Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Stress distribution of restorations in external cervical root resorption under occlusal and traumatic loads: a finite element analysis
- Padmapriya Ramanujam, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Vignesh Srinivasan, Selvakarthikeyan Ulaganathan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e21. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
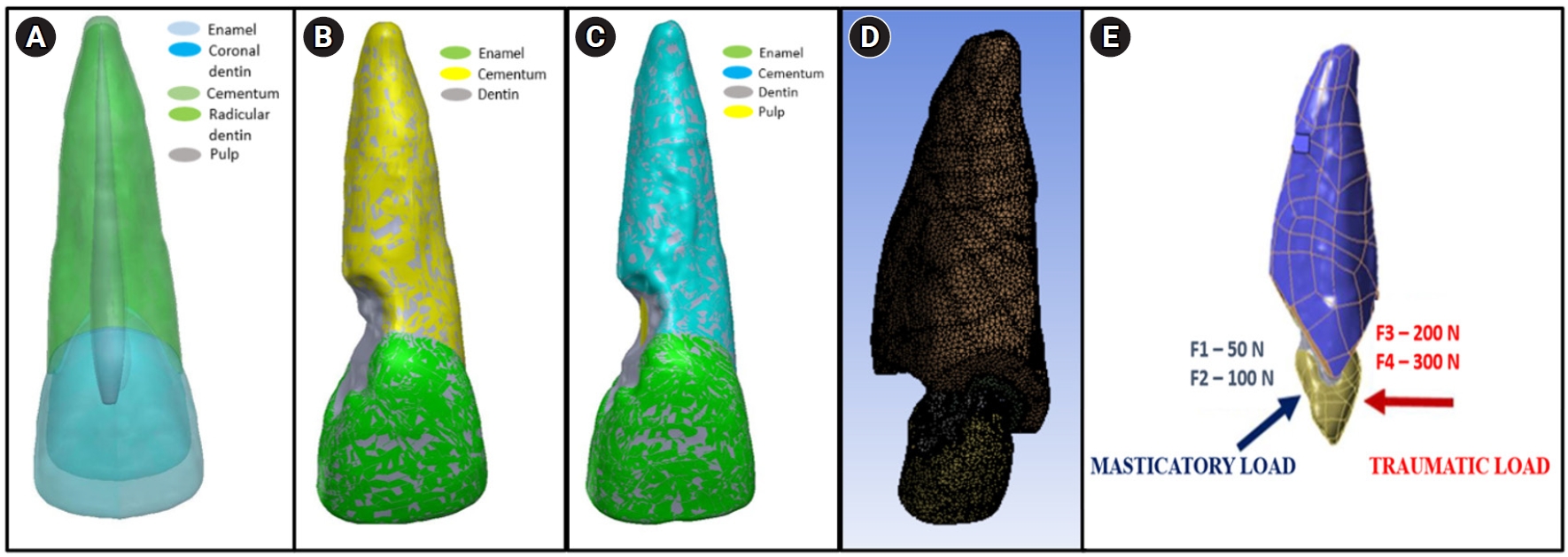
This study analyzed the stress distribution in a maxillary central incisor with external cervical resorptive defect restored with different restorative materials under normal masticatory and traumatic loading conditions using finite element analysis.
Methods
Cone-beam computed tomography of an extracted intact incisor and created resorptive models (Patel’s 3D classification-2Bd and 2Bp) in the maxillary central incisor was performed for finite element models. The 2Bd models were restored either with glass ionomer cement (GIC)/Biodentine (Septodont) or a combination of both with composite resin. 2Bp models were restored externally with a combination technique and internally with root canal treatment. The other model was external restoration with GIC and internal with fiber post. Two masticatory loads were applied at 45˚ to the palatal aspect, and two traumatic loads were applied at 90˚ to the buccal aspect. Maximum von Mises stresses were calculated, and stress distribution patterns were studied.
Results
In 2Bd models, all restorative strategies decreased stress considerably, similar to the control model under all loads. In 2Bp models, the dentin component showed maximum stress at the deepest portion of the resorptive defect, which transfers into the adjacent pulp space. In 2Bp defects, a multilayered restoration externally and root canal treatment internally provides better stress distribution compared to the placement of a fiber post.
