Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
- Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e18. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated alterations in neuronal conductivity related to calcium silicate cements (CSCs) by investigating compound action potentials (cAPs) in rat sciatic nerves.
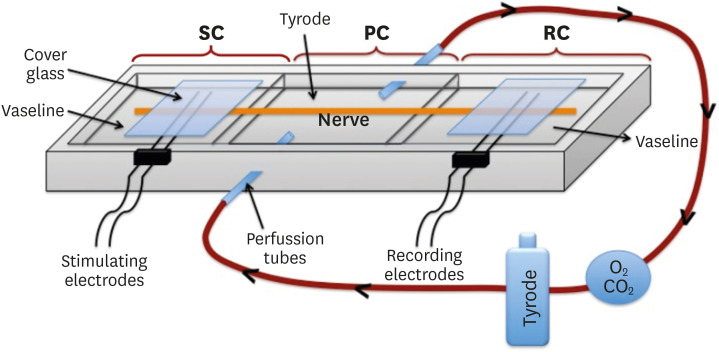
Materials and Methods Sciatic nerves were placed in a Tyrode bath and cAPs were recorded before, during, and after the application of test materials for 60-minute control, application, and recovery measurements, respectively. Freshly prepared ProRoot MTA, MTA Angelus, Biodentine, Endosequence RRM-Putty, BioAggregate, and RetroMTA were directly applied onto the nerves. Biopac LabPro version 3.7 was used to record and analyze cAPs. The data were statistically analyzed.
Results None of the CSCs totally blocked cAPs. RetroMTA, Biodentine, and MTA Angelus caused no significant alteration in cAPs (
p > 0.05). Significantly lower cAPs were observed in recovery measurements for BioAggregate than in the control condition (p < 0.05). ProRoot MTA significantly but transiently reduced cAPs in the application period compared to the control period (p < 0.05). Endosequence RRM-Putty significantly reduced cAPs.Conclusions Various CSCs may alter cAPs to some extent, but none of the CSCs irreversibly blocked them. The usage of fast-setting CSCs during apexification or regeneration of immature teeth seems safer than slow-setting CSCs due to their more favorable neuronal effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
Anna Błaszczyk-Pośpiech, Natalia Struzik, Maria Szymonowicz, Przemysław Sareło, Maria Wiśniewska-Wrona, Kamila Wiśniewska, Maciej Dobrzyński, Magdalena Wawrzyńska
Materials.2025; 18(18): 4259. CrossRef
- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
- 1,606 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


