported. SEI occurred more often in posterior teeth than anterior teeth, mandibular arch than maxillary arch, and in larger files than smaller files. Separation occurred more often in the apical third compared to the other levels. Retrieval was attempted in 88 cases and successful in 70 cases (79.5%). The larger taper and apical position of the SEI negatively influenced the retrieval by 1.4 and 8.7 times, respectively.
Conclusions
Retrieval of SEI was successful in the majority of the cases. An increase in taper and apically placed SEI negatively impacted the retrieval. There was no difference in the pattern of separation nor retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Le Zhao, WangYu Luo, Yue Shen, WanNing Yu, Liu Yang, Xiaolei Zhang
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of microscope-assisted root canal treatment in permanent posterior teeth: A retrospective cohort study
Ya-Ching Chang, Ting-Ya Wang
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 157: 105771. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Nildem İnönü, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, Kaan Orhan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(14): 1744. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF INTRACANAL SEPARATED INSTRUMENTS: FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO ENDODONTIC FILE SEPARATION — A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Tareq Hajaj, Paul Freiman , Serban Talpos Niculescu , Mihai Rominu , Tiberiu Hosszu , Ioana Veja
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(2): 993. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Failure of Separated Instrument Removal: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
- 7,764 View
- 368 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
- Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e36. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
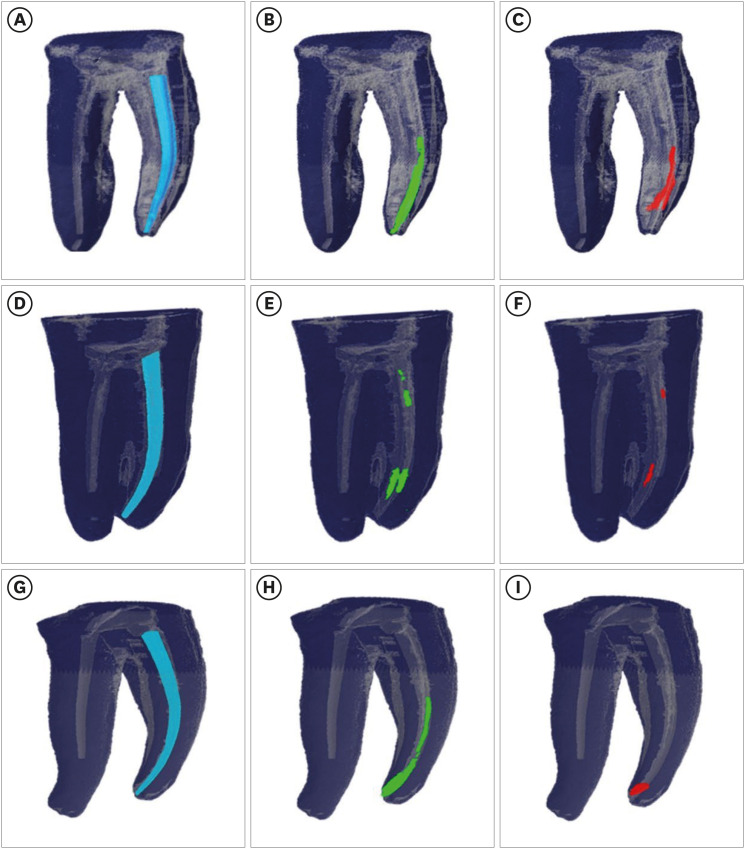
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of a single-file reciprocating system (WaveOne Gold, WOG) and a multi-file rotary system (ProTaper Universal Retreatment, PTUR) in removing canal filling from severely curved canals and to evaluate the possible adjunctive effects of XP-Endo Finisher (XPF), the Self-Adjusting File (SAF), and an erbium, chromium: yttrium, scandium, gallium garnet (Er,Cr:YSGG) laser using micro-computed tomography (μCT).
