-
Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
-
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e13. Published online March 18, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e13
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
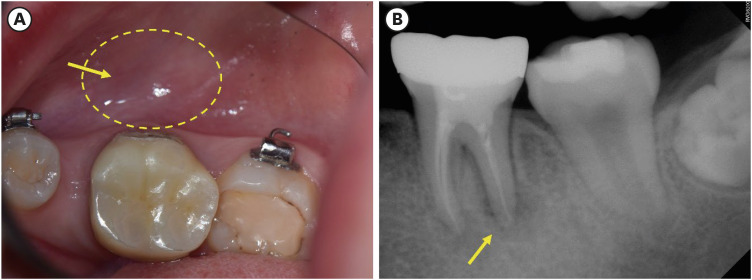
Chronic osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis, known as Garre’s osteomyelitis, is a type of osteomyelitis characterized by a distinctive gross thickening of the periosteum of bones. Peripheral reactive bone formation can be caused by mild irritation or infection. Garre’s osteomyelitis is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and the mandible is more affected than the maxilla. The following is a case report of a 12-year-old female patient with Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible due to an infection of a root canal-treated tooth. Without surgical intervention, the patient’s symptoms were relieved through nonsurgical root canal re-treatment with long-term calcium hydroxide placement. A cone-beam computed tomography image obtained 6 months after treatment completion displayed complete healing of the periapical lesion and resolution of the peripheral reactive buccal bone. Due to the clinical features of Garre's osteomyelitis, which is characterized by thickening of the periosteum, it can be mistaken for other diseases such as fibrous dysplasia. It is important to correctly diagnose Garre's osteomyelitis based on its distinctive clinical features to avoid unnecessary surgical intervention, and it can lead to minimally invasive treatment options. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Focal osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis
Zarah Yakoob
South African Dental Journal.2025; 79(09): 508. CrossRef
-
865
View
-
49
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Buckling resistance, torque, and force generation during retreatment with D-RaCe, HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo retreatment files
-
Yoojin Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e10. Published online February 6, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e10
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
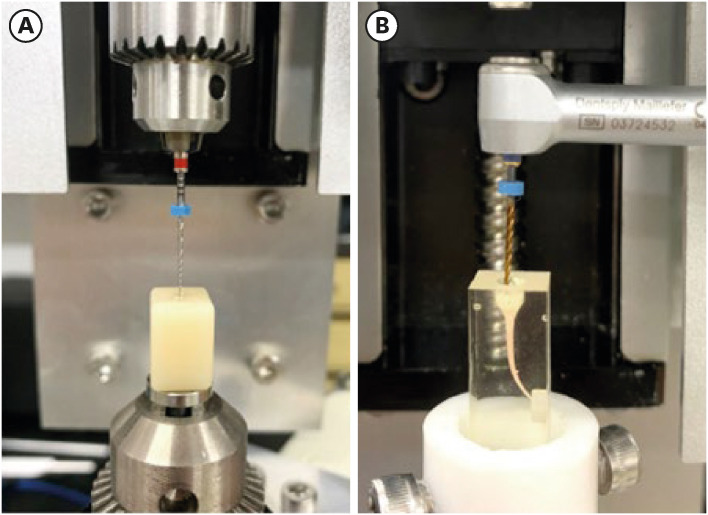
This study compared the buckling resistance of 3 nickel-titanium (NiTi) retreatment file systems and the torque/force generated during retreatment. Materials and MethodsThe buckling resistance was compared among the D-RaCe (DR2), HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo R25/05 retreatment systems. J-shaped canals within resin blocks were prepared with ProTaper NEXT X3 and obturated by the single-cone technique with AH Plus. After 4 weeks, 4 mm of gutta-percha in the coronal aspect was removed with Gates-Glidden drills. Retreatment was then performed using DR1 (size 30, 10% taper) followed by DR2 (size 25, 4% taper), HyFlex Remover (size 30, 7% taper), or Mtrwo R25/05 (size 25, 5% taper) (15 specimens in each group). Further apical preparation was performed with WaveOne Gold Primary. The clockwise torque and upward force generated during retreatment were recorded. After retreatment, resin blocks were examined using stereomicroscopy, and the percentage of residual filling material in the canal area was calculated. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance with the Tukey test. ResultsThe HyFlex Remover files exhibited the greatest buckling resistance (p < 0.05), followed by the Mtwo R25/05. The HyFlex Remover and Mtwo R25/05 files generated the highest maximum clockwise torque and upward force, respectively (p < 0.05). The DR1 and DR2 files generated the least upward force and torque (p < 0.05). The percentage of residual filling material after retreatment was not significantly different between file systems (p > 0.05). ConclusionsNiTi retreatment instruments with higher buckling resistance generated greater clockwise torque and upward force.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation and fracture resistance of endodontically retreated teeth using hyflex remover, Mtwo, and ProTaper retreatment file systems: An in vitro study
Isha Singh, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Pallavi Sharma, Kunal Bedi, Priyanka Rani, Swapnil Vats
