Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The influence of bioactive glass (BGS-7) on enamel remineralization: an in vitro study
- Chaeyoung Lee, Eunseon Jeong, Kun-Hwa Sung, Su-Jung Park, Yoorina Choi
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e33. Published online October 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
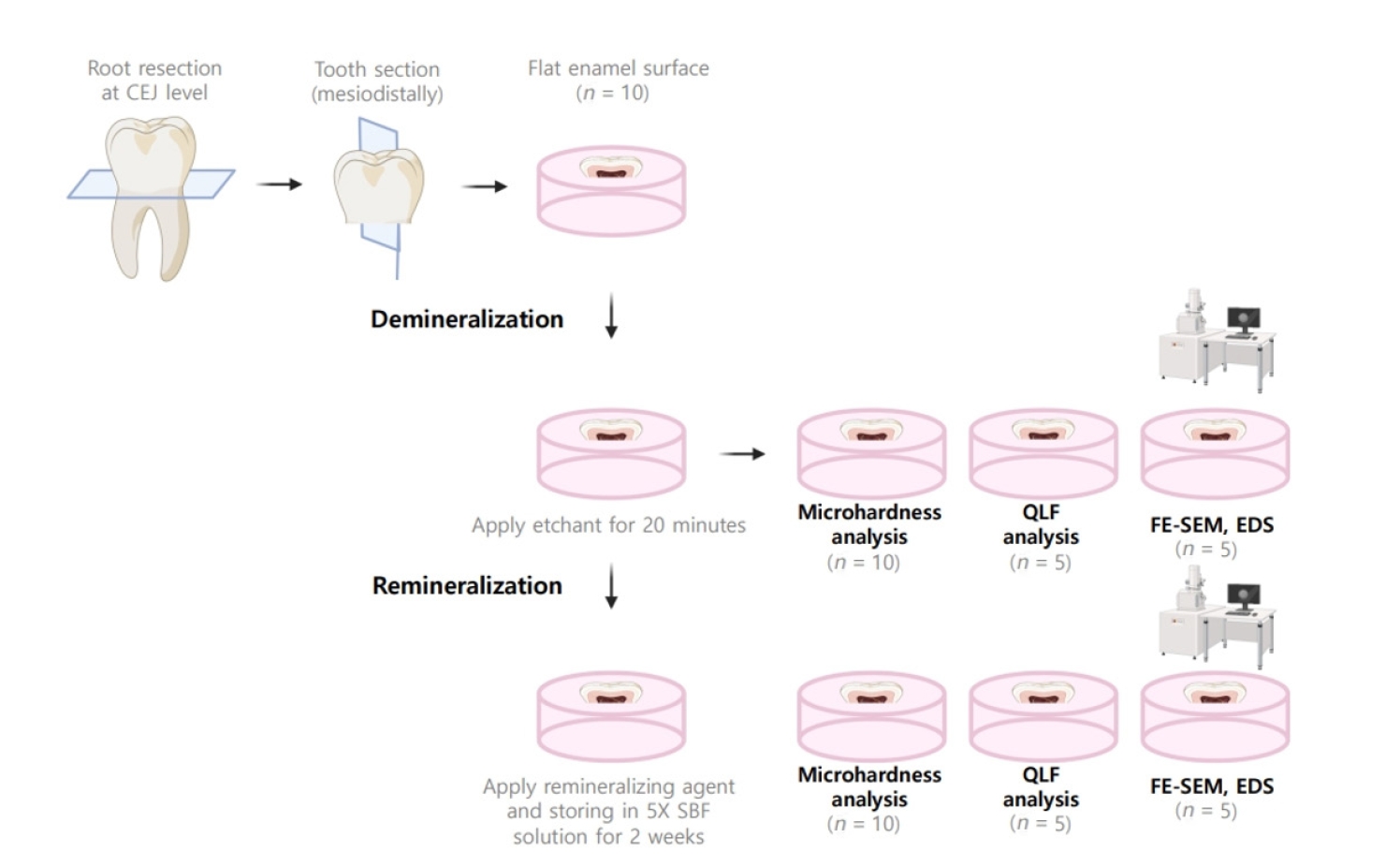
The aim of this study was to compare the remineralizing capacity of bioactive glass (BGS-7, CGBIO) with other agents.
Methods
Twenty caries-free third molars were sectioned and demineralized. Specimens were divided into four groups: (1) control, (2) Clinpro XT varnish (Solventum), (3) 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel, and (4) a new type of CaO-SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 system of bioactive glass ceramics (BGS-7). Agents were applied and stored in simulated body fluid at 37℃ for 2 weeks. Microhardness was measured using the Vickers hardness testing method. Five specimens per group were analyzed using quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF) to assess mineral loss. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) were used to examine the surface morphology and elemental composition. Data were analyzed using paired t-test and one-way analysis of variance (p < 0.05).
