Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Influence of the root canal filling technique on the success rate of primary endodontic treatments: a systematic review
- Daniel Feijolo Marconi, Giovana Siocheta da Silva, Theodoro Weissheimer, Isadora Ames Silva, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Leonardo Thomasi Jahnke, Jovito Adiel Skupien, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e40. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the influence of different obturation techniques compared to cold lateral compaction on the success rate of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments.
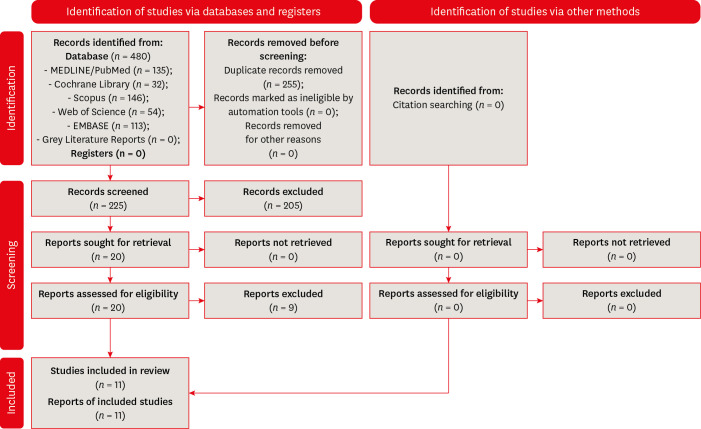
Materials and Methods Systematic searches were performed for studies published up to May 17th, 2022 in MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE, and Grey Literature Reports. Randomized clinical trials and nonrandomized (nonrandomized clinical trials, prospective or retrospective) studies that evaluated the success rate of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments obturated with the cold lateral compaction (control) and other obturation techniques were included. The revised Cochrane risk of bias tools for randomized trials (RoB 2) and nonrandomized studies of interventions (ROBINS-I) were used to evaluate the risk of bias. The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) tool was used to evaluate the certainty of evidence.
Results Eleven studies (4 randomized clinical trials (RCTs), 4 prospective, and 3 retrospectives) were included. Two RCTs were classified as having some concerns risk of bias and 2 as a low risk of bias. Two nonrandomized studies were classified as having a critical risk of bias and 5 as having a moderate risk of bias. The GRADE analysis demonstrated a very low to moderate certainty of evidence.
Conclusions This systematic review generally evidenced no differences in the success rate of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments when the cold lateral compaction technique and other obturation techniques are performed. Further well-designed studies are still necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing Sealing Ability of C-Root SP Strontium Silicate Sealer With Different Obturation Techniques: An in vitro Study
Suixin Hu, Jianshe Li, Meng Xu, Laiqing Xu, Yangming Yin, Peng Xue, Liping Dong, Lin Wang, Huixia He, Ying Liu, Qiang Luo, Fei Chen
International Dental Journal.2026; 76(1): 109283. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Of Obturation Techniques In Endodontics: Lateral Vs. Thermoplasticized. Thermoplasticized
Juan Esteban Díaz Pacheco , Rómulo Guillermo López Torres , Verónica Alejandra Salame Ortíz
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2025; 5: 1626. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
Shuting Feng, Weiqing Zhou, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1380. CrossRef - In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a New Experimental Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Endodontic Sealer
Fabiola Cardoso Maldonado, Cesar Gaitan Fonseca, Carlos Bermudez Jimenez, Luis Alejandro Aguilera Galaviz, Margarita L. Martinez-Fierro, Lorena Troncoso Vazquez, Martha Eugenia Reyes Ortiz
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(11): 402. CrossRef - Evaluation of three obturation techniques in 3D-printed models of oval canals with standardized prepared morphology: a micro-CT study
Wenjun Xia, Qisheng Gu, Yingshuang Song, Yunjia Liu, Xuetao Deng, Wenhao Qian
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiographic Failure of Nonsurgical Endodontic Treatment and Retreatment Using Single-cone Technique With Calcium Silicate-based Sealers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mohammad A. Sabeti, Negah Karimpourtalebi, Arash Shahravan, Omid Dianat
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(6): 735. CrossRef - Method of microbial decontamination of endodontic absorbent paper points: a randomised experimental study
O. A. Pavlovskaya, O. A. Kachanova, V. V. Volobuev, M. N. Mitropanova, A. R. Gazarova, V. Y. Zobenko, A. G. Uvarova
Pediatric dentistry and dental prophylaxis.2024; 24(2): 157. CrossRef - The Push-Out Bond Strength, Surface Roughness, and Antimicrobial Properties of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealers Supplemented with Silver Nanoparticles
Karla Navarrete-Olvera, Nereyda Niño-Martínez, Idania De Alba-Montero, Nuria Patiño-Marín, Facundo Ruiz, Horacio Bach, Gabriel-Alejandro Martínez-Castañón
Molecules.2024; 29(18): 4422. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of non-surgical root canal treatment using different sealers and techniques of obturation in 237 patients: A retrospective study
