Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of surrounding and underlying shades on the color adjustment potential of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer
- Mariana Silva Barros, Paula Fernanda Damasceno Silva, Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e7. Published online December 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e7
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
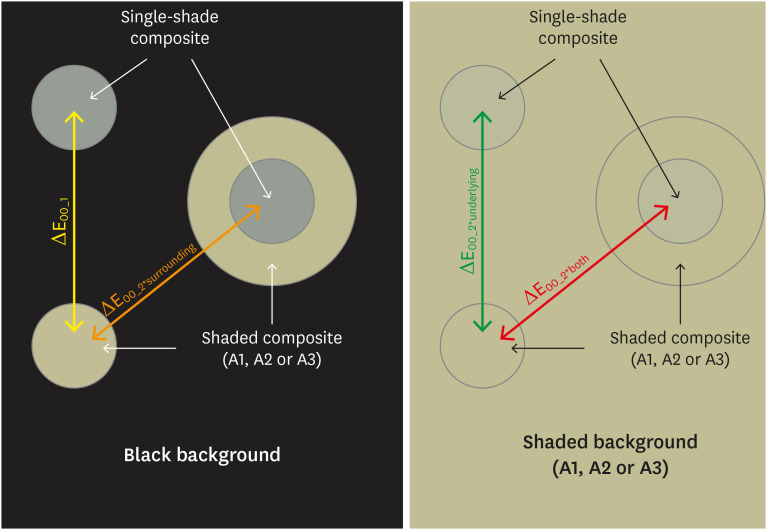
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the surrounding and underlying shades’ effect on the color adjustment potential (CAP) of a single-shade composite used in a thin layer.
Materials and Methods Cylinder specimens (1.0 mm thick) were built with the Vittra APS Unique composite, surrounded (dual specimens) or not (simple specimens) by a control composite (shade A1, A2, or A3). Simple specimens were also built only with the control composites. Each specimen’s color was measured against white and black backgrounds or the simple control specimens with a spectrophotometer (CIELAB system). The whiteness index for dentistry (WID) and translucency parameters (TP00) were calculated for simple specimens. Differences (ΔE00) in color between the simple/dual specimens and the controls were calculated. The CAP was calculated based on the ratios between data from simple and dual specimens.
Results The Vittra APS Unique composite showed higher WID and TP00 values than the controls. The highest values of ΔE00 were observed among simple specimens. The color measurements of Vittra APS Unique (simple or dual) against the control specimens presented the lowest color differences. Only surrounding the single-shade composite with a shaded composite barely impacted the ΔE00. The highest CAP values were obtained using a shaded composite under simple or dual specimens.
Conclusions The CAP of Vittra APS Unique was strongly affected by the underlying shade, while surrounding this composite with a shaded one barely affected its color adjustment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
Luciana Vasconcelos Ramos, Dayana Fernandes Rocha Aparicio, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva, Maíra do Prado, Andréa Vaz Braga Pintor, Marcela Baraúna Magno
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1567. CrossRef - Evaluation of color matching of three single-shade composites employing simulated 3D printed cavities with different thicknesses using CIELAB and CIEDE2000 color difference formulae
Engin Kariper, Aylin Cilingir
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of kombucha, coffee, and turmeric beverages on the color stability of a single-shade versus a multi-shade resin-based composite
Hanin E. Yeslam, Abdulaziz F. Bakhsh
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19759. CrossRef - Comparative Study of Esthetic Outcome of Pedo Shades of Composite Resin—A Randomized Controlled Trial: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
Priyanka Raj, Shikha Choubey, Divya Doneria, Diksha Bhat, Shivani Mathur, Shailja Sinha
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(S1): S22. CrossRef - Influence of cavity wall thickness on the color adjustment potential of single-shade resin composites
Fabrício Luscino Alves de Castro, Letícia Brandão Durand
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2024; 155(7): 605. CrossRef - Assessing color mismatch in single-shade composite resins for enamel replacement
Rafaella Mariana Fontes de Bragança, Diana Leyva Del Rio, Luiz Alves Oliveira-Neto, William Michael Johnston
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 132(3): 613.e1. CrossRef - Color discrepancy of single-shade composites at different distances from the interface measured using cell phone images
Márcia Luciana Carregosa Santana, Gabriella de Jesus Santos Livi, André Luis Faria-e-Silva
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Is It Possible for Single-shade Composites to Mimic the Color, Lightness, Chroma, and Hue of Other Single-shade Composites? An In Vitro Study
M Buldur, G Ayan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 691. CrossRef - Color evaluation of a one-shade used for restoration of non-carious cervical lesions: an equivalence randomized clinical trial
