-
Resolvin E1 incorporated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold accelerates repair of dental pulp stem cells under inflammatory conditions: a laboratory investigation
-
Hemalatha P Balasubramanian, Nandini Suresh, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e40. Published online November 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e40
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
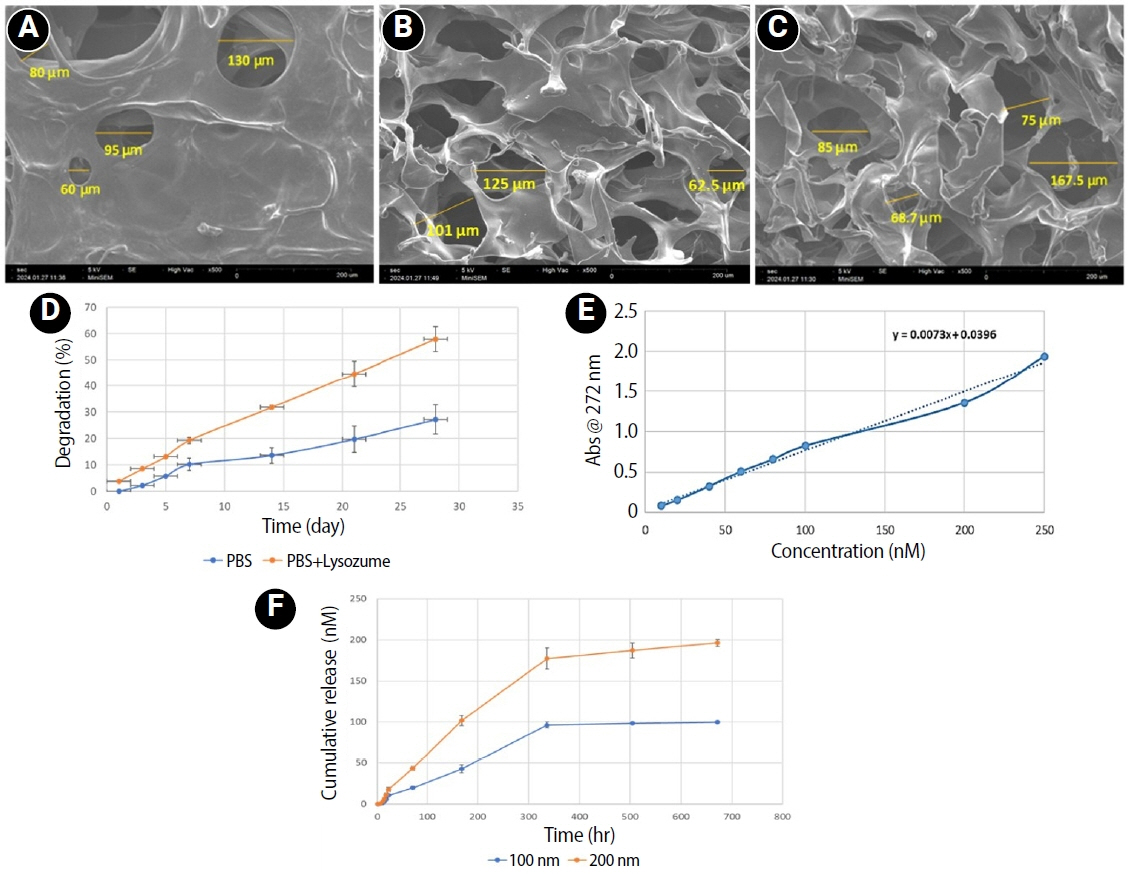
This study fabricated and characterized a resolvin E1 (RvE1)-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) scaffold and determined its cytotoxicity and mineralization potential on inflamed human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Methods
CMC scaffold incorporated with two concentrations of RvE1 (100 and 200 nM) was fabricated and characterized. The scaffolds’ porosity, drug release kinetics, and degradation were assessed. The impact of RvE1 on inflamed hDPSCs proliferation, proinflammatory gene expression (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), alkaline phosphatase activity, and alizarin red S staining was evaluated.
