Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The effects of gingival blood flow on pulpal blood flow detection using ultrasound Doppler flowmetry: animal study
- Dohyun Kim, Hyoung-Seok Ko, Soo-Yeon Park, Seung-Yeon Ryu, Sung-ho Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e9. Published online January 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
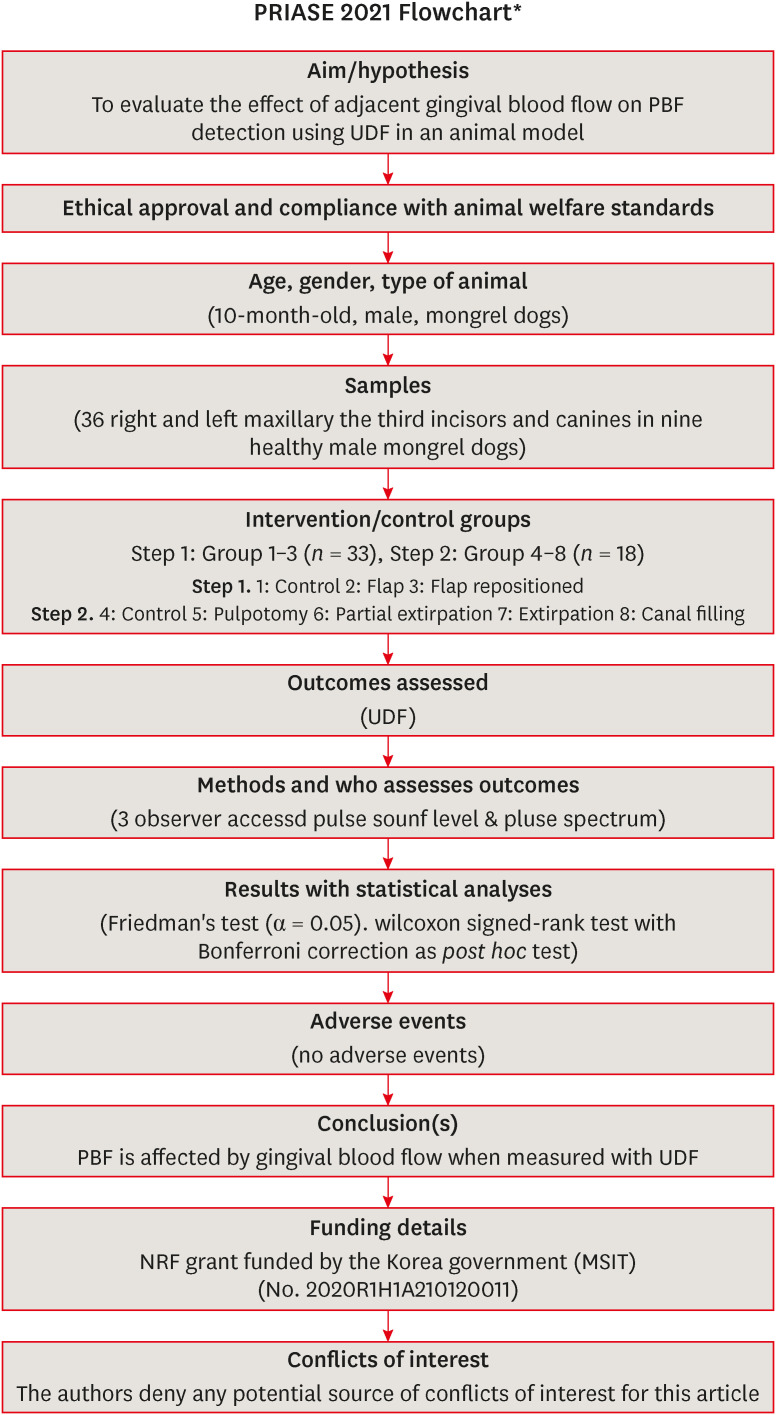
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of adjacent gingival blood flow on detection of pulpal blood flow (PBF) using ultrasound Doppler flowmetry (UDF) through animal study.
Materials and Methods The study included 36 right and left maxillary the third incisors and canines in 9 experimental dogs. The study included 2 main steps: In the first step, the pulse sound level (PSL) was recorded on the cervical part of each tooth without flap elevation (Group 1), with flap elevation (Group 2), and after it was repositioned in place (Group 3). In the second step, the PSL was recorded on the cervical part of each tooth (Group 4), after pulpotomy (Group 5), after partial pulp extirpation (Group 6), after complete extirpation (Group 7), and after canal filling (Group 8). In Groups 5–8, the study was performed with and without flap elevation in the left and right teeth, respectively. The PSL was graded as follows: 0, inaudible; 1, heard faintly; and 2, heard well. The difference between each group was analyzed using Friedman’s test with Wilcoxon signed-rank tests (α = 0.05).
Results In step 1, the PSL results were Group 1 > 2 and 3. In step 2, there was no significant difference between the groups when the flap was not elevated, while PSL results were Group 4 > 5 ≥ 6 and 7 ≥ 8 when the flap was elevated.
