Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of medium or high concentrations of in-office dental bleaching gel on the human pulp response in the mandibular incisors
- Douglas Augusto Roderjan, Rodrigo Stanislawczuk, Diana Gabriela Soares, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa, Michael Willian Favoreto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e12. Published online March 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
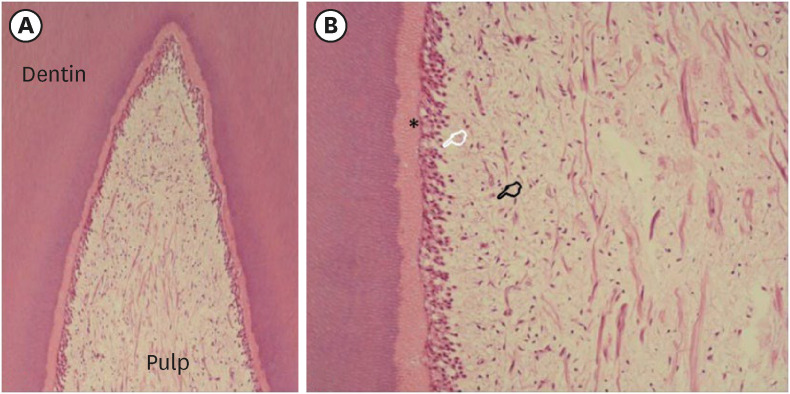
ePub Objectives The present study evaluated the pulp response of human mandibular incisors subjected to in-office dental bleaching using gels with medium or high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (HP).
Materials and Methods The following groups were compared: 35% HP (HP35;
n = 5) or 20% HP (HP20;n = 4). In the control group (CONT;n = 2), no dental bleaching was performed. The color change (CC) was registered at baseline and after 2 days using the Vita Classical shade guide. Tooth sensitivity (TS) was also recorded for 2 days post-bleaching. The teeth were extracted 2 days after the clinical procedure and subjected to histological analysis. The CC and overall scores for histological evaluation were evaluated by the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests. The percentage of patients with TS was evaluated by the Fisher exact test (α = 0.05).Results The CC and TS of the HP35 group were significantly higher than those of the CONT group (
p < 0.05) and the HP20 group showed an intermediate response, without significant differences from either the HP35 or CONT group (p > 0.05). In both experimental groups, the coronal pulp tissue exhibited partial necrosis associated with tertiary dentin deposition. Overall, the subjacent pulp tissue exhibited a mild inflammatory response.Conclusions In-office bleaching therapies using bleaching gels with 20% or 35% HP caused similar pulp damage to the mandibular incisors, characterized by partial necrosis, tertiary dentin deposition, and mild inflammation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- DENTA: A Dual Enzymatic Nanoagent for Self‐Activating Tooth Whitening and Biofilm Disruption
Junseok Kim, Dai‐Hwan Kim, Priyannth R. Sundharbaabu, Chae Yeon Lee, Jina Bae, Jiyu Hyun, Young‐Ju Jang, Haeni Kim, Min‐Ho Hong, Juewen Liu, Tobias Fey, Suk Ho Bhang, Jun Hyuk Heo, Jung Heon Lee
Advanced Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a bioactive desensitizing material on in-office bleaching–induced tooth sensitivity: A randomized double-blind controlled trial
Ghada A. Maghaireh, Hanan Alzraikat, Majd Y. Altarazi
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106326. CrossRef - Application of the Er:YAG laser in pulpotomy for mature permanent teeth with pulpitis: An animal study
Zeqi Li, Pengfei Xin, Siyao Yang, Xiaoxing Hao, Jun Wang, Kuanshou Zhang, Qingmei Liu, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS One.2026; 21(1): e0341017. CrossRef - Can pigments of different natures interfere with the cytotoxicity from in-office bleaching?
Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Beatriz Voss Martins, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Victória Peruchi, Caroline Anselmi, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Vanessa Cavalli, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1447. CrossRef - Does Patient Age Impact In-Office Tooth Bleaching Outcomes? A Parallel Clinical Trial
JL Martins, IS Araújo, JF Rabelo, CJ Soares, AL Faria-e-Silva, AD Loguercio, PCFS Filho, HL Carlo, GR da Silva
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(3): 251. CrossRef - The pH of Bleaching Gels on the Structural and Biological Response of Dental Tissues: A Scoping Review
Jamile Menezes de Souza, Maria Olimpia Paz Alvarenga, Ana Luisa Cassiano Alves Bezerra, Gabriela Queiroz de Melo Monteiro
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(10): 2193. CrossRef - Efficacy of 35 % self-mixed hydrogen peroxide In-office bleaching with reduced application time: A single-blind randomized controlled trial
Gabrielle Gomes Centenaro, Deisy Cristina Ferreira Cordeiro, Maria Alice de Matos Rodrigues, Mariah Maluf Lenhani, Roberta Micheten Dias, Cristina Gómez Polo, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 163: 106178. CrossRef - Evaluation of cytotoxicity and bleaching efficacy of gels with calcium polyphosphate and violet LED
Larissa de Jesus Gomes, Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Mariangela Ivette Guanipa Ortiz, Klaus Rischka, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa, Débora Alves Nunes Leite Lima
Brazilian Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined catalytic strategies applied to in-office tooth bleaching: whitening efficacy, cytotoxicity, and gene expression of human dental pulp cells in a 3D culture model
Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Victória Peruchi, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Filipe Koon Wu Mon, Diana Gabriela Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low and high hydrogen peroxide concentrations of in-office dental bleaching associated with violet light: an in vitro study
Isabela Souza Vardasca, Michael Willian Favoreto, Mylena de Araujo Regis, Taynara de Souza Carneiro, Emanuel Adriano Hul, Christiane Philippini Ferreira Borges, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Carlos Francci
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of hydrogen peroxide permeability, color change, and physical–chemical properties on the in‐office dental bleaching with different mixing tip
Michael Willian Favoreto, Sibelli Olivieri Parreiras, Michel Wendlinger, Taynara De Souza Carneiro, Mariah Ignez Lenhani, Christiane Phillipini Ferreira Borges, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 460. CrossRef - Catalysis-based approaches with biopolymers and violet LED to improve in-office dental bleaching
Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Beatriz Voss Martins, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Victória Peruchi, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Caroline Anselmi, Josimeri Hebling, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Lasers in Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility and Safety of Adopting a New Approach in Delivering a 450 nm Blue Laser with a Flattop Beam Profile in Vital Tooth Whitening. A Clinical Case Series with an 8-Month Follow-Up
Reem Hanna, Ioana Cristina Miron, Stefano Benedicenti
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(2): 491. CrossRef - Hydrogen Peroxide in the Pulp Chamber and Color Change in Maxillary Anterior Teeth After In-Office Bleaching
Alexandra Mena-Serrano, Sandra Sanchez, María G. Granda-Albuja, Michael Willian Favoreto, Taynara de Souza Carneiro, Deisy Cristina Ferreira Cordeiro, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of coating dental enamel with a TiF4-loaded polymeric primer on the adverse effects caused by a bleaching gel with 35% H2O2
Victória Peruchi, Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Lídia de Oliveira Fernandes, Juliana Rios de Oliveira, Maria Luiza Barucci Araújo Pires, Josimeri Hebling, Diana Gabriela Soares, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 153: 106497. CrossRef
- DENTA: A Dual Enzymatic Nanoagent for Self‐Activating Tooth Whitening and Biofilm Disruption
- 3,843 View
- 94 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Clinical assessment of whitening efficacy and safety of in-office tooth whitening system containing 15% hydrogen peroxide with or without light activation
- Young-Suk Noh, Young-Jee Rho, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hyang-Ok Lee, Sang-Min Lim, Hyun-Jeong Kweon, Yeun Kim, Seong-Yeon Park, Hee-Young Yoon, Jung-Hyun Lee, Chan-Hee Lee, So-Ram Oh, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):306-312. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.306
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This clinical study evaluated the effect of light activation on the whitening efficacy and safety of in-office bleaching system containing 15% hydrogen peroxide gel.