Results
BGS-7 showed the highest microhardness values and the greatest recovery in QLF analysis (p < 0.05). FE-SEM revealed granular precipitates on demineralized enamel in the BGS-7 group. EDS confirmed the presence of newly formed silicon and fluoride layers.
Conclusions
BGS-7 demonstrated superior remineralization capacity compared to other agents, suggesting its potential as an effective remineralizing material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
Helal F. Hetta, Ibraheem M. Mwafey, Noura H. Abd Ellah, Fawaz E. Alanazi, Yasmin N. Ramadan
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bacterial ghosts (BGs): A promising approach as candidate vaccine
- 1,627 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Evaluation of at-home bleaching protocol with application on different surfaces: bleaching efficacy and hydrogen peroxide permeability
- Heloisa Forville, Michael Willian Favoreto, Michel Wendlinger, Roberta Micheten Dias, Christiane Philippini Ferreira Borges, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e33. Published online October 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
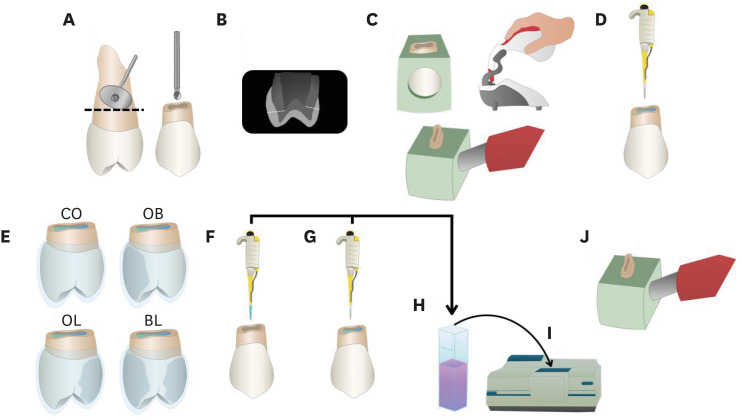
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the bleaching efficacy and hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber by the at-home bleaching gel in protocols applied on different dental surfaces.
Materials and Methods Forty premolars were randomly into 4 groups: control group no bleaching, only application on the buccal surface (OB), only application on the lingual surface (OL) and application in buccal and lingual surfaces, simultaneously (BL). At-home bleaching gel (White Class 7.5%) was used for the procedure. The bleaching efficacy was evaluated with a digital spectrophotometer (color change in CIELAB [Δ
E ab] and CIEDE 2000 [ΔE 00] systems and Whitening Index for Dentistry [ΔWID]). The hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber (µg/mL) was assessed using UV-Vis spectrophotometry and data were analyzed for a 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).Results All groups submitted to bleaching procedure showed bleaching efficacy when measured with Δ
E ab and ΔE 00 (p > 0.05). Therefore, when analyzed by ΔWID, a higher bleaching efficacy were observed for the application on the groups OB and BL (p = 0.00003). Similar hydrogen peroxide permeability was found in the pulp chambers of the teeth undergoing different protocols (p > 0.05).Conclusions The application of bleaching gel exclusively on the OB is sufficient to achieve bleaching efficacy, when compared to BL. Although the OL protocol demonstrated lower bleaching efficacy based on the ΔWID values, it may still be of interest and relevant in certain clinical scenarios based on individual needs, requiring clinical trials to better understand its specificities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of whitening pens on hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber, color change and surface morphology
Laryssa Mylenna Madruga Barbosa, Gabrielle Gomes Centenaro, Deisy Cristina Ferreira Cordeiro, Maria Alice de Matos Rodrigues, Letícia Condolo, Michael Willian Favoreto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 154: 105595. CrossRef - Evaluation of bleaching efficiency of carbamide peroxide applied on different dental surfaces: An in vitro study
R. Gokulnath, R. S. Mohan Kumar, A. Jayasenthil, R. Anjana, G. Sree Vidya
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 366. CrossRef - Characterization and effects on enamel of low-concentration bleaching gels containing hyaluronic acid, NF_TiO2 nanoparticles and irradiated with violet LED light
Marcos Roberto Lima Benati, Matheus Kury, Priscila Borges Gobbo de Melo, Iago César Ribeiro Teles Matos, Roberta Tarkany Basting, Rosanna Tarkany Basting, Fernando Luis Esteban Florez, Vanessa Cavalli
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of bleaching on white spot lesions: hydrogen peroxide permeability and color alteration
