Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
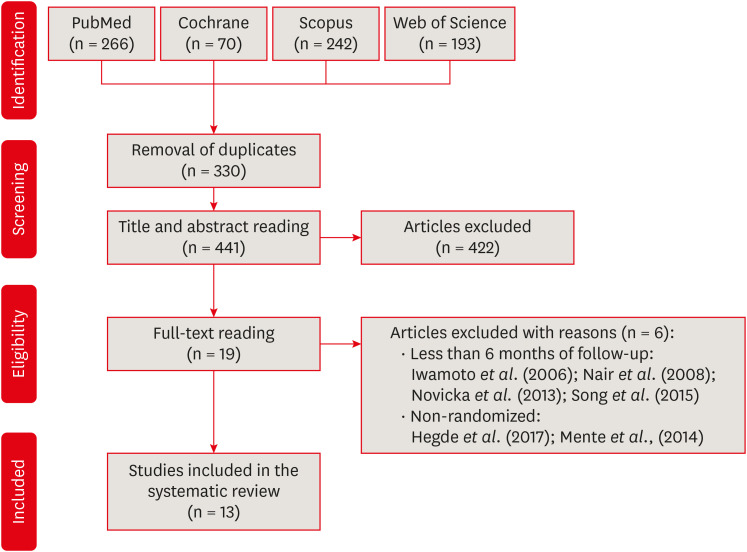
- Success rate of direct pulp capping on permanent teeth using bioactive materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Karem Paula Pinto, Gabriela Ribeiro da Silva, Cláudio Malizia Alves Ferreira, Luciana Moura Sassone, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e34. Published online September 6, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the success rate of direct pulp capping (DPC) on permanent teeth, comparing the use of MTA with calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate-based cements. A systematic search was carried out in 4 databases until July 2023. The selection was based on PICOS criteria and only randomized clinical trials were included. The risk of bias was assessed using RoB-2 tool, and meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The overall quality of evidence was determined using the GRADE tool. Thirteen studies were included. Meta-analyses indicated significantly higher success rate for DPC using MTA compared to calcium hydroxide, while no significant difference was observed between MTA and Biodentine, showing a success rate from 80% to 100% even after 3 years of follow-up. Five studies were classified as having high risk of bias and the GRADE assessment revealed low certainty of evidence. DPC is highly effective for permanent teeth when using MTA or Biodentine. There is a need for future well-designed randomized clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of DPC using newer bioceramic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
Njwan Fadhel SHEHAB
Dental Materials Journal.2026; 45(1): 92. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation-assisted pulp capping using nano-hydroxyapatite and mineral trioxide aggregate: Report of two cases
Priya Pal, Rhythm Bains, Promila Verma, Vivek Kumar Bains
Journal of Healthcare Research and Education.2026; 2: 2. CrossRef - Histological Tissue Response to Calcium Silicate-Based Cements Assessed in Human Tooth Culture Models: A Systematic Review
Alberto Cabrera-Fernández, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Aránzazu Díaz-Cuenca, Juan J. Segura-Egea, Jenifer Martín-González, João Peça, Diana B. Sequeira, João Miguel Marques dos Santos
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 78. CrossRef - Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics consensus statement on deep caries management
Deepak Kumar Sharma, R. S. Mohan Kumar, Shishir Singh, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Meenal Nithin Gulve, Dipali Y. Shah, Sathish Abraham, Shruthi Nagaraja, Raksha Bhat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 714. CrossRef
- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
- 19,177 View
- 569 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

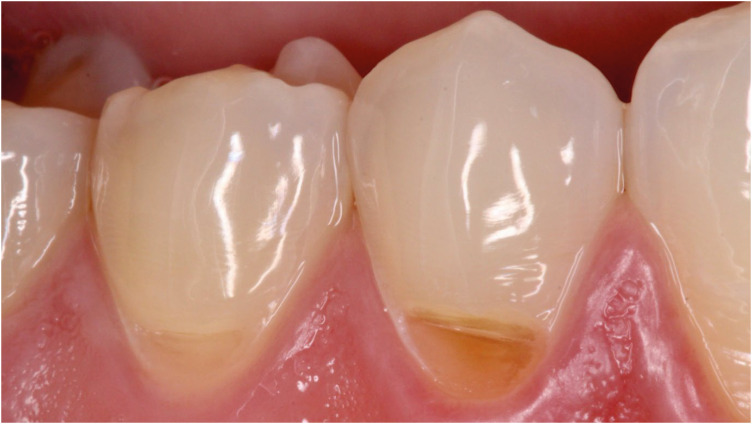
- A 48-month clinical performance of hybrid ceramic fragment restorations manufactured in CAD/CAM in non-carious cervical lesions: case report
- Michael Willian Favoreto, Gabriel David Cochinski, Eveline Claudia Martini, Thalita de Paris Matos, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e32. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub From the restorative perspective, various methods are available to prevent the progression of non-carious cervical lesions. Direct, semi-direct, and indirect composite resin techniques and indirect ceramic restorations are commonly recommended. In this context, semi-direct and indirect restoration approaches are increasingly favored, particularly as digital dentistry becomes more prevalent. To illustrate this, we present a case report demonstrating the efficacy of hybrid ceramic fragments fabricated using computer-aided design (CAD)/computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technology and cemented with resin cement in treating non-carious cervical lesions over a 48-month follow-up period. A 24-year-old male patient sought treatment for aesthetic concerns and dentin hypersensitivity in the cervical region of the lower premolar teeth. Clinical examination confirmed the presence of two non-carious cervical lesions in the buccal region of teeth #44 and #45. The treatment plan involved indirect restoration using CAD/CAM-fabricated hybrid ceramic fragments as a restorative material. After 48 months, the hybrid ceramic material exhibited excellent adaptation and durability provided by the CAD/CAM system. This case underscores the effectiveness of hybrid ceramic fragments in restoring non-carious cervical lesions, highlighting their long-term stability and clinical success.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Conservative Management of Distal Caries in a Maxillary Premolar with Class II Composite Restoration: A Case Report
Hashir Ather
Premier Journal of Case Reports.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Conservative Management of Distal Caries in a Maxillary Premolar with Class II Composite Restoration: A Case Report
- 3,731 View
- 165 Download
- 1 Crossref

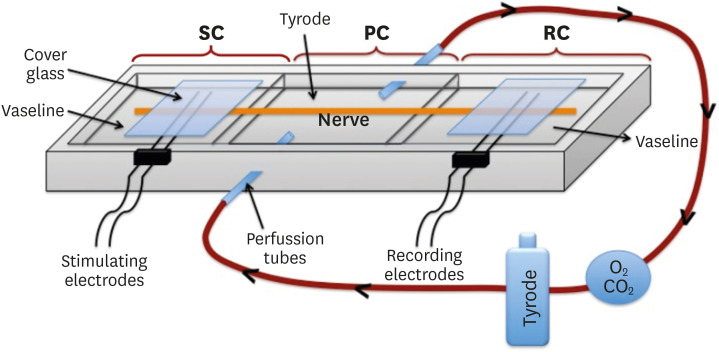
- Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
- Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e18. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated alterations in neuronal conductivity related to calcium silicate cements (CSCs) by investigating compound action potentials (cAPs) in rat sciatic nerves.
Materials and Methods Sciatic nerves were placed in a Tyrode bath and cAPs were recorded before, during, and after the application of test materials for 60-minute control, application, and recovery measurements, respectively. Freshly prepared ProRoot MTA, MTA Angelus, Biodentine, Endosequence RRM-Putty, BioAggregate, and RetroMTA were directly applied onto the nerves. Biopac LabPro version 3.7 was used to record and analyze cAPs. The data were statistically analyzed.
Results None of the CSCs totally blocked cAPs. RetroMTA, Biodentine, and MTA Angelus caused no significant alteration in cAPs (
p > 0.05). Significantly lower cAPs were observed in recovery measurements for BioAggregate than in the control condition (p < 0.05). ProRoot MTA significantly but transiently reduced cAPs in the application period compared to the control period (p < 0.05). Endosequence RRM-Putty significantly reduced cAPs.Conclusions Various CSCs may alter cAPs to some extent, but none of the CSCs irreversibly blocked them. The usage of fast-setting CSCs during apexification or regeneration of immature teeth seems safer than slow-setting CSCs due to their more favorable neuronal effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
Anna Błaszczyk-Pośpiech, Natalia Struzik, Maria Szymonowicz, Przemysław Sareło, Maria Wiśniewska-Wrona, Kamila Wiśniewska, Maciej Dobrzyński, Magdalena Wawrzyńska
Materials.2025; 18(18): 4259. CrossRef
- Endodontic Sealers and Innovations to Enhance Their Properties: A Current Review
- 1,599 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

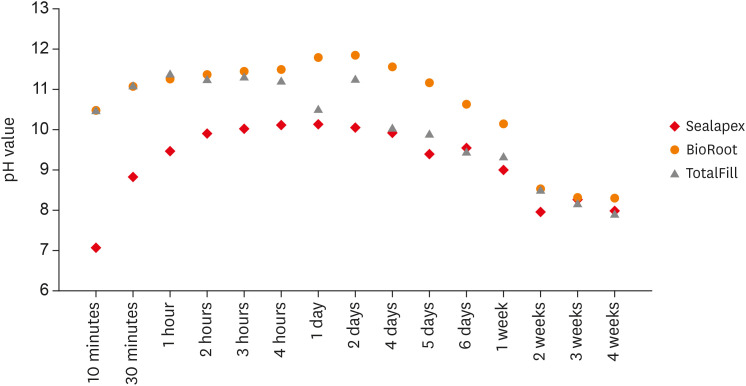
- Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
- Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e42. Published online August 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This study aimed to examine the physical properties (pH and flow) of 2 novel bioceramic sealers.