Materials and Methods Sixty-six curved mandibular molars were divided into 2 groups based on the retreatment technique and then into 3 based on the supplementary method. The residual filling volumes and root canals were evaluated with μCT before and after retreatment, and after the supplementary steps. The data were statistically analyzed with the
t -test, Mann-WhitneyU test, analysis of covariance, and factorial analysis of variance (p < 0.05).Results PTUR and WOG showed no significant difference in removing filling materials (
p > 0.05). The supplementary techniques were significantly more effective than reciprocating or rotary systems only (p < 0.01). The supplementary steps showed no significant differences in canal filling removal effectiveness (p > 0.05), but XPF showed less dentin reduction than the SAF and Er,Cr:YSGG laser (p < 0.01).Conclusions The supplementary methods significantly decreased the volume of residual filling materials. XPF caused minimal changes in root canal volume and might be preferred for retreatment in curved root canals. Supplementary approaches after retreatment procedures may improve root canal cleanliness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology
Kıvanç Kamburoğlu
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrieval of AH Plus Bioceramic and Ceraseal Versus AH Plus in Endodontic Retreatment
Eurok Shim, Jee Woo Son, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(6): 1826. CrossRef - Characteristics and Effectiveness of XP‐Endo Files and Systems: A Narrative Review
Sarah M. Alkahtany, Rana Alfadhel, Aseel AlOmair, Sarah Bin Durayhim, Kee Y. Kum
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the filling technique on the filling removal from oval-shaped canals
Lislaine Valerio, Lisa Yurie Oda, Felipe Andretta Copelli, Clarissa Teles Rodrigues, Everdan Carneiro, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology
- 4,107 View
- 98 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Fracture incidence of Reciproc instruments during root canal retreatment performed by postgraduate students: a cross-sectional retrospective clinical study
- Liliana Machado Ruivo, Marcos de Azevedo Rios, Alexandre Mascarenhas Villela, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Augusto Shoji Kato, Rina Andrea Pelegrine, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e49. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
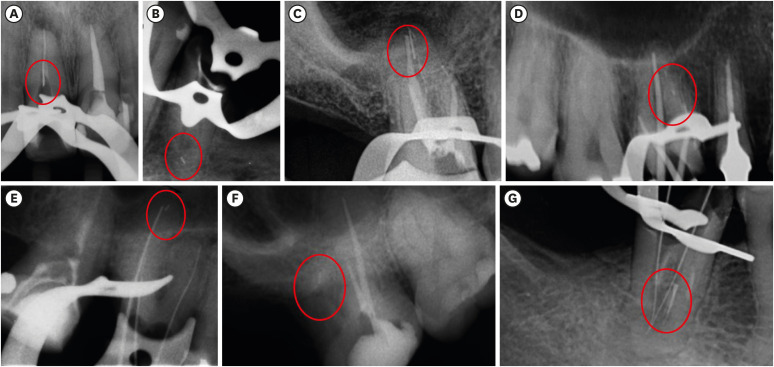
ePub Objectives To evaluate the fracture incidence of Reciproc R25 instruments (VDW) used during non-surgical root canal retreatments performed by students in a postgraduate endodontic program.
Materials and Methods From the analysis of clinical record cards and periapical radiographs of root canal retreatments performed by postgraduate students using the Reciproc R25, a total of 1,016 teeth (2,544 root canals) were selected. The instruments were discarded after a single use. The general incidence of instrument fractures and its frequency was analyzed considering the group of teeth and the root thirds where the fractures occurred. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 test (
p < 0.01).Results Seven instruments were separated during the procedures. The percentage of fracture in relation to the number of instrumented canals was 0.27% and 0.68% in relation to the number of instrumented teeth. Four fractures occurred in maxillary molars, 1 in a mandibular molar, 1 in a mandibular premolar and 1 in a maxillary incisor. A greater number of fractures was observed in molars when compared with the number of fractures observed in the other dental groups (
p < 0.01). Considering all of the instrument fractures, 71.43% were located in the apical third and 28.57% in the middle third (p < 0.01). One instrument fragment was removed, one bypassed, while in 5 cases, the instrument fragment remained inside the root canal.Conclusions The use of Reciproc R25 instruments in root canal retreatments carried out by postgraduate students was associated with a low incidence of fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reciprocating Torsional Fatigue and Mechanical Tests of Thermal-Treated Nickel Titanium Instruments
Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Alejandro Jaime, Carlos Garcia Puente, Giuliana Soimu, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Carlos Nelson Elias, Gustavo de Deus
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(3): 359. CrossRef - Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Perovskite (Nd:YAP) Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 2: Teeth With Significant Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Clément Cerfontaine, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temperature-Dependent Effects on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance in Three Reciprocating Endodontic Systems: An In Vitro Study
Marcela Salamanca Ramos, José Aranguren, Giulia Malvicini, Cesar De Gregorio, Carmen Bonilla, Alejandro R. Perez
Materials.2025; 18(5): 952. CrossRef - The Cost of Instrument Retrieval on the Root Integrity
Marco A. Versiani, Hugo Sousa Dias, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Felipe G. Belladonna, Jorge N. R. Martins, Gustavo De‐Deus
