Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparative study of the effectiveness of different bleaching agents on blood-colored extracted teeth and investigation of recoloring after bleaching: an in vitro experimental study
- Gülşen Arslan, Akın Aladağ, Ayşegül Demirbaş, Murat Türkün
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e22. Published online July 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the efficacy of three distinct bleaching agents over time on blood-stained, devitalized teeth. Furthermore, the recoloring subsequent to bleaching will be monitored.
Methods
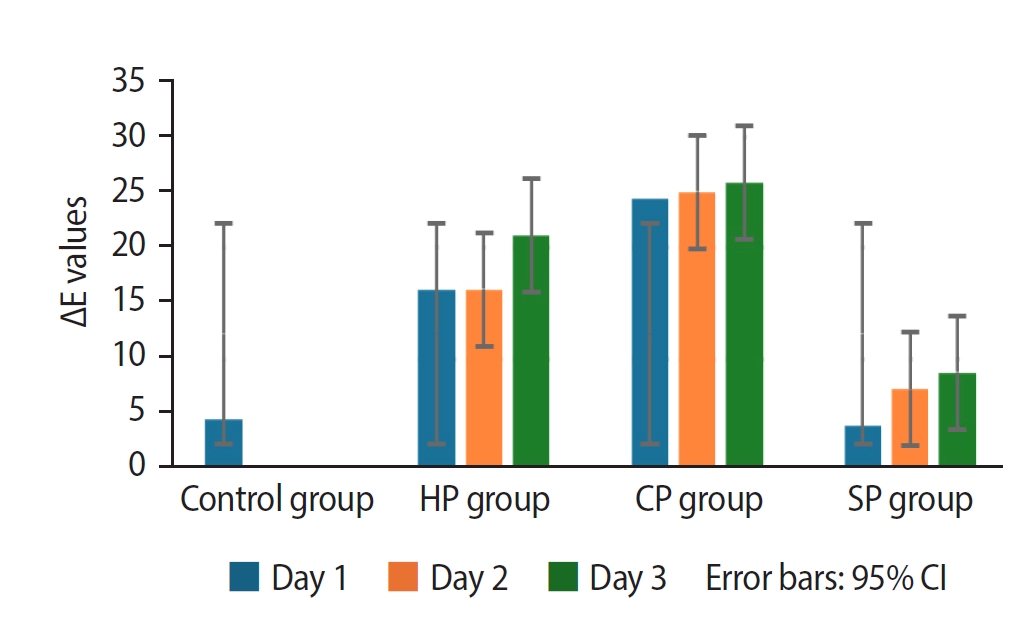
The study was conducted on 60 caries-free, unfilled, upper human incisors. The Freccia and Peters blood staining technique was employed, and four groups (n = 15) were identified: control, 35% hydrogen peroxide-treated, 37% carbamide peroxide-treated, and sodium perborate-treated groups. Color differences were measured using ΔE00, ΔWID, L*, a*, and b* values. To investigate tooth discoloration after bleaching, 10 unbleached teeth with three groups of 10 bleached teeth were compared by vine staining. The group of bleached teeth was restored immediately, another group waited one week, and the third group had sodium ascorbate applied and analyzed using one-way analysis of variance tests (p < 0.05).
Results
Among the groups, carbamide peroxide exhibited the most significant whitening during the 6-day bleaching process, followed by hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate. Subsequent examination of the wine recoloring of post-bleaching samples demonstrated that bleached teeth exhibited a heightened propensity for recoloration in contrast to unbleached teeth. Notably, sodium ascorbate treatments for hydrogen peroxide neutralization and the wait-and-restore approach were not statistically significant in terms of preventing recoloration.