Materials and Methods The tested sealers were a calcium hydroxide sealer (Sealapex) and 2 bioceramic sealers (BioRoot RCS and TotalFill BC Sealer). Flow measurements were conducted according to ISO 6876/2012, with a press method of 0.05 mL of sealer. The pH of fresh samples was tested immediately after manipulation, while set samples were stored for 3 times the recommended setting time. The predetermined time intervals ranged from 3 minutes to 24 hours for fresh samples and from 10 minutes to 7 days and 4 weeks for the set samples. Analysis of variance was performed, with
p = 0.05 considered indicating significance.Results The mean flow values were 26.99 mm for BioRoot, 28.19 for Sealapex, and 30.8 mm for TotalFill BC Sealer, satisfying the ISO standard. In the set samples, BioRoot RCS had higher pH values at 24 hours to 1 week after immersion in distilled water. At 2 weeks, both bioceramic sealers had similar pH values, greater than that of Sealapex. In the fresh samples, the bioceramic sealers had significantly higher initial pH values than Sealapex (
p < 0.05). At 24 hours post-immersion, all sealers showed an alkaline pH, with the highest pH observed for TotalFill.Conclusions The TotalFill BC Sealer demonstrated the highest flow. The bioceramic sealers initially presented higher alkaline activity than the polymeric calcium hydroxide sealer. However, at 3 and 4 weeks post-immersion, all sealers had similar pH values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitro comparative evaluation of physicochemical and mechanical properties, cytocompatibility, and antimicrobial efficacy of various bioceramic root canal sealers
Fushi Wang, Jiaxing Li, Jingjing Wan, Siyuan Li, Shijia Tang, Li Wang, Liuyan Meng
Ceramics International.2026; 52(7): 9561. CrossRef - Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization and Assessment of Physical Properties of 3 Single Syringe Hydraulic Cement–based Sealers
Veksina Raman, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 381. CrossRef - The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles on Dentinal Tubule Penetration of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealer
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Amal Almohaimede, Nourah Alkhayatt, Shahad Alsulaiman, Salma Alohali
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11639. CrossRef - Influence of root canal moisture on the penetration of TotalFill bioceramic sealer into the dentinal tubules: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Archika M Singh, Tarek M Elsewify, Walid S El-Sayed, Husam H Nuawafleh, Ranya F Elemam, Bassem M Eid
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Unusual Canal Morphology in Mandibular Premolars With Two Distal and One Mesial Canal: A Case Series
Jinesh A, Sanjana Jayakumar Nair, Saurabh Gupta, Harsh Chansoria, Gaurav Rawat
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A scientometric, bibliometric, and thematic map analysis of hydraulic calcium silicate root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi, Christos Gogos
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal, chemical and physical analysis of VDW.1Seal, Fill Root ST, and ADseal root canal sealers
Shehabeldin Saber, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Tamer M. Hamdy
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - α-tricalcium phosphate/fluorapatite-based cement - promising dental root canal filling material
Abdul Kazuz, Zeljko Radovanovic, Djordje Veljovic, Vesna Kojic, Dimitar Jakimov, Tamara Vlajic-Tovilovic, Vesna Miletic, Rada Petrovic, Djordje Janackovic
Processing and Application of Ceramics.2022; 16(1): 22. CrossRef
- In vitro comparative evaluation of physicochemical and mechanical properties, cytocompatibility, and antimicrobial efficacy of various bioceramic root canal sealers
- 2,964 View
- 28 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Shade reproduction and the ability of lithium disilicate ceramics to mask dark substrates
- Maryam Iravani, Sayna Shamszadeh, Narges Panahandeh, Seyedeh Mahsa Sheikh-Al-Eslamian, Hassan Torabzadeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e41. Published online July 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the ability of lithium disilicate ceramics to reproduce the A2 shade and to mask A4 substrates.
