-
Effects of 3 different light-curing units on the physico-mechanical properties of bleach-shade resin composites
-
Azin Farzad, Shahin Kasraei, Sahebeh Haghi, Mahboubeh Masoumbeigi, Hassan Torabzadeh, Narges Panahandeh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e9. Published online February 7, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e9
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
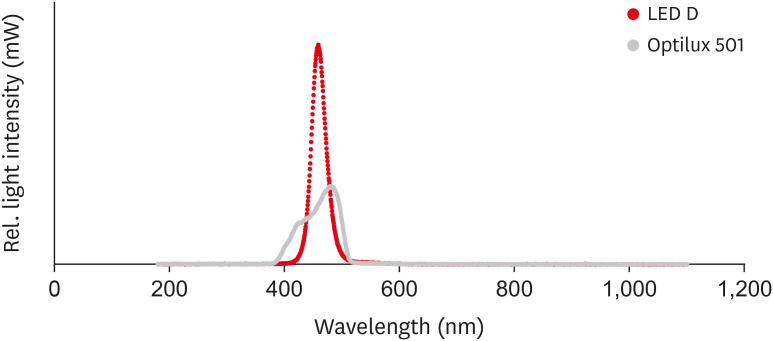
This study investigated the microhardness, flexural strength, and color stability of bleach-shade resin composites cured with 3 different light-curing units. Materials and MethodsIn this in vitro experimental study, 270 samples were fabricated of bleach and A2 shades of 3 commercial resin composites (Point 4, G-aenial Anterior, and Estelite Sigma Quick). Samples (n = 5 for each trial) were cured with Bluephase N, Woodpecker LED.D, and Optilux 501 units and underwent Vickers microhardness and flexural strength tests. The samples were tested after 24 hours of storage in distilled water. Color was assessed using a spectrophotometer immediately after preparation and 24 hours after curing. Data were analyzed using 3-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test (p ≤ 0.001). ResultsSamples cured with Optilux exhibited the highest and those cured with LED.D exhibited the lowest microhardness (p = 0.023). The bleach shade of Point 4 composite cured with Optilux displayed the highest flexural strength, while the same composite and shade cured with Sigma Quick exhibited the lowest (p ≤ 0.001). The color change after 24 hours was greatest for the bleach shade of G-aenial cured with Bluephase N and least for the A2 shade of Sigma Quick cured with Optilux (p ≤ 0.001). ConclusionsLight curing with polywave light-emitting diode (LED) yielded results between or statistically similar to those of quartz-tungsten-halogen and monowave LED in the microhardness and flexural strength of both A2 and bleach shades of resin composites. However, the brands of light-curing devices showed significant differences in color stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mechanical Behaviour of Novel Nanohybrid Resin Composite Using Two Light Cure Systems
Ghada H. Naguib, Jumana Mazhar, Abeer Alnowaiser, Abdulghani Mira, Hisham Mously, Rabab Aljawi, Samar H. Abuzinadah, Mohamed T. Hamed
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(2): 1136. CrossRef - Repair Bond Strength of Aged Composite: Effect of Thermocycling and Surface Treatment
Sina Yarmoradian, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani, Elham Ahmadi, Niyousha Rafeie, Mahdi Abbasi, Nastaran Dabiri Shahabi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(3): 228. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Depth of Cure by Microhardness of Bulk-Fill Composites with Monowave and Polywave LED Light-Curing Units
Socratis Thomaidis, Dimitris Kampouropoulos, Maria Antoniadou, Afrodite Kakaboura
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11532. CrossRef - Effect of hard segment chemistry and structure on the self‐healing properties of UV‐curable coatings based on the urethane acrylates with built‐in Diels–Alder adduct
Paulina Bednarczyk, Karolina Mozelewska, Małgorzata Nowak, Joanna Klebeko, Joanna Rokicka, Paula Ossowicz‐Rupniewska
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dental Bleaching Agents on the Surface Roughness of Dental Restoration Materials
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mihaela Jana Tuculina, Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Claudiu Nicolicescu, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Cristiana Petcu, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Ana Maria Rîcă, Ruxandra Voinea-Georgescu
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1067. CrossRef - Effect of Polywave and Monowave Light Curing Units on Color Change of Composites Containing Trime-thylbenzoyl-Diphenyl-Phosphine Before and After Aging
Negar Madihi, Maryam Hoorizad ganjkar, Negin Nasoohi, Ali Kaboudanian Ardestani
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 249. CrossRef
-
2,013
View
-
34
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
-
Bond strength of resin cement to CO2 and Er:YAG laser-treated zirconia ceramic
-
Shahin Kasraei, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Bijan Heidari, Fariborz Vafaee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):296-302. Published online August 25, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.296
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
It is difficult to achieve adhesion between resin cement and zirconia ceramics using routine surface preparation methods. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of CO2 and Er:YAG laser treatment on the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics. Materials and MethodsIn this in-vitro study 45 zirconia disks (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) were assigned to 3 groups (n = 15). In control group (CNT) no laser treatment was used. In groups COL and EYL, CO2 and Er:YAG lasers were used for pretreatment of zirconia surface, respectively. Composite resin disks were cemented on zirconia disk using dual-curing resin cement. Shear bond strength tests were performed at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min after 24 hr distilled water storage. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey's HSD tests. ResultsThe means and standard deviations of shear bond strength values in the EYL, COL and CNT groups were 8.65 ± 1.75, 12.12 ± 3.02, and 5.97 ± 1.14 MPa, respectively. Data showed that application of CO2 and Er:YAG lasers resulted in a significant higher shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics (p < 0.0001). The highest bond strength was recorded in the COL group (p < 0.0001). In the CNT group all the failures were adhesive. However, in the laser groups, 80% of the failures were of the adhesive type. ConclusionsPretreatment of zirconia ceramic via CO2 and Er:YAG laser improves the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic, with higher bond strength values in the CO2 laser treated samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Impact of Surface Roughness and Different Pre-treatments on the Shear Bond Strength of Super-translucent Multi-layered Zirconia to Adhesive Resin Cement: An In Vitro Study
Manar Almousli
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Surface Roughening Techniques on Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Monolithic Zirconia: In Vitro Study
Nehal F Albelasy, Ahmad M Hafez, Abdullah S Alhunayni
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(12): 1104. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of etching with ytterbium fiber laser on the bond strength, color stability, and fracture analysis of lithium disilicate ceramics to bovine teeth: an in vitro study
Göknil Alkan Demetoğlu, Esra Talay Çevlïk
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Shear bond strength of multilayered zirconia to adhesive resin cement after CO2 laser surface treatment (an in vitro study)
Abdelrahman Badran, Reem Gabr
Lasers in Dental Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Different surface treatments and adhesive monomers for zirconia-resin bonds: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Xinyang Li, Shengjie Liang, Masanao Inokoshi, Shikai Zhao, Guang Hong, Chenmin Yao, Cui Huang
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 175. CrossRef - The impact of CO2 laser on the bond strength of translucent zirconia and traditional zirconia with the resin cement: In vitro study
Rima Saker, Bashar Zleik
Balkan Journal of Dental Medicine.2024; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Evaluation of Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Prepared with Different Surface Roughening Methods: An In Vitro Study
Marwa A Tawfik, Abdullah M Fayyadh, Mohammed A Elbialy
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(8): 766. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser and sllica-coating on zirconia framework-veneering ceramic bonding, surface chemistry and crystallographic changes
Tevfik Yavuz, Muhammed Ali Aslan, Yusuf Ziya Akpinar, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Nadin Al-Haj Husain, Mutlu Özcan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(6): 1059. CrossRef - In vitro comparative study between adhesion forces obtained on zirconia ceramic micromechanically treated with femtosecond laser (1027 nm), carbon dioxide laser (10,600 nm), and aluminum-oxide particles
Ignasi Piulachs, Luis Giner-Tarrida, Antoni España-Tost, Josep Arnabat-Dominguez, Camilo Florian
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating in Combination with Physical Modifications on Microshear Bond Strength of Zirconia to Resin Cement
Faezeh Atri, Vanya Rasaie, Sakineh Nikzad Jamnani, Saba Mohammadi, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Effect of Zirconia Surface Treatment with CO2 and Nd:YAG Lasers on Shear Bond Strength between Zirconia Frameworks and Porcelain Veneers
Bijan Heidari, Hadi Ranjzad, Farzane Ostovar Rad, Amirreza Hendi, Zahra Ghorbani
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(10): 1026. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Three Surface Treatments on the Bond Strength of Zirconia to Resin-luting Agents: An In Vitro Study
Abhinav Sharma, Arka Swarnakar, Angana Pal Swarnakar, Himadri Sekhar Pal, Shivani Tyagi, Pragati Rawat
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(9): 883. CrossRef - Surface modification of zirconia or lithium disilicate-reinforced glass ceramic by laser texturing to increase the adhesion of prosthetic surfaces to resin cements: an integrative review
Júlio C. M. Souza, Angelo Raffaele-Esposito, Oscar Carvalho, Filipe Silva, Mutlu Özcan, Bruno Henriques
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3331. CrossRef - A Shift to Synergistic Surface Treatment Using Laser to Enhance the Bonding of Zirconia to Veneering Ceramic: An In Vitro Study
N Kiran Kumar, Anoop Nair, Savitha B Naik, Annie Swathisha, CH Laxmi Priya, HS Preetham, V Shylaja
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 23(1): 37. CrossRef - Effects of cold atmospheric plasma treatment on resin bonding to high-translucency zirconia ceramics
Xin-Yi YE, Ming-Yue LIU, Jing LI, Xiao-Qiang LIU, Yu LIAO, Ling-Lu ZHAN, Xiao-Ming ZHU, He-Ping LI, Jianguo TAN
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 896. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser zirconia surface treatment on cement shear bond strength
Elif Yeğin, Tevfik Yavuz, Muhammed Ali Aslan, Mustafa Hayati Atala, John A. Sorensen, Hamdi Şükür Kılıç