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Comparison of torsional, bending, and buckling resistances of different nickel-titanium glide path files
Feyyaz Çeliker, İrem Çetinkaya
Matéria (Rio de Janeiro).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the impact of obturation techniques, kinematics and irrigation protocols on apical debris extrusion and time required in endodontic retreatment
Eugenio Pedullà, Francesco Iacono, Martina Pitrolo, Giovanni Barbagallo, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Chiara Pirani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 623. CrossRef
-
281
View
-
10
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
A case report of multiple bilateral dens invaginatus in maxillary anteriors
-
Shin Hye Chung, You-Jeong Hwang, Sung-Yeop You, Young-Hye Hwang, Soram Oh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e39. Published online October 21, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e39
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
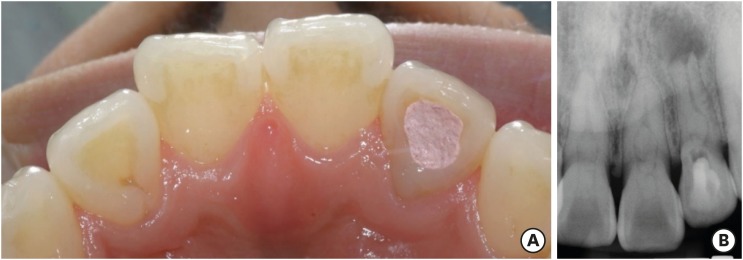
The present report presents a case of dens invaginatus (DI) in a patient with 4 maxillary incisors. A 24-year-old female complained of swelling of the maxillary left anterior region and discoloration of the maxillary left anterior tooth. The maxillary left lateral incisor (tooth #22) showed pulp necrosis and a chronic apical abscess, and a periapical X-ray demonstrated DI on bilateral maxillary central and lateral incisors. All teeth responded to a vitality test, except tooth #22. The anatomic form of tooth #22 was similar to that of tooth #12, and both teeth had lingual pits. In addition, panoramic and periapical X-rays demonstrated root canal calcification, such as pulp stones, in the maxillary canines, first and second premolars, and the mandibular incisors, canines, and first premolars bilaterally. The patient underwent root canal treatment of tooth #22 and non-vital tooth bleaching. After a temporary filling material was removed, the invaginated mass was removed using ultrasonic tips under an operating microscope. The working length was established, and the root canal was enlarged up to #50 apical size and obturated with gutta-percha and AH 26 sealer using the continuous wave of condensation technique. Finally, non-vital bleaching was performed, and the access cavity was filled with composite resin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Endodontic Management of Dens in Dente – A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series
Sanket Dilip Aras, Anamika Chetan Borkar, Sonal Kale, Sayali Maral, Prakriti Jaggi, Shailendra Sonawane
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(1): 17. CrossRef - Dens invaginatus of fourteen teeth in a pediatric patient
Momoko Usuda, Tatsuya Akitomo, Mariko Kametani, Satoru Kusaka, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Pediatric Dental Journal.2023; 33(3): 240. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Maturation of an Immature Dens Invaginatus Despite Unsuccessful Revitalization Procedure: A Case Report and Recommendations for Educational Purposes
Julia Ludwig, Marcel Reymus, Alexander Winkler, Sebastian Soliman, Ralf Krug, Gabriel Krastl
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(2): 47. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Infraorbital Space Infection Secondary to Type III B Dens Invaginatus: A Case Report
Ashima Goyal, Aditi Kapur, Manoj A Jaiswal, Gauba Krishan, Raja Raghu, Sanjeev K Singh
Journal of Postgraduate Medicine, Education and Research.2022; 56(4): 192. CrossRef
-
341
View
-
9
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Endodontic biofilms: contemporary and future treatment options
-
