-
Influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
-
Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu-Özyürek, Sevilay Karahan
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e19. Published online March 10, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e19
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
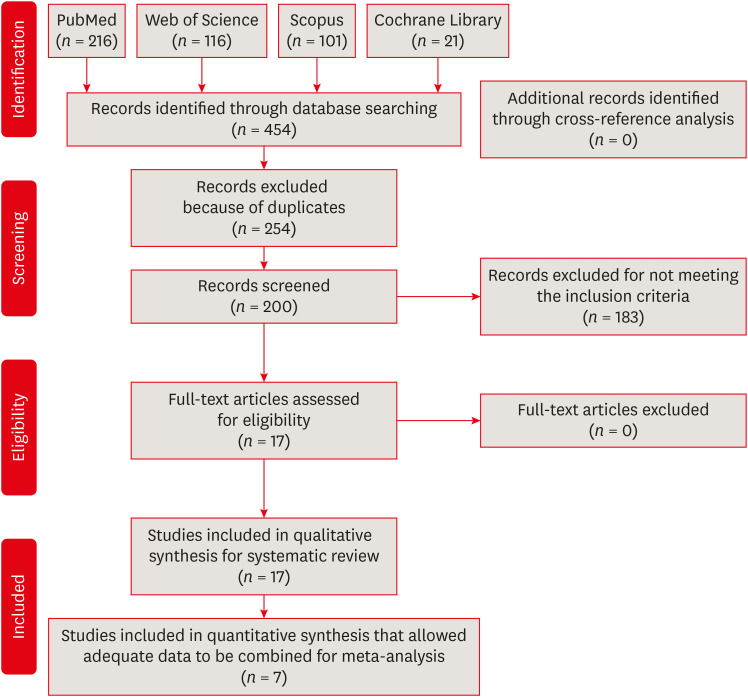
The purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies regarding the effectiveness of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on microbial reduction in root canals. Materials and MethodsPubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, and the gray literature were searched through December 2019. Studies comparing the influence of reciprocating and rotary instrumentation on the removal of microorganisms from root canals that quantified the antimicrobial effect were included. Data extraction was completed using a systematic form for data collection. The risk of bias of the studies was evaluated. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random effects meta-analysis. ResultsSeventeen in vitro studies were included in this systematic review, of which 7 provided adequate data for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Both reciprocating and rotary systems were similarly effective in reducing the microbial load in infected root canals (SMD [95% CI], 0.0481 [−0.271, 0.367]). Three studies showed a low risk of bias, whereas most of the studies (82%) presented a medium risk. ConclusionsAlthough both techniques decrease the microbial content (with reductions of 23.32%–88.47% and 23.33%–89.86% for reciprocating and rotary instrumentation, respectively), they are not able to provide complete disinfection of root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mapping risk of bias criteria in systematic reviews of in vitro endodontic studies: an umbrella review
Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Evandro Piva, Leandro Perello Duro, Adriana Fernandes da Silva, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fifteen years of engine‐driven nickel–titanium reciprocating instruments, what do we know so far? An umbrella review
Felipe Immich, Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Rafaella Rodrigues da Gama, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Evandro Piva, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 409. CrossRef - Does minimally invasive canal preparation provide higher fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review ofin vitrostudies
Sıla Nur Usta, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Seda Falakaloğlu, Mustafa Gündoğar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Different Access Cavity Designs and Ni–Ti Files on the Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal System: An In Vitro Study
Gizem Andac, Atakan Kalender, Buket Baddal, Fatma Basmaci
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(4): 2049. CrossRef - Shaping Properties and Outcomes of Nickel-Titanium Reciprocation Systems in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies
SelvaKumar Haridoss, Bhavyaa R, Kavitha Swaminathan, Aruna P
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Root Canal Sealers and Obturation Techniques on Vertical Root Fracture Resistance. An In Vitro Experiment
Mazen F. Alkahtany, Khalid H. Almadi, Fahad A. Alahmad, Abdullah M. Alshehri, Abdulrahman A. AlSwayyed, Omar M. AlZahran, Ali AlHadan, Abdulaziz S. Almustafa, Fahim Vohra, Tariq Abduljabbar
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(17): 8022. CrossRef
-
1,898
View
-
25
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
Critical evaluation of fracture strength testing for endodontically treated teeth: a finite element analysis study
-
Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Oğuz Eraslan, Sema Belli
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e15. Published online April 18, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e15
