Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Shaping ability and apical debris extrusion after root canal preparation with rotary or reciprocating instruments: a micro-CT study
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Sara Gomes de Moura, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Waleska Florentino Misael, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Luciana Moura Sassone
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e16. Published online February 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e16

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems and the apical extrusion of debris after root canal instrumentation. The ProTaper Universal system was used as a reference for comparison.
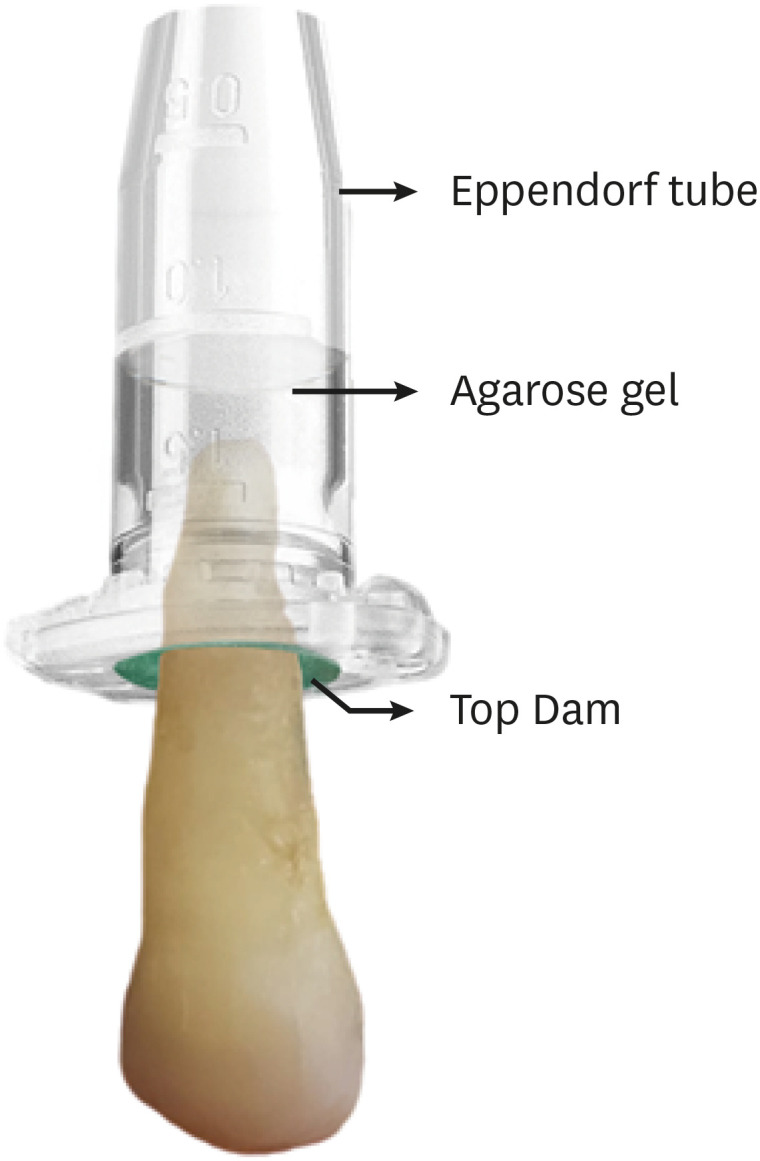
Materials and Methods Thirty-three mandibular premolars with a single canal were scanned using micro-computed tomography and were matched into 3 groups (
n = 11) according to the instrumentation system: TruShape, Reciproc Blue and ProTaper Universal. The teeth were accessed and mounted in an apparatus with agarose gel, which simulated apical resistance provided by the periapical tissue and enabled the collection of apically extruded debris. During root canal preparation, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite was used as an irrigant. The samples were scanned again after instrumentation. The percentage of unprepared area, removed dentin, and volume of apically extruded debris were analyzed. The data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test for multiple comparisons at a 5% significance level.Results No significant differences in the percentage of unprepared area were observed among the systems (
p > 0.05). ProTaper Universal presented a higher percentage of dentin removal than the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems (p < 0.05). The systems produced similar volumes of apically extruded debris (p > 0.05).Conclusions All systems caused apically extruded debris, without any significant differences among them. TruShape, Reciproc Blue, and ProTaper Universal presented similar percentages of unprepared area after root canal instrumentation; however, ProTaper Universal was associated with higher dentin removal than the other systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endomotor integration, file kinematics impact on apical debris extrusion in severely curved canals
Anshika Saxena, Vineeta Nikhil
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 87. CrossRef - Comparison of post-operative pain prevalence after single visit endodontic treatment with two NiTi rotary files - a randomized clinical trial
M. E. Khallaf, Yousra Aly, Amira Ibrahim Mohamed
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Silver-Ion-Coated Rotary Nickel Titanium Files - An In Vitro Study
Jhanvi H. Sadaria, Kondas V. Venkatesh, Dhanasekaran Sihivahanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(3): 344. CrossRef - A quantitative comparison of apically extruded debris during root canal preparation using NiTi full-sequence rotary and single-file rotary systems: An in vitro study