Conclusions
Increase in load, proportionally increased von Mises stress, despite the direction or angulation of the load. Multilayered restoration is preferred for 2Bd defects, and using an internal approach of root canal treatment is suggested to restore 2Bp defects.
- 2,083 View
- 136 Download

- Porosity and pore size distribution in high-viscosity and conventional glass ionomer cements: a micro-computed tomography study
- Aline Borburema Neves, Laísa Inara Gracindo Lopes, Tamiris Gomes Bergstrom, Aline Saddock Sá da Silva, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Aline de Almeida Neves
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e57. Published online October 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
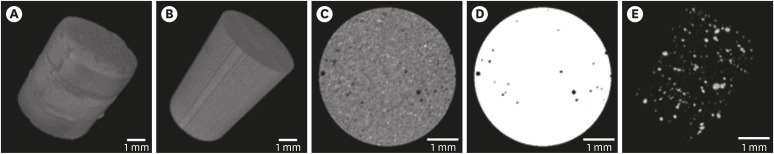
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare and evaluate the porosity and pore size distribution of high-viscosity glass ionomer cements (HVGICs) and conventional glass ionomer cements (GICs) using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
Materials and Methods Forty cylindrical specimens (
n = 10) were produced in standardized molds using HVGICs and conventional GICs (Ketac Molar Easymix, Vitro Molar, MaxxionR, and Riva Self-Cure). The specimens were prepared according to ISO 9917-1 standards, scanned in a high-energy micro-CT device, and reconstructed using specific parameters. After reconstruction, segmentation procedures, and image analysis, total porosity and pore size distribution were obtained for specimens in each group. After checking the normality of the data distribution, the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test was used to detect differences in porosity among the experimental groups with a 5% significance level.Results Ketac Molar Easymix showed statistically significantly lower total porosity (0.15%) than MaxxionR (0.62%), Riva (0.42%), and Vitro Molar (0.57%). The pore size in all experimental cements was within the small-size range (< 0.01 mm3), but Vitro Molar showed statistically significantly more pores/defects with a larger size (> 0.01 mm3).
Conclusions Major differences in porosity and pore size were identified among the evaluated GICs. Among these, the Ketac Molar Easymix HVGIC showed the lowest porosity and void size.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of contouring instruments on immediate quality and porosity of direct restorations
Carlos Soler-Tornero, Pekka Toivonen, Jaakko Suorsa, Sakari S. Karhula, Simo Saarakkala, Vuokko Anttonen, Jukka Leinonen
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Human Blood Contamination on Microhardness of Glass-Ionomer Cements and Glass-Hybrid Material
Katarina Franić, Ana Brundić, Jurica Matijević, Ana Ivanišević, Ivana Miletić, Anja Baraba
Materials.2025; 18(17): 4075. CrossRef - Effect of crown seating methods on the remnant cement in the subgingival region of a cement-retained implant crown
Fanghui Ji, Ji Suk Shim, Jeongyol Lee, Hwiseong Oh, Jae Jun Ryu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing Wear Resistance in Glass Ionomer Cement through Green-mediated Chitosan-, Titanium-, Zirconium-, and Hydroxyapatite-based Nanocomposites: An Analysis before and after Chewing Simulator Endurance
Jessy Paulraj, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Subhabrata Maiti, Srinavasa Surya Sitaram
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(11): 1229. CrossRef - The effect of mesoporous silica doped with silver nanoparticles on glass ionomer cements; physiochemical, mechanical and ion release analysis
Syed Saad Bin Qasim, Ali Bmuajdad
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperbaric Pressure Effect on Dental Luting Cements
Secil OZKAN ATA, Nazım ATA, Rıfat UGURLUTAN
Journal of Basic and Clinical Health Sciences.2023; 7(1): 464. CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum
Hyun-Jin Kim, Jun-Seok Lee, Dong-Hoon Gwak, Yong-Seok Ko, Chun-Il Lim, Seung-Youl Lee
Materials.2023; 17(1): 35. CrossRef - Adhesion and Surface Roughness of Apatite-Containing Carbomer and Improved Ionically Bioactive Resin Compared to Glass Ionomers
Handan Yıldırım Işık, Aylin Çilingir
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(7): 367. CrossRef - An influence of finishing procedures and protective coating on the ultrastructure of conventional and hybrid glass ionomer cement restorations
Antonije Stankovic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Nikolic, Aleksandar Mitic, Nenad Stosic, Radomir Barac, Aleksandra Milovanovic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2023; 70(3): 138. CrossRef - Effect of aging on mechanical and antibacterial properties of fluorinated graphene reinforced glass ionomer: In vitro study
Suzan Khaled Arafa, Dalia Ibrahim Sherief, Mohamed Salah Nassif
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2023; 142: 105803. CrossRef
- The effect of contouring instruments on immediate quality and porosity of direct restorations
- 2,614 View
- 17 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Comparative assessment of antibacterial activity of different glass ionomer cements on cariogenic bacteria
- Rahul Gaybarao Naik, Arun Suresh Dodamani, Mahesh Ravindra Khairnar, Harish Chaitram Jadhav, Manjiri Abhay Deshmukh
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):278-282. Published online September 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.278
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Glass ionomer cements (GICs), which are biocompatible and adhesive to the tooth surface, are widely used nowadays for tooth restoration. They inhibit the demineralization and promote the remineralization of the tooth structure adjacent to the restoration, as well as interfere with bacterial growth. Hence, the present study was conducted to assess and compare the antimicrobial activity of three commercially available GICs against two cariogenic bacteria.