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2022; 36(18): 1951. CrossRef - Effects of different frequencies of Er:YAG laser on the bonding properties of zirconia ceramic
Hong Zhu, Hui-hui Tao, Meng Wei, Pan Liu, Lu Yuan, Yan-nan Zhang, Bo Wang, Jian-feng Chen
Lasers in Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Different Surface Treatments on Repair Bond Strength of CAD/CAM Resin-Matrix Ceramics
Semih Arkoy, Mutahhar Ulusoy
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6314. CrossRef - Effect of different laser treatments on the shear bond strength of zirconia ceramic to resin cement
Mahnaz Hatami, Mohammadhossein Lotfi-Kamran, Abdolrahim Davari, Meisam Molazem
Dental Research Journal.2021; 18(1): 56. CrossRef - Effect of laser irradiation on bond strength between zirconia and resin cement or veneer ceramic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
SandroBasso Bitencourt, LetíciaChaves Ferreira, LeticiaCerri Mazza, DanielaMicheline dos Santos, AldierisAlves Pesqueira, LeticiaHelena Theodoro
The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society.2021; 21(2): 125. CrossRef - Effect of laser irradiation on the adhesion of resin-based materials to zirconia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato, Oscar Carvalho, Mutlu Özcan, Márcio Celso Fredel, Filipe Samuel Silva
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(10): 1035. CrossRef - Laser surface texturing of zirconia-based ceramics for dental applications: A review
Jide Han, Fei Zhang, Bart Van Meerbeek, Jozef Vleugels, Annabel Braem, Sylvie Castagne
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 123: 112034. CrossRef - Effect of Nd:YAG, Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation, and Adjunctive Photodynamic Therapy on Push‐Out Bond Strength of Zirconia Posts to Radicular Dentin
Freah Alshammary, Mohmed I. Karobari, Ali A. Assiry, Anand Marya, Gul M. Shaikh, Ammar A. Siddiqui, Mohammad K. Alam, Iole Vozza
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser and silica coating on the bond strength of zirconia ceramic
Hongbo Zhou, Chen Yu, Cheng Qi, Dingxiang Qiu, Shusen Zhang, Jilin Li, Youwang Hu
Advances in Applied Ceramics.2020; 119(5-6): 276. CrossRef - Laser-Milled Microslits Improve the Bonding Strength of Acrylic Resin to Zirconia Ceramics
Saiji Shimoe, Tzu-Yu Peng, Yuki Wakabayashi, Hiroto Takenaka, Shogo Iwaguro, Masato Kaku
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 817. CrossRef - Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal/resin luting agent bond strength: Influence of Titanium dioxide nanotubes addition in both materials
Ana Paula Rodrigues Magalhães, Carla Müller Ramos-Tonello, Mateus Zamora Galli, Orisson Ponce Gomes, Leandro Edgar Pacheco, Carlos Alberto Fortulan, Paulo Noronha Lisboa-Filho, Rafael Francisco Lia Mondelli, Adilson Yoshio Furuse, Ana Flávia Sanches Borge
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2020; 64(4): 408. CrossRef - Exploring the use of pulsed erbium lasers to retrieve a zirconia crown from a zirconia implant abutment
Ahmed Elkharashi, Kinga Grzech-Leśniak, Janina Golob Deeb, Aous A. Abdulmajeed, Sompop Bencharit, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(6): e0233536. CrossRef - Evaluation of zirconia surface roughness after aluminum oxide airborne-particle abrasion and the erbium-YAG, neodymium-doped YAG, or CO2 lasers: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Felipe V. Martins, Cláudia T. Mattos, Wayne J.B. Cordeiro, Edgard M. Fonseca
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2019; 121(6): 895. CrossRef - Effect of thermal and mechanical cycles on shear bond strength of zirconia core to porcelain veneer under different surface treatments
Tahereh Ghaffari, Elnaz Moslehifard, Mehrnaz Motiei
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(3): 227. CrossRef - Ultrashort-pulse laser as a surface treatment for bonding between zirconia and resin cement
Mahmood Abu Ruja, Grace M. De Souza, Yoav Finer
Dental Materials.2019; 35(11): 1545. CrossRef - Adhesion behavior of conventional and high‐translucent zirconia: Effect of surface conditioning methods and aging using an experimental methodology
Edwin Ruales‐Carrera, Paulo F. Cesar, Bruno Henriques, Márcio C. Fredel, Mutlu Özcan, Claudia A. M. Volpato
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 31(4): 388. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Resin Cement and Glass Ionomer to Nd:YAG Laser‐Treated Zirconia Ceramics
Nafiseh Asadzadeh, Foojan Ghorbanian, Farzaneh Ahrary, Hamidreza Rajati Haghi, Reza Karamad, Amir Yari, Abdollah Javan
Journal of Prosthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation on the Push-Out Bond Strength of Zirconia and Glass Fiber Posts with Radicular Dentin
Raneem S. Alofi, Ibraheem F. Alshiddi, Yasser F. AlFawaz, Abdulaziz Alsahhaf, Khulud Abdulrahman Al-Aali, Tariq Abduljabbar, Fahim Vohra
International Journal of Biomaterials.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Er: YAG Laser, Sandblast and Several Types of Universal Bonding on Shear Bond Strength of Zirconia Ceramic to Composite Resin
Mahdi Akbarzadeh, Loghman R Sofi, Reza Fekrazad, Marjan Maleki
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(10): 1246. CrossRef - The effects of lasers on bond strength to ceramic materials: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Verónica García-Sanz, Vanessa Paredes-Gallardo, Omel Mendoza-Yero, Miguel Carbonell-Leal, Alberto Albaladejo, José María Montiel-Company, Carlos Bellot-Arcís, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(1): e0190736. CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on the shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic and metal alloy
Munir Tolga Yucel, Ismail Kilic, Yener Okutan, Elif Sumeyye Tobi, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Abdullah Kepceoglu, Mustafa Borga Donmez
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2018; 32(20): 2232. CrossRef - Effect of femtosecond laser beam angle and formed shape on surface roughness and shear bond strength between zirconia and resin cement
Munir Tolga Yucel, Ismail Kilic, Hamdi Sukur Kilic, Yasemin Gundogdu, Yener Okutan
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2018; 32(12): 1265. CrossRef - The effect of subpressure on the bond strength of resin to zirconia ceramic
Yong-Mei Li, Rui-Shen Zhuge, Zu-Tai Zhang, Yue-Ming Tian, Ning Ding, Dengshun Miao
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(6): e0179668. CrossRef - Effects of Laser Treatment on the Bond Strength of Differently Sintered Zirconia Ceramics
Doğu Ömür Dede, Murat Yenisey, Nergiz Rona, Figen Öngöz Dede
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2016; 34(7): 276. CrossRef - Zirconia based ceramics, some clinical and biological aspects: Review
Ossama Saleh Abd El-Ghany, Ashraf Husein Sherief
Future Dental Journal.2016; 2(2): 55. CrossRef - Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
Ji-Young Kwak, Hyo-Kyung Jung, Il-Kyung Choi, Tae-Yub Kwon
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - The Effect of Femtosecond Laser Treatment on the Effectiveness of Resin-Zirconia Adhesive: An In Vitro Study
María Vicente Prieto, Ana Luisa Caseiro Gomes, Javier Montero Martín, Alfonso Alvarado Lorenzo, Vicente Seoane Mato, Alberto Albaladejo Martínez
Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences.2016; 7(4): 214. CrossRef - Adhesion to Zirconium Dioxide Used for Dental Reconstructions: Surface Conditioning Concepts, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Mutlu Özcan, Claudia Angela Maziero Volpato
Current Oral Health Reports.2015; 2(4): 190. CrossRef - Shear Bond Strength of MDP-Containing Self-Adhesive Resin Cement and Y-TZP Ceramics: Effect of Phosphate Monomer-Containing Primers
Jin-Soo Ahn, Young-Ah Yi, Yoon Lee, Deog-Gyu Seo
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Preliminary studies on the effects of in situ synthesized polycrystalline particulates on the bonding strength of resin to zirconia ceramic surface
Yueming Tian, Lingling Zhang, Zutai Zhang, Ning Ding, Yan Liu, Guozhong Tian
Applied Surface Science.2015; 357: 961. CrossRef
-
1,735
View
-
10
Download
-
45
Crossref
-
Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus
-
Shahin Kasraei, Lida Sami, Sareh Hendi, Mohammad-Yousef AliKhani, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Zahra Khamverdi
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):109-114. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.109
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
Recurrent caries was partly ascribed to lack of antibacterial properties in composite resin. Silver and zinc nanoparticles are considered to be broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the antibacterial properties of composite resins containing 1% silver and zinc-oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. Materials and MethodsNinety discoid tablets containing 0%, 1% nano-silver and 1% nano zinc-oxide particles were prepared from flowable composite resin (n = 30). The antibacterial properties of composite resin discs were evaluated by direct contact test. Diluted solutions of Streptococcus mutans (PTCC 1683) and Lactobacillus (PTCC 1643) were prepared. 0.01 mL of each bacterial species was separately placed on the discs. The discs were transferred to liquid culture media and were incubated at 37℃ for 8 hr. 0.01 mL of each solution was cultured on blood agar and the colonies were counted. Data was analyzed with Kruskall-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests. ResultsComposites containing nano zinc-oxide particles or silver nanoparticles exhibited higher antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The effect of zinc-oxide on Streptococcus mutans was significantly higher than that of silver (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the antibacterial activity against Lactobacillus between composites containing silver nanoparticles and those containing zinc-oxide nanoparticles. ConclusionsComposite resins containing silver or zinc-oxide nanoparticles exhibited antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Physicochemical and antibacterial evaluation of novel nano α-TCP–AgNPs biocomposites for direct pulp-capping applications
Selviana Wulansari, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Nasrul Wathoni, Rosalina Tjandrawinata, Arief Cahyanto, Moehamad Orliando Roeslan
Frontiers in Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of photoinitiator systems on resin-based composite containing ZnO-nanoparticles