Materials and Methods Thirty-three volunteers were randomly treated with (n = 17, experimental group) or without light activation (n = 16, control group), using Zoom2 white gel (15% H2O2, Discus Dental) for a total treatment time of 45 min. Visual and instrumental color measurements were obtained using Vitapan Classical shade guide and Shadepilot (DeguDent) at screening test, after bleaching, and 1 month and 3 month after bleaching. Data were analyzed using
t -test, repeated measure ANOVA, and chi-squared test.Results Zoom2 white gel produced significant shade changes in both experimental and control group when pre-treatment shade was compared with that after bleaching. However, shade difference between two groups was not statistically significant (
p > 0.05). Tooth shade relapse was not detected at 3 months after bleaching. The incidence of transient tooth sensitivity was 39.4%, with being no differences between two groups.Conclusions The application of light activation with Zoom2 white gel system neither achieved additional whitening effects nor showed more detrimental influences.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide–Containing Whitening Toothpaste and Gel on Tooth Lightness: An In Vitro Study
Ye-Bin Kim, Hyon-Mo Ku, Ji-Hyeon Park
International Journal of Clinical Preventive Dentistry.2025; 21(4): 148. CrossRef - Effect of preference drinks on tooth color reduction after tooth bleaching: A 12-momth follow-up study
Hyo Jin Goo, Min Jeong Cho, Yun Sook Jung, Ji Hye Kim, Fan Dong, Keun Bae Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(1): 55. CrossRef - Development of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Tooth-whitening Apparatus
Young-Jin Lee, Jong-Hoo Paik, Jeong-Bae Lee, Seung-Jae Choi
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2013; 14(5): 268. CrossRef
- Comparative Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide–Containing Whitening Toothpaste and Gel on Tooth Lightness: An In Vitro Study
- 1,944 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The effectiveness of sealing technique on in-office bleaching
- Yoon Lee, So-Ran Kwon, Jeong-Won Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(5):463-471. Published online September 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.5.463
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study investigated the clinical effectiveness and safety of sealed bleaching compared to conventional in-office bleaching using a randomized clinical trial of split arch design. Ten participants received a chairside bleaching treatment on the upper anterior teeth, and each side was randomly designated as sealed or control side. A mixture of Brite powder (PacDent, Walnut, USA), 3% hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide (KoolWhite, PacDent, Walnut, USA) were used as bleaching agent. The control side was unwrapped and the experimental side was covered with a linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) wrap for sealed bleaching. The bleaching gel was light activated for 1 hour. The tooth shades were evaluated before treatment, after treatment, and at one week check up by means of a visual shade (VS) assessment using a value oriented shade guide and a computer assisted shade assessment using a spectrophotometer (SP). The data were analyzed by paired t-test.
In the control and sealed groups, the visual shade scores after bleaching treatment and at check up showed statistically significant difference from the preoperative shade scores (p < .05). The shade scores of the sealed group were significantly lighter than the control immediately after bleaching and at the check-up appointment (p < 0.05). Compared to prebleaching status, the ΔE values at post-bleaching condition were 4.35 ± 1.38 and 5.08 ± 1.34 for the control and sealed groups, respectively. The ΔE values at check up were 3.73 ± 1.95 and 4.38 ± 2.08 for the control and sealed groups. ΔE values were greater for the sealed group both after bleaching (p < .05) and at check up (p < .05).
In conclusion, both ΔE and shade score changes were greater for the sealed bleaching group than the conventional bleaching group, effectively demonstrating the improvement of effectiveness through sealing.
- 2,301 View
- 3 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