Materials and Methods An agar plate diffusion test was used for evaluating the antimicrobial effect of three different GICs (Fuji IX, Ketac Molar, and d-tech) on
Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans ) andLactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus ). Thirty plates were prepared and divided into two groups. The first group was inoculated withS. mutans , and the second group was inoculated withL. acidophilus . These plates were then incubated at 37℃ for 24 hours. Zones of bacterial growth inhibition that formed around each well were recorded in millimeters (mm).Results The zones of inhibition for Fuji IX, Ketac Molar, and d-tech on
S. mutans were found to be 10.84 ± 0.22 mm, 10.23 ± 0.15 mm, and 15.65 ± 0.31 mm, respectively, whereas those forL. acidophilus were found to be 10.43 ± 0.12 mm, 10.16 ± 0.11 mm, and 15.57 ± 0.13 mm, respectively.Conclusions D-tech cement performed better in terms of the zone of bacterial inhibition against the two test bacteria, than the other two tested glass ionomers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of conditioning and 3-year aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin
Ahmed Zubaer, Rime Shamme Akter, Al Azad Salahuddin, Rahman Mir Ayubur, Sano Hidehiko, Hoshika Shuhei
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(2): 1229. CrossRef - Surface energetics of antibiofilm property of dental material added with green synthesized copper nanoparticles
Haris Saddique, Muhammad Aasim, Tariq Khan, Ajab Khan, Haroon Muhammad Ali, Umar Aziz
AMB Express.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of titanium dioxide nanotubes incorporated into conventional glass ionomer cement on L. acidophilus
Layse de Góis SENA, Maria Davoli MEYER, Mariana Gallante RICARDO, Isaac Jordão de Souza ARAÚJO, Julia Puppin RONTANI, Vanessa Arias PECORARI, Elizabeth Ferreira MARTINEZ, Lucas Novaes TEIXEIRA, Francisco Humberto NOCITI-JUNIOR, Paulo Noronha LISBOA-FILHO,
Brazilian Oral Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Modifications of polyalkenoic acid and its effect on glass ionomer cement
Sreejith Sasidharan Lathikumari, Manju Saraswathy
Materials Advances.2024; 5(7): 2719. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Clinical Impact and In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Two Bioactive Restoratives against S. mutans ATCC 25175 in Class II Carious Restorations
YA Maher, MT Rajeh, FA Hamooda, GO Zerain, RM Habis, RH Sulaimani, ST Albar, FMH Ali, NA Abdelaleem
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 26(4): 404. CrossRef - Comparison and Advanced Antimicrobial Strategies of Silver and Copper Nanodrug-Loaded Glass Ionomer Cement against Dental Caries Microbes
Amal Adnan Ashour, Mohammed Fareed Felemban, Nayef H. Felemban, Enas T. Enan, Sakeenabi Basha, Mohamed M. Hassan, Sanaa M. F. Gad El-Rab
Antibiotics.2022; 11(6): 756. CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity and Biofilm Inhibition of New-Generation Hybrid/Fluoride-Releasing Restorative Materials