Mateusz Radwanski, Krystyna Pietrzycka, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing Sealing Ability of C-Root SP Strontium Silicate Sealer With Different Obturation Techniques: An in vitro Study
- 7,162 View
- 105 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Obturation efficiency of non-standardized gutta-percha cone in curved root canals prepared with 0.06 taper nickel-titanium instruments
- Eun-Ah Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(2):79-85. Published online March 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.079
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the obturation efficiency of a non-standardized gutta-percha cone in curved root canals prepared with 0.06 taper nickel-titanium instruments.
Sixty simulated curved root canals in clear resin blocks were prepared with crown-down technique using 0.06 taper rotary ProTaper™ and ProFile (Dentsply-Maillefer) until apical canal was size 30. Root canals were randomly divided into 4 groups of 15 blocks and obturated with cold-laterally compacted gutta-percha technique by using either a non-standardized size medium gutta-percha cone or an ISO-standardized size 30 one as a master cone. Gutta-percha area ratio were calculated at apical levels of 1, 3, and 5 mm using AutoCAD 2000 after cross-sectioning, and the data were analyzed with one-way and two-way ANOVAs and Duncan's multiple range test.
Non-standardized size medium cone groups showed significantly higher gutta-percha area ratio than standardized cone groups at all apical levels (
p < 0.01).Non-standardized cone groups used significantly less accessory cones than standardized cone groups (
p < 0.01).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficiency of Using Different Greater Taper Gutta-Percha Cones in Continuous Warm Vertical Condensation: An Ex Vivo Study
Mamata Hebbal, Reem Barakat, Rahaf Almohareb, Ghada Alaskar, Lama Alghufaily, Nouf AlFarraj, Alia Albaz
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 56. CrossRef
- Efficiency of Using Different Greater Taper Gutta-Percha Cones in Continuous Warm Vertical Condensation: An Ex Vivo Study
- 1,822 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of plugger penetration depth on the apical extrusion of root canal sealer in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique
- Ho-Young So, Young-Mi Lee, Kwang-Keun Kim, Ki-Ok Kim, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(5):439-445. Published online January 14, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.439
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of plugger penetration depth on the apical extrusion of root canal sealer during root canal obturation with Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique.
Root canals of forty extracted human teeth were divided into four groups and were prepared up to size 40 of 0.06 taper with ProFile. After drying, canals of three groups were filled with Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique with System B™ and different plugger penetration depths of 3, 5, and 7 mm from the apex. Canals of one group were filled with cold lateral compaction technique as a control. Canals were filled with non-standardized master gutta-percha cones and 0.02 mL of Sealapex. Apical extruded sealer was collected in a container and weighed. Data was analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s Multiple Range Test. 3 and 5 mm penetration depth groups in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique showed significantly more extrusion of root canal sealer than 7 mm penetration depth group (
p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between 7 mm depth group in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique and cold lateral compaction group (p < 0.05).The result of this study demonstrates that deeper plugger penetration depth causes more extrusion of root canal sealer in root canal obturation by Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique. Therefore, special caution is needed when plugger penetration is deeper in the canal in Continuous Wave of Condensation Technique to minimize the amount of sealer extrusion beyond apex.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of plugger penetration depth on the area of the canal space occupied by gutta-percha
Young Mi Lee, Ho-young So, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(1): 66. CrossRef
- Influence of plugger penetration depth on the area of the canal space occupied by gutta-percha
- 1,432 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