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(12): 1948. CrossRef - Multimethod analysis of large‐ and low‐tapered single file reciprocating instruments: Design, metallurgy, mechanical performance, and irrigation flow
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Fernando Peña‐Bengoa, Natasha C. Ajuz, Victor T. L. Vieira, Jorge N. R. Martins, Duarte Marques, Ricardo Pinto, Mario Rito Pereira, Francisco Manuel Braz‐Fernandes, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 601. CrossRef - Nd: YAP Laser in the Elimination of Endodontic Nickel-Titanium Files Fractured in Rooted Canals (Part 1: Teeth With Minimal Root Curvature)
Amaury Namour, Marwan El Mobadder, Patrick Matamba, Lucia Misoaga, Delphine Magnin , Praveen Arany, Samir Nammour
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue of Different Reciprocating Endodontic Instruments Using Matching Artificial Root Canals at Body Temperature In Vitro
Sebastian Bürklein, Paul Maßmann, Edgar Schäfer, David Donnermeyer
Materials.2024; 17(4): 827. CrossRef - Endodontic Orthograde Retreatments: Challenges and Solutions
Alessio Zanza, Rodolfo Reda, Luca Testarelli
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 245. CrossRef - Design, metallurgy, mechanical properties, and shaping ability of 3 heat-treated reciprocating systems: a multimethod investigation
Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Jorge N. R. Martins, Natasha C. Ajuz, Henrique dos Santos Antunes, Victor Talarico Leal Vieira, Francisco Manuel Braz-Fernandes, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Aurélio Versiani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(5): 2427. CrossRef - Noncontact 3D evaluation of surface topography of reciprocating instruments after retreatment procedures
Miriam Fatima Zaccaro-Scelza, Renato Lenoir Cardoso Henrique Martinez, Sandro Oliveira Tavares, Fabiano Palmeira Gonçalves, Marcelo Montagnana, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Pantaleo Scelza
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(3): 38. CrossRef
- Reciprocating Torsional Fatigue and Mechanical Tests of Thermal-Treated Nickel Titanium Instruments
- 2,610 View
- 23 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
- Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e22. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
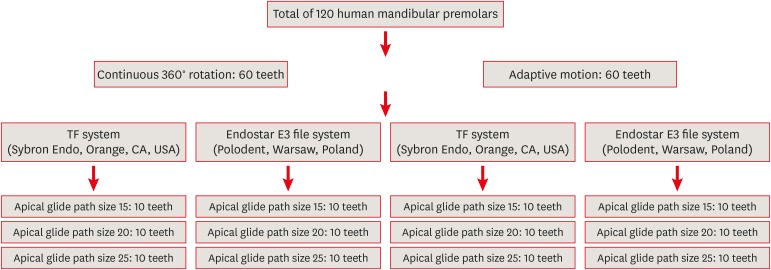
ePub Objectives This study investigated the influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on the time to reach the working length and the fracture resistance of Twisted File (TF) and Endostar E3 files.
Materials and Methods A total of 120 mandibular single-rooted premolars were selected. Two methods of kinetic motion (TF adaptive and continuous rotary motion) and file systems (TF and Endostar E3) were employed. The files were used in root canals prepared to apical glide path sizes of 15, 20, and 25. The time taken to reach the working length and the number of canals used before the instrument deformed or fractured were noted. Fractured instruments were examined with scanning electron microscopy.
Results The TF system took significantly more time to reach the working length than the Endostar E3 system. Both systems required significantly more time to reach the working length at the size 15 glide path than at sizes 20 and 25. A greater number of TFs than Endostar E3 files exhibited deformation, and a higher incidence of instrument deformation was observed in adaptive than in continuous rotary motion; more deformation was also observed with the size 15 glide path. One TF was fractured while undergoing adaptive motion.
Conclusions No significant difference was observed between continuous rotary and adaptive motion. The TF system and adaptive motion were associated with a higher incidence of deformation and fracture. Apical glide path sizes of 20 and 25 required significantly less time to reach the working length than size 15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Assessment of Different File Systems for Working Time Based on Glide Path, Operating Kinetics, and the Fracture Resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Divya Batra, Debkant Jena, Nandita Bansal, Alka Arora, Divya Gaurav Dudulwar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 69. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 1,876 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured instruments: a bibliometric analysis
- Lora Mishra, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Naomi Ranjan Singh, Priti Pragati Rath
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e2. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this research was to identify the top 10 most-cited articles on the management of fractured or broken instruments and to perform a bibliometric analysis thereof.
Materials and Methods Published articles related to fractured instruments were screened from online databases, such as Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect, and highly cited papers, with at least 50 citations since publication, were identified. The most-cited articles were selected and analysed with regard to publication title, authorship, the journal of publication, year, institution, country of origin, article type, and number of citations.
