Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of hydrofluoric acid-based etchant at an elevated temperature on the bond strength and surface topography of Y-TZP ceramics
- Mi-Kyung Yu, Myung-Jin Lim, Noo-Ri Na, Kwang-Won Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e6. Published online December 3, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
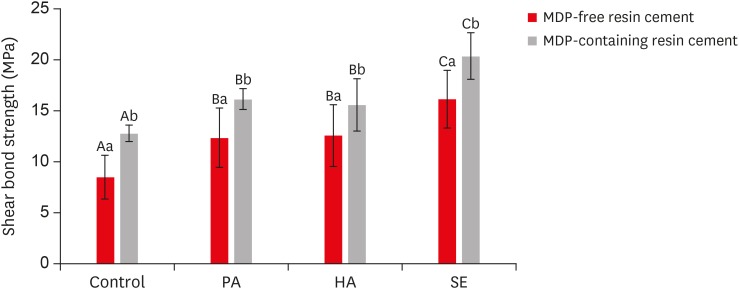
ePub Objectives This study investigated the effects of a hydrofluoric acid (HA; solution of hydrogen fluoride [HF] in water)-based smart etching (SE) solution at an elevated temperature on yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) ceramics in terms of bond strength and morphological changes.
Materials and Methods Eighty sintered Y-TZP specimens were prepared for shear bond strength (SBS) testing. The bonding surface of the Y-TZP specimens was treated with 37% phosphoric acid etching at 20°C–25°C, 4% HA etching at 20°C–25°C, or HA-based SE at 70°C–80°C. In all groups, zirconia primers were applied to the bonding surface of Y-TZP. For each group, 2 types of resin cement (with or without methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate [MDP]) were used. SBS testing was performed. Topographic changes of the etched Y-TZP surface were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The results were analyzed and compared using 2-way analysis of variance.
Results Regardless of the type of resin cement, the highest bond strength was measured in the SE group, with significant differences compared to the other groups (
p < 0.05). In all groups, MDP-containing resin cement yielded significantly higher bond strength values than MDP-free resin cement (p < 0.05). It was also shown that the Y-TZP surface was etched by the SE solution, causing a large change in the surface topography.Conclusions Bond strength significantly improved when a heated HA-based SE solution was applied to the Y-TZP surface, and the etched Y-TZP surface was more irregular and had higher surface roughness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Etchability of zirconia ceramics and its effect on adhesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Anina Sieber, Luiza Freitas Brum Souza, Tan Fırat Eyüboğlu, Mutlu Özcan
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 148: 104303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Surface Roughening Techniques on Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Monolithic Zirconia: In Vitro Study
Nehal F Albelasy, Ahmad M Hafez, Abdullah S Alhunayni
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(12): 1104. CrossRef - Effect of Acid Surface Treatments on the Shear Bond Strength of Metal Bracket to Zirconia Ceramics
Punchanit Wongrachit, Bancha Samruajbenjakun, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon, Tanapat Jearanai, Supontep Teerakanok, Pannapat Chanmanee
Ceramics.2024; 7(2): 689. CrossRef - Exploring Zirconia Adhesion: Pre and Postsintering Physical Surface Treatment, Chemical Treatment, and Cement Interactions
Flávia Gonçalves, Mirko Dennys Ayala-Perez, Francisco Carlos dos Santos Reis, Walter Gomes Miranda-Júnior, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of zirconia surfaces and shear bond strength after acid–etching with ultrasonic vibration
Xiaozhen Zhang, Hepeng Nie, Jiaxin Lv, Shanshan Yuan, Juan Wang, Kunzhan Cai, Jin Wu, Qingqing Zhang, Chunbo Tang
Materials Research Express.2024; 11(2): 025401. CrossRef - Effects of Surface-Etching Systems on the Shear Bond Strength of Dual-Polymerized Resin Cement and Zirconia
Sang-Hyun Kim, Kyung Chul Oh, Hong-Seok Moon
Materials.2024; 17(13): 3096. CrossRef - Zirconia bond strength durability following artificial aging: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Athanasios E. Rigos, Katia Sarafidou, Eleana Kontonasaki
Japanese Dental Science Review.2023; 59: 138. CrossRef - Y-TZP Physicochemical Properties Conditioned with ZrO2 and SiO2 Nanofilms and Bond Strength to Dual Resin Cement
Ricardo Faria Ribeiro, Danilo Flamini Oliveira, Camila Bussola Tovani, Ana Paula Ramos, Ana Flavia Sanches Borges, Adriana Claudia Lapria Faria, Rossana Pereira de Almeida, Renata Cristina Silveira Rodrigues
Materials.2022; 15(22): 7905. CrossRef - Effect of the nanofilm-coated zirconia ceramic on resin cement bond strength
Viviane Maria Gonçalves de Figueiredo, Alecsandro de Moura Silva, Marcos Massi, Argemiro Soares da Silva Sobrinho, José Renato Cavalcanti de Queiroz, João Paulo Barros Machado, Renata Falchete do Prado, Lafayette Nogueira Junior
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2022; 16(3): 170. CrossRef - Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Bond Strength and Topography for Y-TZP Etched with Hydrofluoric Acid Depending on Concentration and Temperature Conditions
Hyo-Eun Kim, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
Medicina.2020; 56(11): 568. CrossRef - Do different sintering conditions influence bond strength between the resin cements and a currently used esthetic zirconia?
Fatma Ayse Sanal, Hamiyet Kilinc
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(16): 1809. CrossRef
- Etchability of zirconia ceramics and its effect on adhesion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,208 View
- 11 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Iatrogenic chemical burn on facial skin by 37% phosphoric acid etchant
- Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):38-41. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub When we use the total-etch dentin adhesive system for composite resin restorations, gel or liquid acid etchant such as 37% phosphoric acid is commonly used. Thirty seven percentage phosphoric acid is very powerful erosive agent, and can cause severe harmful effects when it contacts with an oral mucosa and facial skin.
This case describes iatrogenic chemical burn on facial skin caused by phosphoric acid which was happened during composite resin restorative procedure.
Chemical burn by acid etchant can be evoked by careless handling of remnant and syringe. In order to prevent these iatrogenic injuries, we should check the complete removal of the etching agent both in intra and extra-oral environments after etching and rinsing procedure and it is necessary to use of the rubber dam or isolation instruments.
If accidental burn were occurred, immediate wash with copious water. And bring the patient to the dermatologist as soon as possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytotoxicity of V-Prep Versus Phosphoric Acid Etchant on Oral Gingival Fibroblasts
Victor Ghoubril, Sylvie Changotade, Didier Lutomski, Joseph Ghoubril, Carole Chakar, Maher Abboud, Louis Hardan, Naji Kharouf, Elie Khoury
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 13(4): 266. CrossRef - Effects of dental acid etchants in oral epithelial cells
Do-kyeong Kim, Jae-won Kwak, Ryeong-mi Jo, Da-som Jung, Da-young Youn, Na-yeon Oh, Ji-hye Jang
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(4): 299. CrossRef
- Cytotoxicity of V-Prep Versus Phosphoric Acid Etchant on Oral Gingival Fibroblasts
- 3,976 View
- 61 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