Abdulaziz Alayed, Nikolaos Silikas, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2025; 41(2): 220. CrossRef - Synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant effects of propolis nanoparticles and cinnamon nanostructures in preventive dentistry: Experimental and theoretical approaches
Faeze Hamze, Mahnaz Amiri, Zeinab Sadat Islami, Tayebeh Shamspur, Razieh Razavi, Payam Khazaeli
Phytochemical Analysis.2025; 36(8): 2236. CrossRef - Synthesis of boron nitride@copper oxide‐based light‐curing resin composites: Investigating mechanical and antibacterial properties
Shuya Li, Dawei Liu, Zegang Shi, Wenyi Yu, Tingting Yang, Yufeng Bai, Tianlu He, Tai Peng
Polymer Composites.2025; 46(3): 2073. CrossRef - Long-lasting antimicrobial effect of multipurpose ZnO nanoparticle-loaded dental resins enhanced by blue light photodynamic therapy
Maria Luisa Leite, Patricia Comeau, Ala Zaghwan, Ya Shen, Adriana Pigozzo Manso
Dental Materials.2025; 41(3): 347. CrossRef - Use of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles for the Management of Dental Diseases
Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Anjaneyulu Udduttulla, Veena Wenqing Xu, Kitty Jieyi Chen, Monica Yuqing Zhang, Chun Hung Chu
Nanomaterials.2025; 15(3): 209. CrossRef - Assessment of cytotoxicity of clear aligners coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles
Indu Ravi, Vignesh Kailasam
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2025; 15(2): 262. CrossRef - Emerging developments in plant-based metal nanomaterials for diverse versatile applications - A review
Garima Rana, Vivek Kumar Dhiman, Syed Kashif Ali, Ankush Chauhan, Majid S. Jabir, Suresh Ghotekar
Results in Chemistry.2025; 15: 102231. CrossRef - An in vitro comparative evaluation of silver and chitosan nanoparticles on shear bond strength of nanohybrid composite using different adhesion protocols
Roopadevi Garlapati, Nagesh Bolla, Mayana Aameena Banu, Anila Bandlapally Sreenivasa Guptha, Niharika Halder, Ram Chowdary Basam
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 522. CrossRef - Assessment of the Antimicrobial Properties of Mesoporous Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Against Streptococcus mutans: An In Vitro Investigation
Zahra Jowkar, Shima Askarzadeh, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi, Zahra Fattah, Ali Moaddeli, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of theranostic nanoparticles in dental infectious diseases: A review
Mitra Rostami, Pouria Farahani, Moslem Karimzadeh, Samar Esmaelian, Abbas Fadel Hussein, Kamyar Nasiri, Hareth A. Alrikabi, Naghmeh Shenasa
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2025; 112: 107223. CrossRef - Effect on hygroscopic characteristics of n‐ZnO additions to resin composite
Abdulaziz Alayed, Nikolaos Silikas, David C. Watts
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Applications of Nanoparticles in Endodontics as an Antibacterial Agent: A Mini-review
Mina Saliminasab
Advances in Applied NanoBio-Technologies.2025; 6(2): 46. CrossRef - Effect of Nanohydroxyapatite and Silver Nanoparticle Incorporation on the Flexural Strength of Resin Composites
Marzie Moradaian, Maryam Saadat, Shahab Agharezaei, Zahra Khorshidi Asl, Baisakhi Banerjee
BioMed Research International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage and Microhardness of Omnichroma and Silver Nanoparticles- incorporated Omnichroma
Mrithyunjay Satish Mendon, Mansi Jain, Suma Sogi, Gulbar Shah, Gagandeep Bhagat, Simran Gupta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(10): 1181. CrossRef - EVOLUTION OF DENTAL IMPLANT AND IMPLANT SURFACE TREATMENTS- A NARRATIVE REVIEW
Wamiq Fareed, Hossam Mossa, Medhat Mohamed, Malik Almutairi, Rashed Alfehaid, Yousef Ahmad
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 303. CrossRef - Comprehensive review on zinc oxide nanoparticle production and the associated antibacterial mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Aeshah M. Mohammed, Mohammed Mohammed, Jawad K. Oleiwi, Falah H. Ihmedee, Tijjani Adam, Bashir O. Betar, Subash C.B. Gopinath
Nano Trends.2025; 11: 100145. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy and surface roughness of orthodontic brackets coated with silver–copper hybrid or zinc oxide nanoparticles: An in-vitro study
Aseem Sharma, Tanushree Sharma, Nambi. Rammohan. Shrinivaasan, Geetika Tomer, Nisha Gupta, Pramada Kishore, Prashant Babaji, Azhar Mohammed, Ananya Neralla
Journal of Orthodontic Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy, antibiofilm effect, and resistance to biodegradation of a novel composite against Streptococcus mutans
S. Pallavi, A. Devadathan, Lizymol Philipose Pampadykandathil, Vibha Chandrababu, N J Nagaraj, Arvind Kumar Alexander
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(10): 1001. CrossRef - Cymbopogon citratus essential oil infused zinc oxide nanoparticles for eco-friendly anticariogenic action
Preeti Pallavi, Saswat Aryan, Pragnya Paramita Sahoo, Adyasha Anapurba Sahoo, Sangeeta Raut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Computational Insights Into Antimicrobial Peptide‐Enhanced Dental Resin Composites: Targeting Porphyromonas gingivalis Heme‐Binding Proteins and Biofilms
Ravinder S. Saini, Doni Dermawan, Abdulkhaliq Ali F. Alshadidi, Rayan Ibrahim H. Binduhayyim, Rajesh Vyas, Fahad Hussain Alhamoudi, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Mohamed Saheer Kuruniyan, Lujain Ibrahim N. Aldosari, Artak Heboyan
MicrobiologyOpen.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabricated modified compomer bearing CF/SBA-15 nanomaterials: Physicochemical and antibacterial properties
Fatma Nur Kızılay, Mustafa Aydınbelge, Sezer Demirbuğa, Kevser Kolçakoğlu, Nilay Ildız, Serkan Dayan
Dental Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The formation of cariogenic plaque to contemporary adhesive restorative materials: an in vitro study
Anna Lehrkinder, Olivia Rydholm, Anna Wänström, Keisuke Nakamura, Ulf Örtengren
Odontology.2024; 112(4): 1090. CrossRef - The Impact of Incorporating Five Different Boron Materials into a Dental Composite on Its Mechanical Properties
Mehmet Kutluhan Ucuk, Musa Kazim Ucuncu
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(3): 1054. CrossRef - Albumin nanoparticles are a promising drug delivery system in dentistry
Mohammad Kiarashi, Saman Yasamineh
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Three Antibacterial Nanoparticle Coatings on the Surface Characteristics of Stainless Steel
Ahmed Al-Mayali, Ammar Kadhum, Thair Alzubaydi
Metals.2024; 14(8): 853. CrossRef - Bioresponsive nanotechnology in pediatric dental drug delivery
Seyed Ebrahim Alavi, Lieba Malik, Raghad Matti, Farah Al-Najafi, Hasan Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, Lavanya A. Sharma
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2024; 93: 105436. CrossRef - Visible light-activated curcumin-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles integrated into orthodontic adhesive on Micro-tensile bond strength, degree of conversion, and antibacterial effectiveness against Staphylococcus Aureus. An investigation using scanning elect
Abdullah A. Alnazeh, Muhammad Abdullah Kamran, Salem Almoammar, Mohammed Mohsen Al Jearah, Muhammad Qasim, Ibrahim Alshahrani
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology.2024; 253: 112888. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of PMMA enriched with nano-clay loaded with metronidazole and chlorhexidine
Eduardo Buozi Moffa, Samuel Santana Malheiros, Larissa Tavares Sampaio Silva, Delcio Ildefonso Branco, Regis Cléo Fernandes Grassia Junior, William Cunha Brandt, Flavia Goncalves, Valentim Adelino Ricardo Barao, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating Antibacterial Frontiers: A Panoramic Exploration of Antibacterial Landscapes, Resistance Mechanisms, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Krittika Ralhan, Kavita A. Iyer, Leilani Lotti Diaz, Robert Bird, Ankush Maind, Qiongqiong Angela Zhou
ACS Infectious Diseases.2024; 10(5): 1483. CrossRef - Use of nanotechnology-based nanomaterial as a substitute for antibiotics in monogastric animals
Abdul Qadeer, Aamir Khan, Noor Muhammad Khan, Abdul Wajid, Kaleem Ullah, Sylvie Skalickova, Pompido Chilala, Petr Slama, Pavel Horky, Mohammed S. Alqahtani, Maha Awjan Alreshidi
Heliyon.2024; 10(11): e31728. CrossRef - Local and systemic adverse effects of nanoparticles incorporated in dental materials- a critical review
Harini Karunakaran, Jogikalmat Krithikadatta, Mukesh Doble
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(1): 158. CrossRef - Determining the cytotoxicity of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles in ESBL and carbapenemase producing Proteus mirabilis isolated from clinical samples in Shiraz, Southwest Iran
Farshad Kakian, Esmaeil Mirzaei, Afagh Moattari, Sara Takallu, Abdollah Bazargani
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New insights into nanotherapeutics for periodontitis: a triple concerto of antimicrobial activity, immunomodulation and periodontium regeneration
Jiaxin Li, Yuxiao Wang, Maomao Tang, Chengdong Zhang, Yachen Fei, Meng Li, Mengjie Li, Shuangying Gui, Jian Guo
Journal of Nanobiotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of silver and calcium fluoride nanoparticles on antibacterial activity of composite resin against Streptococcus mutans: An in vitro study
Mehdi Fathi, Zahra Hosseinali, Tina Molaei, Somayeh Hekmatfar
Dental Research Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Flowable resin-based composites modified with chlorhexidine-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles induce superior antibiofilm properties
Barsha Shrestha, Sultan Aati, Sheetal Maria Rajan, Amr Fawzy
Journal of Nanoparticle Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Temporary Acrylic Soft Denture Lining Material Enriched with Silver-Releasing Filler-Cytotoxicity, Mechanical and Antifungal Properties
Grzegorz Chladek, Igor Kalamarz, Wojciech Pakieła, Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Zenon Czuba, Anna Mertas
Materials.2024; 17(4): 902. CrossRef - The Antibacterial Properties of a Reinforced Zinc Oxide Eugenol Combined with Cloisite 5A Nanoclay: An In-Vitro Study
Bahareh Nazemisalman, Shaghayegh Niaz, Shayan Darvish, Ayda Notash, Ali Ramazani, Ionut Luchian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(7): 198. CrossRef - Assessing the physico-mechanical, anti-bacterial, and anti-demineralization properties of orthodontic resin composite containing different concentrations of photoactivated zinc oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans biofilm around ceramic and metal o
Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Rashin Bahrami, Maryam Pourhajibagher