Results The top 10 most-cited articles were from various journals. Most were published in the
Journal of Endodontics , followed by theInternational Endodontic Journal , andDental Traumatology . The leading countries were Australia, Israel, Switzerland, the USA, and Germany, and the leading institution was the University of Melbourne. The majority of articles among the top 10 articles were clinical research studies (n = 8), followed by a basic research article and a non-systematic review article.Conclusions This bibliometric analysis revealed interesting information about scientific progress in endodontics regarding fractured instruments. Overall, clinical research studies and basic research articles published in high-impact endodontic journals had the highest citation rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Endodontide Mikro-Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Kullanımı Konusunda Yayımlanan Makalelerin Bibliyometrik Analizi: Nicel Araştırma
Özge Kurt, Emine Şimşek
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 18(3): 309. CrossRef - A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Top-Cited Articles on Vertical Root Fractures
Pillai Arun Gopinathan , Ikram UI Haq, Nawaf Alfahad, Saleh Alwatban, Abdullah Alghamdi, Amal Alamri, Kiran Iyer
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive factors in the retrieval of endodontic instruments: the relationship between the fragment length and location
Ricardo Portigliatti, Eugenia Pilar Consoli Lizzi, Pablo Alejandro Rodríguez
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most‐cited case reports and case series in Endodontic journals
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Jelena Jacimovic, Aleksandar Jakovljevic, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Paul M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(3): 185. CrossRef - The Most Highly Cited Publications on Basketball Originate From English-Speaking Countries, Are Published After 2000, Are Focused on Medicine-Related Topics, and Are Level III Evidence
Zachary D. Griffin, Jordan R. Pollock, M. Lane Moore, Kade S. McQuivey, Jaymeson R. Arthur, Anikar Chhabra
Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation.2022; 4(3): e891. CrossRef - Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Publication trends in micro‐CT endodontic research: a bibliometric analysis over a 25‐year period
U. Aksoy, M. Küçük, M. A. Versiani, K. Orhan
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(3): 343. CrossRef
- Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
- 1,604 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effect of surface treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium files with a similar cross-section
- Sang Won Kwak, Joo Yeong Lee, Hye-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):216-223. Published online June 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the mechanical properties of various nickel-titanium (NiTi) files with similar tapers and cross-sectional areas depending on whether they were surface-treated.
Materials and Methods Three NiTi file systems with a similar convex triangular cross-section and the same ISO #25 tip size were selected for this study: G6 (G6), ProTaper Universal (PTU), and Dia-PT (DPT). To test torsional resistance, 5 mm of the straightened file's tip was fixed between polycarbonate blocks (
n = 15/group) and continuous clockwise rotation until fracture was conducted using a customized device. To evaluate cyclic fatigue resistance, files were rotated in an artificial curved canal until fracture in a dynamic mode (n = 15/group). The torsional data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukeypost-hoc comparison test, while the cyclic fatigue data were analyzed using the Mann-WhitneyU test at a significance level of 95%.Results PTU showed significantly greater toughness, followed by DPT and G6 (
p < 0.05). G6 showed the lowest resistance in ultimate torsional strength, while it showed a higher fracture angle than the other files (p < 0.05). In the cyclic fatigue test, DPT showed a significantly higher number of cycles to failure than PTU or G6 (p < 0.05).Conclusions Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that the torsional resistance of NiTi files was affected by the cross-sectional area, while the cyclic fatigue resistance of NiTi files was influenced by the surface treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
Abdulkadir ÖZŞAHİN, Meltem DARTAR ÖZTAN, Emine ODABAŞI TEZER
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Heat Treatment and Surface Treatment of Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Ya Shen, He Liu, Zhejun Wang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Markus Haapasalo
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- FARKLI YAPISAL ÖZELLİKTEKİ NİKEL-TİTANYUM KÖK KANAL EĞELERİNİN SODYUM HİPOKLORİT VE SERUM FİZYOLOJİK ÇÖZELTİLERİNDEKİ DÖNGÜSEL YORGUNLUK DİRENÇLERİNİN KARŞILAŞTİRİLMASI
- 1,330 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
- Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):304-309. Published online November 8, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to compare the maximum screw-in forces generated during the movement of various Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) file systems.
Materials and Methods Forty simulated canals in resin blocks were randomly divided into 4 groups for the following instruments: Mtwo size 25/0.07 (MTW, VDW GmbH), Reciproc R25 (RPR, VDW GmbH), ProTaper Universal F2 (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Next X2 (PTN, Dentsply Maillefer,
n = 10). All the artificial canals were prepared to obtain a standardized lumen by using ProTaper Universal F1. Screw-in forces were measured using a custom-made experimental device (AEndoS-k , DMJ system) during instrumentation with each NiTi file system using the designated movement. The rotation speed was set at 350 rpm with an automatic 4 mm pecking motion at a speed of 1 mm/sec. The pecking depth was increased by 1 mm for each pecking motion until the file reach the working length. Forces were recorded during file movement, and the maximum force was extracted from the data. Maximum screw-in forces were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey'spost hoc comparison at a significance level of 95%.Results Reciproc and ProTaper Universal files generated the highest maximum screw-in forces among all the instruments while M-two and ProTaper Next showed the lowest (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Geometrical differences rather than shaping motion and alloys may affect the screw-in force during canal instrumentation. To reduce screw-in forces, the use of NiTi files with smaller cross-sectional area for higher flexibility is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Restoration of teeth lacking complete ferrules using cast precious metal alloy post-and-cores and knife-edged crowns: A retrospective clinical study