Results
Scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated a highly porous interconnected microstructure. Release kinetics showed gradual RvE1 release peaking at day 14. Cumulative degradation of the CMC scaffold at 28 days was 57.35%. Inflamed hDPSCs exposed to 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold exhibited significantly improved viability compared to 100 nM. Both RvE1-CMC scaffolds significantly suppressed the expression of TNF-α at 7 days. Alkaline phosphatase activity was enhanced by both RvE1 concentrations on days 7 and 14. Alizarin red staining revealed superior mineralization potential of 200 nM RvE1 on days 14 and 21.
Conclusions
This study concludes 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold is a promising therapy for inflamed pulp conditions, enhancing cell proliferation and biomineralization potential in inflamed hDPSCs.
-
Stress distribution of restorations in external cervical root resorption under occlusal and traumatic loads: a finite element analysis
-
Padmapriya Ramanujam, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Vignesh Srinivasan, Selvakarthikeyan Ulaganathan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e21. Published online May 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
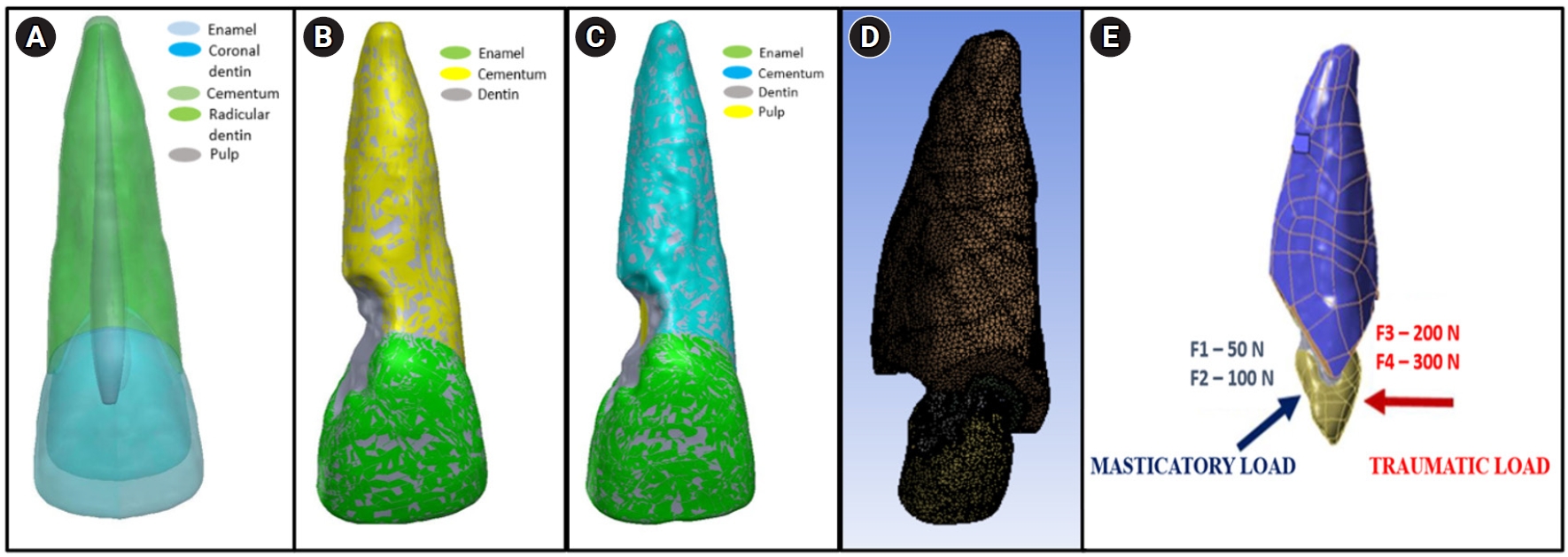
This study analyzed the stress distribution in a maxillary central incisor with external cervical resorptive defect restored with different restorative materials under normal masticatory and traumatic loading conditions using finite element analysis.
Methods
Cone-beam computed tomography of an extracted intact incisor and created resorptive models (Patel’s 3D classification-2Bd and 2Bp) in the maxillary central incisor was performed for finite element models. The 2Bd models were restored either with glass ionomer cement (GIC)/Biodentine (Septodont) or a combination of both with composite resin. 2Bp models were restored externally with a combination technique and internally with root canal treatment. The other model was external restoration with GIC and internal with fiber post. Two masticatory loads were applied at 45˚ to the palatal aspect, and two traumatic loads were applied at 90˚ to the buccal aspect. Maximum von Mises stresses were calculated, and stress distribution patterns were studied.