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
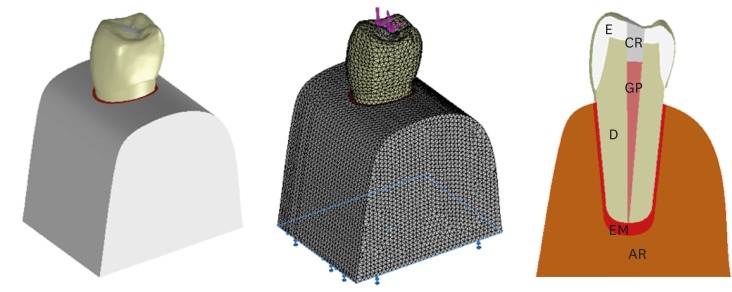
The aim of this study was to investigate whether the diameter and direction of the plunger and simulation of the periodontal ligament (PDL) affected the stress distribution in endodontically treated premolars. MethodsA fracture strength test was simulated via finite element analysis. A base model was set up, and the following parameters were modified: plunger diameter (3 mm vs. 6 mm), plunger direction (vertical vs. 135° angular to the central fossa), and PDL simulation. The analysis was conducted using the CosmosWorks structural analysis program, and the results are presented in terms of von Mises stresses. ResultsThe smaller plunger increased the stresses at the contact area of the crown, but the plunger diameter had no effect on the stress distribution within the root. An angular plunger direction increased stresses within the root, as well as at the buccal cusp of the crown, compared with the vertical direction. Simulation of the PDL caused higher stress accumulation, especially in the cervical region of the root. ConclusionsThe plunger diameter had no effect on the stress distribution in the roots, whereas the plunger direction and PDL simulation did affect the stress distribution. More stringent standards can be established by taking such parameters into account when performing fracture testing in future studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Access cavity in endodontics: Balancing precision, preservation, and clinical needs
Dina Abdellatif, Ismail Davut Capar, De Fontaine Sarah, Alfredo Iandolo, Christophe Meyer, Davide Mancino
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(6): 573. CrossRef - Assessment of Stress Distribution with 3 Taper Design Preparation of Root Canal Using Finite Element Analysis
Tejasree Rathod, G. Durgabhavani, Pudu Tirupathi, Nusrath Parveen, Yelloji Paramesh, Prabhakar Dharavattu
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S112. CrossRef - The impact of the filling technique with two sealers in bulk or associated with gutta-percha on the fatigue behavior and failure patterns of endodontically treated teeth
Isabella Marian Lena, Luiza Colpo Chiaratti, Rafaela Oliveira Pilecco, Renan Vaz Machry, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Renata Dornelles Morgental
PeerJ.2024; 12: e18221. CrossRef - Stronger than Ever: Multifilament Fiberglass Posts Boost Maxillary Premolar Fracture Resistance
Naji Kharouf, Eugenio Pedullà, Gianluca Plotino, Hamdi Jmal, Mohammed-El-Habib Alloui, Philippine Simonis, Patrice Laquerriere, Valentina Macaluso, Dina Abdellatif, Raphaël Richert, Youssef Haikel, Davide Mancino
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2975. CrossRef - Neural network approach to evaluate the physical properties of dentin
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Ali Mohammad Saghiri, Elham Samadi, Devyani Nath, Julia Vakhnovetsky, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2023; 111(1): 68. CrossRef - Modelling and evaluating periodontal ligament mechanical behaviour and properties: A scoping review of current approaches and limitations
Enaiyat Ghani Ovy, Dan L. Romanyk, Carlos Flores Mir, Lindsey Westover
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2022; 25(2): 199. CrossRef - FEAr no more! Finite element analysis in orthodontics
Shilpa Chawla, Shailesh Deshmukh
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2022; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - Influence of Methodological Variables on Fracture Strength Tests Results of Premolars with Different Number of Residual Walls. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Carlo Gaeta, Crystal Marruganti, Emanuele Mignosa, Giovanni Franciosi, Edoardo Ferrari, Simone Grandini
Dentistry Journal.2021; 9(12): 146. CrossRef
-
1,971
View
-
33