Fangyue Xiang, Keying Shi, Haoyang Hua, Jing Zhao, Yuanna Zheng
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(5): 1729. CrossRef - Comparison of mechanical properties and shaping performance of ProGlider and ProTaper ultimate slider
Jeyi Song, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Treatment Prevents Effects of Downward Loads on the Screw-In Force Generation and Canal-Centering Ability of Nickel–Titanium Rotary Instruments
Keiichiro Maki, Arata Ebihara, Yanshan Luo, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Satoshi Omori, Shunsuke Kimura, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2025; 18(15): 3610. CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of rotation and insertion speeds of rotary Ni-Ti file on the vertical force and torque during root canal preparation: by a new automatic root canal shaping simulation method
Hyungwoo Lee, In-Bog Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2025; 52(4): 221. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Effect of Core Mass and Alloy on Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Different Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Instruments in Matching Artificial Canals
Sebastian Bürklein, Lennart Zupanc, David Donnermeyer, Karsten Tegtmeyer, Edgar Schäfer
Materials.2021; 14(19): 5734. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of torque and apical force to assess the cutting behaviour of ProTaper Next and ProTaper Universal endodontic instruments
Gustavo de Cristofaro Almeida, Diego Pinheiro Aun, Pedro Damas Resende, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Ana Cecília Diniz Viana, Vicente Tadeu Lopes Buono, Maria Guiomar de Azevedo Bahia
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 52. CrossRef - Enhanced root canal-centering ability and reduced screw-in force generation of reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments with a post-machining thermal treatment
Keiichiro MAKI, Arata EBIHARA, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Kana MIYARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(2): 251. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Evaluation of stress distribution in nickel-titanium rotary instruments with different geometrical designs subjected to bending and torsional load: a finite element study
Manar Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of mechanical properties of WaveOne Gold Primary reciprocating instruments
Tong FANGLI, Keiichiro MAKI, Shunsuke KIMURA, Miki NISHIJO, Daisuke TOKITA, Arata EBIHARA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(3): 490. CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Gripping the Gripped: Removal of Foreign Bodies from Root Canal System
Shweta Jain, Sachin Jain, Shikha Jain, Sophia Thakur
Dental Research and Management.2019; : 13. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Orifice Preflaring Nickel-titanium Rotary Instrument Heat Treated Using T-Wire Technology
Maamoun Ataya, Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Rashid El Abed, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1867. CrossRef - How biomechanics can affect the endodontic treated teeth and their restorative procedures?
Carlos José Soares, Monise de Paula Rodrigues, André Luis Faria-e-Silva, Paulo Cesar Freitas Santos-Filho, Crisnicaw Veríssimo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Antheunis Versluis
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Nickel–titanium instruments in endodontics: a concise review of the state of the art
Giulio Gavini, Marcelo dos Santos, Celso Luis Caldeira, Manoel Eduardo de Lima Machado, Laila Gonzales Freire, Elaine Faga Iglecias, Ove Andrea Peters, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef
- Restoration of teeth lacking complete ferrules using cast precious metal alloy post-and-cores and knife-edged crowns: A retrospective clinical study
- 1,581 View
- 11 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Preference of undergraduate students after first experience on nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
- Sang Won Kwak, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):176-181. Published online June 23, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare two nickel-titanium systems (rotary
vs . reciprocating) for their acceptance by undergraduate students who experienced nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments for the first time.Materials and Methods Eighty-one sophomore dental students were first taught on manual root canal preparation with stainless-steel files. After that, they were instructed on the use of ProTaper Universal system (PTU, Dentsply Maillefer), then the WaveOne (WO, Dentsply Maillefer). They practiced with each system on 2 extracted molars, before using those files to shape the buccal or mesial canals of additional first molars. A questionnaire was completed after using each file system, seeking students' perception about 'Ease of use', 'Flexibility', 'Cutting-efficiency', 'Screwing-effect', 'Feeling-safety', and 'Instrumentation-time' of the NiTi files, relative to stainless-steel instrumentation, on a 5-point Likert-type scale. They were also requested to indicate their preference between the two systems. Data was compared between groups using
t -test, and with Chi-square test for correlation of each perception value with the preferred choice (p = 0.05).Results Among the 81 students, 55 indicated their preferred file system as WO and 22 as PTU. All scores were greater than 4 (better) for both systems, compared with stainless-steel files, except for 'Screwing-effect' for PTU. The scores for WO in the categories of 'Flexibility', 'Screwing-effect', and 'Feeling-safety' were significantly higher scores than those of PTU. A significant association between the 'Screwing-effect' and students' preference for WO was observed.