Materials and Methods Twenty-four discs (8 mm in diameter, shade A2) of high translucency (groups 1–3) and low translucency (groups 4–6) of IPS e.max ceramic with different thicknesses (0.5, 0.75, and 1 mm) were fabricated as monolithic structures. In addition, discs of medium opacity (group 7–8) with different core/veneer combinations (0.3 mm/0.7 mm and 0.5 mm/0.5 mm) were fabricated as bilayer structures. Specimens were superimposed on an A4 substrate (complex). The color changes of the complex were measured using a spectrophotometer on a black background, and the ΔE values of the complex were compared with either the A4 substrate or the A2 shade tab. One-way analysis of variance, the Tukey honest significant difference test, and the Fisher test were used to analyze the data (
p < 0.05).Results Significant between-group differences were found for comparisons to both the A4 substrate and the A2 shade (
p < 0.05). When compared with the A4 substrate, the ΔE values in all groups were in the non-acceptable range. When compared with the A2 shade, the ΔE values in all groups, except groups 2 and 3, were in the clinically acceptable range.Conclusions All translucencies and thicknesses masked the underlying dark substrate. However, the low-translucency IPS e.max Press better reproduced the A2 shade.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of material thicknesses and substrates on the translucency and color masking ability of additively manufactured definitive crown materials
Ting Wang, Yun‐Ju Wang, Chao‐Chieh Yang, John A. Levon, Tien‐Min G. Chu, Wei‐Shao Lin
Journal of Prosthodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Surface Treatments and 3D Printing Machines on the Biaxial Flexural Strength of 3D-Printed Composite Resins
Mohammed K. Fahmi
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Masking Ability of the Combined Application of Opaque Resin Composite and High‐Translucency Zirconia on Discolored Substrates
Shuping Chen, Lei Jiang, Run Chen
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(10): 2298. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Translucency of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Veneered With Two Different Materials: An In Vitro Study
M P Chinmayi, Gautam Shetty, S M Kedar, Lokesh B Kanchan, Rohit S Kundu, Krishna Kumar U, Maria Jenifer
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Masking capacity of minimally invasive lithium disilicate restorations on discolored teeth—The impact of ceramic thickness, the material's translucency, and the cement color
Kevser Pala, Eva Maria Reinshagen, Thomas Attin, Jürg Hüsler, Ronald E. Jung, Alexis Ioannidis
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 107. CrossRef - Comparing the color match of monolithic CAD-CAM dental ceramics with the VITA Classical shade guide
Mohammadjavad Shirani, Maryam Emami, Ramin Mosharraf, Omid Savabi, Mehrdad Akhavankhaleghi, Kamran Azadbakht
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2024; 132(3): 605. CrossRef - Quantitative examination of factors influencing the colour reproduction ability of lithium disilicate glass-ceramics
József Saláta, Ferenc Szabó, Péter Csuti, Melinda Antal, Péter Márton, Péter Hermann, Judit Borbély, Emese Ábrám
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Aesthetic restoration using liner-treated lithium disilicate laminate veneers in discolored teeth after endodontic treatment : A case report
Ji-Hyun Kim, Min-Soo Bae, Yeon-Hee Park, Jung-Jin Lee, Tae-Sung Bae3, Jae-Min Seo
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2023; 50(2): 91. CrossRef - Can we use the translucency parameter to predict the CAD/CAM ceramic restoration aesthetic?