Results
In 2Bd models, all restorative strategies decreased stress considerably, similar to the control model under all loads. In 2Bp models, the dentin component showed maximum stress at the deepest portion of the resorptive defect, which transfers into the adjacent pulp space. In 2Bp defects, a multilayered restoration externally and root canal treatment internally provides better stress distribution compared to the placement of a fiber post.
Conclusions
Increase in load, proportionally increased von Mises stress, despite the direction or angulation of the load. Multilayered restoration is preferred for 2Bd defects, and using an internal approach of root canal treatment is suggested to restore 2Bp defects.
-
Pattern of endodontic instrument separation and factors affecting its retrieval: a 10-year retrospective observational study in a postgraduate institute
-
Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Aswathi Varghese, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Srinivasan Narasimhan
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e7. Published online February 19, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
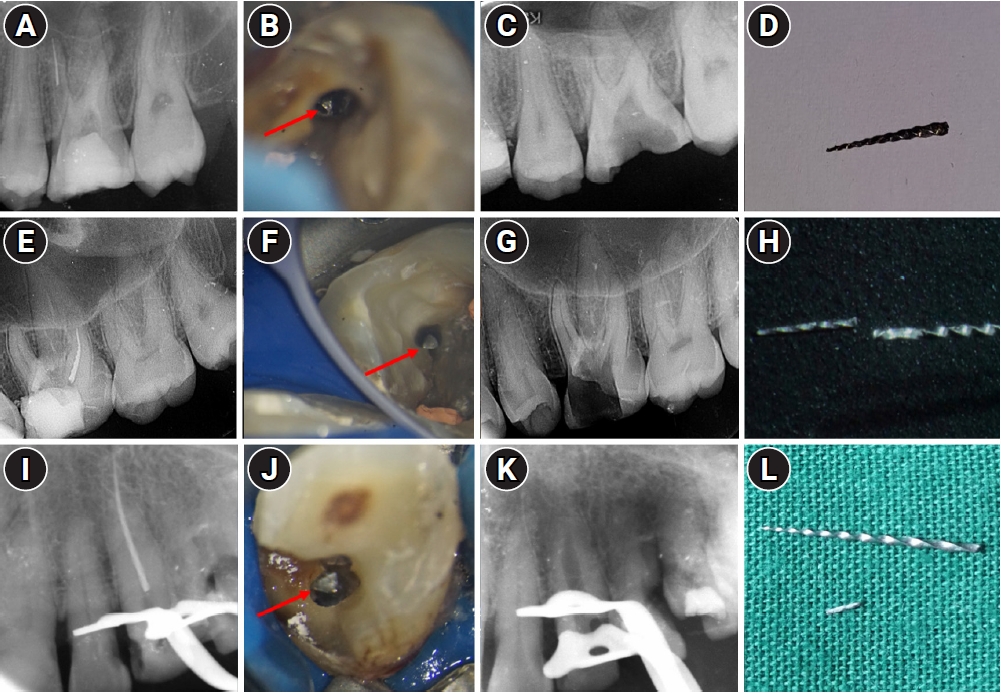
This study aimed to assess the pattern of endodontic instrument separation, their retrievability, and factors affecting its retrieval, in a postgraduate institute.
Methods
Cases referred for the management of separated endodontic instruments (SEI) from 2013 to 2023 were considered for this study. Data related to demographics, tooth type, file type, and retrieval were documented in an Excel sheet. Eight prognostic factors assumed to influence the retrieval were analyzed in this study. The secondary aim was to compare the pattern of SEI and retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files. Retrieval was attempted by a senior endodontist under the dental operating microscope. Various ultrasonic tips and a Broken Tool Removal loop system were used during retrieval. Simple descriptive statistics were performed. Binomial logistic regression was done to identify the effect of the eight prognostic factors on the retrieval outcome.
Results
A total of 190 SEI was reported. SEI occurred more often in posterior teeth than anterior teeth, mandibular arch than maxillary arch, and in larger files than smaller files. Separation occurred more often in the apical third compared to the other levels. Retrieval was attempted in 88 cases and successful in 70 cases (79.5%). The larger taper and apical position of the SEI negatively influenced the retrieval by 1.4 and 8.7 times, respectively.