Conclusions PBF is affected by gingival blood flow when measured with UDF. UDF measurements require isolation of gingiva from the tooth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modern aspects of the use of hardware methods for diagnosing pulp vitality (Part 2. Non-traditional diagnostic methods)
K. V. Shadrina, L. Yu. Orekhova, V. D. Goncharov, V. Yu. Vashneva, E. S. Silina, E. V. Kosova, A. A. Petrov
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(3): 423. CrossRef - Exploring approaches to pulp vitality assessment: A scoping review of nontraditional methods
Farzaneh Afkhami, Patricia Paule Wright, Philip Yuan‐Ho Chien, Chun Xu, Laurence James Walsh, Ove Andreas Peters
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(8): 1065. CrossRef
- Modern aspects of the use of hardware methods for diagnosing pulp vitality (Part 2. Non-traditional diagnostic methods)
- 2,433 View
- 39 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

-
Antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment: a literature review - Part II.
in vivo studies - Dohyun Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):97-103. Published online December 9, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The first part of this study reviewed the characteristics of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and summarized the results of
in vitro studies related to its antimicrobial effects. The second part of this review coversin vivo studies including human clinical studies and animal studies. The use of Ca(OH)2 as an intracanal medicament represented better histological results in animal studies. However, human clinical studies showed limited antimicrobial effects that microorganisms were reduced but not eliminated through the treatment, and that some species had resistance to Ca(OH)2. Most of clinical outcome studies supported that there is no improvement in healing of periapical lesions when Ca(OH)2 was applied between appointments. Further studies are required for the antimicrobial effects of Ca(OH)2, and search for the ideal material and technique to completely clean infected root canals should be continued.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Antibacterial Efficacy of Graphene Nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis: In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Preena Sidhu, Kiran Rehman, Thiagrajan Madheswaran, Amalraj Fabian Davamani
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 103. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of propolis as an intercanal medicament against Enterococcus faecalis (a randomized controlled in vitro study)
Alaa Almahameed, Joul Kassis, Magd Aboud, Kinda Layous
Heliyon.2025; 11(1): e41733. CrossRef - Neoangiogenetic potential of Nd:YAG 1064 nm photobiomodulation in non-surgical healing of trauma induced periapical bone defects: a clinicalprospective pilot study
Jagruti Mutalikdesai, Rhythm Bains, Aseem P. Tikku, Ramesh Bharti, Vijay Kumar Shakya, Sukriti Kumar, Promila Verma
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Jasminum-based Nano-reinforced Calcium Hydroxide Reduces Postoperative Pain in Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nehal Amir, Emaan Mansoor, Nabiha Eeman, Muhammad Nouman Ahmed, Ezza Mansoor, Efrah Mansoor, Khadim Hussain, Vera Afreixo, Afsheen Mansoor, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(8): 996. CrossRef - Management of Enterococcus faecalis associated endodontic infection using gold nanogel: An in-vitro study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Goh Chong Ming Jonathan, Seow Liang Lin, Fabian Davamani, Preena Sidhu, Minati Choudhury
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano-sized Calcium Hydroxide-Zinc Oxide Intracanal Medicament: Physicochemical Characterization and Potential Endodontic Applications
Kashmiri Chowdhury, S. Delphine Priscilla Antony, Praveen Kumar Elango, Pradeep Solete, Shreshtha Muskan
Journal of International Oral Health.2025; 17(3): 196. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Tooth Discoloration Induced by an Experimental Antibiotic Paste Modified with Nano Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Mohamed Ahmed Elsayed, Md Sofiqul Islam, Safiya Ali, Zainab Hussain, Muhammed Mustahsen Rahman, Okba Mahmoud
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 307. CrossRef - An in vitro study on the antimicrobial efficacy of a calcium hydroxide versus a calcium silicate-based endodontic medicament
Dheepthi Jana, Eda Dzinovic, Ahmed Almaroof, Dipti Mehta, Sherif Elsharkawy, Sanjukta Deb, Sadia Niazi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of canal medicaments triple antibiotic paste, Bio-C Temp, and Nano-silver gel activated by visible blue light on canal dentin microhardness and extrusion bond strength of AH plus sealer: A SEM and EDX analysis
Ahoud Alshamrani, Laila AlDeeb, Thamer Almohareb, Khold Alahdal, Ahmed Maawadh, Ali Alrahlah
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2024; 47: 104088. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydrogel-Based Intracanal Medicaments in Endodontics: A Systematic Review of Development and Antibacterial Efficacy
Rathna Piriyanga, Manish Ranjan, Anand Sherwood, Swathi Priyadharshini
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 449. CrossRef - The advancement in irrigation solution within the field of endodontics, A Review
Fatima Fahad , Raghad A Al-Hashimi , Munther J Hussain
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 54. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Action of Novel Panax ginseng Paste, Calcium Hydroxide and Bio-C Temp as an Intracanal Medicament Against Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus mutans
Zadeno Kithan, Sonali Taneja, Abhik Mukherjee