Laryssa Mylenna Madruga Barbosa, Bruno Baracco, Taynara S. Carneiro, Michael Willian Favoreto, Michel Wendlinger, Daniel Jiménez-Díez, Laura Ceballos, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of a buccal and lingual at‐home bleaching protocol—A randomized, split‐mouth, single‐blind controlled trial
Heloisa Forville, Laís Giacomini Bernardi, Michael Willian Favoreto, Felipe Coppla, Taynara de Souza Carneiro, Fabiana Madalozzo Coppla, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(9): 1301. CrossRef - REANATOMIZAÇÃO DE DENTE CONOIDE ASSOCIADA A ESTÉTICA VERMELHA: RELATO DE CASO
Ana Karolayne Sousa de Morais, Daniele Fernanda Sousa Barros, Daniel Messias Limeira, Rhana Leticia de Oliveira Faria, Roberta Furtado Carvalho, Sandna Nolêto de Araújo, Laura Barbosa Santos Di Milhomem
Revista Contemporânea.2024; 4(10): e6299. CrossRef - Effect of the reduction in the exposure time to at-home bleaching gel on color change and tooth sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Priscila Borges Gobbo de Melo, Letícia Vasconcelos Silva Souza, Lucianne Cople Maia, Guido Artemio Marañón-Vásquez, Matheus Kury, Vanessa Cavalli
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of whitening pens on hydrogen peroxide permeability in the pulp chamber, color change and surface morphology
- 4,139 View
- 78 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Evaluation of the effects of whitening mouth rinses combined with conventional tooth bleaching treatments
- Jaqueline Costa Favaro, Omar Geha, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Murilo Baena Lopes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e6. Published online January 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
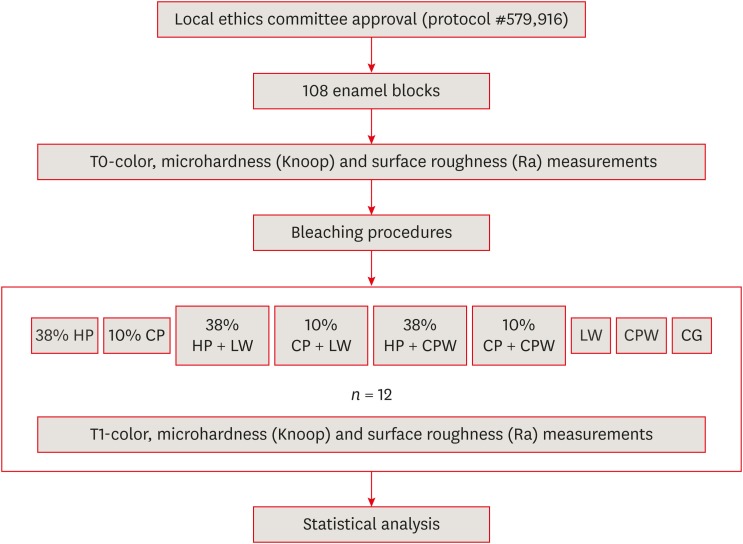
ePub Objectives The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of whitening mouth rinses alone and in combination with conventional whitening treatments on color, microhardness, and surface roughness changes in enamel specimens.
Materials and Methods A total of 108 enamel specimens were collected from human third molars and divided into 9 groups (
n = 12): 38% hydrogen peroxide (HP), 10% carbamide peroxide (CP), 38% HP + Listerine Whitening (LW), 10% CP + LW, 38% HP + Colgate Plax Whitening (CPW), 10% CP + CPW, LW, CPW, and the control group (CG). The initial color of the specimens was measured, followed by microhardness and roughness tests. Next, the samples were bleached, and their color, microhardness, and roughness were assessed. Data were analyzed through 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA; microhardness and roughness) and 1-way ANOVA (color change), followed by the Tukeypost hoc test. The Dunnett test was used to compare the roughness and microhardness data of the CG to those of the treated groups.Results Statistically significant color change was observed in all groups compared to the CG. All groups, except the LW group, showed statistically significant decreases in microhardness. Roughness showed a statistically significant increase after the treatments, except for the 38% HP group.
Conclusions Whitening mouth rinses led to a whitening effect when they were used after conventional treatments; however, this process caused major changes on the surface of the enamel specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
Mariana Ferreira da Silva, Giovana Contin Germinari, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Tatiane Cristina Dotta, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Júnior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2026; 25: e260366. CrossRef - Which Whitening Mouthwash With Different Ingredients Is More Effective on Color and Bond Strength of Enamel?
Elif Varli Tekingur, Fatih Bedir, Muhammet Karadas, Rahime Zeynep Erdem
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 960. CrossRef - Do Different Tooth Bleaching–Remineralizing Regimens Affect the Bleaching Effectiveness and Enamel Microhardness In Vitro?