Conclusions
Sodium perborate is less effective and more time-consuming than hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide for bleaching purposes. Carbamide peroxide is the most effective bleaching agent. The sodium ascorbate treatment and the wait-and-restore approach are ineffective in preventing recoloring. Bleached teeth have more discoloration than unbleached teeth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Adhesive Systems on Shade Matching of Composite Veneer
Fadak Al Marar, Raghad Aljarboua, Fatimah M. Alatiyyah, Shahad AlGhamdi, Faraz Ahmed Farooqi, Lama Almuhanna, Rasha AlSheikh, Abdul Samad Khan
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(2): 85. CrossRef
- The Effect of Adhesive Systems on Shade Matching of Composite Veneer
- 3,235 View
- 242 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Can carbamide peroxide be as effective as hydrogen peroxide for in-office tooth bleaching and cause less sensitivity? A systematic review
- Patrick Wesley Marques de Boa, Kaiza de Sousa Santos, Francisca Jennifer Duarte de Oliveira, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e14. Published online March 20, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to answer the question through a systematic review: Can carbamide peroxide be as effective as hydrogen peroxide and cause less in-office bleaching sensitivity? A literature survey was performed in PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, and gray literature. Primary clinical trials that compared the efficacy or the in-office bleaching sensitivity between carbamide and hydrogen peroxides were included. The risk of bias was evaluated using the RoB2. The certainty of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE approach. DPI training significantly improved the mean scores of the dental undergraduates from 7.53 in the pre-DPI-training test to 9.01 in the post-DPI-training test (
p < 0.001). After 6 weeks, the mean scores decreased marginally to 8.87 in the retention test (p = 0.563). DPI training increased their confidence level from 5.68 pre-DPI training to 7.09 post-DPI training. The limited evidence suggests that the 37% carbamide peroxide may be similarly effective to the 35% hydrogen peroxide for bleaching teeth in-office and causes less bleaching sensitivity. However, more well-designed split-mouth clinical trials are necessary to strengthen the evidence.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of nanostructured additives in tooth bleaching agents on enhancing color change and reducing side effects: a scoping review
Patrick Wesley Marques de Boa, Kaiza de Sousa Santos, Aleph Matthews da Silva Souza, Arnóbio Antônio da Silva-Júnior, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Enamel Surface Roughness Following High-Concentration Peroxide Bleaching: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Mamnoon Ghafir, Nida Mehmood, Leeza Bharati, Shreya Bhukal, Ritika Sethi, Aanchal Chaudhary, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Using violet light during in-office tooth bleaching to enhance the efficacy of carbamide peroxide without increasing bleaching sensitivity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mariana Silva de Bessa, Kaiza de Sousa Santos, Patrick Wesley Marques de Boa, Francisca Jennifer Duarte de Oliveira, Bárbara Faria de Sá Barbosa, Boniek Castillo Dutra Borges
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Different Light-Activated Bleaching Gels on Pulp Chamber Temperature: An In Vitro Study
Mandana Karimi, Elmira Ataee, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani, Mahdi Abbasi, Elham Ahmadi
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(4): 225. CrossRef
- Impact of nanostructured additives in tooth bleaching agents on enhancing color change and reducing side effects: a scoping review
- 11,287 View
- 162 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Impact of combined at-home bleaching and whitening toothpaste use on the surface and color of a composite resin
- Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira-Junior, Marcia Hiromi Tanaka, Laura Nobre Ferraz
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e26. Published online July 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objective This
in vitro study aimed to evaluate the effects of different whitening toothpastes on a composite resin during at-home bleaching with 10% carbamide peroxide.Materials and Methods Sixty samples (7 mm × 2 mm) were used for color and roughness analyses, while another 60 samples (3 mm × 2 mm) were utilized to assess microhardness. The factors analyzed included toothpaste, for which 5 options with varying active agents were tested (distilled water; conventional toothpaste; whitening toothpaste with abrasive agents; whitening toothpaste with abrasive and chemical agents; and whitening toothpaste with abrasive, chemical, and bleaching agents). Brushing and application of whitening gel were performed for 14 days. Surface microhardness (SMH), surface roughness (Ra), and color (∆L*, ∆a*, ∆b, ∆E*ab, and ∆E00) were analyzed. The Ra and SMH data were analyzed using mixed generalized linear models for repeated measures, while the color results were assessed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests.
Results Between the initial and final time points, all groups demonstrated significant increases in Ra and reductions in SMH. No significant differences were found between groups for SMH at the final time point, at which all groups differed from the distilled water group. Conventional toothpaste exhibited the lowest Ra, while whitening toothpaste with abrasive agent had the highest value. No significant differences were observed in ∆L*, ∆a*, and ∆b.