Pallavi Goel, R. Vikram, R. Anithakumari, M. S. Adarsha, M. E. Sudhanva
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 235. CrossRef - Extrusion of Sodium Hypochlorite in Oval-Shaped Canals: A Comparative Study of the Potential of Four Final Agitation Approaches Employing Agarose-Embedded Mandibular First Premolars
Aalisha Parkar, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Alexander Maniangat Luke
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(10): 2748. CrossRef - Shaping Efficiency of Rotary and Reciprocating Kinematics of Engine-driven Nickel-Titanium Instruments in Moderate and Severely curved Root Canals Using Microcomputed Tomography: A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Claudiu Călin, Ana-Maria Focșăneanu, Friedrich Paulsen, Andreea C. Didilescu, Tiberiu Niță
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 907. CrossRef - Intracanal removal and apical extrusion of filling material after retreatment using rotary or reciprocating instruments: A new approach using human cadavers
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Victor O. Cortes‐Cid, Marilia F. V. Marceliano‐Alves, Andrea F. Campello, Luan F. Bastos, Ricardo T. Lopes, José F. Siqueira, Flávio R. F. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(1): 100. CrossRef - Assessment of debris extrusion on using automated irrigation device with conventional needle irrigation – An ex vivo study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Raja Kumar, Sindhu Ramesh
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 263. CrossRef - Postoperative pain perception and associated risk factors in children after continuous rotation versus reciprocating kinematics: A randomised prospective clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Dania Ibrahem Sermani, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 345. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of new reciprocating or rotary instruments with two cross‐sectional designs: An ex vivo study
Isabela G. Guedes, Renata C. V. Rodrigues, Marília F. Marceliano‐Alves, Flávio R. F. Alves, Isabela N. Rôças, José F. Siqueira
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Endomotor integration, file kinematics impact on apical debris extrusion in severely curved canals
- 2,753 View
- 51 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Efficacy of reciprocating and rotary retreatment nickel-titanium file systems for removing filling materials with a complementary cleaning method in oval canals
- Said Dhaimy, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Lamyae Bedida, Imane Benkiran
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e13. Published online February 3, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate and compare the efficacy of the S1 reciprocating system and the D-Race retreatment rotary system for filling material removal and the apical extrusion of debris.