Jie Wang, Jiawei Yang, Kaige Lv, Hongming Zhang, Hui Huang, Xinquan Jiang
Dental Materials.2023; 39(3): e1. CrossRef - Final Color of CAD-CAM Produced Thin Lithium Disilicate Ceramics Cemented with Different Colored Resin Cements on Darker Backgrounds
Merve BANKOĞLU GÜNGÖR
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2023; 12(2): 234. CrossRef - Masking Ability of Monolithic and Layered Zirconia Crowns on Discolored Substrates
Cristina Gasparik, Manuela Maria Manziuc, Alexandru Victor Burde, Javier Ruiz-López, Smaranda Buduru, Diana Dudea
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2233. CrossRef - Effects of background color and thickness on the optical properties of CAD-CAM resin-matrix ceramics
Afnan F. Alfouzan, Sarah M. Alnafaiy, Lama S. Alsaleh, Noor H. Bawazir, Hanan N. Al-Otaibi, Sara M. Al Taweel, Huda A. Alshehri, Nawaf Labban
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(3): 497.e1. CrossRef - Effect of CAD/CAM Ceramic Thickness on Shade Masking Ability of Discolored Teeth: In Vitro Study
Passent Ellakany, Marwa Madi, Nourhan M. Aly, Zainb S. Al-Aql, Maher AlGhamdi, Abdulrahman AlJeraisy, Adel S. Alagl
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(24): 13359. CrossRef
- The effects of material thicknesses and substrates on the translucency and color masking ability of additively manufactured definitive crown materials
- 2,008 View
- 19 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Endocrown restorations for extensively damaged posterior teeth: clinical performance of three cases
- Konstantinos Tzimas, Maria Tsiafitsa, Paris Gerasimou, Effrosyni Tsitrou
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e38. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restoration of endodontically treated teeth (ETT) with more than one cusp missing and thin remaining walls is challenging for the general practitioner. The use of posts combined with full coverage restorations is a well-established approach, yet not following the minimal invasive principles of adhesive dentistry. Endocrowns are indirect monoblock restorations that use the pulp chamber of the ETT for retention. In this study the fabrication of 4 endocrowns and their clinical performance will be discussed. Two clinical cases include computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing manufactured molar endocrowns (one feldspathic ceramic and one hybrid composite-ceramic restoration) and the other two are dental laboratory manufactured resin composite premolar endocrown restorations. The modified United States Public Health Service criteria were used to assess the clinical behavior of the restorations at different follow up periods. Endocrown restorations present a satisfactory clinical alternative, either by the use of resin composite or glass ceramic and hybrid materials. Specific guidelines with minimal alterations should be followed for an endocrown restoration to be successful. Due to limited evidence regarding the long term evaluation of this restorative technique, a careful selection of cases should be applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical performance of endocrown restorations in anterior teeth: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Julia Fehrenbach, Jéssica Lopes Soares de Soares, João Carlos Silva do Nascimento Foly, Leonardo Lamberti Miotti, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2025; 41(1): 28. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and mode of failure of modified Polyether-ether-ketone versus lithium disilicate endocrowns
Mohamed G. A. Kharboush, Hesham I. Othman, Mohamed F. Aldamaty, Ahmed M. L. Alameldin
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic assessment of composite CAD/CAM endocrowns and stainless steel crowns for endodontically treated first permanent molars in Egyptian children: randomized controlled pilot study
Basheer Ali Mabkhot, Sheriene Ezz Eldin Taha, Shaimaa Mohamed Sabry
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of cavity design on the mechanical behavior of endo-crown restorations: an ex-vivo study
Mohamed Gomaa Altamimi, Omaima El Mahallawi, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Mohammed Turky
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Microtensile Bonding Strength and Microleakage of Endocrowns Restorations Prepared With Two Different Materials
Emrah Ayna, Burcu Ayman, Cansel Belge
HRU International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Research.2025; 5(2): 66. CrossRef - Exploring the evolution of endocrowns: a bibliometric analysis (2010-2024)
Sanjana Jayakumar Nair, Jinesh Azhuvancheri, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Gopika Krishnan
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2025; 13(10): 4296. CrossRef - Beyond Traditional Restorations: Management With Endocrown in a Late Adolescent
Abdulaziz Binrayes, Abdullatif A AlGhazzi, Saud M Alotaibi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrown-retained fixed partial dentures: Revolutionizing tooth restoration or risky business? A finite element study