Hamideh Sadat Mohammadipour, Parnian Shokrollahi, Sima Gholami, Hosein Bagheri, Fatemeh Namdar, Salehe Sekandari, Cesar Rogério Pucci
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrogen peroxide versus charcoal-based whitening mouthwashes on color, surface roughness, and color stability of enamel
Mayada S. Sultan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of online marketplace-sourced over-the-counter tooth whitening products on the colour, microhardness, and surface topography of enamel: an in vitro study
Radhika Agarwal, Nikki Vasani, Urmila Sachin Mense, Niharika Prasad, Aditya Shetty, Srikant Natarajan, Arindam Dutta, Manuel S. Thomas
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Whitening Mouthwashes on Color Change and Enamel Mineralization: An In Vitro Study
Rosa Josefina Roncal Espinoza, José Alberto Castañeda Vía, Alexandra Mena-Serrano, Lidia Yileng Tay
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(9): 739. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Over-the-Counter Whitening Products on Dental Tissues
Maiara Rodrigues de Freitas, Marynara Mathias de Carvalho, Priscila Christiane Suzy Liporoni, Ana Clara Borges Fort, Rodrigo de Morais e Moura, Rayssa Ferreira Zanatta
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Renklendirilmiş kompozit rezinin renk değişimine ve yüzey pürüzlülüğüne beyazlatıcı ağız gargarasının etkisi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Tuğba TUNCDEMIR
Selcuk Dental Journal.2020; 7(3): 435. CrossRef
- Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
- 1,660 View
- 14 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
- Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):246-254. Published online August 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.246
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this investigation was to give insights into the impact of carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks on the likely capacity of enamel surface dissolution and the influence of human saliva exposure as a biological protective factor.
Materials and Methods The pH, titratable acidity (TA) to pH 7.0, and buffer capacity (β) of common beverages ingested by patients under physical activity were analyzed. Then, we randomly distributed 50 specimens of human enamel into 5 groups. Processed and natural coconut water served as controls for testing three carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks. In all specimens, we measured surface microhardness (Knoop hardness numbers) and enamel loss (profilometry, µm) for baseline and after simulated intake cycling exposure model. We also prepared areas of specimens to be exposed to human saliva overnight prior to the simulated intake cycling exposure. The cycles were performed by alternated immersions in beverages and artificial saliva. ANOVA two-way and Tukey HDS tests were used.
Results The range of pH, TA, and β were 2.85 - 4.81, 8.33 - 46.66 mM/L and 3.48 - 10.25 mM/L × pH, respectively. The highest capacity of enamel surface dissolution was found for commercially available sports drinks for all variables. Single time human saliva exposure failed to significantly promote protective effect for the acidic attack of beverages.
Conclusions In this study, carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks usually consumed during endurance training may have a greater capacity of dissolution of enamel surface depending on their physicochemical proprieties associated with pH and titratable acidity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of developmentally hypomineralised enamel after surface pretreatment with Papacarie Duo gel and different etching modes: an in vitro SEM and AFM study
Y.-L. Lee, K. C. Li, C. K. Y. Yiu, D. H. Boyd, M. Ekambaram
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2022; 23(1): 117. CrossRef - Is the consumption of beverages and food associated to dental erosion? A cross-sectional study in Portuguese athletes
M.-R.G. Silva, M.-A. Chetti, H. Neves, M.-C. Manso
Science & Sports.2021; 36(6): 477.e1. CrossRef - Assessment of surface roughness changes on orthodontic acrylic resin by all-in-one spray disinfectant solutions
Kuei-ling Hsu, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Isadora Martini Garcia, Fabricio Mezzomo Collares, Louis DePaola, Mary Anne Melo
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2020; 14(2): 77. CrossRef - Nitrate-rich beetroot juice offsets salivary acidity following carbohydrate ingestion before and after endurance exercise in healthy male runners
Mia C. Burleigh, Nicholas Sculthorpe, Fiona L. Henriquez, Chris Easton, Yi-Hung Liao
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(12): e0243755. CrossRef - Dental erosion’ prevalence and its relation to isotonic drinks in athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pedro Henrique Pereira de Queiroz Gonçalves, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azeredo, Letícia Maira Wambier, Lívia Azeredo A. Antunes, Leonardo Santos Antunes
Sport Sciences for Health.2020; 16(2): 207. CrossRef - Atomic force microscopy analysis of enamel nanotopography after interproximal reduction
Shadi Mohebi, Nazila Ameli
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2017; 152(3): 295. CrossRef
- Evaluation of developmentally hypomineralised enamel after surface pretreatment with Papacarie Duo gel and different etching modes: an in vitro SEM and AFM study
- 2,128 View
- 17 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