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Soram Oh, A-Reum Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e7. Published online January 31, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Apical periodontitis is a biofilm-mediated infection. The biofilm protects bacteria from host defenses and increase their resistance to intracanal disinfecting protocols. Understanding the virulence of these endodontic microbiota within biofilm is essential for the development of novel therapeutic procedures for intracanal disinfection. Both the disruption of biofilms and the killing of their bacteria are necessary to effectively treat apical periodontitis. Accordingly, a review of endodontic biofilm types, antimicrobial resistance mechanisms, and current and future therapeutic procedures for endodontic biofilm is provided. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Anti-Biofilm Property of Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Anil Kumar Ramachandran, Priyanka Kodaganallur Pitchumani, Blessy Mathai, Davis C Thomas
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Sacrificial Antibacterial Coating with Photothermal Response for Inhibiting Implant Infection
Jinglin Zhang, Aijian Cao, Lizhen Chen, Dongliang Huo, Jingxian Zhang, Langhuan Huang, Shaozao Tan
ACS Applied Nano Materials.2024; 7(23): 26907. CrossRef - Biofilm in Endodontic Infection and its Advanced Therapeutic Options – An Updated Review
Srilekha Jayakumar, Dinesh Sridhar, Bindu M. John, Karthikeyan Arumugam, Prashanth Ponnusamy, Hema Pulidindi
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1104. CrossRef - Analysis of the chemical interaction of polyhexanide with endodontic irrigants
Z. S. Zurab, Yu. A. Generalova, A. A. Kulikova, A. Yu. Umarov, F. V. Badalov, A. Wehbe, E. M. Kakabadze
Endodontics Today.2024; 22(4): 319. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of three engineered multispecies endodontic biofilms on a dentinal disk substrate
Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallasy, May Mallah, Carla Zogheib
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of enterococcus faecalis growth in different conditions on dentinal substrate
Wajih Hage, Dolla Karam Sarkis, Mireille Kallassy, May Mallah, Carla Zogheib
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacteria associated with apical periodontitis promotes in vitro the differentiation of macrophages to osteoclasts
A. P. Torres-Monjarás, R. Sánchez-Gutiérrez, B. Hernández-Castro, L. González-Baranda, D. L. Alvarado-Hernández, A. Pozos-Guillén, A. Muñoz-Ruiz, V. Méndez-González, R. González-Amaro, M. Vitales-Noyola
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 3139. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of Kerr pulp canal sealer (EWT) in combination with 10% amoxicillin on Enterococcus faecalis: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Madhureema De Sarkar, Kundabala Mala, Suchitra Shenoy Mala, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu, Srikant Natarajan, Neeta Shetty, Priyanka Madhav Kamath, Manuel Thomas
F1000Research.2023; 12: 725. CrossRef - Combined effect of electrical energy and graphene oxide on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Myung-Jin LEE, Mi-Ah KIM, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 844. CrossRef - Innovative Curved-Tip Reactor for Non-Thermal Plasma and Plasma-Treated Water Generation: Synergistic Impact Comparison with Sodium Hypochlorite in Dental Root Canal Disinfection
Raúl Arguello-Sánchez, Régulo López-Callejas, Benjamín Gonzalo Rodríguez-Méndez, Rogelio Scougall-Vilchis, Ulises Velázquez-Enríquez, Antonio Mercado-Cabrera, Rosendo Peña-Eguiluz, Raúl Valencia-Alvarado, Carlo Eduardo Medina-Solís
Materials.2023; 16(22): 7204. CrossRef - Impact of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on the bond-strength and penetration of endodontic sealers: A systematic review
Khalid H Almadi
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 41: 103249. CrossRef - Apical periodontitis in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: influence of anatomy and quality of root canal treatment, a CBCT study
Samantha Jannone Carrion, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential relationship between clinical symptoms and the root canal microbiomes of root filled teeth based on the next‐generation sequencing
Yajing Hou, Liu Wang, Lan Zhang, Xuelian Tan, Dingming Huang, Dongzhe Song
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(1): 18. CrossRef - Efficacy of 6% Sodium Hypochlorite on Infectious Content of Teeth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis
Rodrigo Arruda-Vasconcelos, Marlos Barbosa-Ribeiro, Lidiane M. Louzada, Beatriz I.N. Lemos, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Caio C.R. Ferraz, José F.A. Almeida, Marina A. Marciano, Brenda P.F. A. Gomes
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(2): 179. CrossRef - Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in endodontics: a narrative review
Davy Aubeux, Ove A. Peters, Sepanta Hosseinpour, Solène Tessier, Valérie Geoffroy, Fabienne Pérez, Alexis Gaudin
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of curcumin-mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy associated to different chelators against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Daniela Alejandra Cusicanqui Méndez, Maricel Rosario Cardenas Cuéllar, Victor Feliz Pedrinha, Evelyn Giuliana Velásquez Espedilla, Flaviana Bombarda de Andrade, Patrícia de Almeida Rodrigues, Thiago Cruvinel
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2021; 35: 102464. CrossRef - Effectiveness of D,L‐2‐hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA) and alpha‐mangostin against endodontopathogenic microorganisms in a multispecies bacterial–fungal biofilm in anex vivotooth model
Warat Leelapornpisid, Lilyann Novak‐Frazer, Alison Qualtrough, Riina Rautemaa‐Richardson
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(12): 2243. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of a New Combination of Three Antibiotic Paste Against Common Endodontic Pathogens
Prasanna Dahake, Nilima Thosar
Journal of Islamic Dental Association of IRAN.2021; 33(3): 58. CrossRef - Effect of using diode laser on Enterococcus faecalis and its lipoteichoic acid (LTA) in chronic apical periodontitis
Zhaohui Zou, Junu Bhandari, Baiyan Xiao, Xiaoyue Liang, Yu Zhang, Guohui Yan
Lasers in Medical Science.2021; 36(5): 1059. CrossRef - Prevalence of Bacteria of Genus Actinomyces in Persistent Extraradicular Lesions—Systematic Review
Mario Dioguardi, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Lorenzo Lo Muzio, Giuseppe Troiano
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 457. CrossRef - Evaluation of in vitro biofilm elimination of Enterococcus faecalis using a continuous ultrasonic irrigation device
Jennifer Galván-Pacheco, Marlen Vitales-Noyola, Ana M. González-Amaro, Heriberto Bujanda-Wong, Antonio Aragón-Piña, Verónica Méndez-González, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Journal of Oral Science.2020; 62(4): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of the use of d-enantiomeric and l-enantiomeric antimicrobial peptides incorporated in a calcium-chelating irrigant against Enterococcus faecalis root canal wall biofilms
Wei-hu Ye, Lara Yeghiasarian, Christopher W. Cutler, Brian E. Bergeron, Stephanie Sidow, Hockin H.K. Xu, Li-na Niu, Jing-zhi Ma, Franklin R. Tay
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 91: 103231. CrossRef
-
578
View
-
30
Download
-
23
Crossref
-
Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
-
Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):12-21. Published online December 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.12
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the effects of three acids on the microhardness of set mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and root dentin, and cytotoxicity on murine macrophage. Materials and MethodsOrthoMTA (BioMTA) was mixed and packed into the human root dentin blocks of 1.5 mm diameter and 5 mm height. Four groups, each of ten roots, were exposed to 10% citric acid (CA), 5% glycolic acid (GA), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and saline for five minutes after setting of the OrthoMTA. Vickers surface microhardness of set MTA and dentin was measured before and after exposure to solutions, and compared between groups using one-way ANOVA with Tukey test. The microhardness value of each group was analyzed using student t test. Acid-treated OrthoMTA and dentin was examined by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Cell viability of tested solutions was assessed using WST-8 assay and murine macrophage. ResultsThree test solutions reduced microhardness of dentin. 17% EDTA demonstrated severe dentinal erosion, significantly reduced the dentinal microhardness compared to 10% CA (p = 0.034) or 5% GA (p = 0.006). 