-
Clinical and radiographic outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment performed by endodontic postgraduate students: a retrospective study
-
Hadi Rajeh Alfahadi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Fawaz Hamad Alkazman, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Nada Al-Nazhan
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(2):e24. Published online May 9, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e24
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
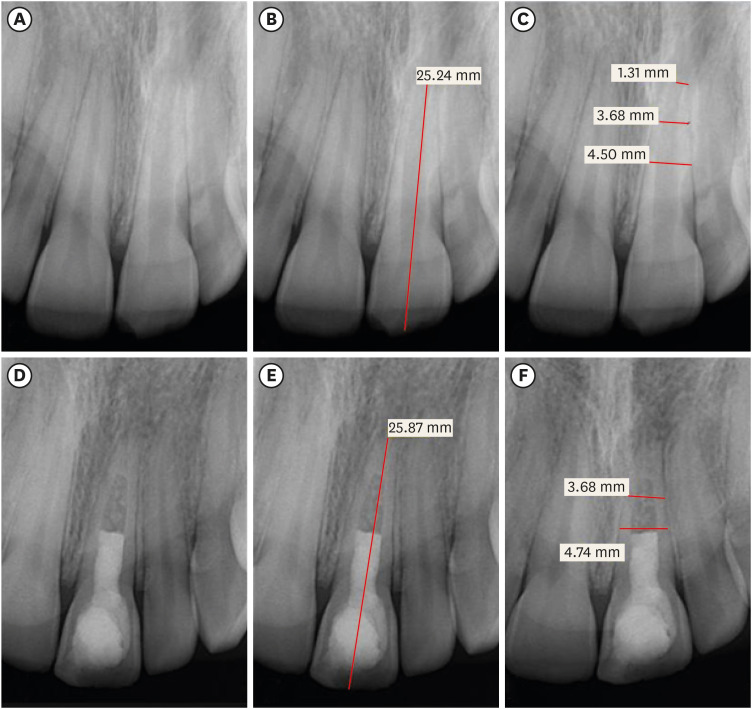
Regenerative endodontic treatment is a clinical procedure aimed at biologically regenerating damaged root canal tissue of immature permanent teeth. This study aimed to report the outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment performed by endodontic postgraduate students. Materials and MethodsClinical and radiographic data of 27 patients, aged 10–22 years, who underwent regenerative treatment of immature permanent teeth from 2015 to 2019 were followed up, wherein clinical and radiographic examinations were performed for each patient. Postoperative success rate and tooth survival were analyzed, and the postoperative radiographic root area changes were quantified. ResultsA total of 23 patients attended the dental appointments, showing that all teeth survived and were asymptomatic. Specifically, 7 periapical pathosis cases were completely healed, 12 were incompletely healed, and 4 cases failed. Moreover, significant differences were found between discolored and non-discolored teeth, and between the presence or absence of periapical radiolucency. Additionally, 3 anterior teeth showed complete closure of the apical foramen, while the apical foramen width was reduced in 17 teeth and failed in 3 teeth. Root length was also found to have been increased in 7 anterior and 4 posterior teeth, and the average length ranged from 4.00–0.63 mm in the anterior teeth, 2.85–1.48 mm of the mesial root, and 2.73–2.16 mm of the molar teeth distal root. Furthermore, calcified tissue deposition was observed in 7 teeth. ConclusionsA favorable outcome of regenerative endodontic treatment of immature permanent teeth with necrotic pulp was achieved with a high survival rate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Regenerative Endodontics and Stem Cell-Based Therapies – A Systematic Review
Wjoud Ahmed Alshamrani, Sarah Sulaiman Alzarea, Joud Khalid Alabbas, Ayah Khalid Alabbas, Mawiyah Ibrahim Aljaddua, Osama Khattak, Rakhi Issrani
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2026; 18(Suppl 1): S29. CrossRef - Pre‐Operative Factors on Prognosis of Regenerative Endodontic Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Filipe Colombo Vitali, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Pablo Silveira Santos, Ana Paula Portes Zeno, Patrícia de Andrade de Risso, Lucianne Cople Maia, Francine Benetti, Cleonice da Silveira da Teixeira
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(12): 1814. CrossRef - Clinical, radiographic, and biomarker perspectives of low-level laser therapy during regenerative endodontic procedures in necrotic immature young teeth: a randomized clinical study