Materials and Methods Sixty-four freshly extracted maxillary canines were shaped with size 10 and size 15 K-files, instrumented using ProTaper Gold under irrigation with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), obturated according to the principle of thermo-mechanical condensation with gutta-percha and zinc oxide eugenol sealer, and allowed to set for 3 weeks at 37°C. Subsequently, the teeth were divided into a control group (
n = 4), the D-Race rotary instrument group (n = 30), and the S1 reciprocating instrument group (n = 30). After classical retreatment, the canals were subjected to a complementary approach with the XP-Endo Shaper. Desocclusol was used as a solvent, and irrigation with 2.5% NaOCl was performed. Each group was divided into subgroups according to the timing of radiographic readings. The images were imported into a software program to measure the remaining filling material, the apical extrusion, and the root canal space. The data were statistically analyzed using the Z-test and JASP graphics software.Results No significant differences were found between the D-Race and S1 groups for primary retreatment; however, using a complementary cleaning method increased the removal of remnant filling (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Classical removal of canal filling material may not be sufficient for root canal disinfection, although a complementary finishing approach improved the results. Nevertheless, all systems left some debris and caused apical extrusion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of different supplementary protocols for remaining filling material removal in endodontic reintervention: an integrative review
Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Bruna Venzke Fischer, Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Anna Victoria Costa Serique, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Odontology.2024; 112(1): 51. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Economic analysis of the different endodontic instrumentation techniques used in the Unified Health System
Laura Paredes Merchan, Livia Fernandes Probst, Ana Clara Correa Duarte Simões, Augusto Cesar Santos Raimundo, Yuri Wanderley Cavalcanti, Denise de Fátima Barros Cavalcante, João Victor Frazão Câmara, Antonio Carlos Pereira
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabrication of a Potential Electrodeposited Nanocomposite for Dental Applications
Chun-Wei Chang, Chen-Han Tsou, Bai-Hung Huang, Kuo-Sheng Hung, Yung-Chieh Cho, Takashi Saito, Chi-Hsun Tsai, Chia-Chien Hsieh, Chung-Ming Liu, Wen-Chien Lan
Inorganics.2022; 10(10): 165. CrossRef - Influence of Filling Material Remnants on the Diffusion of Hydroxyl Ions in Endodontically Retreated Teeth: An Ex Vivo Study
Vania Portela Ditzel Westphalen, Marilisa Carneiro Leao Gabardo, Natanael Henrique Ribeiro Mattos, Camila Paiva Perin, Liliane Roskamp, Cristiano Miranda de Araújo, Luiz Fernando Fariniuk, Flares Baratto–Filho
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(8): 768. CrossRef - Efficacy of Removing Thermafil and GuttaCore from Straight Root Canal Systems Using a Novel Non-Surgical Root Canal Re-Treatment System: A Micro-Computed Tomography Analysis
Vicente Faus-Llácer, Rubén Linero Pérez, Ignacio Faus-Matoses, Celia Ruiz-Sánchez, Álvaro Zubizarreta-Macho, Salvatore Sauro, Vicente Faus-Matoses
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(6): 1266. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of different supplementary protocols for remaining filling material removal in endodontic reintervention: an integrative review
- 2,081 View
- 37 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Impact of root canal curvature and instrument type on the amount of extruded debris during retreatment
- Burcu Serefoglu, Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, İlknur Kaşıkçı Bilgi, Mehmet Kemal Çalışkan
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e5. Published online December 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of the current study was to assess whether the amount of extruded debris differs for straight and severely curved root canals during retreatment using H-files, R-Endo, Reciproc and ProTaper Universal Retreatment (PTU-R) files. Additionally, the area of residual filling material was evaluated.