Conclusions While toothpaste composition did not affect the color stability and microhardness of resin composite, combining toothbrushing with whitening toothpaste and at-home bleaching enhanced the change in Ra.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current evidence on the impact of whitening toothpastes on dental restorative materials: A comprehensive review
Soyeon Kim, Shin Hye Chung, Satoshi Yamaguchi, Taro Arima, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2026; 70(1): 4. CrossRef - Property changes in resin composite exposed to mouth rinses during 10% carbamide peroxide bleaching
Mariana Ferreira da Silva, Giovana Contin Germinari, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Tatiane Cristina Dotta, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Júnior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2026; 25: e260366. CrossRef - At‐Home and In‐Office Bleaching Protocols on the Color Match of Restorations Made With Single‐Shade Composites
Luciana Vasconcelos Ramos, Dayana Fernandes Rocha Aparicio, André Luis Faria‐e‐Silva, Maíra do Prado, Andréa Vaz Braga Pintor, Marcela Baraúna Magno
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1567. CrossRef - Surface properties and susceptibility to staining of a resin composite after brushing with different whitening toothpastes
Aline da Silva Barros, Carolina Meneghin Barbosa, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Waldemir Francisco Vieira Junior, Laura Nobre Ferraz
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(1): e6. CrossRef - Dental Care Behaviors and Oral Health Challenges in School-Age Populations
Ahmad Mahmoud Saleh , Aishah Al Daragemeh , Asmaa Morgan Farahat Khatap , Prakash Palanivelu , Arul Vellaiyan , Elturabi Elsayed Ebrahim , Ahmad Rayan , Nermen Abdelftah Mohamed
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2025; 5: 1372. CrossRef - Effect of bleaching and repolishing on whiteness change and staining susceptibility of resin-based materials
Sultan Aktuğ Karademir, Samet Atasoy, Beyza Yılmaz
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of using different toothpaste during bleaching with violet LED light (405 nm) on the colour and roughness of dental enamel: an in vitro study
Franco Sousa Leticia, Mazzalli Redondo Victor, Ferraz Nobre Laura, Vitti Pino Rafael, Renata Siqueira Scatolin
Lasers in Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of coffee staining and simulated oral hygiene methods on the color and translucency of a nanoceramic resin
Luiz Felipe Schneider, Bruna Mueller, Rubens Nisie Tango, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 1020. CrossRef
- Current evidence on the impact of whitening toothpastes on dental restorative materials: A comprehensive review
- 5,279 View
- 62 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of applying antioxidants on bond strength of bleached bovine dentin
- Hyo-Jin Whang, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):37-43. Published online October 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Some antioxidants are believed to restore dentin bond strength after dental bleaching. This study was done to evaluate the influence of antioxidants on the bond strength of bleached bovine dentin.
Materials and Methods Thirty incisors were randomly assigned to 10 groups (two unbleached control and eight bleached groups: immediate bonding IB, 4 wk delayed bonding DB, 10% sodium ascorbate treated SA, 10% α-tocopherol treated TP groups). Teeth in half of groups were subjected to thermal stress, whereas the remaining groups were not. Resin-dentin rods with a cross-sectional area of 2.25 mm2 were obtained and microtensile bond strength was determined at a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min. Fifteen specimens were prepared for SEM to compare the surface characteristics of each group. The change in dentin bond strength from thermal stress and antioxidant treatment was evaluated using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Sheffe's
post hoc test at a significance level of 95%.Results The control group exhibited the highest bond strength values, whereas IB group showed the lowest value before and after thermocycling. The DB group recovered its bond strength similar to that of the control group. The SA and TP groups exhibited similar bond strength values with those of the control and DB groups before thermocycling. However, The TP group did not maintain bond strength with thermal stress, whereas the SA group did.
Conclusions Applying a 10% sodium ascorbate solution rather than 10% α-tocopherol solution for 60 sec is recommended to maintain dentin bond strength when restoring non-vitally bleached teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the effect of the application of Quercus cerris extract and the use of fluoride bonding material on the bonding strength of orthodontic brackets after tooth bleaching with hydrogen peroxide
Ezgi Ay, Derya Dursun
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19335. CrossRef - Antioxidant effect on shear bond strength of resin composite to in-office versus home bleached enamel surface
Maha Mosaad Mohamed, Magda E. -A. Shalaby, Eman A. E. -G. Shebl
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(3): 409. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the impact of modern cavity disinfectants on dentin bond strength
Simge Gümüş Ayaz, Ezgi Sonkaya, Gökçe Keçeci
