Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
-
Evaluation of mineral induction ability and cytotoxicity of carbonated hydroxyapatite for pulp tissue regeneration: an
in vitro study - S. Swathi Priyadharshini, Chinnasamy Ragavendran, Anand Sherwood, J. Ramana Ramya, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e40. Published online October 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
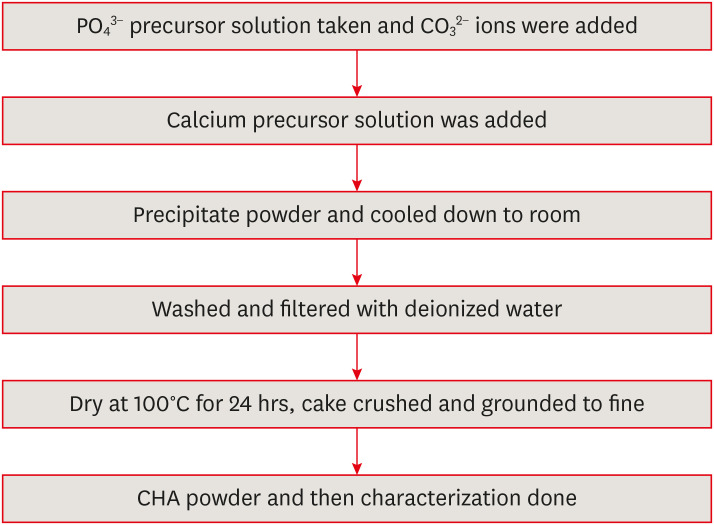
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate carbonated hydroxyapatite (CHA)’s ability for mineral induction and its
in vitro cytotoxicity with human dental pulp cells.Materials and Methods Precursors for the study include di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate and calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, with sodium hydrogen carbonate added to achieve different levels of carbonate substitution. The synthesized CHA samples are characterized using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe morphology. For 14 days at 37°C, samples were submerged in simulated body fluid to assess their mineral induction capabilities. SEM was used to confirm apatite formation on sample surfaces. The cytotoxicity assay was used to assess the vitality of the cells following their exposure to various concentrations of CHA.
Results The Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards data for HA aligned well with the results from X-ray diffraction analysis of CHA across 3 different concentrations, indicating strong agreement. Fourier transform infrared spectra indicated the presence of phosphate, hydroxyl, and carbonate groups within the samples. SEM and Energy-dispersive X-ray analysis show agglomerated and flaky nanoparticles. All the samples are bioactive, but the formation of apatite differs from one another.
In vitro cytotoxicity assay showed that over 70% of cells maintain viability.Conclusions The results of this study may provide insight into the potential use of carbonated HA as a dental pulp-capping material for vital pulp therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of compressive strength and morphological interface of carbonated hydroxyapatite with other pulp capping materials: An in vitro analysis
S. Swathi Priyadharshini, Chinnasamy Ragavendran, I. Anand Sherwood, Ramanaramya Jeyapalan
Endodontology.2025; 37(1): 90. CrossRef - Smart Nanomaterials: Current State and Future Prospects in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering
E. Elizabeth Rani, D. Sakthi Sanjana, E. Karthikeyan, J. Nandhini
Biomedical Materials & Devices.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermoresponsive Nanomaterials: Revolutionizing Cancer Theranostics
Bellarmin Michael, Mohanakrishnan Srinivasan, Karthikeyan Elumalai, Lokeshwar Ravikumar, Sivaprakash Kathiresan, Nandhini Jayaprakash
Biomedical Materials & Devices.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Dioxo-Phosphobetaines derived from the reaction of Dichlorodinitrobenzofuroxane with various phosphines
Irina V. Galkina, Haiyan Fan, Semen R. Romanov, Dmitriy I. Bakhtiyarov, Luisa M. Usupova, Svetlana N. Egorova, Yulia V. Bakhtiyarova, Enrico Benassi
Bioorganic Chemistry.2025; 163: 108695. CrossRef - Near-infrared laser-activated PLGA-PDA core-shell nanohybrids for synergistic photothermal antibacterial therapy and sustained ion release in orthodontic white spot lesions prevention
Zezhou Feng, Yujiang Liu, Silu Sun, Minmin Si, Di Huang, Zhiyuan Feng
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 162: 106078. CrossRef - Formation and utilization of soluble microbial products in denitrifying biofilters at different carbon-to-nitrogen ratios: Microbial community characteristics
Fangyuan Jiang, Xianyang Shi
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 119554. CrossRef - Bioactivity and biocompatibility of bioceramic-based pulp capping materials in laboratory and animal models
Rafiqul Islam, Md. Refat Readul Islam, Kenta Tsuchiya, Yu Toida, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical, Chemical, and Biological Properties of Graphene Nanoparticle-added Tricalcium Silicate Formulations: A Systematic Review
Soundaria Srinivasan, Deepa Gurunathan, Lakshmi Thangavelu
Journal of International Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advanced structural and compositional profiling of mineral trioxide aggregate incorporated with nano-carbonated hydroxyapatite: a comprehensive X-ray diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray investigation
Njwan Fadhel Shehab, Nadia Hameed Hasan, Alaa Edrees Dawood, Nawal Atiya Khalaf
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2025; 12: 216. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of compressive strength and morphological interface of carbonated hydroxyapatite with other pulp capping materials: An in vitro analysis
- 2,398 View
- 117 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
- Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e22. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on the time to reach the working length and the fracture resistance of Twisted File (TF) and Endostar E3 files.
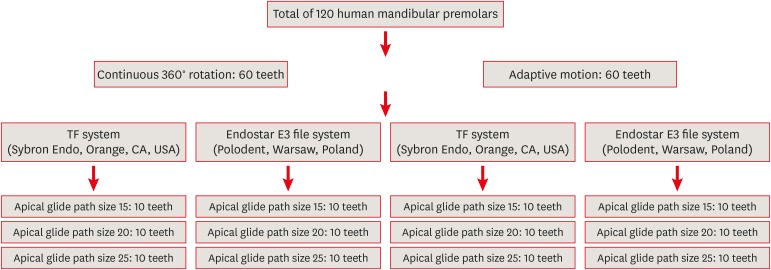
Materials and Methods A total of 120 mandibular single-rooted premolars were selected. Two methods of kinetic motion (TF adaptive and continuous rotary motion) and file systems (TF and Endostar E3) were employed. The files were used in root canals prepared to apical glide path sizes of 15, 20, and 25. The time taken to reach the working length and the number of canals used before the instrument deformed or fractured were noted. Fractured instruments were examined with scanning electron microscopy.
Results The TF system took significantly more time to reach the working length than the Endostar E3 system. Both systems required significantly more time to reach the working length at the size 15 glide path than at sizes 20 and 25. A greater number of TFs than Endostar E3 files exhibited deformation, and a higher incidence of instrument deformation was observed in adaptive than in continuous rotary motion; more deformation was also observed with the size 15 glide path. One TF was fractured while undergoing adaptive motion.
Conclusions No significant difference was observed between continuous rotary and adaptive motion. The TF system and adaptive motion were associated with a higher incidence of deformation and fracture. Apical glide path sizes of 20 and 25 required significantly less time to reach the working length than size 15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Assessment of Different File Systems for Working Time Based on Glide Path, Operating Kinetics, and the Fracture Resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Divya Batra, Debkant Jena, Nandita Bansal, Alka Arora, Divya Gaurav Dudulwar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 69. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 1,707 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