International Orthodontics.2024; 22(4): 100901. CrossRef - Biosynthesis of a Novel Composite Resin Incorporating Gamma Radiation Synthesized Pomegranate Extract–Coated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and In Vitro Assessment Against Streptococcus mutans Causing Dental Caries
Amany Badr El-Deen Abd El-Aziz, Mehreshan El-Mokadem, Hoda Hassan Abo-Ghalia, Zakaria Ahmed Mattar, Abdelrazq Ibrahim Sallam
BioNanoScience.2024; 14(5): 5017. CrossRef - Global trend and hotspot of resin materials for dental caries repair: a bibliometric analysis
Baodi Han, Lian Wang
Frontiers in Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Studying the Application of Nanoparticles in Orthodontics: A Review Study
Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafal J. Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Adam Lubojanski, Karolina Kurek, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Zakrzewski
Annals of Dental Specialty.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs): Photocatalysis, antibacterial, toxicity and genotoxicity
Olcay Gençyılmaz, Fahriye Zemheri Navruz, Sinan İnce, Abdulsattar Ali Abbas, Abdullah Hüssein Salim Salim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2024; 456: 115847. CrossRef - Advancements in Nanoparticle-Based Strategies for Enhanced Antibacterial Interventions
Madineh Moradialvand, Nastaran Asri, Mahtab Jahdkaran, Maryam Beladi, Hamidreza Houri
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics.2024; 82(4): 3071. CrossRef - Performance evaluation of carbon quantum dots impregnated glass ionomer cement to avoid peri-implant disease
Febina Josephraj, Ashwin Kumar N, Vidyashree Nandini V, Sujatha S, Varshini Karthik
Biomedical Materials.2024; 19(3): 035040. CrossRef - Recent advances in nanomaterial-based biosensor for periodontitis detection
Mohammad Hosseini Hooshiar, Masoud Amiri Moghaddam, Mohammad Kiarashi, Athraa Y. Al-Hijazi, Abbas Fadel Hussein, Hareth A.Alrikabi, Sara Salari, Samar Esmaelian, Hassan Mesgari, Saman Yasamineh
Journal of Biological Engineering.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the antibacterial properties of Resin cements with and without the addition of nanoparticles: a systematic review
Ravinder Saini, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Masroor Ahmed Kanji, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Saeed Awod Bin Hassan, Sukumaran Anil, Deepti Shrivastava, Kumar Chandan Srivastava
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanotecnologia aplicada a Biomateriais em técnicas preventivas e restauradoras
Lucas Mateus Do Nascimento, Ricardo Felipe Ferreira Da Silva
Revista Sociedade Científica.2024; 7(1): 2326. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetration of Various Nano-sized Intra-canal Medicaments: An In Vitro Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Mounika Veeraiyan, Chikine Yashas Chandhar, Deepa Mastammanavar, Kantheti Kavya, Deepa Jarupula, Gangishetti Sairam
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 2): S1690. CrossRef - Preparation and characterization of nano silver antibacterial gel for gynecolog
Qiuqun Xiao, Jingnan Zhu, Tao Fang, Ruyi Peng, Jiayi Chen, Kailan Liu, Yanshi Ceng, Meng Yuan, Yunrui Hu
Ferroelectrics.2024; 618(13-14): 2249. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their biocompatibility in L929 fibroblasts
Zahra Jowkar, Ali Moaddeli, Fereshteh Shafiei, Tara Tadayon, Seyed Ahmadreza Hamidi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Nanoparticles on Dental Composites: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dhruv Ahuja, M. R. Akhila, Ashish Kumar Singh, Puneet Batra
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 439. CrossRef - Nanotechnology in Orthodontics: Current Applications and Future Perspectives
Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Rafal J. Wiglusz, Zbigniew Rybak, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Adam Lubojanski, Karolina Kurek, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Zakrzewski
Asian Journal of Periodontics and Orthodontics.2024; 4(1): 24. CrossRef - Inorganic Compounds as Remineralizing Fillers in Dental Restorative Materials: Narrative Review
Leena Ibraheem Bin-Jardan, Dalal Ibrahim Almadani, Leen Saleh Almutairi, Hadi A. Almoabid, Mohammed A. Alessa, Khalid S. Almulhim, Rasha N. AlSheikh, Yousif A. Al-Dulaijan, Maria S. Ibrahim, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8295. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Nanoparticles on Addition to Orthodontic
Materials- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Crystal Runa Soans, Deesha Kumari, Shalin Shersha, Rahila Mansoor, M.S. Ravi
Nanoscience & Nanotechnology-Asia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of inorganic nanoparticles on dental materials’ mechanical properties. A narrative review
Ghada Naguib, Abdulrahman A. Maghrabi, Abdulghani I. Mira, Hisham A. Mously, Maher Hajjaj, Mohamed T. Hamed
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Nanomaterials in Restorative Dentistry
Rutvik Mandhalkar, Priyanka Paul, Amit Reche
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The germicidal effect, biosafety and mechanical properties of antibacterial resin composite in cavity filling
Jiamu Ren, Xinwei Guo
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19078. CrossRef - Influence of the Loading with Newly Green Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Equisetum sylvaticum on the Antibacterial Activity and Surface Hardness of a Composite Resin
Ionuț Tărăboanță, Ana Flavia Burlec, Simona Stoleriu, Andreia Corciovă, Adrian Fifere, Denisa Batir-Marin, Monica Hăncianu, Cornelia Mircea, Irina Nica, Andra Claudia Tărăboanță-Gamen, Sorin Andrian
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(8): 402. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Ocimum tenuiflorum and Stevia rebaudiana-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles – An In vitro Study
Indumathy Pandiyan, Meignana Indiran Arumugham, Sri Sakthi Doraikannan, Pradeep Kumar Rathinavelu, Jayashri Prabakar, S. Rajeshkumar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2023; 14(2): 109. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Properties of an Orthodontic Composite Containing Silver and Amor-phous Tricalcium Phosphate Nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans: An In Vitro Study
Zahra Tavakolinejad, Mahmood Sheikh Fathollahi, farzaneh Mirzaei, Farzaneh Mirzaei, Elham Mirzaei
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2023; 8(4): 257. CrossRef - Effect of incorporating silica-hydroxyapatite-silver hybrid nanoparticles into the resin-modified glass ionomer on the adhesive remnant index score and shear bond strength of orthodontic metal brackets: An in vitro study
Nazila Biglar, Elahe Chaychi Raghimi, Somayeh Sadighian, Farzaneh Karamitanha, Elham Zajkani, Azin Nourian
International Orthodontics.2023; 21(3): 100761. CrossRef - Method development for the intraoral release of nanoparticles from dental restorative materials
Laura Kleinvogel, Gregor Wemken, Cosima Reidelbach, Manuel Garcia-Käufer, Kirstin Vach, Elmar Hellwig, Benedikt C. Spies, Olga Polydorou
Dental Materials.2023; 39(8): 693. CrossRef - Recent advancements in blended and reinforced polymeric systems as bioscaffolds
Jasmin Joseph, Ramesh Parameswaran, Unnikrishnan Gopalakrishna Panicker
International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials.2023; 72(11): 834. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Copper-Doped Phosphate Glass on Pathogenic Bacteria
Sunaina Shetty, Priyadharshini Sekar, Raghavendra M. Shetty, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel
Molecules.2023; 28(7): 3179. CrossRef - Effect of Zinc Oxide Incorporation on the Antibacterial, Physicochemical, and Mechanical Properties of Pit and Fissure Sealants
Ji-Won Choi, Song-Yi Yang
Polymers.2023; 15(3): 529. CrossRef - Novel bioactive dental restorations to inhibit secondary caries in enamel and dentin under oral biofilms
Wen Zhou, Hong Chen, Michael D. Weir, Thomas W. Oates, Xuedong Zhou, Suping Wang, Lei Cheng, Hockin H.K. Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 133: 104497. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of glass-ionomer cement incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles against mutans streptococci and lactobacilli under orthodontic bands: An in vivo split-mouth study
Maryam Shirazi, Fatemeh Fotoohi Qazvini, Saeed Mohamadrezaie
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the cell viability and antimicrobial effects of orthodontic bands coated with silver or zinc oxide nanoparticles: An in vitro study
Rashin Bahrami, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Alireza Badiei, Reza Masaeli, Behrad Tanbakuchi
Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2023; 53(1): 16. CrossRef - Evaluation and comparison of the effect of incorporating zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the bond strength and microleakage of two orthodontic fixed retainer adhesives
Leila Jazi, Ahmad Sodagar, Sepehr Sobhani Kazemi, Amirhossein Mirhashemi
Journal of the World Federation of Orthodontists.2023; 12(1): 22. CrossRef - Bioactive Materials for Caries Management: A Literature Review
Olivia Lili Zhang, John Yun Niu, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Ollie Yiru Yu, May Lei Mei, Chun Hung Chu
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(3): 59. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of zinc oxide nanoparticle-coated aligners on Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans
Prathima Anita, Haritha Pottipalli Sathyanarayana, Kennedy Kumar, Krishnapriya Ramanathan, Vignesh Kailasam
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2023; 163(3): 338. CrossRef - The Impact of Adhesive-Containing Nanoparticles of ZrO2and TiO2 on Antimicrobial Effectiveness, the Strength of Bonding, and the Extent of Microleakage in Dentin Affected by Caries
Fayez Hussain Niazi, Shadi El Bahra, Nisren Ansary, Zeeshan Qamar, Hajar Albahkaly, Badr Bamousa, Ahlam Smran, Ahmed Al Ahmari, Saleh Wael S. Al-Akki, Abdulaziz Samran
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2023; 13(9): 946. CrossRef - Comparitive evaluation of antimicrobial effectiveness of silver oxide coatings on different types of ceramic brackets against Streptococcus mutans
S. V. Ramesh Goud, K. Raja Sigamani, Bhaskar, Kurinchi Kumaran, Mohammed Arafat, S.N Reddy Duvvuri
The Journal of Dental Panacea.2022; 4(2): 75. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial and mechanical features of dental adhesives containing colloidal gold nanoparticles
Sara Dadkan, Mehrdad Khakbiz, Lida Ghazanfari, Meizi Chen, Ki-Bum Lee