Conclusions Novice operators preferred nickel-titanium instruments to stainless-steel, and majority of them opted for reciprocating file instead of continuous rotating system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
B. Baracco, N. Escribano, D. Da Silva, V. Belliard, L. Ceballos, V. Fuentes
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Technical Quality and Students' Perception of Endodontic Preclinical Training Using Natural or LikeReal Artificial Teeth
Gabriela Biagioni, Fernanda Comodo, Marcelo Santos Coelho
European Journal of Dental Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Procedural Errors and Associated Factors among Undergraduate Dental Students: A Cross-sectional Study
Vivek Padmanabhan, Md Sofiqul Islam, Mohamed A Elsayed, Duaa R Saleh, Amal M Alnahdi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 24(12): 998. CrossRef - Clinicians’ perspectives, inducements, preferences, and clinical experiences regarding the use of electronic apex locator and apex locator integrated engine-driven instrumentation: a cross-sectional study
Sena Kaşıkçı, Sena Kolunsağ Özbek, Ebru Şirinoğlu, Olcay Özdemir
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Comparison of Manual and Mechanical Endodontic Instrumentation Completed by Undergraduate Dental Students on Endodontic Blocks
António Ginjeira, Abayomi O. Baruwa, Karla Baumotte
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(11): 363. CrossRef - The first experiences of preclinical dentistry students with rotary instruments: A pilot study
Işıl Kaya Büyükbayram, Gizem Çolakoğlu, Sana Mahroos Al-Shammari, Katia Stoicefidis
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 205. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Manual vs. Rotary/Reciprocating NiTi Instrumentation by Novice Dental Students on Simulated Root Canals
Ethan Smith, Olivia Davis
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2024; 4(2): 82. CrossRef - First Experience of an Undergraduate Dental Student with a Reciprocating System in Simulated Root Canals—A Pilot Study
Ana Rita Arede, Inês Ferreira, Ana Cristina Braga, Irene Pina-Vaz
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(8): 4848. CrossRef - Effect on undergraduate student self-confidence in using 3D printed primary molars for root canal treatment simulation training
C. Delfosse, T. Marquillier, S. Ndoye, P.-Y. Cousson, M. Hennequin, C. Catteau
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(1): 105. CrossRef - Influence of operator expertise on glide path and root canal preparation of curved root canals with rotary and reciprocating motions
Ana Belén Dablanca‐Blanco, Ana Arias, María José Ginzo‐Villamayor, María Consuelo Pérez, Pablo Castelo‐Baz, Benjamín Martín‐Biedma
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 37. CrossRef - Quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate students using nickel‐titanium reciprocating versus hand instruments
Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Pelin Güneri, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
Journal of Dental Education.2022; 86(12): 1662. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of endodontic mishaps in an undergraduate student clinic: a 2-year retrospective study
Manal Matoug-Elwerfelli, Ahmed Abdou, Wejdan Almutairi, Malak Alhuthayli, Shaikhah Aloyaynaa, Rahaf Almohareb
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13858. CrossRef - Ex vivo shaping ability of reciprocating instruments operated by new users: Reciproc versus WaveOne
Mary S. H. Lam, Jeffrey W. W. Chang, Gary S. P. Cheung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2791. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Undergraduate Students’ Acceptance of a Reciprocating One-File System for Endodontic Treatment
Benjamin Mahmoodi, Adriano Azaripour, Kawe Sagheb, Keyvan Sagheb, Brita Willershausen, Jens Weusmann
European Journal of Dentistry.2020; 14(03): 393. CrossRef - Fracture of endodontic instruments - Part 1: Literature review on factors that influence instrument breakage
Maheshan Pillay, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2020; 75(10): 553. CrossRef - A comparative study of root canal shaping using protaper universal and protaper next rotary files in preclinical dental education
Gül Çelik, Feyza Özdemir Kısacık, Emir Faruk Yılmaz, Arife Mersinlioğlu, İhsan Furkan Ertuğrul, Hikmet Orhan
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7419. CrossRef - Undergraduate dentistry students’ perception of difficulties regarding endodontic treatment
Lorrane G. Tavares, Stella M. F. Lima, Miriane G. Lima, Marcos P. Arruda, Thiago C. Menegazzi, Taia M. B. Rezende
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 98. CrossRef - First Experience of Rotary Nickel Titanium Root Canal Instrumentation Performed by Undergraduate Students and General Dentists
marwa sharaan, Noreen Kamel, Dimitrios Tziafas
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Care.2017; 3(2): 1. CrossRef
- Factors influencing the agreement between teachers and students in the assessment of preclinical endodontics using a rubric
- 1,600 View
- 10 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
- Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):215-219. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the screw-in effect and torque generation depending on the size of glide path during root canal preparation.