10% CA or 5% GA significantly reduced the surface microhardness of set MTA compared to 17% EDTA and saline (p < 0.001). Acid-treated OrthoMTA demonstrated microporous structure with destruction of globular crystal. EDTA exhibited significantly more cellular toxicity than the other acidic solutions at diluted concentrations (0.2, 0.5, 1.0%). ConclusionsTested acidic solutions reduced microhardness of root dentin. Five minute's application of 10% CA and 5% GA significantly reduced the microhardness of set OrthoMTA with lower cellular cytotoxicity compared to 17% EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - Effect of Various Acid Solutions as an Aid in Removing the OrthoMTA-Based Root Canal Filling
Naveen Chhabra, Abhishek Parolia
Materials.2023; 16(13): 4535. CrossRef - Effect of Glycolic Acid, Maleic Acid, and EDTA in the Removal of Smear Layer from Root Canal Dentin
Tarini Mullick, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the effect of various chelating agents on the microhardness of root canal dentin: An in vitro study
Mineet Kaul, Zinnie Nanda, Kranthikumar Reddy, Rahul Deore, Divya Mandlecha, Esha Jaiswal
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Influence of Acidic Environmental Conditions on Push-Out Bonding Strength of Four Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Beliz Özel, Raif Erişen, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the microhardness of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and TotalFill Bioceramic Putty
Jacklyn H.R. Chu, Kalie Y. Chia, Alexander L. Qui, Alex Moule, William N. Ha
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 33. CrossRef - Pre-application of dentin bonding agent prevents discoloration caused by mineral trioxide aggregate
Yoo-Lim Choi, Young-Eun Jang, Bom Sahn Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Yemi Kim
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolic acid as the final irrigant in endodontics: Mechanical and cytotoxic effects
Yuri Dal Bello, Hisadora Fracaro Porsch, Ana Paula Farina, Matheus Albino Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Ana Karina Bedran-Russo, Doglas Cecchin
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 100: 323. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 246. CrossRef
-
275
View
-
4
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
Analysis of para-chloroaniline after chemical interaction between alexidine and sodium hypochlorite using mass spectrometry: A preliminary study
-
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Soram Oh, Sang-Min Lim, Yu Gu, Kee-Yeon Kum
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):295-301. Published online July 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.295
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The purposes of this study were firstly to investigate the any formation of precipitate after interaction between ALX and NaOCL and secondarily to analyze the PCA formation by using time of flight secondary ion mass (TOF-SIM) spectrometry. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed for the mixture of 0.5% ALX and 5.25% NaOCl. As controls, 2.5% CHX with 5.25% NaOCl and 1% PCA solutions were used. Any formation of precipitates in 10 tested solutions was evaluated by naked eye. Results of mass spectrum showed that the typical peak of PCA was not detected in mixed solution of ALX and NaOCl, whereas CHX/NaOCl mixture showed the same peak that found in the PCA spectrum. Precipitate formation was only observed in CHX/NaOCL mixture. The present TOF-SIM spectrometry results indicated that ALX can be a useful root canal irrigant combined with NaOCl during canal instrumentation. Further study is necessary to confirm the antimicrobial effect of ALX against endodontic pathogen before its clinical application as an endodontic irrigant. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Chemical Interaction of Alexidine and Sodium Hypochlorite
Hyeon-Sik Kim, Qiang Zhu, Seung-Ho Baek, Il-Young Jung, Won-Jun Son, Seok-Woo Chang, Woocheol Lee, Yu Gu, Yoon Lee, Sung-Tae Hong, Kwang-Shik Bae, Ji-Woong Kim, Kun Cho, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2012; 38(1): 112. CrossRef
-
145
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
|