Journal of Natural Remedies.2024; : 2705. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Two Different Calcium Hydroxide Endodontic Dressings on the Eradication of Enterococcus faecalis in Single-Rooted Canals: An In Vitro Study
Paola G Rumhein, Kinda J Layous, Hassan Achour, Mudar Mohammad Mousa, Haya Deeb, Mohammad Y Hajeer
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Seda Falakaloğlu, Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Betül Güneş, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mustafa Gündoğar, Burcu Güçyetmez Topal
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial potential of new diclofenac hydrogels for disinfection in regenerative endodontics: An in vitro and ex vivo study
Matilde Ruiz‐Linares, Javier F. Monroy‐Rojas, Carmen Solana, Pilar Baca, Beatriz Aguado, Ana Soriano‐Lerma, María Teresa Arias‐Moliz, Carmen María Ferrer‐Luque
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(1): 103. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial effect ofAllium sativum, calcium hydroxide and their combination as intracanal medicaments in infected mature anterior teeth: A randomized clinical trial
Shaimaa Mohamed Mahfouz Omer, Dalia Abd‐Allah Mohamed, Reham Mohamed Ali Abdel Latif
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(10): 1010. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of antibiotic pastes versus calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies
Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Kamyar Khosravi, Nazanin Zargar, Armin Shirvani, MohammadHossein Nekoofar, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 463. CrossRef - Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Lactobacilli probiotics supernatants against Enterococcus faecalis (in-vitro study)
Shymaa Shaaban, Gamal M. Hamad, Salma Genena, Marwa A. Meheissen, Sybel Moussa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Superior Antibacterial Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxide–Propolis Paste against Enterococcus faecalis in Infected Root Canals: A Randomized Controlled In Vitro Study
Alessandro Marino, Luca De Santis, Paolo Romano
Interdisciplinary Research in Medical Sciences Specialty.2022; 2(1): 49. CrossRef - Post-operative Pain and Antibacterial Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Formulations Intracanal Medication: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study
Nermine Hassan, Alaa Diab, Geraldine Ahmed
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 248. CrossRef - EFFICACY OF VARIOUS LASER-ASSISTED IRRIGATION ACTIVATION TECHNIQUES ON CALCIUM HYDROXIDE REMOVAL
Ezgi DOĞANAY YILDIZ, Fatma DURNA YURTSEVEN, Dilek HANÇERLİOĞULLARI
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Experimental study the anti-inflammatory and osteo-regenerative qualities of the paste based on symphytum officinale tincture and calcium hydroxide
Iryna Kostyiuk, Victor Kostiuk, Halyna Kimak, Yuriy Oktysyuk, Lilia Tarnavska
Pharmacia.2021; 68(3): 585. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - Preserving pulp vitality: part two - vital pulp therapies
David Edwards, Simon Stone, Oliver Bailey, Phillip Tomson
British Dental Journal.2021; 230(3): 148. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Daptomycin, Gentamicin, and Calcium Hydroxide—Antibiotic Combinations on Enterococcus faecalis Dentinal Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Arunajatesan Subbiya, Suresh Mitthra, Kesavaram Padmavathy, Krishnan Mahalakshmi, Alagarsamy Venkatesh, Kotishwaran Gayathri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(2): 128. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of sprinkling powdered slaked lime on microorganisms for the prevention of domestic animal infectious diseases
Miho Mori, Yoshikazu Sakagami, Yousuke Hamazaki, Toru Jojima
Environmental Technology.2019; 40(23): 3094. CrossRef - Efficacy of XP-Endo finisher in removal of calcium hydroxide from root canal system: A systematic review
Shruti Kamath, Rajesh Shetty, Soumya Shetty, Nikhil Nighot, Karuna Ramnani, Dhananjay Bhujbal
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2019; 11(2): 54. CrossRef - Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicament in Pulp Necrosis with Periapical Lesion : A Case Report
Elvi Sahara, Rahmi Alma Farah, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
Key Engineering Materials.2019; 829: 226. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - 2016 ASE undergraduate essay competition candidate information
Alice Chen
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 7. CrossRef - Efficacy of self‐adjusting file, XP‐endo finisher and passive ultrasonic irrigation on the removal of calcium hydroxide paste from an artificial standardized groove
Anda Kfir, Nuphar Blau‐Venezia, Tomer Goldberger, Itzhak Abramovitz, Ronald Wigler
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 26. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of Annona crassiflora Mart. against Candida albicans
de Mendonça Cavalcante Amaro, Antonio Lisboa Ribeiro Junior Karlos, CameloPessoa de Azevedo Ximenes Eulália, Porfirio Silva Zenaldo, Ivo Limeira dos Reis José, Euzebio Goulart de Santana Antonio
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.2017; 11(13): 253. CrossRef - Antifungal effects of synthetic human β-defensin 3-C15 peptide
Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Christine Kim, Jong-Won Kum, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yu Gu, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seok Woo Chang, Seung Hyun Han, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 91. CrossRef - Microbiology of Root Canal Infections
Marjut Sakko, Leo TjÄDerhane, Riina Rautemaa-Richardson
Primary Dental Journal.2016; 5(2): 84. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 3,245 View
- 38 Download
- 37 Crossref

-
Antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment: a literature review - Part I.