Nivedha Muthukumar, Parthasarathy Natarajan, Seenivasan Madhan Kumar, Shanmuganathan Natarajan
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(12): 1234. CrossRef - Chinese dentists’ restorative preferences and choices for endodontically treated teeth: a representative survey
Wenhui Li, Ziting Zheng, Yuting Zeng, Zhiyan Zhou, Ping Xiao, Xincen Zhong, Wenjuan Yan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PHỤC HÌNH ENDOCROWN TRÊN RĂNG CỐI NHỎ ĐÃ NỘI NHA: BÁO CÁO MỘT CA LÂM SÀNG
Trịnh Minh Trí Trịnh Minh Trí, Lê Võ Thảo Phương Lê Võ Thảo Phương, Nguyễn Tấn Đạt Nguyễn Tấn Đạt, Phạm Nguyên Quân Phạm Nguyên Quân, Văn Hồng Phượng Văn Hồng Phượng
Tạp Chí Khoa Học Trường Đại Học Quốc Tế Hồng Bàng.2024; : 241. CrossRef - Application of one-piece endodontic crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM system to molars
Haruto Hiraba, Kensuke Nishio, Yoshimasa Takeuchi, Takashi Ito, Tetsuo Yamamori, Atsushi Kamimoto
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 81. CrossRef - Clinical performance and wear resistance of milled resin composite material versus direct nanohybrid bulk-fill resin composite in the restoration of endodontically treated posterior teeth over 1 year: Randomized clinical trial
Esraa Esmeail H. Elhaddad, Mohamed M. A. Mohsen, Dina Ezz Eldin Mohamed
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(4): 400. CrossRef - Roughness analysis on porcelain sectional surface of porcelain fused to Co-Cr alloy endocrowns
Xuesheng Li
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimal İnvaziv Protetik Tedavilerde CAD-CAM Kullanımı: İki Olgu Sunumu
Aynur Beyza Çavuşculu Güdül, Şükriye Ece Geduk, Gaye Sağlam
Journal of International Dental Sciences.2024; 10(3): 167. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Toughness and Marginal Adaptation of PEEK and Cast Metal Crowns for Restoring Posterior Teeth with Endocrown and Richmond Crown: An In Vitro Study
Lalit Kumar, Komalpreet Kaur, Shefali Singla, Charnpreet Singh, Sunint Singh
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 14(4): 234. CrossRef - Retrospective study on the evolution of teeth with endodontic treatment in a group of patients from Craiova – Romania
Mihaela-Roxana Boțilă, Mihaela Jana Țuculina , Oana Andreea Diaconu , Mihaela Ionescu , Petre Costin Mărășescu , Luana Corina Lascu , Veronica Mercut
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(2): 225. CrossRef - Criterios clínicos y radiológicos de los tratamientos endodónticos para rehabilitación Endocrown: meta análisis
Domenica Camila Astudillo Benavides, Rafael Bernardo Piedra Andrade, Amanda Isabel Pesantez Coronel, Jose Esteban Torrachi Carrasco
Anatomía Digital.2024; 7(4): 81. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Central Incisors Restored Using Different Post and Crown Materials
Nour Al-Deen Kharboutly, Mirza Allaf, Shaza Kanout
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of extended pulp chamber preparations on the clinical performance of endocrowns in Indian patients: A 1-year observational study
Preethi Duraisamy, Naveen Gopi Chander, Jetty Ramesh Reddy, Muthukumar Balasubramanium
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(5): 616. CrossRef - Endocrowns: Indications, Preparation Techniques, and Material Selection
Dalal S AlDabeeb, Nouf S Alakeel, Raneem M Al jfshar, Thakra K Alkhalid
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Awareness of Dental Practitioners About the Utilization of Endocrown in Post-endodontic Management
Ahmed A Madfa, Moazzy I Almansour, Asma F Alshammari, Nada M. Alenezi, Essa F. Alrashidi, Adel A. Aldhaban, Thoraya Aljohani, Faris A. Alshammari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Performance of Two CAD/CAM Fabricated Ceramic Restorations with Different Designs for MIH Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ayat G. Montaser, Sara N. Hashem, Menna-Allah S. Ali, Nour Alhoda Fathy, Hebatullah Ahmed Safwat, Alaa M. Eldehna
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrown as a restorative strategy in endodontically treated teeth: an integrative literature review
Robson de Lima GOMES, Andressa Cristina da Silva QUEIROZ, Viviane Maria Gonçalves de FIGUEIREDO
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ENDOCROWN RESTORATION OF THE ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH BY USING CAD/CAM: CASE SERIES
Begüm ÜNLÜ KURŞUN, Ender AKAN
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2022; 49(Suppl 1): 13. CrossRef - Clinical Evaluation of CAD/CAM Ceramic Endocrown Versus Prefabricated Zirconia Crown in the Restoration of Pulpotomized Primary Molars: A Two-Year Spilt-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial
Nagwa Mohmmad Ali Khattab, Yasmine Mohamed Farouk El Makawi, Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 627. CrossRef - Hyperplastic Pulpitis Management with Endocrown: A Case Report