Conclusions
Retrieval of SEI was successful in the majority of the cases. An increase in taper and apically placed SEI negatively impacted the retrieval. There was no difference in the pattern of separation nor retrievability between conventional nickel-titanium files and newer generation heat-treated nickel-titanium files.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness of microscope-assisted root canal treatment in permanent posterior teeth: A retrospective cohort study
Ya-Ching Chang, Ting-Ya Wang
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 157: 105771. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Detection of Separated Root Canal Instruments in Panoramic Radiographs Using a U2-Net Architecture
Nildem İnönü, Umut Aksoy, Dilan Kırmızı, Seçil Aksoy, Nurullah Akkaya, Kaan Orhan
Diagnostics.2025; 15(14): 1744. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF INTRACANAL SEPARATED INSTRUMENTS: FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO ENDODONTIC FILE SEPARATION — A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Tareq Hajaj, Paul Freiman , Serban Talpos Niculescu , Mihai Rominu , Tiberiu Hosszu , Ioana Veja
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2025; 17(2): 993. CrossRef
-
6,348
View
-
312
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
The influence of sodium hypochlorite concentration on the fibrin structure of human blood clots and transforming growth factor-beta 1 release: an ex vivo study
-
Anisha Mishra, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e42. Published online October 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
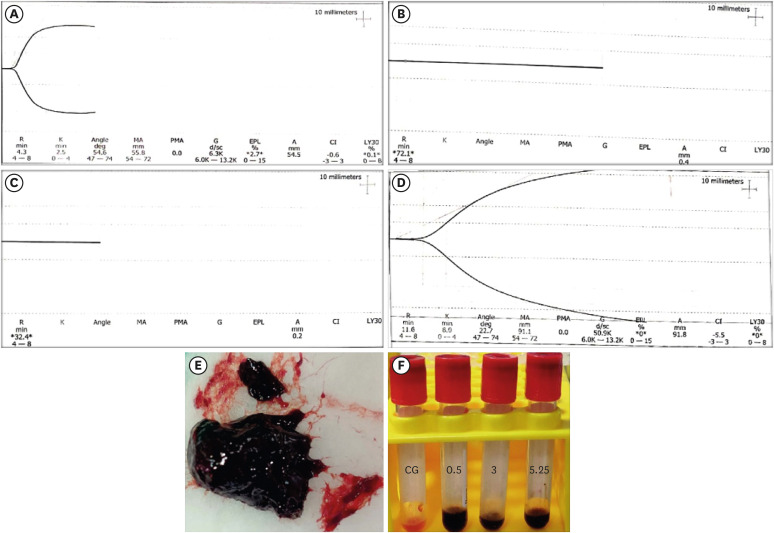
- Objective
This study investigated the effects of various concentrations of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) on human whole-blood clotting kinetics, the structure of the blood clots formed, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 release. Materials and MethodsHuman whole blood was collected from 5 healthy volunteers and divided into 4 groups: CG (control, 0.5 mL of blood), BN0.5 (0.5 mL of blood with 0.5 mL of 0.5% NaOCl), BN3 (0.5 mL of blood with 0.5 mL of 3% NaOCl), and BN5.25 (0.5 mL of blood with 0.5 mL of 5.25% NaOCl). The effects of NaOCl on clotting kinetics, structure of fibrin and cells, and release of TGF-β1 were assessed using thromboelastography (TEG), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and enzyme-linked immunosobent assay, respectively. Statistical analysis was conducted using the Kruskal Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests, followed by the post hoc Dunn test. A p value < 0.05 indicated statistical significance. ResultsThe blood samples in BN0.5 and BN3 did not clot, whereas the TEG of BN5.25 showed altered clot formation. Samples from the CG and BN3 groups could only be processed with SEM, which showed that the latter lacked fibrin formation and branching of fibers, as well as clumping of red blood cells with surface roughening and distortion. TGF-β1 release was significantly highest in BN3 when all groups were compared to CG (p < 0.05). ConclusionsEach concentration of NaOCl affected the release of TGF-β1 from blood clots and altered the clotting mechanism of blood by affecting clotting kinetics and cell structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cytotoxic Effects of Synthetic and Herbal Endodontic Irrigants on Human Red Blood Cells: An In Vitro Study
Panna Mangat, Bhaviya Chandel, Mampi Biswas, Sara Trivedy, Akshata Gupta, Nayan Shree, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,434
View
-
28
Download
-
1
Crossref
|