Sevil Gurgan, Uzay Koc Vural, Cansu Atalay, Herve Tassery, Ivana Miletic, Suna Sibel Gurpinar
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(5): 2434. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of long-term fluoride release and antibacterial activity of an alkasite, nanoionomer, and glass ionomer restorative material – An in vitro study
RV Aparajitha, PSenthamil Selvan, AShafie Ahamed, S Bhavani, V Nagarajan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 485. CrossRef - Dental Restorative Materials for Elderly Populations
Yuyao Huang, Bingqing Song, Xuedong Zhou, Hui Chen, Haohao Wang, Lei Cheng
Polymers.2021; 13(5): 828. CrossRef - The Comparison of Biofilm Formation, Mechanical and Chemical Properties between Glass Ionomer Cement and Giomer
Sylva Dinie Alinda, Anggraini Margono, Aditya Wisnu Putranto, Ike Dwi Maharti, Retno Amalina, Sherly Firsta Rahmi
The Open Dentistry Journal.2021; 15(1): 274. CrossRef - Effect of conditioning and 1 year aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin
Shuhei Hoshika, Shihchun Ting, Zubaer Ahmed, Fei Chen, Yu Toida, Norihito Sakaguchi, Bart Van Meerbeek, Hidehiko Sano, Sharanbir K. Sidhu
Dental Materials.2021; 37(1): 106. CrossRef - The synergistic effects of SrF2 nanoparticles, YSZ nanoparticles, and poly-ε-l-lysin on physicomechanical, ion release, and antibacterial-cellular behavior of the flowable dental composites
Saeed Hesaraki, Mohammad Karimi, Nader Nezafati
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2020; 109: 110592. CrossRef
- Effect of conditioning and 3-year aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin
- 1,696 View
- 8 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Do conventional glass ionomer cements release more fluoride than resin-modified glass ionomer cements?
- Maria Fernanda Costa Cabral, Roberto Luiz de Menezes Martinho, Manoel Valcácio Guedes-Neto, Maria Augusta Bessa Rebelo, Danielson Guedes Pontes, Flávia Cohen-Carneiro
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(3):209-215. Published online May 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.3.209
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the fluoride release of conventional glass ionomer cements (GICs) and resin-modified GICs.
Materials and Methods The cements were grouped as follows: G1 (Vidrion R, SS White), G2 (Vitro Fil, DFL), G3 (Vitro Molar, DFL), G4 (Bioglass R, Biodinâmica), and G5 (Ketac Fil, 3M ESPE), as conventional GICs, and G6 (Vitremer, 3M ESPE), G7 (Vitro Fil LC, DFL), and G8 (Resiglass, Biodinâmica) as resin-modified GICs. Six specimens (8.60 mm in diameter; 1.65 mm in thickness) of each material were prepared using a stainless steel mold. The specimens were immersed in a demineralizing solution (pH 4.3) for 6 hr and a remineralizing solution (pH 7.0) for 18 hr a day. The fluoride ions were measured for 15 days. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test with 5% significance were applied.