In vitro studies - Dohyun Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):241-252. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The goal of endodontic treatment is the prevention and control of pulpal and periradicular infections. Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) has been widely used in endodontics as an intracanal medicament to eliminate the remaining microorganisms after chemomechanical preparation. The purpose of this article is to review the antimicrobial properties of Ca(OH)2 as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment. The first part of this review details the characteristics of Ca(OH)2 and summarizes the results of
in vitro studies related to its antimicrobial effect. The antimicrobial effect of Ca(OH)2 results from the release of hydroxyl ions when it comes into contact with aqueous fluids. Ca(OH)2 has a wide range of antimicrobial effects against common endodontic pathogens, but is less effective againstEnterococcus faecalis andCandida albicans . The addition of vehicles or other agents might contribute to the antimicrobial effect of Ca(OH)2.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Sustained-release medicament incorporated with cetylpyridinium chloride: An in vitro assessment of Enterococcus faecalis disinfection
Sankar Vishwanath, Sadasiva Kadandale, Revathy Parthasarathy, Srividhya Srinivasan, Sangita Ilango, Nikesh Shakthivel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 66. CrossRef - Influence of Different Types of Intracanal Medicaments and Root Canal Sealers on Root Dentine Fracture Resistance at 2 Different Time Intervals
Damla Akkaya, Tugba Kosar
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Properties of 50% Grape Seed Extract, N-acetyl Cysteine and 5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite against Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 19433) – An In vitro Study
Nikita Vishweshwar Kurtkoti, Madhura Vivek Pawar, Vaishnavi Ketan Mathawala, Shraddha Mahadeo Shirsat
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(2): 237. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antimicrobial Performance of Calcium Dihydroxide (Ca(OH)2) Coating on Ti for Potential Metallic Orthopedic Implant Applications
Harald Holeczek, Michael de Wild, Jasmine Ruegg, Philipp Gruner, Walter Moser, Olivier Braissant
Antibiotics.2025; 14(1): 91. CrossRef - Synthesis of uniform core‐shell calcium hydroxide‐calcium carbonate biocidal particles via encapsulation into dry ice
Noora Darwish, Mehdi Mohammadi Ashani, Ahmed Mehairi, Ian A. Lewis, Maen M. Husein
The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 103(10): 4774. CrossRef - PROANTHOCYANIDIN-PLGA NANOPARTICLE INFUSED CALCIUM HYDROXIDE SEALER: ADVANCING MATERIAL PERFORMANCE AND CLINICAL STABILITY IN ENDODONTICS
VANDANA SADANANDA, GOWRISH S., R. NARAYANA CHARYULU, MITHRA N. HEGDE
International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics.2025; : 126. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Assessment of Modified Triple Antibiotic Paste, Calcium Hydroxide, Chitosan-loaded Modified Triple Antibiotic Paste against Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Asiya Mujawar, Varsha Pandit, Sumaiyya Shaikh, Bilal A Shaikh
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 16(2): 142. CrossRef - Recent advances in antibacterial nanoformulations for endodontic applications
Tiago Dionísio, Pedro Brandão, Vanessa Machado, João Botelho, José João Mendes, Pedro Fonte
Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2025; 22(8): 1117. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Novel Calcium Hydroxide Nanoparticles in the Different Vehicles against Mixed-species Biofilm: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Study
Parinthron Rattanakijkamol, Patarawadee Promta, Phenphichar Wanachantararak, Warat Leelapornpisid
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(3): 265. CrossRef - Comparison of Efficacy of Trunatomy Irrigation Needle, Sonic Irrigation Technique, and Ultrasonic Irrigation Technique in Retrievability of Rc Cal, Metapex, and Bio C Temp from Root Canals: An In-Vitro CBCT Analysis
Ajay Nevil, Faisal M. A. Gaffoor, Rethi Gopakumar, C. Sabari Girish, N. C. Sajeena, V. N. Anoop
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 2): S1827. CrossRef - Non-surgical Management of Immature Permanent Anterior Tooth followed by Single-step Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apexification
Harsha Haridas, K. Surya, V. Vanitha
Kerala Dental Journal.2025; 48(2): 95. CrossRef - Evaluating antimicrobial, anti-biofilm, and cytotoxic effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles-coated calcium hydroxide for intracanal use
Khaled Beshr, Hisham M. Elhalabi, Heba Yehia
Advances in Traditional Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Effectiveness of Endodontic Triple Antibiotic Paste Associated With Daptomycin
Sabrina S Azevedo, Gabriela C Chianca, Bruna A Thurler, Raiane C Chamon, Helvécio C Corrêa Póvoa, Leonardo S Antunes, Natalia L Pontes Póvoa Iorio
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhanced penetration and antibacterial efficacy of calcium hydroxide modified with titanium dioxide nanoparticles
