Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
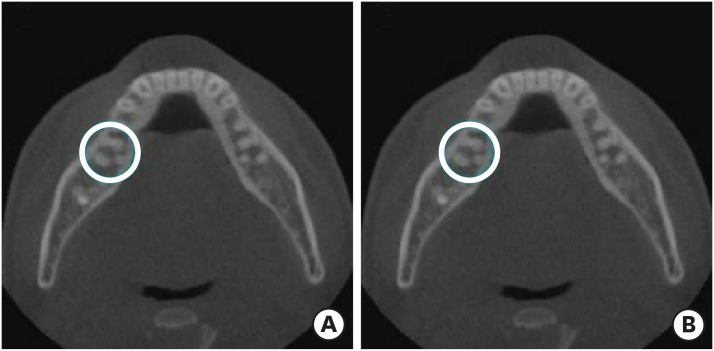
- CBCT study of mandibular first molars with a distolingual root in Koreans
- Hee-Ho Kim, Hyoung-Hoon Jo, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e33. Published online July 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of a separate distolingual root and to measure the thickness of the buccal cortical bone in mandibular first molars in Koreans using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Materials and Methods High-quality CBCT data from 432 patients were analyzed in this study. The prevalence of a separate distolingual root of the mandibular first molar was investigated. The distance from the distobuccal and distolingual root apices to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was measured. We also evaluated the thickness of the buccal cortical bone.
Results The prevalence of a separate distolingual root (2 separate distal roots with 1 canal in each root; 2R2C) was 23.26%. In mandibular first molars with 2R2C, the distance from the distobuccal root apex to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was 5.51 mm. Furthermore, the distance from the distolingual root apex to the outer surface of the buccal cortical bone was 12.09 mm. In mandibular first molars with 2R2C morphology, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone at the distobuccal root apex of the mandibular first molar was 3.30 mm. The buccal cortical bone at the distobuccal root apex was significantly thicker in the right side (3.38 mm) than the left side (3.09 mm) (
p < 0.05).Conclusions A separate distolingual root is not rare in mandibular first molars in the Korean population. Anatomic and morphologic knowledge of the mandibular first molar can be useful in treatment planning, including surgical endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between complex root canal morphology of mandibular anteriors and distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Turkish population
Özge Kurt, Elif Solakoğlu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radix molaris is a hidden truth of mandibular first permanent molars: A descriptive- analytic study using cone beam computed tomography
Mohammed A. Alobaid, Saurabh Chaturvedi, Ebtihal Mobarak S. Alshahrani, Ebtsam M. Alshehri, Amal S. Shaiban, Mohamed Khaled Addas, Giuseppe Minervini
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1957. CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris in India and its comparison with the rest of the world
Sumit MOHAN, Jyoti THAKUR
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of laboratory and clinical research methods to study root and canal anatomy
Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 229. CrossRef - Three‐Rooted Permanent Mandibular First Molars: A Meta‐Analysis of Prevalence
Nyan M. Aung, Kyaw K. Myint, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Reproducibilidad en el diagnóstico imagenológico de periodontitis apical a partir de CBCT
Sandra Milena Buitrago Rojas, Yeny Zulay Castellanos Dominguez, Jhonny Alexander Contreras Vargas, Yosdi Tomás Solano Diaz, Eder Fabián Gutierrez Argote
Acta Odontológica Colombiana.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Root and Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Molars using CBCT
Yoomin Choi, Seonmi Kim, Namki Choi
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2020; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography
Hassan AL-Alawi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Mazen A. Aldosimani, Mohammed Nabil Zahid, Ghadeer N. Shihabi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Evaluation of roots and canal systems of mandibular first molars in a vietnamese subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography
KhoaVan Pham, AnhHoang Lan Le
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2019; 9(4): 356. CrossRef
- The association between complex root canal morphology of mandibular anteriors and distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Turkish population
- 1,909 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Apical foramen morphology according to the length of merged canal at the apex
- Hee-Ho Kim, Jeong-Bum Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):26-30. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between the apical foramen morphology and the length of merged canal at the apex in type II root canal system.
Materials and Methods This study included intact extracted maxillary and mandibular human premolars (
n = 20) with fully formed roots without any visible signs of external resorption. The root segments were obtained by removing the crown 1 mm beneath the cementum-enamel junction (CEJ) using a rotary diamond disk. The distance between the file tip and merged point of joining two canals was defined as Lj. The roots were carefully sectioned at 1 mm from the apex by a slow-speed water-cooled diamond saw. All cross sections were examined under the microscope at ×50 magnification and photographed to estimate the shape of the apical foramen. The longest and the shortest diameter of apical foramen was measured using ImageJ program (1.44p, National Institutes of Health). Correlation coefficient was calculated to identify the link between Lj and the apical foramen shape by Pearson's correlation.Results The average value of Lj was 3.74 mm. The average of proportion (P), estimated by dividing the longest diameter into the shortest diameter of the apical foramen, was 3.64. This study showed a significant negative correlation between P and Lj (
p < 0.05).Conclusions As Lj gets longer, the apical foramen becomes more ovally shaped. Likewise, as it gets shorter, the apical foramen becomes more flat shaped.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mandibular first premolar apical morphology: A stereomicroscopic study
Lama Awawdeh, Mousa Abu Fadaleh, Aladdin Al‐Qudah
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 233. CrossRef - Surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canals of maxillary incisors
Ji-Hyun Jang, Jung-Min Lee, Jin-Kyu Yi, Sung-Baik Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(1): 79. CrossRef
- Mandibular first premolar apical morphology: A stereomicroscopic study
- 1,899 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