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2022; 365: 119824. CrossRef - Preparation of electrospun silver/poly(vinyl alcohol) fibrous membranes and characterization of the effect of sterilization processes on the antibacterial activity
Wen-Cheng Chen, Chia-Ying Ko, Kai-Chi Chang, Chih-Hua Chen, Dan-Jae Lin
Journal of Industrial Textiles.2022; 51(4_suppl): 7205S. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-Based Zinc Ion Interference Therapy to Combat Bacterial Infections
Yongbin Wei, Jiaming Wang, Sixuan Wu, Ruixue Zhou, Kaixiang Zhang, Zhenzhong Zhang, Junjie Liu, Shangshang Qin, Jinjin Shi
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative Investigation of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Used in Dentistry
Ajay Kumar Tiwari, Saket Jha, Abhimanyu Kumar Singh, Sheo Kumar Mishra, Ashok Kumar Pathak, Rudra Prakash Ojha, Raghvendra Singh Yadav, Anupam Dikshit
Crystals.2022; 12(8): 1063. CrossRef - Efficient Route for the Preparation of Composite Resin Incorporating Silver Nanoparticles with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties
Drake Beery, Mohammad Abdul Mottaleb, Mohammed J. Meziani, James Campbell, Isabella Pires Miranda, Michael Bellamy
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(3): 471. CrossRef - Antibacterial performance of composite containing quaternary ammonium silica (QASi) filler – A preliminary study
Michal Dekel-Steinkeller, Ervin I. Weiss, Trudi Lev-Dor Samovici, Itzhak Abramovitz
Journal of Dentistry.2022; 123: 104209. CrossRef - Therapeutic Applications of Antimicrobial Silver-Based Biomaterials in Dentistry
Qiyu Wang, Yu Zhang, Qiang Li, Li Chen, Hui Liu, Meng Ding, Heng Dong, Yongbin Mou
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2022; Volume 17: 443. CrossRef - In-vitro Comparative Assessment of Antibacterial and Anti-adherent Effect of Two Types of Surface Modificants on Stainless Steel Orthodontic Brackets Against Streptococcus mutans
Mrunmaye Math, Alok G. Shah, Parag Gangurde, Anita G. Karandikar, Anjali Gheware, Bhagyashree S. Jadhav
Journal of Indian Orthodontic Society.2022; 56(3): 282. CrossRef - Dental Composites with Magnesium Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Prevent Secondary Caries in the Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Model
Tahreem Tanweer, Nosheen Fatima Rana, Iqra Saleem, Iqra Shafique, Sultan M. Alshahrani, Hanadi A. Almukhlifi, Amenah S. Alotaibi, Sohad Abdulkaleg Alshareef, Farid Menaa
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15926. CrossRef - Effect of Different Concentrations of Silver Nanoparticles on the Quality of the Chemical Bond of Glass Ionomer Cement Dentine in Primary Teeth
Faisal Mohammed Abed, Sunil Babu Kotha, Haneen AlShukairi, Fatmah Nasser Almotawah, Rwan Abdulali Alabdulaly, Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Activity of Dental Composite with Ciprofloxacin Loaded Silver Nanoparticles
Wafa Arif, Nosheen Rana, Iqra Saleem, Tahreem Tanweer, Muhammad Khan, Sohad Alshareef, Huda Sheikh, Fatima Alaryani, Manal AL-Kattan, Hanan Alatawi, Farid Menaa, Aroosa Nadeem
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7182. CrossRef - Experimental composite containing silicon dioxide-coated silver nanoparticles for orthodontic bonding: Antimicrobial activity and shear bond strength
Rogéria Christina de Oliveira AGUIAR, Larissa Pereira NUNES, Eduardo Silva BATISTA, Marina Mariante VIANA, Marcela Charantola RODRIGUES, Bruno BUENO-SILVA, Marina Guimarães ROSCOE
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - DEAE-Dextran Coated AgNPs: A Highly Blendable Nanofiller Enhances Compressive Strength of Dental Resin Composites
Shabia Azhar, Nosheen Fatima Rana, Amer Sohail Kashif, Tahreem Tanweer, Iqra Shafique, Farid Menaa
Polymers.2022; 14(15): 3143. CrossRef - Synthesis of a Novel, Biocompatible and Bacteriostatic Borosiloxane Composition with Silver Oxide Nanoparticles
Denis N. Chausov, Veronika V. Smirnova, Dmitriy E. Burmistrov, Ruslan M. Sarimov, Alexander D. Kurilov, Maxim E. Astashev, Oleg V. Uvarov, Mikhail V. Dubinin, Valery A. Kozlov, Maria V. Vedunova, Maksim B. Rebezov, Anastasia A. Semenova, Andrey B. Lisitsy
Materials.2022; 15(2): 527. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties, Biocompatibility and Anti-Bacterial Adhesion Property Evaluation of Silicone-Containing Resin Composite with Different Formulae
Muzi Liao, Hui Tong, Xiangya Huang, Fang Liu, Jingwei He, Sui Mai
Journal of Renewable Materials.2022; 10(12): 3201. CrossRef - Current trends and future perspectives on dental nanomaterials – An overview of nanotechnology strategies in dentistry
Vidhya Rekha Umapathy, Prabhu Manickam Natarajan, C. SumathiJones, Bhuminathan Swamikannu, W.M.S. Johnson, V. Alagarsamy, Ashequr Rahman Milon
Journal of King Saud University - Science.2022; 34(7): 102231. CrossRef - Boron nitride nanosheets modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles as novel fillers of dental resin composite
Ameenah Saad Alansy, Thekra Ali Saeed, Reem Al-Attab, Yuqing Guo, Yanwei Yang, Bin Liu, Zengjie Fan
Dental Materials.2022; 38(10): e266. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review on Its Applications in Dentistry
C Pushpalatha, Jithya Suresh, VS Gayathri, SV Sowmya, Dominic Augustine, Ahmed Alamoudi, Bassam Zidane, Nassreen Hassan Mohammad Albar, Shankargouda Patil
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Antibacterial Activity of Nano Titania-Enriched Alkasite Restorative Material: An In Vitro Study
Neven S. Aref, Reham M. Abdallah
The Open Dentistry Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Properties of a Methacrylate-Based Dental Material Loaded with ZnO Nanoparticles
Patricia Comeau, Julia Burgess, Niknaz Malekafzali, Maria Luisa Leite, Aidan Lee, Adriana Manso
Materials.2022; 15(14): 5075. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef - Development of Direct Immobilization Technique of Ag Nanoparticles on Resin Substrates Imparting High Antibacterial and Antiviral Activities
Satoshi Seino, Yuji Ohkubo, Tomonari Magara, Hiroki Enomoto, Eri Nakajima, Tomoki Nishida, Yasuo Imoto, Takashi Nakagawa
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(17): 3046. CrossRef - Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
Pooja Jain, Uzma Farooq, Nazia Hassan, Mohammed Albratty, Md. Shamsher Alam, Hafiz A. Makeen, Mohd. Aamir Mirza, Zeenat Iqbal
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 1935. CrossRef - Impact of Different Antibacterial Substances in Dental Composite Materials: A Comprehensive Review
Badr Soliman AlHussain, Abdulrahman Abdulaziz AlFayez, Abdullah Abdulrahman AlDuhaymi, Essam Abdulaziz AlMulhim, Mohammad Yahya Assiri, Shahzeb Hasan Ansari
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2022; 2(1): 1. CrossRef - Chlorhexidine in operative dentistry - A review
TanviSanjay Satpute, SanjyotA Mulay
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 80. CrossRef - Nanotechnology-based materials as emerging trends for dental applications
Tejas Barot, Deepak Rawtani, Pratik Kulkarni
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2021; 60(1): 173. CrossRef - A Brief Review on the Evolution of Metallic Dental Implants: History, Design, and Application
Sumanth Ratna Kandavalli, Qingge Wang, Mahmoud Ebrahimi, Ceren Gode, Faramarz Djavanroodi, Shokouh Attarilar, Shifeng Liu
Frontiers in Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans, antioxidant property and cytotoxicity of novel nano-zinc oxide varnish
Manali Deb Barma, Indumathy Muthupandiyan, Srinivasan Raj Samuel, Bennett T. Amaechi
Archives of Oral Biology.2021; 126: 105132. CrossRef - Nanomaterials Application in Orthodontics
Wojciech Zakrzewski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Anna Zawadzka-Knefel, Mateusz Janecki, Karolina Kurek, Adam Lubojanski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 337. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of new denture base material modified with gold nanoparticles
Adamović Tijana, Veselinović Valentina, Trtić Nataša, Hadži-Mihailović Miloš, Gotovac Atlagić Suzana, Balaban Milica, Hattori Yoshiyuki, Sugiyama Hironori, Andrej Ivanič, Rudolf Rebeka
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2021; 65(2): 155. CrossRef - Dynamics of different ion release from denture-base acrylic resins and their mechanical properties after the addition of bioactive materials
Zbigniew Raszewski
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(8): 1071. CrossRef - Genotoxic assay of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by leaf extract of Garcinia livingstonei T. Anderson: A comparative study
AzharuddinB Daphedar, SiddappaB Kakkalameli, Govindappa Melappa, TarikereChandrashekharappa Taranath, Chandrashekar Srinivasa, Chandan Shivamallu, Asad Syed, Najat Marraiki, AbdallahM Elgorban, Ravindra Veerapur, SharangoudaS Patil, ShivaPrasad Kollur
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2021; 17(5): 114. CrossRef - Nanostructures as Targeted Therapeutics for Combating Oral Bacterial Diseases
Shima Afrasiabi, Nasim Chiniforush, Hamid Reza Barikani, Alireza Partoazar, Ramin Goudarzi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(10): 1435. CrossRef - Well-Orientation Strategy Biosynthesis of Cefuroxime-Silver Nanoantibiotic for Reinforced Biodentine™ and Its Dental Application against Streptococcus mutans
Sanaa M. F. Gad El-Rab, Amal A. Ashour, Sakeenabi Basha, Amal Ahmed Alyamani, Nayef H. Felemban, Enas Tawfik Enan
Molecules.2021; 26(22): 6832. CrossRef - Application of Selected Nanomaterials and Ozone in Modern Clinical Dentistry
Adam Lubojanski, Maciej Dobrzynski, Nicole Nowak, Justyna Rewak-Soroczynska, Klaudia Sztyler, Wojciech Zakrzewski, Wojciech Dobrzynski, Maria Szymonowicz, Zbigniew Rybak, Katarzyna Wiglusz, Rafal J. Wiglusz
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(2): 259. CrossRef - Nanomaterials as drug delivery systems with antibacterial properties: current trends and future priorities
Khatereh Khorsandi, Reza Hosseinzadeh, Homa Sadat Esfahani, Saeedeh Keyvani-Ghamsari, Saeed Ur Rahman
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy.2021; 19(10): 1299. CrossRef - Synthesis and antibacterial activity of polymer–antibiotic conjugates incorporated into a resin-based dental adhesive
Ziwen Zhang, Megan M. Jones, Camila Sabatini, Stephen T. Vanyo, Ming Yang, Abhishek Kumar, Yancheng Jiang, Mark T. Swihart, Michelle B. Visser, Chong Cheng
Biomaterials Science.2021; 9(6): 2043. CrossRef - Effect Of Various Antibacterial Materials In Dental Composites: A Systematic Review
Abdulrahman Abdulaziz Alfayez, Abdullah Abdulrahman Alduhaymi, Essam Abdulaziz Almulhim, Mohammad Yahya Assiri, Shahzeb Hasan Ansari
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(3): 39. CrossRef - Low-temperature flow-synthesis-assisted urethane-grafted zinc oxide-based dental composites: physical, mechanical, and antibacterial responses