Materials and Methods Forty Endo-Training Blocks (REF A 0177, Dentsply Maillefer) were used. They were divided into 4 groups. For groups 1, 2, 3, and 4, the glide path was established with ISO #13 Path File (Dentsply Maillefer), #15 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX (Dentsply Maillefer), modified #16 Path File (equivalent to #18), and #20 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX, respectively. The screw-in force and resultant torque were measured using a custom-made experimental apparatus while canals were instrumented with ProTaper S1 (Dentsply Maillefer) at a constant speed of 300 rpm with an automated pecking motion. A statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance and the Duncan
post hoc comparison test.Results Group 4 showed lowest screw-in effect (2.796 ± 0.134) among the groups (
p < 0.05). Torque was inversely proportional to the glide path of each group. In #20 glide path group, the screw-in effect and torque decreased at the last 1 mm from the apical terminus. However, in the other groups, the decrease of the screw-in effect and torque did not occur in the last 1 mm from the apical terminus.Conclusions The establishment of a larger glide path before NiTi rotary instrumentation appears to be appropriate for safely shaping the canal. It is recommended to establish #20 glide path with NiTi file when using ProTaper NiTi rotary instruments system safely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
Taher Al Omari, Layla Hassouneh, Khawlah Albashaireh, Alaa Dkmak, Rami Albanna, Ali Al-Mohammed, Ahmed Jamleh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Printed Teeth in Endodontics: A New Protocol for Microcomputed Tomography Studies
Tiago Reis, Cláudia Barbosa, Margarida Franco, Ruben Silva, Nuno Alves, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Jose Martín-Cruces, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Materials.2024; 17(8): 1899. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation and fracture resistance of endodontically retreated teeth using hyflex remover, Mtwo, and ProTaper retreatment file systems: An in vitro study
Isha Singh, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Pallavi Sharma, Kunal Bedi, Priyanka Rani, Swapnil Vats
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Morphological and structural variations of Nickel-Titanium endodontic instruments subjected to instrumentation loads: in vitro study
Yenny Marcela Orozco-Ocampo, César Augusto Álvarez-Vargas, Francy Nelly Jiménez-García, Daniel Escobar-Rincón, Paola Ximena Jaramillo-Gil
Revista UIS Ingenierías.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Efficiency to Remove the Infected Dentin via Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Count and to Adequately Shape the Canal Using Hand Kedo-SH Files, Rotary Kedo-SG (Blue) and Pro AF Baby Gold Files in Primary Molars: An In Vitro Study
Shruthi B Patil, Kaavya Shanker
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S142. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, torque, and force generation during retreatment with D-RaCe, HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo retreatment files
Yoojin Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic and torsional fatigue resistance of a new rotary file on a rotary and reciprocating motion
Gabriel Barcelos Só, Giovana Siocheta, Pedro Calefi, Murilo Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antônio H. Duarte, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(12): 1635. CrossRef - Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Hayate Unno, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1170. CrossRef - Dynamic torque and screw-in force of four different glide path instruments assessed in simulated single- and double-curved canals: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Moe-Sandar Kyaw, Yuka Kasuga, Miki Nishijo, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(4): 1598. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - Evolution and development: engine-driven endodontic rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Yuhong Liang, Lin Yue
International Journal of Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Endodontic Rotary Files, What Should an Endodontist Know?
Ana-Belén Dablanca-Blanco, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Ramón Miguéns-Vila, Pablo Álvarez-Novoa, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 719. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Canal shaping
Ana Arias, Ove A. Peters
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 637. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimum glide path motion is safer than continuous rotation of files in glide path preparation
Giulio Gavini, Eduardo Akisue, Dirce Akemi Sacaguti Kawakami, Celso Luiz Caldeira, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Húngaro Duarte
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 544. CrossRef - Root canals shaped by nickel-titanium instrumentation with automated computerized numerical control systems
Liming Wang, Wenxiang Li, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Kee-Yeon Kum, Yu Gu
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Update on Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Endodontics: Mechanical Characteristics, Testing and Future Perspective—An Overview
Alessio Zanza, Maurilio D’Angelo, Rodolfo Reda, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2021; 8(12): 218. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Cleaning Efficiency and Apical Extrusion of Debris Using Two Pediatric Rotary Endodontic Files: An In Vitro Study
Nilima Thosar, Sudhindra Baliga, Faraz Ahmed, Nilesh Rathi, Shreyans A Jain, Jayati Mehta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(2): 196. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 188. CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TORQUE SETTINGS ON THE AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS DURING ROTARY INSTRUMENTATION
Demet ALTUNBAŞ, Mustafa TOYOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2020; 23(3): 160. CrossRef - Glide Path: “Path to the successful root canal instrumentation”- Review
Anjali Mairal Oak
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional fatigue strength of reciprocating and rotary pathfinding instruments manufactured from different NiTi alloys
Rodrigo Ricci VIVAN, Murilo Priori ALCALDE, George CANDEIRO, Giulio GAVINI, Celso Luis CALDEIRA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne nickel-titanium files
Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Real‐time dynamic torque values and axial forces during preparation of straight root canals using three different endodontic motors and hand preparation
S. Bürklein, J. P. Stüber, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(1): 94. CrossRef - Comparison of glide paths created with K-files, PathFiles, and the ProGlider file, and their effects on subsequent WaveOne preparation in curved canals
Linxia Zheng, Xiongfei Ji, Chengxi Li, Lulu Zuo, Xin Wei
BMC Oral Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance and bending properties of two reciprocating nickel‐titanium glide path files
T. Özyürek, G. Uslu, M. Gündoğar, K. Yılmaz, N. M. Grande, G. Plotino