Frontiers in Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of glutathione on bond strength of composite resin to enamel following extracoronal bleaching
Nair Devika, Chandrasekaran Charanya, K Athira, James Vandana, Sundaresan Balagopal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1110. CrossRef - Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticle as an Antioxidant Material on Shear Bond Strength of Composite Resin to Enamel after External Bleaching
Diatri Nari Ratih, Shintatika Erlagista, Tunjung Nugraheni
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2024; 12: 1. CrossRef - Effects of alpha‐tocopherol antioxidant on fracture strength and adhesion of endodontically treated teeth restored after dental bleaching
Natália Marcomini, Maria Carolina da Costa Albaricci, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, João Felipe Besegato, Eduardo Fernández Godoy, Andréa Abi Rached Dantas, Milton Carlos Kuga
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Alpha-tocopherol: An alternative solution for the adverse effects of dental bleaching on dentin adhesion
Maria Carolina da Costa Albaricci, Natália Marcomini, Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes Costa, Antonia Patricia Oliveira Barros, Lucas David Galvani, Milton Carlos Kuga, Andréa Abi Rached Dantas
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2024; 131: 103655. CrossRef - Efficacy of organic and antioxidant agents to regain bond strength to bleached enamel in different dental adhesive solvents
Satheesh B Haralur, Renad Mohammed Al-Ibrahim, Faten Abdullah Al-Shahrani, Rahaf Abdullah Al-Qahtani, Saurabh Chaturvedi, Naseer M Alqahtani
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Present status and future directions – Managing discoloured teeth
Bill Kahler
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S4): 922. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the postbleaching application of sodium ascorbate, alpha‐tocopherol, and quercetin on shear bond strength of composite resin to enamel
Marzieh Moradian, Maryam Saadat, Mohammad Hossein S. Shiri, Fatemeh Sohrabniya
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(6): 1598. CrossRef - Use of antioxidants to restore bond strength after tooth bleaching with peroxides
Dorcas E. R. P. Olmedo, Matheus Kury, Bruna A. Resende, Vanessa Cavalli
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Elemental and morphological analysis of enamel following the application of two bleaching systems with amorphous calcium phosphate: effect on enamel erosion susceptibility
Shaymaa M. Nagi, Shahinaz H. Nabil, Mohamed H. Zaazou
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) gel extract as an antioxidant on the shear bond strength of a resin composite post-bleaching application with 40% hydrogen peroxide
Indes Rosmalisa Suratno, Irfan Dwiandhono, Ryana Budi Purnama
Dental Journal.2021; 54(2): 87. CrossRef - In Vitro Re-Hardening of Bleached Enamel Using Mineralizing Pastes: Toward Preventing Bacterial Colonization
Andrea Scribante, Claudio Poggio, Simone Gallo, Paolo Riva, Antonella Cuocci, Manuel Carbone, Carla Arciola, Marco Colombo
Materials.2020; 13(4): 818. CrossRef - DİŞ BEYAZLATMA İŞLEMİNİN LİTYUM DİSİLİKAT SERAMİĞİN BAĞLANMA DAYANIMINA ETKİSİ
Merve YILDIRAK, Rıfat GÖZNELİ
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef - The improvement of biocompatibility of adhesives
Cigdem Atalayin, Huseyin Tezel, Zeynep Ergucu, Nimet Unlu, Guliz Armagan, Taner Dagci, Timur Kose
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(8): 3213. CrossRef - Dentin bond strength and nanoleakage of the adhesive interface after intracoronal bleaching
Vanessa Cavalli, Maicon Sebold, Mirela Sanae Shinohara, Patrícia Nóbrega Rodrigues Pereira, Marcelo Giannini
Microscopy Research and Technique.2018; 81(4): 428. CrossRef - Composite resin shear bond strength on bleached dentin increased by 35% sodium ascorbate application
Tunjung Nugraheni, N Nuryono, Siti Sunarintyas, Ema Mulyawati
Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi).2017; 50(4): 178. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Immediate Bond Strength to Bleached Enamel Following Application of Various Antioxidant Solutions
Anshu Minocha, Ashu K. Gupta, Alisha Dhingra, Nayantara Sen
Dental Journal of Advance Studies.2017; 5(2): 84. CrossRef - Effects of Erbium Family Laser on Shear Bond Strength of Composite to Dentin After Internal Bleaching
Nazanin Kiomarsi, Yasaman Arjmand, Mohammad Javad Kharrazi Fard, Nasim Chiniforush
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2017; 9(1): 58. CrossRef - Antioxidant therapy enhances pulpal healing in bleached teeth
Adriano Fonseca Lima, Marcelo Rocha Marques, Diana Gabriela Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Giselle Maria Marchi, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of alpha-tocopherol on fracture resistance after endodontic treatment, bleaching and restoration
Keren Cristina Fagundes JORDÃO-BASSO, Milton Carlos KUGA, Andrea Abi Rached DANTAS, Mateus Rodrigues TONETTO, Suellen Nogueira Linhares LIMA, Matheus Coêlho BANDÉCA
Brazilian Oral Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Resin Bonding of Self-Etch Adhesives to Bovine Dentin Bleached from Pulp Chamber
Akiko Haruyama, Atsushi Kameyama, Junji Kato, Shinji Takemoto, Yutaka Oda, Eiji Kawada, Toshiyuki Takahashi, Masahiro Furusawa