Jaffar Hussain Bukhari, Abdul Samad Khan, Kashif Ijaz, Shahreen Zahid, Aqif Anwar Chaudhry, Muhammad Kaleem
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of nano‐technology applications in resin‐based restorative materials
Natalia Almeida Bastos, Sandro Basso Bitencourt, Emerson Alves Martins, Grace Mendonca De Souza
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(4): 567. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Therapies for the Management of Dental Caries—A Literature Review
Hetal Desai, Cameron Stewart, Yoav Finer
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 147. CrossRef - In-vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles and Its Indigenous Mouthwash
Lichi. A. Solanki, KK Shantha Sundari, S Rajeshkumar
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2021; 15(2): 735. CrossRef - Antibacterial response of oral microcosm biofilm to nano-zinc oxide in adhesive resin
Isadora Martini Garcia, AbdulRahman A. Balhaddad, Maria S. Ibrahim, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares, Mary Anne S. Melo
Dental Materials.2021; 37(3): e182. CrossRef - Toxic mechanisms of Roth801, Canals, microparticles and nanoparticles of ZnO on MG-63 osteoblasts
Mei-Chi Chang, Chia-Mei Tang, Yu-Heng Lin, Hsin-Cheng Liu, Tong-Mei Wang, Wen-Chien Lan, Ru-Hsiu Cheng, Yan-Ru Lin, Hsiao-Hua Chang, Jiiang-Huei Jeng
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2021; 119: 111635. CrossRef - Initial Mechanical Stabilization of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cements with Different Active Principles
Caroline Santos Ribeiro, Mayra Manoella Perez, Pablo Lenin Benitez-Sellan, Renata de Oliveira Guaré, Eduardo Bresciani, Michele Baffi Diniz
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinc oxide nanoparticles inhibit bacterial biofilm formation via altering cell membrane permeability
Tanvir Kaur, Chayanika Putatunda, Ashish Vyas, Gaurav Kumar
Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology.2021; 51(4): 309. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, mechanical, and bonding properties of a dental adhesive modified with antibacterial monomer and cross-linker
Hoda Moussa, Megan M. Jones, Ningbo Huo, Runsheng Zhang, Mayuresh Keskar, Michelle B. Visser, Mark T. Swihart, Chong Cheng, Camila Sabatini
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2877. CrossRef - The Benefits of Smart Nanoparticles in Dental Applications
Silvia Vasiliu, Stefania Racovita, Ionela Aurica Gugoasa, Maria-Andreea Lungan, Marcel Popa, Jacques Desbrieres
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(5): 2585. CrossRef - Microshear Bond Strength of Nanoparticle-Incorporated Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer to Caries-Affected Dentin
Zahra Fattah, Zahra Jowkar, Safoora Rezaeian, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - An Insight in to Various Metallic Oxide Nanoparticles as Antimicrobials and Their Applications in Dentistry
Hema Kanathila, Ashwin M. Pangi, Suvidha Patil, Shilpa Shirlal, Rahul Jaiswal
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(33): 2803. CrossRef - Innovative Strategies in Minimally Invasive Dentistry for Caries Management: A Literature Synthesis
Mariana Vega, Hugo Fuentes, Valeria Cordero, Luis Silva, Regina Cabrera
International Journal of Dental Research and Allied Sciences.2021; 1(2): 66. CrossRef - Nanoparticle technology and its implications in endodontics: a review
Natasha Raura, Anirudh Garg, Arpit Arora, M. Roma
Biomaterials Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Use of Silver Nanomaterials for Caries Prevention: A Concise Review
Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Irene Shuping Zhao, May Lei Mei, Quanli Li, Ollie Yiru Yu, Chun Hung Chu
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 3181. CrossRef- Study on a novel antibacterial light-cured resin composite containing nano-MgO
Zhongyuan Wu, Haiping Xu, Wei Xie, Meimei Wang, Cunjin Wang, Cheng Gao, Fang Gu, Jie Liu, Jing Fu
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces.2020; 188: 110774. CrossRef - Effect of Addition of Nano-TiO2, Nano-SiO2, and a Combination of Both, on Antimicrobial Activity of an Orthodontic Composite
Abbas Bahador, Mohammad J Kharazifard, Nazanin Kiomarsi, Paniz Zamani, Sedighe S Hashemikamangar, Maryam Pourhajibagher
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(8): 857. CrossRef - Biomimetic Aspects of Oral and Dentofacial Regeneration
Akshaya Upadhyay, Sangeeth Pillai, Parisa Khayambashi, Hisham Sabri, Kyungjun T. Lee, Maryam Tarar, Stephanie Zhou, Ingrid Harb, Simon D. Tran
Biomimetics.2020; 5(4): 51. CrossRef Dental Materials Incorporated with Nanometals and Their Effect on the Bacterial Growth of Staphylococcus aureus
Rabeah Yousef Rawashdeh, Reyad Sawafta, Hanan I Malkawi
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 4325. CrossRef- Does the Addition of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Improve the Antibacterial Properties of Direct Dental Composite Resins? A Systematic Review
Divya Arun, Dulanja Adikari Mudiyanselage, Rumana Gulam Mohamed, Michael Liddell, Nur Mohammad Monsur Hassan, Dileep Sharma
Materials.2020; 14(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on broilers’ performance and health status
Usama T. Mahmoud, Hosnia S. Abdel-Mohsein, Manal A. M. Mahmoud, Omar A. Amen, Rasha I. M. Hassan, Ashraf M. Abd-El-Malek, Sohair M. M. Rageb, Hanan S. A. Waly, Aly A. Othman, Mohamed A. Osman
Tropical Animal Health and Production.2020; 52(4): 2043. CrossRef - The potential anti‐infective applications of metal oxide nanoparticles: A systematic review
Yasmin Abo‐zeid, Gareth R. Williams
WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - ZnO Modulates Swine Gut Microbiota and Improves Growth Performance of Nursery Pigs When Combined with Peptide Cocktail
Xiaoyuan Wei, Tsungcheng Tsai, Joshua Knapp, Kristopher Bottoms, Feilong Deng, Robert Story, Charles Maxwell, Jiangchao Zhao
Microorganisms.2020; 8(2): 146. CrossRef - Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial activity of silica-coated silver nanoparticles for esthetic dental applications
Marcela Charantola Rodrigues, Wallace Rosado Rolim, Marina Mariante Viana, Thaís Rodrigues Souza, Flavia Gonçalves, Caio Junji Tanaka, Bruno Bueno-Silva, Amedea Barozzi Seabra
Journal of Dentistry.2020; 96: 103327. CrossRef - Advances of Anti-Caries Nanomaterials
Hui Chen, Lisha Gu, Binyou Liao, Xuedong Zhou, Lei Cheng, Biao Ren
Molecules.2020; 25(21): 5047. CrossRef - Antibacterial Properties of Nanoparticles in Dental Restorative Materials. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elena Ferrando-Magraner, Carlos Bellot-Arcís, Vanessa Paredes-Gallardo, José Manuel Almerich-Silla, Verónica García-Sanz, Mercedes Fernández-Alonso, José María Montiel-Company
Medicina.2020; 56(2): 55. CrossRef - Polymeric and inorganic nanoscopical antimicrobial fillers in dentistry
Pooyan Makvandi, Jun Ting Gu, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Behnaz Ashtari, Arash Moeini, Franklin R. Tay, Li-na Niu
Acta Biomaterialia.2020; 101: 69. CrossRef - The effect of incorporation Nano Cinnamon powder on the shear bond of the orthodontic composite (an in vitro study)
Saba N. Yaseen, Amer A. Taqa, Ali R. Al-Khatib
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 128. CrossRef - Synthesis of an anti-cariogenic experimental dental composite containing novel drug-decorated copper particles
Mehwish Pasha, Nawshad Muhammad, Maleeha Nayyer, Jaffar Hussain Bokhari, Hina Ashraf, Sher Zaman Safi, Muhammad Kaleem
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2020; 114: 111040. CrossRef The Effects of Silver, Zinc Oxide, and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Used as Dentin Pretreatments on the Microshear Bond Strength of a Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement to Dentin
Zahra Jowkar, Zahra Fattah, Saeedreza Ghanbarian, Fereshteh Shafiei
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 4755. CrossRef- Metal‐Based Nanomaterials in Biomedical Applications: Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity Aspects
Pooyan Makvandi, Chen‐yu Wang, Ehsan Nazarzadeh Zare, Assunta Borzacchiello, Li‐na Niu, Franklin R. Tay
Advanced Functional Materials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Biomedical Materials
Maria P. Nikolova, Murthy S. Chavali
Biomimetics.2020; 5(2): 27. CrossRef - Comparison of antibacterial effects of orthodontic composites containing different nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans at different times
Soghra Yassaei, Ali Nasr, Hengameh Zandi, Mohammad Nima Motallaei
Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics.2020; 25(2): 52. CrossRef - Nanoparticles as Anti-Microbial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Remineralizing Agents in Oral Care Cosmetics: A Review of the Current Situation
Florence Carrouel, Stephane Viennot, Livia Ottolenghi, Cedric Gaillard, Denis Bourgeois
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(1): 140. CrossRef - Nanometals in Dentistry: Applications and Toxicological Implications—a Systematic Review
Rupali Agnihotri, Sumit Gaur, Sacharia Albin
Biological Trace Element Research.2020; 197(1): 70. CrossRef - Ex vivo investigation on internal tunnel approach/internal resin infiltration and external nanosilver-modified resin infiltration of proximal caries exceeding into dentin
Andrej M. Kielbassa, Marlene R. Leimer, Jens Hartmann, Stephan Harm, Markus Pasztorek, Ina B. Ulrich, Yogendra Kumar Mishra
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(1): e0228249. CrossRef - Nanocomposites based on low density polyethylene filled with carbon nanotubes prepared by high energy ball milling and their potential antibacterial activity
Erika Benigno, Miguel A Lorente, Dania Olmos, Gustavo González‐Gaitano, Javier González‐Benito
Polymer International.2019; 68(6): 1155. CrossRef - Titanium dioxide and modified titanium dioxide by silver nanoparticles as an anti biofilm filler content for composite resins
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Taís Maria Bauab, Antônio Carlos Hernandes, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): e36. CrossRef - Synthesis, characterization and application of Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles in a composite resin
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Valéria Spolon Marangoni, Adilson César de Abreu Bernardi, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli, Antônio Carlos Hernandes
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 96: 391. CrossRef - The effect of silver nanoparticles incorporation in the self-etch adhesive system on its antibacterial activity and degree of conversion: an in-vitro study