Results The highest amounts of fluoride release were found during the first 24 hr for all cements, decreasing abruptly on day 2, and reaching gradually decreasing levels on day 7. Based on these results, the decreasing scale of fluoride release was as follows: G2 > G3 > G8 = G4 = G7 > G6 = G1 > G5 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions There were wide variations among the materials in terms of the cumulative amount of fluoride ion released, and the amount of fluoride release could not be attributed to the category of cement, that is, conventional GICs or resin-modified GICs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Impact of biofilm model of
Streptococcus mutans
on the pH, ions release, and sorption/solubility of glass ionomer cements enriched with 45S5 bioglass
Fábia Regina Vieira de Oliveira Roma, Mayron Guedes Silva, Tarcisio Jorge Leitão de Oliveira, José Bauer, Leily Macedo Firoozmand
Biofouling.2026; 42(1): 42. CrossRef - Fluoride Uptake and Surface Characteristics of Ion-Releasing Restoratives After Brushing with Fluoride Toothpastes
Llubitza Slaviza Banic Vidal, Ivan Šalinović, Nikolina Nika Veček, Anja Ivica, Ivana Miletić, Silvana Jukić Krmek
Materials.2025; 18(9): 2152. CrossRef - Strategic approaches for enhancing the bioactivity of glass ionomer cement: A mechanistic and clinical perspective in terms of structural and surface modifications
Ali Saatchifard, Nader Nezafati, Saeed Hesaraki
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 163: 106126. CrossRef - Antibacterial effects of bioactive restorative dental materials on Streptococcus mutans: An in vitro study using the direct contact test
Sirirat Boondireke, Onsasi Kitrueangphatchara, Charnsak Sukajintanakarn, Sirichan Chiaraputt
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ion release of the glass ionomer restoration with silver diamine fluoride dentin pretreatment
Kelsey Xingyun Ge, Ryan Quock, Feng Yan, Walter Yu-Hang Lam, Chun-Hung Chu, Ollie Yiru Yu
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 148: 105247. CrossRef - Dual function of anti-biofilm and modulating biofilm equilibrium of orthodontic cement containing quaternary ammonium salt
Wenqi YU, Chaochao REN, Ning ZHANG, Li CAO, Michael D. WEIR, Kai YANG, Hockin H. K. XU, Yuxing BAI
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(2): 149. CrossRef - Fluoride exchange by glass-ionomer dental cements and its clinical effects: a review
John W. Nicholson, Sharanbir K. Sidhu, Beata Czarnecka
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Protective Surface Coating on Fluoride Release and Recharge of Recent Uncoated High-Viscosity Glass Ionomer Cement
Nantawan Krajangta, Chayanee Dulsamphan, Tongjai Chotitanmapong
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(12): 233. CrossRef - Reinforcing an immature tooth model using three different restorative materials
Pooja Misar, Hemalatha Hiremath, Chhaya Harinkhere, ShailendraS Sonawane, Vinay Sharma, KuldeepSingh Rana
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 28. CrossRef - Fluoride release from two types of fluoride-containing orthodontic adhesives: Conventional versus resin-modified glass ionomer cements—An in vitro study
Yasemin Dziuk, Sachin Chhatwani, Stephan C. Möhlhenrich, Sabrina Tulka, Ella A. Naumova, Gholamreza Danesh, Richard Johannes Wierichs
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0247716. CrossRef - Phosphate Ion Release and Alkalizing Potential of Three Bioactive Dental Materials in Comparison with Composite Resin
Shahin Kasraei, Sahebeh Haghi, Sara Valizadeh, Narges Panahandeh, Sogol Nejadkarimi, Shinn Jyh Ding
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - The effect of the polishing procedure and surface sealant application on the fluoride release of different restorative materials
Muhittin Ugurlu, Hikmet Orhan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(2): 135. CrossRef - Mechanical and antimicrobial property of different surface treated glass ionomer cements under desiccated condition
Hemalatha Hiremath, Chhaya Harinkhere, Pooja Misar, Kshitij Sabley, Trupti Bajpai
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 64. CrossRef - Dental Restorative Materials for Elderly Populations
Yuyao Huang, Bingqing Song, Xuedong Zhou, Hui Chen, Haohao Wang, Lei Cheng
Polymers.2021; 13(5): 828. CrossRef - Monomer conversion, dimensional stability, biaxial flexural strength, and fluoride release of resin-based restorative material containing alkaline fillers
Piyaphong PANPISUT, Arnit TONELUCK
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(4): 608. CrossRef - Factors influencing fluoride release in atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) materials: A review
P.Divya Kumari, Shahnawaz Khijmatgar, Avidyuti Chowdhury, Edward Lynch, Chitta R. Chowdhury
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2019; 9(4): 315. CrossRef - Incorporation of chlorhexidine and nano-sized sodium trimetaphosphate into a glass-ionomer cement: Effect on mechanical and microbiological properties and inhibition of enamel demineralization
Márjully Eduardo Rodrigues da Silva, Marcelle Danelon, José Antonio Santos Souza, Dinah Fressato Silva, Jesse Augusto Pereira, Denise Pedrini, Emerson Rodrigues de Camargo, Alberto Carlos Botazzo Delbem, Cristiane Duque
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 84: 81. CrossRef
-
Impact of biofilm model of
Streptococcus mutans
on the pH, ions release, and sorption/solubility of glass ionomer cements enriched with 45S5 bioglass
- 3,051 View
- 9 Download
- 17 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