Michael Willian Favoreto, Amanda de Oliveira de Miranda, Thalita P. Matos, Andrea dos Santos de Castro, Mylena de Abreu Cardoso, Julia Beatriz, Jenny Collantes-Acuña, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Thickness on the Translucency Parameter and Whiteness Index of Single-Shade Resin Composites
Ö Yağcı, M Fidan
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(2): 189. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Ishihara Test With Various Displays
Thomas Klinke, Wolfgang Hannak, Klaus Böning, Holger Jakstat
International Dental Journal.2024; 74(4): 892. CrossRef - Color match evaluation using instrumental method for three single-shade resin composites before and after in-office bleaching
Aylin Cilingir, Engin Kariper
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of interface distance and underlying substrate on the color adjustment potential of single‐shade composites
Gabriella Jesus Santos de Livi, Tauan Rosa Santana, Rafaella Mariana Fontes Bragança, Rosa Maria Viana de Bragança Garcez, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1279. CrossRef
- At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
- 4,469 View
- 95 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Errors in light-emitting diodes positioning when curing bulk fill and incremental composites: impact on properties after aging
- Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora M. Garcia, Haifa Maktabi, Maria Salem Ibrahim, Qoot Alkhubaizi, Howard Strassler, Fabrício M. Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e51. Published online September 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e51

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the effect of improper positioning single-peak and multi-peak lights on color change, microhardness of bottom and top, and surface topography of bulk fill and incremental composites after artificial aging for 1 year.
Materials and Methods Bulk fill and incremental composites were cured using multi-peak and single-peak light-emitting diode (LED) following 4 clinical conditions: (1) optimal condition (no angulation or tip displacement), (2) tip-displacement (2 mm), (3) slight tip angulation (α = 20°) and (4) moderate tip angulation (α = 35°). After 1-year of water aging, the specimens were analyzed for color changes (ΔE), Vickers hardness, surface topography (Ra, Rt, and Rv), and scanning electron microscopy.
Results For samples cured by single-peak LED, the improper positioning significantly increases the color change compared to the optimal position regardless of the type of composite (
p < 0.001). For multi-peak LED, the type of resin composite and the curing condition displayed a significant effect on ΔE (p < 0.001). For both LEDs, the Vickers hardness and bottom/top ratio of Vickers hardness were affected by the type of composite and the curing condition (p < 0.01).Conclusions The bulk fill composite presented greater resistance to wear, higher color stability, and better microhardness than the incremental composite when subjected to improper curing. The multi-peak LED improves curing under improper conditions compared to single-peak LED. Prevention of errors when curing composites requires the attention of all personnel involved in the patient's care once the clinical relevance of the appropriate polymerization reflects on reliable long-term outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
Elizbeth Christy Jose, Sakshi Jha, Prema Shantagouda Biradar, J Arun, TN Nandini, Thushara Mohanan
International Journal of Oral Health Sciences.2025; 15(1): 41. CrossRef - The demineralization resistance and mechanical assessments of different bioactive restorative materials for primary and permanent teeth: an in vitro study
Maria Salem Ibrahim, Fahad Rakad Aldhafeeri, Abdullah Sami Banaemah, Mana S. Alhaider, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef
- A clinical survey of the output intensity of 50 light-curing units in dental clinics across Davangere and Mangalore region using a spectrometer system
- 1,569 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