Materials and Methods Severely curved (
n = 104) and straight (n = 104) root canals of maxillary molar teeth were prepared with WaveOne Primary file and obturated with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer. Root canal filling materials were removed with one of the preparation techniques: group 1: H-file; group 2: R-Endo; group 3: Reciproc; group 4: PTU-R (n = 26). The amount of extruded material and the area of the residual filling material was measured. The data were analyzed with 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and 1-way ANOVA at the 0.05 significance level.Results Except for Reciproc group (
p > 0.05), PTU-R, R-Endo, and H-file systems extruded significantly more debris in severely curved canals (p < 0.05). Each file system caused more residual filling material in severely curved canals than in straight ones (p < 0.05).Conclusions All instruments used in this study caused apical debris extrusion. Root canal curvature had an effect on extruded debris, except for Reciproc system. Clinicians should be aware that the difficult morphology of the severely curved root canals is a factor increasing the amount of extruded debris during the retreatment procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Effectiveness of MicroMega Remover, ProTaper Universal Retreatment, Reciproc, and Hedstrom Files in the Retreatment of Curved Root Canals Obturated with Different Techniques: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
Pınar Hava Dursun, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Arda Buyuksungur, Berkan Celikten
Medicina.2026; 62(1): 188. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Root Canal Curvature Measurement Methods for Permanent Mandibular Molars Distal Root: An Observational Study
Tanu Singh, Saurav Bathla, Anuraag Gurtu, Shubhi Gupta, Sana Saifi, Madhusudan Astekar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(10): 945. CrossRef - Do Continuous Rotating Endodontic Instruments Extrude Fewer Apical Debris Than Reciprocating Instruments in Non-Surgical Endodontic Retreatments? A Systematic Review
Francesco Puleio, Francesco Giordano, Ugo Bellezza, David Rizzo, Valentina Coppini, Roberto Lo Giudice
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(4): 1621. CrossRef - Intracanal removal and apical extrusion of filling material after retreatment using rotary or reciprocating instruments: A new approach using human cadavers
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Victor O. Cortes‐Cid, Marilia F. V. Marceliano‐Alves, Andrea F. Campello, Luan F. Bastos, Ricardo T. Lopes, José F. Siqueira, Flávio R. F. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(1): 100. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of methods for measuring root canal curvature based on periapical radiography: A laboratory study
Rafael Chies Hartmann, Eduardo Silva Ferraz, Theodoro Weissheimer, Jose Antônio Poli de Figueiredo, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele, Maximiliano Schünke Gomes
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(12): 1848. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris during root canal filling material removal in teeth with external apical root resorption: a comparison of different obturation techniques
Büşra Melike Çağlar, İsmail Uzun
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - A quantitative comparison of apically extruded debris during root canal preparation using NiTi full-sequence rotary and single-file rotary systems: An in vitro study
Pallavi Goel, R. Vikram, R. Anithakumari, M. S. Adarsha, M. E. Sudhanva
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 235. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of filling material removal and apical debris extrusion after retreatment using Reciproc blue, Hyflex EDM and ProTaper retreatment files
Passent Abdelnaby, Mohamed Ibrahim, Rania ElBackly
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Shaping Ability and Cleaning Efficiency of Two Different Single-File Systems, Reciprocating Wave One Versus Continuous Rotation F360, Evaluated by Scanning Electron Microscope: An In Vitro Study
Arunkumar Samudrala, Chandrakanth Majeti, Kommineni Harika Chowdary, Lakshmi Bhavani Potru, Anusha Yaragani, Yata Prashanth Kumar, Gagandeep K Sidhu, Navneet S Kathuria
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT ROTARY INSTRUMENT SYSTEMS ON THE AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS
Recai ZAN, Bilge LENGER
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(2): 172. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Effectiveness of MicroMega Remover, ProTaper Universal Retreatment, Reciproc, and Hedstrom Files in the Retreatment of Curved Root Canals Obturated with Different Techniques: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
- 2,518 View
- 33 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

-
Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an
in vitro study - Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):316-323. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the amount of apically extruded bacteria during the glide-path preparation by using multi-file and single-file glide-path establishing nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary systems.