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the effect of the application of Quercus cerris extract and the use of fluoride bonding material on the bonding strength of orthodontic brackets after tooth bleaching with hydrogen peroxide
- 1,549 View
- 7 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Effect of vital tooth bleaching agent on dentin bonding
- Na-Young Jeong, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(2):79-85. Published online March 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.2.079
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub To evaluate the effect of vital tooth bleaching agent and alcohol pretreatment on dentin bonding, flat dentin windows were produced on the buccal side of the crowns of fifty-five extracted, human premolars. A bleaching gel, Opalescence® with 10% of carbamide peroxide (Ultradent Product, USA) was daily applied on the teeth of three experimental groups for six hours for 10 consecutive days, while teeth of a control group were not bleached. After 6 hours of bleaching gel application, the specimens were washed and stored in saline until the next day application. After application of One-step® dentin bonding agent (Bisco, USA), Z-250® resin (3M-ESPE, USA) was bonded to dentin with a mount jig. Shear bond strength was measured with an Instron machine (Type 4202, Instron Corp., USA) after 24 hours. The results were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test at
p < 0.05.Immediate bonding group showed significantly lower bond strength than un-bleached control group (
p < 0.05).Ethanol-treated group showed significantly higher bond strength compared to immediate bonding group (
p < 0.05). However, the bond strength of the ethanol treatment group was lower than that of the un-bleached control group (p < 0.05).There were no significant difference in shear bond strength between the 2-week delayed bonding group and the ethanol-treated group (
p > 0.05) and between delayed bonding group and un-bleached control group (p > 0.05).In the condition of the present study, it seems that alcohol pretreatment after bleaching procedure can reduce the adverse effect of vital bleaching agent on dentin bonding.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Applying Malatang Sauce by Type Before and After Expert Whitening Agent Treatment on Bovine Tooth Coloring
Chi-Yoon Sung, Hee-Jung Lim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Do-Seon Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(2): 79. CrossRef - Effect of the bleaching light on whitening efficacy
Jong-Hyun Park, Hye-Jin Shin, Deok-Young Park, Se-Hee Park, Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(2): 95. CrossRef
- Effect of Applying Malatang Sauce by Type Before and After Expert Whitening Agent Treatment on Bovine Tooth Coloring
- 2,280 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Bleaching effect of carbamide peroxide gel on discolored nonvital teeth
- Sun-Ah Park, Sun-Ho Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Byung-Ju Oh, Chang Youn, Yeong-Joon Park, Sun-Wa Jeong, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(4):441-447. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.4.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The bleaching of discolored nonvital teeth is conservative treatment that satisfy the cosmetic desire. The most common method for this treatment, walking bleaching, is using 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate.
Many alternatives are suggested for preventing the external cervical root resorption that is the common complication of the nonvital teeth bleaching with 30% hydrogen peroxide.
The same extent of oxidation reactions as that resulted by the bleaching with the application of 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate can also be acquired more safely by materials that contain 10% carbamide peroxide, used primarily for the bleaching of vital teeth. Therefore, this study was performed to evaluate the efficacy of 10% and 15% carbamide peroxide bleaching gel in nonvatal teeth bleaching.
The internal bleaching of intentionally discolored teeth was performed in vitro with 10% carbamide peroxide (Group 1), 15% carbamide peroxide (Group 2), mixture of distilled water and sodium perborate (Group 3), and mixture of 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate (Group 4). The bleaching materials were refreshed following 3, 6, 9 and 12 days. To evaluate the bleaching effect, the color change of the crowns was measured at 1, 2, 3, 4, 7 and 15 days of bleaching using the colorimeter.
The results were as follows :
1. L* and ΔE* values were increased with time in all bleaching agents(p<0.01).
2. There was no significant difference in L* and ΔE* value among bleaching agents.
3. ΔE* value higher than 3 was shown after 3 days of bleaching with 10% carbamide peroxide gel, 1 day with 15% carbamide peroxide gel, 4 days with mixture sodium perborate and distilled water and 4 days with mixture sodium perborate and 30% hydrogen peroxide, respectively.
These results revealed that the use of 10% and 15% carbamide peroxide bleaching gel in non-vital teeth bleaching is as effective as mixture of distilled water and sodium perborate and mixture of 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate. Accordingly, carbamide peroxide could be used clinically to bleach discolored non-vital teeth.
- 1,333 View
- 22 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