Teena Sheethal Dsouza, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Ashma Dorothy Monteiro, Heeresh Shetty
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - An in vitro study on the antimicrobial efficacy of a calcium hydroxide versus a calcium silicate-based endodontic medicament
Dheepthi Jana, Eda Dzinovic, Ahmed Almaroof, Dipti Mehta, Sherif Elsharkawy, Sanjukta Deb, Sadia Niazi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Cannabinoids on Bacteria Associated with Persistent Endodontic Infections
Cassandra Wieczerza, Haoyan Zhai, Mazin Askar, Zheng Zhou, Susan Paurazas
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11936. CrossRef - Effect of niobium pentoxide incorporated calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament on fracture resistance of root canal dentin
Nadimpalli Teja Varma, Venkatappan Sujatha, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(12): 1211. CrossRef - Anterior Palatal Radicular Cyst: A Case Report
Prasanna R Sonar, Aarati Panchbhai, Ankita Pathak, Aachal N Lande, Sandeep Kalisipudi, Osama Ahmed
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetration Depth and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxide, MAS Paste, Nitrofurantoin, and Levonadifloxacin against Enterococcus faecalis: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Nishitha Gunnam, Swathi Aravelli, Nimeshika Ramachandruni, Mounika Gandla, Swetha Kasam, Uday Kumar Podugu
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(5): 394. CrossRef - The Evaluation of Anti-Osteoclastic Activity of the Novel Calcium Hydroxide Biodegradable Nanoparticles as an Intracanal Medicament
Patarawadee Promta, Patcharaporn Chaiyosang, Aussara Panya, Pongrapee Laorodphun, Warat Leelapornpisid, Napatsorn Imerb
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 667. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Glycyrrhizin on the Viability and Proliferation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Compared to Intracanal Medicaments
Mohamed G Elbeltagy, Manal F Badawi, Amany E Badr, Mohammad A Alrashidi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(3): 267. CrossRef - Impact of Calcium Hydroxide Particle Size on the Intracanal Medicament Penetration Efficacy
Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Achdi Afidi, Mutiara Sukma Suntana, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria, I Made Joni, Ani Melani Maskoen
Diffusion Foundations and Materials Applications.2024; 37: 29. CrossRef - Antibiofilm efficacy of a calcium silicate-based intracanal medicament against Fusobacterium nucleatum strains
Hanan Balto, Reem Barakat, Sumaya Basudan, Ghazal Fakeeha, Sarah R. Alharbi, Rahaf Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-surgical management of mandibular first premolar with vertucci type v root canal configuration: A case report
Mohd Faisal Azeez, Neelam Mittal, Shelly Sharma
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2024; 9(3): 146. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of an impacted migrated mandibular canine using platelet-rich fibrin and physio-dispenser system: a report of two cases
Rajmohan Shetty, Vabitha Shetty, Nikhitha Aswath, Kavitha Rai
Dental Update.2024; 51(3): 203. CrossRef - Enterococcus Phage vB_EfaS_HEf13 as an Anti-Biofilm Agent Against Enterococcus faecalis
Dongwook Lee, Jintaek Im, A Reum Kim, Woohyung Jun, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2024; 62(8): 683. CrossRef - In-vitro and In-silico evaluation of antimicrobial and antibiofilm effect of Neem oil and Calcium hydroxide nanoparticles against Mutans Streptococci and Enterococcus faecalis isolated from endodontic infections
Wedad M. Nageeb, Sherouk Hussein Adam, Nasr Hashem, Nelly Abdelsalam
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effects of Formulations of Various Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide as Intra-canal Medications Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review
Seema H Bukhari, Dax Abraham, Shakila Mahesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Intracanal Medicaments (Curcuma longa, Honey, Nitrofurantoin, and Calcium Hydroxide) on Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro Study
M. S. Rangareddy, Shanti Priya P., Basa Srinivas Karteek, Chigurupati Swetha, B. Sravan Kumar, Sumaiya Waheed, Jagrati Agrawal
Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics.2024; 15(1): 19. CrossRef - A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide
Yu Abe, Michiyo Honda
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(6): 1629. CrossRef - Periapical Pathologies Treated with Conservative Approach
Mohammad Imran Khan, Khushboo Arif, Abhisheik Khare, Pradyumna Mishra
The Traumaxilla.2023; 5(1-3): 64. CrossRef - Effect of different activation methods on the intratubular penetration of CaOH2 paste: Ex‐vivo analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy
João Pedro Gasparin Tadano, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Cláudia Fernandes de Magalhães Silveira, Tainara Bielecki Yamanaka, Gabriela Gonçalez Piai, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Alexandre Sigrist De Martin
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 18. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of postoperative pain with continuous ultrasonic irrigation, laser-activated irrigation, and laser irradiation: A randomized clinical trial