Pérez Jardón A, Otero Gayoso N, Otero. Rey E.M, Guerra Caamaño M, Chamorro-Petronacci C.M, Blanco Carrión A, Rivas Mundiña B
The Open Dentistry Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inner crown thickness on the bonding strength of porcelain fused to Co-Cr alloy endocrown
Xuesheng Li
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of pulp chamber depth on the accuracy of endocrown scans made with different intraoral scanners versus an industrial scanner: An in vitro study
Bahar Gurpinar, Onjen Tak
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(3): 430. CrossRef - Efectividad de las restauraciones en piezas con tratamiento de conducto: Una revisión clínica actual
Guiselle Andrea Verástegui Baldárrago
Revista Odontológica Basadrina.2022; 6(2): 41. CrossRef - “Conservative Bonded Restoration (An Alternative to Full Coverage Crown): A Case Report on Endocrown
Josey Mathew, Liza George, Sinju Paul, Aleesha Joy, Beulah M Bejoy, Sethuparvathi Anitha
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 42. CrossRef - Fractography of clinical failures of indirect resin composite endocrown and overlay restorations
Carlo M. Saratti, Giovanni T. Rocca, Stéphane Durual, Ulrich Lohbauer, Jack L. Ferracane, Susanne S. Scherrer
Dental Materials.2021; 37(6): e341. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - A Thorough Analysis of the Endocrown Restoration: A Literature Review
Dimokritos Papalexopoulos, Theodora-Kalliopi Samartzi, Aspasia Sarafianou
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(4): 422. CrossRef - Full‐Crown Versus Endocrown Approach: A 3D‐Analysis of Both Restorations and the Effect of Ferrule and Restoration Material
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Niek de Jager, Marco Antonio Bottino, Paul de Kok, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(4): 335. CrossRef - Monolithic Endocrown Vs. Hybrid Intraradicular Post/Core/Crown Restorations for Endodontically Treated Teeth; Cross-sectional Study
Mai Soliman, Lamar Alshamrani, Basma Yahya, Ghadah Alajlan, Alhanoof Aldegheishem, Elzahraa Eldwakhly
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(11): 6523. CrossRef - Which materials would account for a better mechanical behavior for direct endocrown restorations?
José Augusto Sedrez-Porto, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2020; 103: 103592. CrossRef - Indications and Success Rate of Endo Crowns – A Systematic Review
Shahzeb Hasan Ansari, Abdullah Ahmed Alfaqeeh, Abdullah Al Buryk, Sara Ahmed Alfaqeeh, Abdullatif Yousif A. Almusharraf, Atheer Hussain N. Aljarullah
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(43): 3247. CrossRef
- Mechanical performance of endocrown restorations in anterior teeth: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- 5,727 View
- 115 Download
- 37 Crossref

- Light transmittance of CAD/CAM ceramics with different shades and thicknesses and microhardness of the underlying light-cured resin cement
- Zahra Jafari, Homayoon Alaghehmand, Yasaman Samani, Mina Mahdian, Soraya Khafri
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e27. Published online June 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this
in vitro study was to evaluate the effects of the thickness and shade of 3 types of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) materials.Materials and Methods A total of 120 specimens of 2 shades (A1 and A3) and 2 thicknesses (1 and 2 mm) were fabricated using VITA Mark II (VM; VITA Zahnfabrik), IPS e.max CAD (IE; IvoclarVivadent), and VITA Suprinity (VS; VITA Zahnfabrik) (
n = 10 per subgroup). The amount of light transmission through the ceramic specimens was measured by a radiometer (Optilux, Kerr). Light-cured resin cement samples (Choice 2, Bisco) were fabricated in a Teflon mold and activated through the various ceramics with different shades and thicknesses using an LED unit (Bluephase, IvoclarVivadent). In the control group, the resin cement sample was directly light-cured without any ceramic. Vickers microhardness indentations were made on the resin surfaces (KoopaPazhoohesh) after 24 hours of dark storage in a 37°C incubator. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance followed by the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05).Results Ceramic thickness and shade had significant effects on light transmission and the microhardness of all specimens (
p < 0.05). The mean values of light transmittance and microhardness of the resin cement in the VM group were significantly higher than those observed in the IE and VS groups. The lowest microhardness was observed in the VS group, due to the lowest level of light transmission (p < 0.05).Conclusion Greater thickness and darker shades of the 3 types of CAD/CAM ceramics significantly decreased the microhardness of the underlying resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
Shervin Reybod, Fariba Ezoji, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenouz, Behnaz Esmaeili