Heba F. Mohammed, Mona I. Riad
F1000Research.2019; 8: 244. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on resin-dentin bond strength durability in a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive system
Zahra Jowkar, Fereshteh Shafiei, Elham Asadmanesh, Fatemeh Koohpeima
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and status of resin composite as dental restorative materials
Xinxuan Zhou, Xiaoyu Huang, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Lei Cheng
Journal of Applied Polymer Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticle solution on the mechanical properties of resin cements and intrarradicular dentin
Thaís Yumi Umeda Suzuki, Juno Gallego, Wirley Gonçalves Assunção, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Chun-Pin Lin
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(6): e0217750. CrossRef - Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole
Yasaman Delaviz, Timothy W. Liu, Ashley R. Deonarain, Yoav Finer, Babak Shokati, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2019; 35(2): 229. CrossRef - Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry
Wenjing Song, Shaohua Ge
Molecules.2019; 24(6): 1033. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of a tissue conditioner used in complete dentures after incorporation of ZnO‒Ag nanoparticles
Seyed Amin Mousavi, Reza Ghotaslou, Abolfazl Akbarzadeh, Niloufar Azima, Ali Aeinfar, Azin Khorramdel
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(1): 11. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Mechanical Properties of Pit and Fissure Sealants Containing Zinc Oxide and Calcium Fluoride Nanoparticles
Dara Lakshmi Swetha, C. Vinay, K. S. Uloopi, Kakarla Sri RojaRamya, Rayala Chandrasekhar
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 477. CrossRef - Addition of antibacterial agent effect on color stability of composites after immersion of different beverages
Makbule T. Tuncdemir, Nilgun Gulbahce
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2019; 31(5): 508. CrossRef - Toward dental caries: Exploring nanoparticle-based platforms and calcium phosphate compounds for dental restorative materials
Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad, Anmar A. Kansara, Denise Hidan, Michael D. Weir, Hockin H.K. Xu, Mary Anne S. Melo
Bioactive Materials.2019; 4: 43. CrossRef - Antibacterial effects of polymeric PolymP-n Active nanoparticles. An in vitro biofilm study
M.C. Sánchez, M. Toledano-Osorio, J. Bueno, E. Figuero, M. Toledano, A.L. Medina-Castillo, R. Osorio, D. Herrera, M. Sanz
Dental Materials.2019; 35(1): 156. CrossRef - Potencial antimicrobiano de diferentes retentores intrarradiculares frente a Enterococcus faecalis: uma avaliação in vitro
Nicole Hoffmann FINGER, Marília PAULUS, Alexandra Flávia GAZZONI
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomedicine for anticancer and antimicrobial treatment: an overview
Shatavari Kulshrestha, Asad U. Khan
IET Nanobiotechnology.2018; 12(8): 1009. CrossRef - Effect of Silver Nanoparticles, Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Microshear Bond Strength to Enamel and Dentin
Fatemeh Koohpeima, Zahra Jowkar, Nazbanoo Farpour, Mohammad J Mokhtari, Fereshteh Shafiei
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(11): 1405. CrossRef - Studies on the Curing Efficiency and Mechanical Properties of Bis-GMA and TEGDMA Nanocomposites Containing Silver Nanoparticles
Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Grzegorz Chladek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(12): 3937. CrossRef - Properties of Experimental Dental Composites Containing Antibacterial Silver-Releasing Filler
Robert Stencel, Jacek Kasperski, Wojciech Pakieła, Anna Mertas, Elżbieta Bobela, Izabela Barszczewska-Rybarek, Grzegorz Chladek
Materials.2018; 11(6): 1031. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial properties on polysulfone composite membranes using synthesized biogenic silver nanoparticles with Ulva compressa (L.) Kütz. and Cladophora glomerata (L.) Kütz. extracts
Fozia T. Minhas, Gulsin Arslan, I. Hilal Gubbuk, Cengiz Akkoz, Betul Yılmaz Ozturk, Baran Asıkkutlu, Ugur Arslan, Mustafa Ersoz
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2018; 107: 157. CrossRef - Human In Situ Study of the effect of Bis(2-Methacryloyloxyethyl) Dimethylammonium Bromide Immobilized in Dental Composite on Controlling Mature Cariogenic Biofilm
Mary Anne S. Melo, Michael D. Weir, Vanara F. Passos, Juliana P. M. Rolim, Christopher D. Lynch, Lidiany K. A. Rodrigues, Hockin H. K. Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(11): 3443. CrossRef - A systematic review on antibacterial activity of zinc against Streptococcus mutans
Manal Mohamed Almoudi, Alaa Sabah Hussein, Mohamed Ibrahim Abu Hassan, Nurhayati Mohamad Zain
The Saudi Dental Journal.2018; 30(4): 283. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and diametrical tensile strength of an interim cement modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles and terpenes: An in vitro study
Verónica Andrade, Alejandra Martínez, Ninón Rojas, Helia Bello-Toledo, Paulo Flores, Gabriela Sánchez-Sanhueza, Alfonso Catalán
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2018; 119(5): 862.e1. CrossRef - Developing a New Generation of Therapeutic Dental Polymers to Inhibit Oral Biofilms and Protect Teeth
Ke Zhang, Bashayer Baras, Christopher Lynch, Michael Weir, Mary Melo, Yuncong Li, Mark Reynolds, Yuxing Bai, Lin Wang, Suping Wang, Hockin Xu
Materials.2018; 11(9): 1747. CrossRef - Do quaternary ammonium monomers induce drug resistance in cariogenic, endodontic and periodontal bacterial species?
Suping Wang, Haohao Wang, Biao Ren, Hao Li, Michael D. Weir, Xuedong Zhou, Thomas W. Oates, Lei Cheng, Hockin H.K. Xu
Dental Materials.2017; 33(10): 1127. CrossRef - Antimicrobial nanomaterials against biofilms: an alternative strategy
Chunhua Liu, Jing Guo, Xiaoqing Yan, Yongbing Tang, Asit Mazumder, Shikai Wu, Yan Liang
Environmental Reviews.2017; 25(2): 225. CrossRef - Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future
Azhwar Raghunath, Ekambaram Perumal
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.2017; 49(2): 137. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Polymers in the Nano-World
Marta Álvarez-Paino, Alexandra Muñoz-Bonilla, Marta Fernández-García
Nanomaterials.2017; 7(2): 48. CrossRef - Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles on Orthodontic Elastomeric Modules: Evaluation of Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties
Alma Hernández-Gómora, Edith Lara-Carrillo, Julio Robles-Navarro, Rogelio Scougall-Vilchis, Susana Hernández-López, Carlo Medina-Solís, Raúl Morales-Luckie
Molecules.2017; 22(9): 1407. CrossRef - Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Influence Microflora in Ileal Digesta and Correlate Well with Blood Metabolites
Yanni Feng, Lingjiang Min, Weidong Zhang, Jing Liu, Zhumei Hou, Meiqiang Chu, Lan Li, Wei Shen, Yong Zhao, Hongfu Zhang
Frontiers in Microbiology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial activity of glass ionomer cement modified by zinc oxide nanoparticles
Patrícia Petromilli Nordi Sasso Garcia, Mariana Florian Bell Cardia, Renata Serignoli Francisconi, Lívia Nordi Dovigo, Denise Madalena Palomari Spolidório, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli, Ana Carolina Botta
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(5): 456. CrossRef - Effects on cytotoxicity and antibacterial properties of the incorporations of silver nanoparticles into the surface coating of dental alloys
Xiao-ting Shen, Yan-zhen Zhang, Fang Xiao, Jing Zhu, Xiao-dong Zheng
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2017; 18(7): 615. CrossRef - Nanosilver coated orthodontic brackets:in vivoantibacterial properties and ion release
Gamze Metin-Gürsoy, Lale Taner, Gülçin Akca
The European Journal of Orthodontics.2017; 39(1): 9. CrossRef - Prenatal Exposure to Nanosized Zinc Oxide in Rats: Neurotoxicity and Postnatal Impaired Learning and Memory Ability
Feng Xiaoli, Wu Junrong, Lai Xuan, Zhang Yanli, Wei Limin, Liu Jia, Shao Longquan
Nanomedicine.2017; 12(7): 777. CrossRef - Heat-Polymerized Resin Containing Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate Inhibits Candida albicans Biofilm
Hui Chen, Qi Han, Xuedong Zhou, Keke Zhang, Suping Wang, Hockin Xu, Michael Weir, Mingye Feng, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Lei Cheng
Materials.2017; 10(4): 431. CrossRef - Zinc oxide 3D microstructures as an antimicrobial filler content for composite resins
Hércules Bezerra Dias, Maria Inês Basso Bernardi, Matheus Aparecido dos Santos Ramos, Tamara Carolina Trevisan, Taís Maria Bauab, Antônio Carlos Hernandes, Alessandra Nara de Souza Rastelli
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(6): 634. CrossRef - Polymer-Ceramic Bionanocomposites for Dental Application
Jung-Hwan Lee, Hae-Won Kim, Seog-Jin Seo
Journal of Nanomaterials.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of nanosilver-coated orthodontic brackets: an in vivo study
Gamze Metin-Gürsoy, Lale Taner, Emre Barış
Progress in Orthodontics.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Restorative materials containing antimicrobial agents: is there evidence for their antimicrobial and anticaries effects? A systematic review
GS do Amaral, T Negrini, M Maltz, RA Arthur
Australian Dental Journal.2016; 61(1): 6. CrossRef - Evaluation of Bond Strength and Microleakage of a Novel Metal-titanate Antibacterial Agent
S Deng, KH Chung, DCN Chan, C Spiekerman
Operative Dentistry.2016; 41(3): E48. CrossRef - Investigation of optical, structural, morphological and antimicrobial properties of carboxymethyl cellulose capped Ag-ZnO nanocomposites prepared by chemical and mechanical methods
Magdalena-Valentina Lungu, Eugeniu Vasile, Mariana Lucaci, Delia Pătroi, Natalia Mihăilescu, Florentina Grigore, Virgil Marinescu, Alexandra Brătulescu, Sorina Mitrea, Arcadie Sobetkii, Arcadii A. Sobetkii, Marcela Popa, Mariana-Carmen Chifiriuc
Materials Characterization.2016; 120: 69. CrossRef - Substantivity of Ag–Ca–Si mesoporous nanoparticles on dentin and its ability to inhibit Enterococcus faecalis
Wei Fan, Yujie Wu, Tengjiao Ma, Yanyun Li, Bing Fan
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanomaterials for Tissue Engineering In Dentistry
Manila Chieruzzi, Stefano Pagano, Silvia Moretti, Roberto Pinna, Egle Milia, Luigi Torre, Stefano Eramo
Nanomaterials.2016; 6(7): 134. CrossRef - Alternative Antimicrobial Approach: Nano-Antimicrobial Materials
Nurit Beyth, Yael Houri-Haddad, Avi Domb, Wahid Khan, Ronen Hazan