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(9): 1047. CrossRef - Root Canal Shaping Effect of Instruments with Offset Mass of Rotation in the Mandibular First Molar: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Jung Hong Ha, Myoung Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 822. CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Effect of the Glide Path Establishment on the Torque Generation to the Files during Instrumentation: An In Vitro Measurement
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 496. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel Glide Path Instruments with Different Alloy Properties and Kinematics
Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Micoogullari Kurt, Mehmet Kemal Çalişkan
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(9): 1422. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of R‐Pilot, HyFlex EDM and PathFile nickel‐titanium glide path files in artificial canals with double (S‐shaped) curvature
G. Uslu, T. Özyürek, K. Yılmaz, M. Gündoğar
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(5): 584. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Used and New Glide Path Files
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 477. CrossRef - Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an in vitro study
Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 316. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Torsional Performance of ProTaper Gold Rotary Instruments during Shaping of Small Root Canals after 2 Different Glide Path Preparations
Ana Arias, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Alexis Hernández, Ove A. Peters
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 447. CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef -
In vitro comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, One G, and ProGlider nickel titanium glide path instruments in single and double curvature canals
Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 282. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef - Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 304. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Differences in torsional performance of single- and multiple-instrument rotary systems for glide path preparation
Ana Arias, Rupinderpal Singh, Ove A. Peters
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 192. CrossRef - Effect of glide path and apical preparation size on the incidence of apical crack during the canal preparation using Reciproc, WaveOne, and ProTaper Next systems in curved root canals: A stereomicroscope study
Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu, Salih Düzgün, Firdevs Akpek, Gamze Topçuoğlu
Scanning.2016; 38(6): 585. CrossRef - Geometric Optimization for Development of Glide Path Preparation Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Sang-Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Dongseok Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 916. CrossRef - Glide Path Management with Single- and Multiple-instrument Rotary Systems in Curved Canals: A Micro–Computed Tomographic Study
Alison Luís Kirchhoff, Rene Chu, Isabel Mello, Andres Dario Plazas Garzon, Marcelo dos Santos, Rodrigo Sanches Cunha
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1880. CrossRef - Safe root canal preparation using reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments
Jung-Hong Ha
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 253. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 123. CrossRef - Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 286. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of 5 Different Rotary Pathfinding Instruments Made of Conventional Nickel-Titanium Wire, M-wire, and Controlled Memory Wire
Ismail Davut Capar, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Hüseyin Ertas, Bilge Hakan Sen
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(4): 535. CrossRef - Comparision of two different preparation protocol of Ni-Ti Rotary PathFile-ProTaper instruments in simulated s-shaped canals
Elıf Delve Başer Can, Müzeyyen Gerek, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Kambız Mohsenı, Hakki Sunay, Gündüz Bayirli
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2014; 72(1): 76. CrossRef - Torsional and cyclic fatigue resistances of glide path preparation instruments: G‐file and PathFile
Sang Yup Sung, Jung‐Hong Ha, Sang‐Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Kyeongmin Byeon, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2014; 36(5): 500. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Different Nickel-Titanium Systems in Simulated S-shaped Canals with and without Glide Path
Sebastian Bürklein, Thomas Poschmann, Edgar Schäfer
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1231. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Self-Adjusting File Movement: Minimally Invasive Instrumentation
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Yup Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Michael Solomonov, Jung-Min Lee, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1572. CrossRef
- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
- 2,470 View
- 13 Download
- 76 Crossref

- Stress distribution for NiTi files of triangular based and rectangular based cross-sections using 3-dimensional finite element analysis
- Hyun-Ju Kim, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the stress distributions of NiTi rotary instruments based on their cross-sectional geometries of triangular shape-based cross-sectional design, S-shaped cross-sectional design and modified rectangular shape-based one using 3D FE models.
NiTi rotary files of S-shaped and modified rectangular design of cross-section such as Mtwo or NRT showed larger stress change while file rotation during simulated shaping.
The stress of files with rectangular cross-section design such as Mtwo, NRT was distributed as an intermittent pattern along the long axis of file. On the other hand, the stress of files with triangular cross-section design was distributed continuously.
When the residual stresses which could increase the risk of file fatigue fracture were analyzed after their withdrawal, the NRT and Mtwo model also presented higher residual stresses.
From this result, it can be inferred that S-shaped and modified rectangular shape-based files were more susceptible to file fracture than the files having triangular shape-based one.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Autogenous teeth used for bone grafting: a comparison with traditional grafting materials
Young-Kyun Kim, Su-Gwan Kim, Pil-Young Yun, In-Sung Yeo, Seung-Chan Jin, Ji-Su Oh, Heung-Joong Kim, Sun-Kyoung Yu, Sook-Young Lee, Jae-Sung Kim, In-Woong Um, Mi-Ae Jeong, Gyung-Wook Kim
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2014; 117(1): e39. CrossRef - Analysis of crystalline structure of autogenous tooth bone graft material: X-Ray diffraction analysis
Gyung-Wook Kim, In-Sung Yeo, Su-Gwan Kim, In-Woong Um, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2011; 37(3): 225. CrossRef
- Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
- 1,449 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