Karishma Krishnakumar, Anita Sanap Tandale, Twinkle Talreja, Ridhi Dube
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 267. CrossRef - Therapeutic Potential of Chlorhexidine-Loaded Calcium Hydroxide-Based Intracanal Medications in Endo-Periodontal Lesions: An Ex Vivo and In Vitro Study
Kadiatou Sy, Charlène Chevalier, Mickaël Maton, Ilham Mokbel, Séverine Mahieux, Isabelle Houcke, Christel Neut, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Etienne Deveaux, Kerstin Gritsch, Kevimy Agossa
Antibiotics.2023; 12(9): 1416. CrossRef - Non surgical management of a large periapical cyst like lesion using metapex, a three year followup - A case report
Subhashini Ayodhi, Ashok Laburu, Madhuram Krishnamurthy, Naveen Kumar
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 7(4): 186. CrossRef - Single versus multiple visits endodontic therapy on healing rate of periapical lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Athanasios Theodoridis, Nikolaos Economides
Balkan Journal of Dental Medicine.2023; 27(3): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Irrigation Solution of Sodium Hypochlorite, Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid, Chitosan Oligosaccharide and Agitation Techniques on Calcium Hydroxide Removal in Root Canal: In Vitro Study
Melia Heptania, Trimurni Abidin, Widi Prasetia, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2023; : 6008. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of various types of endodontic sealers in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells
Mi-Jeong JEON, Hyunjung KO, Su-Jung SHIN, Miri KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 774. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Antibiotic Pastes and Calcium Hydroxide Using Chitosan as a Carrier Against Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Srinidhi S R, Sania Singh, Ajit Hindlekar, Niranjan Desai, Nishant Vyavahare
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Irrigation Solutions in Root Canal Treatment: A Glance at the Past, the Present, and the Future
Abubaker Qutieshat, Nutayla Al Harthy, Shima Al Busaidi, Ahmed Al Sadoon, Dima Al Sayahien, Maryam Sedqi, Sumaiya Al Rashdi, Samiya Al Ghammari
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different intracanal medicaments on the dislodgement resistance of mineral trioxide aggregate
Farzaneh Afkhami, Shahrzad Razavi, Sholeh Ghabraei
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibitory Effect of Medicament Camphorated Parachlorophenol to Bacteria in Chronic Apical Abscess
Diani Prisinda, Yuti Malinda
Applied Mechanics and Materials.2022; 910: 9. CrossRef - The Assessment of Quality of the Root Canal Filling and the Number of Visits Needed for Completing Primary Root Canal Treatment by Operators with Different Experience
Krystyna Pietrzycka, Mateusz Radwanski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Davide Mancino, Youssef Haikel, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Bioengineering.2022; 9(9): 468. CrossRef - Evaluation of antimicrobial action and push-out bond strength and compressive strength using mineral trioxide aggregate and triple antibiotic medicament combination as root-end filling material
Rahul S. Halkai, Raeesunisa Begum, Kiran R. Halkai, Kiran Ghatole, Ashwini Hambire, Amaan Ahmed
Endodontology.2022; 34(1): 61. CrossRef - Propionate Attenuates Growth of Oral Streptococci through Enhancing Methionine Biosynthesis
Taehwan Park, Jintaek Im, A Reum Kim, Dongwook Lee, Sungho Jeong, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2022; 32(10): 1234. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of two different intercanal medicaments on human gingival fibroblasts - A Laboratory study
Behnaz Barakatein, Alireza Farhad, Elham Shadmehr, Hamidreza Mohammad Sharifi, Masoud Mohammadi Hamidreza Mohamad Sharif, Amin Davoudi
Endodontology.2022; 34(2): 76. CrossRef - The efficacy of EndoActivator, passive ultrasonic irrigation, and Ultra X in removing calcium hydroxide from root canals: an in-vitro study
Alireza Adl, Alireza Razavian, Fateme Eskandari
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Calcium Hydroxide with Vehicles Relate to the pH Change, Calcium Ion Diffusion, Roughness, and Frequency of Chemical Compound in Root Canal
Dwi Yani Sastika, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2976. CrossRef - Influence of different calcium hydroxide removal protocols on the bond strength of epoxy resin‐based sealer in long oval root canals
Patrícia Maria Escobar, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes, Kleber Carvalho, Vicente Fretes, Gabriela Gavilán Hadid, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Manoel Damião Sousa‐Neto
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(2): 781. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of antibiotic pastes versus calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies
Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Kamyar Khosravi, Nazanin Zargar, Armin Shirvani, MohammadHossein Nekoofar, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 463. CrossRef - EFFICACY OF VARIOUS LASER-ASSISTED IRRIGATION ACTIVATION TECHNIQUES ON CALCIUM HYDROXIDE REMOVAL