Materials and Methods Sixty mandibular first molar teeth were used to prepare the test apparatus. They were decoronated, blocked into glass vials, sterilized in ethylene oxide gas, infected with a pure culture of
Enterococcus faecalis, randomly assigned to 5 experimental groups, and then prepared using manual stainless-steel files (group KF) and glide-path establishing NiTi rotary files (group PF with PathFiles, group GF with G-Files, group PG with ProGlider, and group OG with One G). At the end of canal preparation, 0.01 mL NaCl solution was taken from the experimental vials. The suspension was plated on brain heart infusion agar and colonies of bacteria were counted, and the results were given as number of colony-forming units (CFU).Results The manual instrumentation technique tested in group KF extruded the highest number of bacteria compared to the other 4 groups (
p < 0.05). The 4 groups using rotary glide-path establishing instruments extruded similar amounts of bacteria.Conclusions All glide-path establishment instrument systems tested caused a measurable apical extrusion of bacteria. The manual glide-path preparation showed the highest number of bacteria extruded compared to the other NiTi glide-path establishing instruments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Warley O. Silva, Jeferson O. Marques, Ana Carolina S.P. Guerra, Flávio R.F. Alves
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 866. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Evaluation of apically extruded debris using protaper universal, protaper next, one curve, Xp shaper, and edge file: An in vitro study
Murtada Qadir Muhaibes, Shatha Abdulkareem Alwakeel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Multiple Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Severely Curved Mesial Roots of Mandibular Molars: An In Vitro Study
Niranjan Desai, Ashish S Bhadane, Nishant K Vyavahare, Dipali Y Shah, Akash S Kale, Simran K Chaudhari
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Impact of Different Glidepath Techniques on the Overall Performance of WaveOne Gold in an Artificial S-Shape Canal
Vlad Mircea Lup, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Carlo Gaeta, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 182. CrossRef - Influence of different irrigant activation methods on apical debris extrusion and bacterial elimination from infected root canals
KSadia Ada, Shibani Shetty, KB Jayalakshmi, PrasannaLatha Nadig, PG Manje Gowda, ArulK Selvan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Apically Extruded Debris from Root Canals Prepared by R-Motion NiTi File System
Farah B. Al-Saffar, Hikmet A. Al-Gharrawi, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of glide path files with different metallurgy on intracanal bacterial extrusion by HyFlex electrical discharge machining file
Priyanka Soni, Pragya Kumar, Sonali Taneja, Anshi Jain
Endodontology.2022; 34(3): 168. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris using Three Rotary and One Reciprocating Instrumentation Ni-Ti Systems
Maha Adnan Habeeb
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2022; 14(2): 93. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of a glide path creation necessity at the initial stages of endodontic treatment
Z. S. Khabadze, Yu. A. Generalova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of glide path kinematics during endodontic treatment on the occurrence and intensity of intraoperative and postoperative pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials
Thaís Christina Cunha, Felipe de Souza Matos, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Ítalo de Macedo Bernardino, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Apically extruded debris produced during glide path preparation using R‐Pilot, WaveOne Gold Glider and ProGlider in curved root canals
Cangül Keskin, Özlem Sivas Yilmaz, Uğur Inan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(3): 439. CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Glide Path Preparation Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Joo-Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(2): 199. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Postoperative pain after glide path preparation using manual, reciprocating and continuous rotary instruments: a randomized clinical trial
C. Keskin, Ö. Sivas Yilmaz, U. Inan, Ö. Özdemir
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(5): 579. CrossRef - Intraoperative Pain During Glide Path Creation with the Use of a Rotary or Reciprocating System
Pelin TUFENKCİ, Mehmet ADIGUZEL, Koray YILMAZ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(1): 66. CrossRef - Effects of Different Glide Path Files on Apical Debris Extrusion in Curved Root Canals
Betul Gunes, Kubra Yesildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(7): 1191. CrossRef
- Apical Extrusion of Bacteria during Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review of Laboratory Studies
- 1,669 View
- 13 Download
- 23 Crossref

- The effect of early coronal flaring about apical extrusion of debris
- Min-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Beom Min, Ho-Keel Hwang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(2):147-152. Published online March 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.2.147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to investigate the quantity of debris which was extruded apically after canal instrumentation using different types of enlarging instrument in endodontic resin models.
Five groups of 9 endodontic resin models were instrumented using each different technique: hand instrumentation without early coronal flaring, hand instrumentation after early coronal flaring, and three nickel-titanium engine-driven instrumentations (Hero 642, Protaper, K3). Debris extruded from apical foramen during instrumentation was collected on preweighed CBC bottle, desiccated and weighted using electronic balance. The results were analyzed using Kruskal-wallis test and Mann-Whitney
U rank sum test at a significance level of 0.05.The results were as follows:
All of instrumentation techniques produced apically extruded debris.
Group without early coronal flaring extruded significant more debris than groups with early coronal flaring.
There was no significant difference among early coronal flaring groups.
The early coronal flaring is very important to reduce the amount of debris extruded apically.
- 904 View
- 0 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