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Ultrasonic Scaling on Microleakage in Lithium Disilicate Crowns Luted With Different Resin Cements
Waleed AL-Mutairi, Marwa Eltayeb I. Elagra, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Polymerization through Glass-ceramics: Influence of Light-polymerizing Unit’s Emitted Power and Restoration Parameters (Shade, Translucency, and Thickness) on Transmitted Radiant Power
Ra’fat I. Farah, Ibrahim A. Alblihed, Alhareth A. Aljuoie, Bandar Alresheedi
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 35. CrossRef - Effect of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing bleach shade ceramic thickness on its light transmittance and microhardness of light-cured resin cement
Pardis Sheibani, Ghazaleh Ahmadizenous, Behnaz Esmaeili, Ali Bijani
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of shade and thickness on the translucency parameter of anatomic-contour zirconia, transmitted light intensity, and degree of conversion of the resin cement
Noppamath Supornpun, Molly Oster, Kamolphob Phasuk, Tien-Min G. Chu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 129(1): 213. CrossRef - The Effect of Different Surface Treatments on the Color Stabilities of Lithium Disilicate Material
Onur Doğan DAĞ, Göknil ALKAN DEMETOĞLU, Ayşegül KURT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(2): 395. CrossRef - Effect of thickness of CAD/CAM materials on light transmission and resin cement polymerization using a blue light‐emitting diode light‐curing unit
Eduardo Fernandes de Castro, Bruna Marin Fronza, Jorge Soto‐Montero, Marcelo Giannini, Carlos Tadeu dos‐Santos‐Dias, Richard Bengt Price
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(2): 368. CrossRef - Effect of Optical Properties of Lithium Disilicate Glass Ceramics and Light-Curing Protocols on the Curing Performance of Resin Cement
Kejing Meng, Lu Wang, Jintao Wang, Zhuoqun Yan, Bin Zhao, Bing Li
Coatings.2022; 12(6): 715. CrossRef - Effect of the thickness of CAD‐CAM materials on the shear bond strength of light‐polymerized resin cement
Yener Okutan, Banucicek Kandemir, Mustafa Borga Donmez, Munir Tolga Yucel
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inhomogeneity of the polymerization light beam on the microhardness of resin cement under a CAD-CAM block
Yu-Ra Go, Kwang-Man Kim, Sung-Ho Park
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(5): 802.e1. CrossRef - Evaluation of microhardness and water sorption/solubility of dual-cure resin cement through monolithic zirconia in different shades
Elham Ansarifard, Zahra Panbehzan, Rashin Giti
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(1): 50. CrossRef - Comparison between Different Shades of Monolithic Zirconia over Microhardness and Water Solubility and Sorption of Dual-cure Resin Cement
Sarika Sharma, Soni Kumari, Nikita Raman, Ashish K Srivastava, Gunja LNU, Arunendra S Chauhan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1019. CrossRef - Effect of light intensity, light-curing unit exposure time, and porcelain thickness of ips e.max press and vintage LD press on the hardness of resin cement
Silvia Naliani, Suzan Elias, Rosalina Tjandrawinata
Scientific Dental Journal.2020; 4(1): 21. CrossRef
- Investigating the Ability to Mask Dental Discoloration by CAD/CAM Bleach Shade Ceramics in Different Thicknesses
- 2,047 View
- 8 Download
- 13 Crossref

- An esthetic appliance for the management of crown-root fracture: a case report
- Sang-Min Jeon, Kang-Hee Lee, Bock-Young Jung
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):226-229. Published online May 22, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Orthodontic extrusion is usually performed by means of a fixed orthodontic appliance that utilizes arch wire attached to adjacent teeth and transfers the desired force by elastic from the wire to the root. However, clinicians often encounter cases where the bonding required for tooth traction is not possible because the adjacent teeth have been restored with ceramic or veneer. The purpose of this case report is to describe a modified orthodontic extrusion appliance that is useful when conventional orthodontic treatment is not possible. The modified appliance was fabricated using an artificial tooth, clear plastic sheeting, and a braided fiber-reinforced composite strip that covered adjacent teeth without bonding. It satisfied the esthetic and functional needs of the patient and established the optimal biologic width.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Esthetic enhancement of a traumatized anterior tooth with a combination of forced eruption and tooth alignment: a case report
So-Hee Kang, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Sung-Kyo Kim, Young-Kyung Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(3): 210. CrossRef
- Esthetic enhancement of a traumatized anterior tooth with a combination of forced eruption and tooth alignment: a case report
- 1,263 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