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Advances in Dental Materials through Nanotechnology: Facts, Perspectives and Toxicological Aspects
Gislaine C. Padovani, Victor P. Feitosa, Salvatore Sauro, Franklin R. Tay, Gabriela Durán, Amauri J. Paula, Nelson Durán
Trends in Biotechnology.2015; 33(11): 621. CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of conventional restorative filling materials and advances in antimicrobial properties of composite resins and glass ionomer cements—A literature review
Cher Farrugia, Josette Camilleri
Dental Materials.2015; 31(4): e89. CrossRef - Biofilm and Dental Biomaterials
Marit Øilo, Vidar Bakken
Materials.2015; 8(6): 2887. CrossRef - Antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles as a vehicle for calcium hydroxide medicament against Enterococcus faecalis
Farzaneh Afkhami, Seyyed Jalal Pourhashemi, Mona Sadegh, Yasaman Salehi, Mohammad Javad Kharrazi Fard
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(12): 1573. CrossRef - Physical Properties of an Ag-Doped Bioactive Flowable Composite Resin
Hiba Kattan, Xanthippi Chatzistavrou, James Boynton, Joseph Dennison, Peter Yaman, Petros Papagerakis
Materials.2015; 8(8): 4668. CrossRef - Effect of sterilization techniques prior to antimicrobial testing on physical properties of dental restorative materials
Cher Farrugia, Glenn Cassar, Vasilis Valdramidis, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(6): 703. CrossRef - The effects of gold coated and uncoated zinc oxide nanohexagons on the photophysicochemical properties of the low symmetry zinc phthalocyanine
Sarah D'Souza, Racheal Ogbodu, Tebello Nyokong
Journal of Molecular Structure.2015; 1099: 551. CrossRef - In Vitro Activity of Curcumin and Silver Nanoparticles Against Blastocystis hominis
Mona Abdel-Fattah Ahmed, Khadiga Ahmed Ismail, Sabah Abd-El-Ghany Ahmed, Ayman Nabil Ibrahim, Yousry Mahmoud Gohar
Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice.2015; 23(3): 135. CrossRef - Development and characterization of novel ZnO-loaded electrospun membranes for periodontal regeneration
Eliseu A. Münchow, Maria Tereza P. Albuquerque, Bianca Zero, Krzysztof Kamocki, Evandro Piva, Richard L. Gregory, Marco C. Bottino
Dental Materials.2015; 31(9): 1038. CrossRef - Review of Nanomaterials in Dentistry: Interactions with the Oral Microenvironment, Clinical Applications, Hazards, and Benefits
Alexandros Besinis, Tracy De Peralta, Christopher J. Tredwin, Richard D. Handy
ACS Nano.2015; 9(3): 2255. CrossRef - Study on the Bactriostasis of Nano-Silver against Penicillium
Lu Qiu, Mei Hua Xie, Jia Yan Lv, Shu Guo Fan, Jian Hui Gao
Advanced Materials Research.2014; 1051: 62. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Satureja hortensis Extract on Isolated Bacillus cereus from Soil of Sistan Plain
Ebrahim Shirmohammadi, Saeide Saeidi, Taher Mohasseli, Ali Rahimian Boogar
International Journal of Infection.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Strategies to Improve Biocompatibility of Dental Materials
Gottfried Schmalz
Current Oral Health Reports.2014; 1(4): 222. CrossRef
-
5,297
View
-
49
Download
-
205
Crossref
-
Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate on shear bond strength of composite resin to bleached enamel: an in vitro study
-
Zahra Khamverdi, Loghman Rezaei-Soufi, Shahin Kasraei, Negin Ronasi, Shiva Rostami
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):241-247. Published online November 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.241
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to determine the effect of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on the shear bond strength of composite resin to bleached enamel. Materials and MethodsNinety enamel surfaces of maxillary incisors were randomly divided into 9 groups as follows: G1: control (no bleaching); G2: bleaching; G3: bleaching and storage for seven days; G4 - 6: bleaching and application of 600, 800 and 1,000 µmol of EGCG-containing solution for 10 minutes, respectively; G7 - 9: bleaching and application of 600, 800 and 1,000 µmol of EGCG-containing solution for 20 minutes, respectively. The specimens were bleached with 30% hydrogen peroxide gel and a composite resin cylinder was bonded on each specimen using a bonding agent. Shear bond strength of the samples were measured in MPa. Data was analyzed using the two-way ANOVA and Tukey HSD tests (α = 0.05). ResultsThe maximum and minimum mean shear bond strength values were observed in G1 and G2, respectively. Time and concentration of EGCG showed no significant effects on bond strength of the groups (p > 0.05). Multiple comparison of groups did not reveal any significant differences between the groups except for G2 and all the other groups (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThere is a significant decrease in bond strength of composite resin to enamel immediately after bleaching. A delay of one week before bonding and the use of EGCG increased bond strength of composite resin to bleached enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Investigating the effect of two types of antioxidants, pomegranate peel and green tea, on the shear bond strength of composites on bleached enamel using universal bondings (lnvitro study)
Sara Khosravi, Salimeh Shobchari, Keivan Saati, Shahriar Jalalian
Journal of Research in Dental Sciences.2025; 22(3): 192. CrossRef - Investigating the effect of two types of antioxidants, pomegranate peel and green tea, on the shear bond strength of microhybrid composites on bleached enamel using sixth generation bondings (lnvitro study)
Parisa Hekmatnejad, Mansoureh Emami Arjomand2, Maryam Rahimikhoob, Bahareh Farar, Shahriar Jalalian
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(2): 116. CrossRef - Color stability of enamel treated with different antioxidant agents following at-home bleaching with 10% hydrogen peroxide
Rodrigo Chiles PEREIRA, Letícia Vasconcelos Silva de SOUZA, Matheus KURY, Iago César Ribeiro Teles MATOS, Reginna Vyctória da Trindade Souza de Melo CARNEIRO, Sandrine Bittencourt BERGER, Vanessa CAVALLI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Pomegranate Peel and Green Tea Extract as Antioxidants on Shear Bond Strength of a
Microhybrid Composite to Bleached Enamel
F Ghorbani, SH Pourhaghani, H Heshmat, SH Jalalian, MJ Kharazifard
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2022; 7(2): 62. CrossRef - Effect of nonthermal atmospheric plasma, grape seed extract, and bromelain on immediate bonding of composite to bleached and microabraded surfaces
MayanaAameena Banu, Nagesh Bolla, Sravanthi Tammineedi, Sayesh Vemuri, RamChowdary Basam, AnilKumar Ganapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(1): 42. CrossRef - Antioxidant Potential of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, Ascorbic Acid, and Sodium Ascorbate in Solution and Gel Forms by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
Virdah Dwi Dewaantari, Setyabudi Setyabudi, Kun Ismiyatin
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2021; 11(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of 6% cranberry, 10% green tea, 50% aloe vera and 10% sodium ascorbate on reversing the immediate bond strength of bleached enamel: In vitro study
Hena Rahman, Mohd Irfan Ansari, Monika Khangwal, Ravindra Solanki, Shahnaz Mansoori
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2021; 11(2): 107. CrossRef - Vital Bleaching Influences the Bond Strength of Adhesive Systems to Enamel and Dentin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis ofIn VitroStudies
TG Savian, J Oling, FZM Soares, RO Rocha
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(2): E80. CrossRef - Use of antioxidants to restore bond strength after tooth bleaching with peroxides
Dorcas E. R. P. Olmedo, Matheus Kury, Bruna A. Resende, Vanessa Cavalli
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Epigallocathecin-3-gallate as an Antioxidant After Dental Bleaching on Shear Bond Strength of Composite Resin Restoration
Syarifah Nadhira Assyafira Al-Habsyi, Kun Ismiyatin, Galih Sampoerno
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2021; 11(1): 42. CrossRef - Natural antioxidants to restore immediate bond strength to bleached enamel: Systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Juana Rodríguez‐Barragué, Joanna Vola‐Gelmini, Marcel Skuras‐Siedemburg, José Alejandro Rivera‐Gonzaga, Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suarez
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(5): 702. CrossRef - DİŞ BEYAZLATMA İŞLEMİNİN LİTYUM DİSİLİKAT SERAMİĞİN BAĞLANMA DAYANIMINA ETKİSİ
Merve YILDIRAK, Rıfat GÖZNELİ
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Influence of green tea extract in the color of composite resin restorations
R.G. Lopes, B. Oliveira-Reis, A.T. Maluly-Proni, M.H.T. Silva, A.L.F. Briso, P.H. dos Santos
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 100: 103408. CrossRef - Influence of protease inhibitors on the degradation of sound, sclerotic and caries-affected demineralized dentin
B. Oliveira-Reis, A.T. Maluly-Proni, T.C. Fagundes, G. Vasconcelos, E. Bresciani, A. Prakki, P.H. dos Santos
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2019; 97: 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Immediate Bond Strength to Bleached Enamel Following Application of Various Antioxidant Solutions
Anshu Minocha, Ashu K. Gupta, Alisha Dhingra, Nayantara Sen
Dental Journal of Advance Studies.2017; 5(2): 84. CrossRef - Bond Strength of Abraded and Non-Abraded Bleached Enamel to Resin After Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Irradiation
Pedro H.C. Oliveira, Alessandra Cassoni, Aldo Brugnera, Ilana P. Tenório, José A. Rodrigues
Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.2017; 35(10): 530. CrossRef - Effect of dentin biomodifiers on the immediate and long-term bond strengths of a simplified etch and rinse adhesive to dentin
Payal Singh, Rajni Nagpal, Udai Pratap Singh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(3): 188. CrossRef - The effect of green tea on the shear strength of brackets after home whitening treatment
Renata C. A. Schwertner, Joyce S. Y. Leoncio, Alessandro Schwertner, Ricardo D. Guiraldo, Murilo B. Lopes, Hellen C. De Carvalho, Alcides Gonini-Júnior, Sandrine B. Berger
Applied Adhesion Science.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Green Tea Application Time on Bond Strength after Enamel Bleaching
Andrezza Astafief Ozelin, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Rodrigo Varella de Carvalho, Murilo Baena Lopes, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
Brazilian Dental Journal.2014; 25(5): 399. CrossRef
-
1,521
View
-
4
Download
-
19
Crossref
|