Ezgi DOĞANAY YILDIZ, Fatma DURNA YURTSEVEN, Dilek HANÇERLİOĞULLARI
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity, cytocompatibility and effect of Bio‐C Temp bioceramic intracanal medicament on osteoblast biology
J. C. M. Guerreiro, V. M. Ochoa‐Rodrígez, E. M. Rodrigues, G. M. Chavez‐Andrade, M. Tanomaru‐Filho, J. M. Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, G. Faria
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1155. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Effects of Heracleum persicum and Ziziphora tenuior L. Extracts, Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine on Enterococcus faecalis as Intracanal Medicaments in Root Canal Therapy – An In Vitro Study
Aida Mehdipour, Maryam Akbarzadeh, Somayeh Kermani, Saeed Shams, Alireza Karimi
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(38): 3395. CrossRef - Interdisciplinary management of a maxillary central incisor with a palato‐radicular groove: A case report with 27 years follow‐up
David P. Mathews, David E. Hansen
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(8): 1077. CrossRef - How Adding Chlorhexidine or Metallic Nanoparticles Affects the Antimicrobial Performance of Calcium Hydroxide Paste as an Intracanal Medication: An In Vitro Study
Kadiatou Sy, Kevimy Agossa, Mickaël Maton, Henry Chijcheapaza-Flores, Bernard Martel, Florence Siepmann, Etienne Deveaux, Nicolas Blanchemain, Christel Neut
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1352. CrossRef - Selenium intracanal dressing: effects on the periapical immune response
Marcela Carvalho Espaladori, Julia Mourão Braga Diniz, Luciana Carla Neves de Brito, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares, Toshihisa Kawai, Leda Quercia Vieira, Antônio Paulino Ribeiro Sobrinho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2951. CrossRef - Post-operative Pain and Antibacterial Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Formulations Intracanal Medication: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study
Nermine Hassan, Alaa Diab, Geraldine Ahmed
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 248. CrossRef - Comparative Assessment of Role of Intracanal Medicaments in Pain Reduction during Endodontic Treatment
Sadashiv G. Daokar, Aishwarya Rajesh Mantri, Kalpana S. Patil, Kapil D. Wahane, Suraj V. Rathi, Shivangi Shashikant Sharma
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2021; 11(2): 73. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of Asphaline Temp, Triple antibiotic Paste and Ultracal XS against Enterococcus faecalis – An in vitro study
Siddhesh Bandekar, Aditi Amin, Shirin Kshirsagar, N Vathsala, Vyas Chinmay, Anjum Sayyad
Endodontology.2021; 33(1): 6. CrossRef - Antibacterial evaluation of guava leaves extract and its effect on reactive oxygen species formed by calcium hydroxide and chlorhexidine mixture
KarmaDeepak Chandran, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Venkatappan Sujatha, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 389. CrossRef - The Effects of Intracanal Irrigants and Medicaments on Dental-Derived Stem Cells Fate in Regenerative Endodontics: An update
Sara Ayoub, Ali Cheayto, Sanaa Bassam, Mehdi Najar, Antoine Berbéri, Mohammad Fayyad-Kazan
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(4): 650. CrossRef - Nonsurgical management of persistent periapical lesions in the anterior region - A systematic review
SayaliAnil Maral, AnamikaChetan Borkar, AnitaBabasaheb Tandale, NikhilBabaji Nighot, SanchitVilas Mujumdar, ShrutiSudhakar Khade
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 8. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Removal of Overextended Gutta-Percha Root Canal Filling in a Permanent Maxillary Central Incisor with Apical Root Resorption - A Case Report
Gaurav Umesh Chaudhari, Sumanthini Venkatsubramanyam Margasahayam, Vanitha Umesh Shenoy, Akash Kiran More, Anuradha Bhausaheb Patil
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(42): 3159. CrossRef - Oroactive dental biomaterials and their use in endodontic therapy
Ebrahim Patel, Priyamvada Pradeep, Pradeep Kumar, Yahya E. Choonara, Viness Pillay
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2020; 108(1): 201. CrossRef - The Use of Calcium Hydroxide as an Intracanal Medicament in the Treatment of Large Periapical Lesions. A Review
Timea Dako, Mihai Pop, Julia Fulop, Janos Kantor, Monica Monea
Acta Medica Transilvanica.2020; 25(2): 58. CrossRef - Facile synthesis of highly tunable monodispersed calcium hydroxide composite particles by using a two-step ion exchange reaction
Chih-Hui Yang, Ya-Chin Wang, Ta-Chen Wang, Yi-Ching Chang, Yun-Chul Lin, Pei-Fan Chen, Wei-Jie Huang, Hsin-Yi Wen, Yu-Mei Lin, Wen-Shuo Kuo, Yi-Ting Wang, Keng-Shiang Huang
RSC Advances.2020; 10(23): 13700. CrossRef - The Comparison of Different Irrigation Systems to Remove Calcium Hydroxide from the Root Canal: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Samira Jamali, Golchin Jabbari, Elnaz Mousavi, Hashem Ahmadizadeh, Mohammad Khorram, Azad Jamee
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection, treatment and prevention of endodontic biofilm infections: what’s new in 2020?