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Mineral content analysis of root canal dentin using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
-
Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Emel Uzunoğlu, Banu Sezer, Zeliha Yılmaz, İsmail Hakkı Boyacı
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e11. Published online February 4, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e11
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
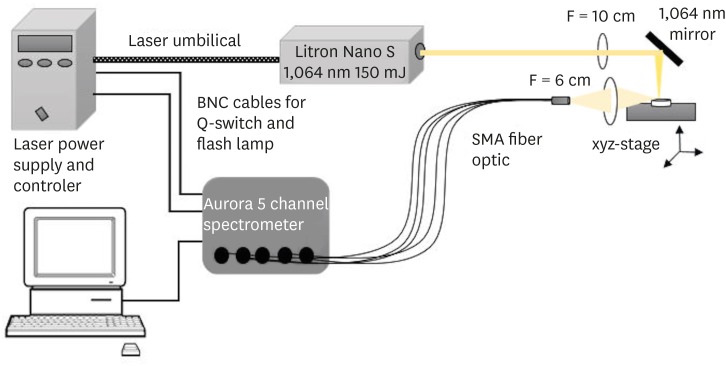
This study aimed to introduce the use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for evaluation of the mineral content of root canal dentin, and to assess whether a correlation exists between LIBS and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) methods by comparing the effects of irrigation solutions on the mineral content change of root canal dentin. Materials and MethodsForty teeth with a single root canal were decoronated and longitudinally sectioned to expose the canals. The root halves were divided into 4 groups (n = 10) according to the solution applied: group NaOCl, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 1 hour; group EDTA, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 2 minutes; group NaOCl+EDTA, 5.25% NaOCl for 1 hour and 17% EDTA for 2 minutes; a control group. Each root half belonging to the same root was evaluated for mineral content with either LIBS or SEM/EDS methods. The data were analyzed statistically. ResultsIn groups NaOCl and NaOCl+EDTA, the calcium (Ca)/phosphorus (P) ratio decreased while the sodium (Na) level increased compared with the other groups (p < 0.05). The magnesium (Mg) level changes were not significant among the groups. A significant positive correlation was found between the results of LIBS and SEM/EDS analyses (r = 0.84, p < 0.001). ConclusionsTreatment with NaOCl for 1 hour altered the mineral content of dentin, while EDTA application for 2 minutes had no effect on the elemental composition. The LIBS method proved to be reliable while providing data for the elemental composition of root canal dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photosensitizers and calcium hydroxide on bond strength, chemical composition, and sealing of glass-fiber posts to root dentin
Thalya Fernanda Horsth Maltarollo, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Henrique Augusto Banci, Mariana de Oliveira Bachega, Beatriz Melare de Oliveira, Marco Hungaro Antonio Duarte, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Luciano Angelo Tavares
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Using 5% Apple Vinegar Irrigation Solution Adjunct to Diode Laser on Smear Layer Removal and Calcium/Phosphorus Ion Ratio during Root Canal Treatment
Tarek AA Salam, Haythem SA Kader, Elsayed E Abdallah
CODS - Journal of Dentistry.2024; 15(1): 3. CrossRef - Evaluation of chemical composition of root canal dentin between two age groups using different irrigating solutions: An in vitro sem-eds study
Naresh Kumar K, Abhijith Kallu, Surender L.R, Sravani Nirmala, Narender Reddy
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 12(1): 18. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of a Novel Nanohydroxyapatite Gel and Er: YAG Laser Treatment on Dentin Hypersensitivity
Demet Sahin, Ceren Deger, Burcu Oglakci, Metehan Demirkol, Bedri Onur Kucukyildirim, Mehtikar Gursel, Evrim Eliguzeloglu Dalkilic
Materials.2023; 16(19): 6522. CrossRef - Chitosan Homogenizing Coffee Ring Effect for Soil Available Potassium Determination Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy
Xiaolong Li, Rongqin Chen, Zhengkai You, Tiantian Pan, Rui Yang, Jing Huang, Hui Fang, Wenwen Kong, Jiyu Peng, Fei Liu
Chemosensors.2022; 10(9): 374. CrossRef - Quantitative analysis of cadmium in rice roots based on LIBS and chemometrics methods
Wei Wang, Wenwen Kong, Tingting Shen, Zun Man, Wenjing Zhu, Yong He, Fei Liu
Environmental Sciences Europe.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,404
View
-
9
Download
-
7
Crossref
|