Sumaya Abusrewil, Om Alkhir Alshanta, Khawlah Albashaireh, Saeed Alqahtani, Christopher J. Nile, James Alun Scott, William McLean
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2020; 46(2): 194. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity of various calcium hydroxide solvents against Fusobacterium nucleatum and Enterococcus faecalis
Siti Rusdiana Puspa Dewi, Riki Agung Santoso, Billy Sujatmiko, Ickman Seto Wibowo
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2019; 1246(1): 012010. CrossRef - Efficacy of XP-Endo finisher in removal of calcium hydroxide from root canal system: A systematic review
Shruti Kamath, Rajesh Shetty, Soumya Shetty, Nikhil Nighot, Karuna Ramnani, Dhananjay Bhujbal
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2019; 11(2): 54. CrossRef - Antibacterial power effectiveness of calcium hydroxide and propolis mixture on Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteria
Ira Widjiastuti, S. Sukaton, Agnes Melinda Wong, Nanik Zubaidah
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2019; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Potential of Calcium Hydroxide Chlorhexidine, Octenidol, Endoseptone and Combination of Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine against Enterococcus faecalis as Intracanal Medicament
Aakriti Aakriti, Dildeep Bali, Preeti Sharma, Vijaya Dhar Bhatt, Prashant Bhasin, Era Arora, Suhrab Singh, Pradeep Kumar
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2019; 13(3): 1725. CrossRef - Efficacy of self‐adjusting file, XP‐endo finisher and passive ultrasonic irrigation on the removal of calcium hydroxide paste from an artificial standardized groove
Anda Kfir, Nuphar Blau‐Venezia, Tomer Goldberger, Itzhak Abramovitz, Ronald Wigler
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 26. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of calcium hydroxide dressing when used for long‐term application: A systematic review
Garima Sharma, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Peter S. Zilm, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 60. CrossRef - Influence of dental materials on cells of the equine periodontium
H. Ringeisen, A. Pöschke, B. Krähling, C. Schröck, M. Stoll, J. Vogelsberg, K. Failing, C. Staszyk
Equine Veterinary Journal.2018; 50(3): 363. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Dressing on the Dentinal Tubule Penetration of 2 Different Root Canal Sealers: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Özge Erdoğan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(6): 1018. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Calcium Hydroxide from Indonesian Limestone as Endodontic Intracanal Medicament
Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Ira Artilia, Arief Cahyanto
Key Engineering Materials.2018; 782: 268. CrossRef - Slightly acidic electrolyzed water combined with chemical and physical treatments to decontaminate bacteria on fresh fruits
Charles Nkufi Tango, Imran Khan, Paul-François Ngnitcho Kounkeu, Rubab Momna, Mohammad Shakhawat Hussain, Deog-Hwan Oh
Food Microbiology.2017; 67: 97. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of Annona crassiflora Mart. against Candida albicans
de Mendonça Cavalcante Amaro, Antonio Lisboa Ribeiro Junior Karlos, CameloPessoa de Azevedo Ximenes Eulália, Porfirio Silva Zenaldo, Ivo Limeira dos Reis José, Euzebio Goulart de Santana Antonio
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.2017; 11(13): 253. CrossRef - Comparison of ozone gas and sodium hypochlorite/chlorhexidine two-visit disinfection protocols in treating apical periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial
Stefan Kist, Maximilian Kollmuss, Jette Jung, Sören Schubert, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth
Clinical Oral Investigations.2017; 21(4): 995. CrossRef - Cytotoxicities and genotoxicities of cements based on calcium silicate and of dental formocresol
Hyunjung Ko, Youngdan Jeong, Miri Kim
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2017; 815: 28. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Mixture of Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine, with Triple Antibiotic Paste and Combination of Calcium Hydroxide, Chlorhexidine, and Lycopene on Incidence of Interappointment Flare-up: An in vivo Study
Priyanka S Bilgi, Jash Mehta
International Journal of Clinical Dentistry and Research.2017; 1(1): 10. CrossRef - Antibacterial effectiveness in vitro of different formulations of calcium hydroxide paste
Israel Alexandre De Araujo SENA, Isaac Jordão De Souza ARAÚJO, Marquiony Marques Dos SANTOS, Isabela Pinheiro Cavalcanti LIMA
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2017; 65(4): 293. CrossRef - Challenges in developing valid techniques for equine endodontic treatment of apically infected cheek teeth
R. M. Baratt
Equine Veterinary Education.2016; 28(11): 609. CrossRef - Discuss the role of microorganisms in the aetiology and pathogenesis of periapical disease
Vincent Aw
Australian Endodontic Journal.2016; 42(2): 53. CrossRef - Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair (LSTR): A Review
Anila B, Murali H, Cheranjeevi J, Kapil RS
Journal of Scientific Dentistry.2014; 4(2): 49. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 7,370 View
- 92 Download
- 92 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