Pragya Pandey, Neha Jasrasaria, Ramesh Bharti, Rakesh Kumar Yadav, Monika Kumari, Abinia Vaishnavi, Rahul Pandey
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Allogeneic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Transplantation Induces Dentin Pulp Complex-like Formation in Immature Teeth with Pulp Necrosis and Apical Periodontitis
Jose Francisco Gomez-Sosa, José E. Cardier, Olga Wittig, Dylana Díaz-Solano, Eloisa Lara, Kharelys Duque, Giselle Ramos-González
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(4): 483. CrossRef - Radiographic assessment of dental post and core placement at different educational levels in an undergraduate student clinic: a 4-year retrospective study
Turki Alshehri, Nourhan M. Aly, Raand Altayyar, Deena Alghamdi, Shahad Alotaibi, Passent Ellakany
F1000Research.2024; 12: 976. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy of injectable platelet‐rich fibrin versus platelet‐rich plasma in the regeneration of traumatized necrotic immature maxillary anterior teeth: A randomized clinical trial
Maha Mohamed Abo‐Heikal, Jealan M. El‐Shafei, Samia A. Shouman, Nehal N. Roshdy
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(1): 61. CrossRef - Radiographical assessment of post and core placement errors encountered by Saudi dental students at different educational levels
Turki Alshehri, Nourhan M. Aly, Raand Altayyar, Deena Alghamdi, Shahad Alotaibi, Passent Ellakany
F1000Research.2023; 12: 976. CrossRef
-
4,297
View
-
78
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography
-
Hassan AL-Alawi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, Mazen A. Aldosimani, Mohammed Nabil Zahid, Ghadeer N. Shihabi
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e1. Published online November 14, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
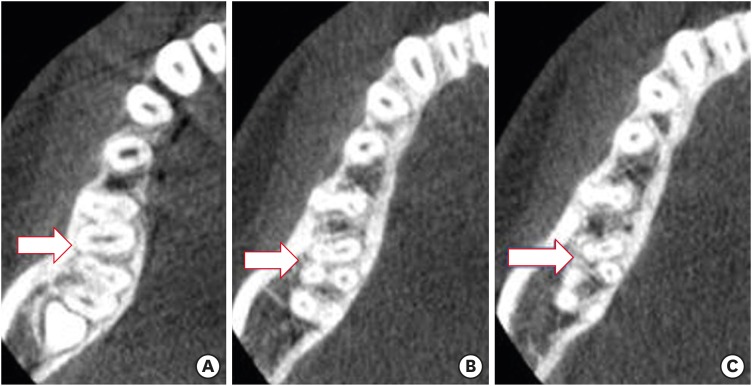
The purpose of this study was to determine the incidence of radix molaris (RM) (entomolaris and paramolaris) in the mandibular first permanent molars of a sample Saudi Arabian subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Materials and MethodsA total of 884 CBCT images of 427 male and 457 female Saudi citizens (age 16 to 70 years) were collected from the radiology department archives of 4 dental centers. A total of 450 CBCT images of 741 mature mandibular first molars that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed. The images were viewed at high resolution by 3 examiners and were analyzed with Planmeca Romexis software (version 5.2). ResultsThirty-three (4.5%) mandibular first permanent molars had RM, mostly on the distal side. The incidence of radix entomolaris (EM) was 4.3%, while that of radix paramolaris was 0.3%. The RM roots had one canal and occurred more unilaterally. No significant difference in root configuration was found between males and females (p > 0.05). Types I and III EM root canal configurations were most common, while type B was the only RP configuration observed. ConclusionsThe incidence of RM in the mandibular first molars of this Saudi subpopulation was 4.5%. Identification of the supernumerary root can avoid missing the canal associated with the root during root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of the variations of mandibular molars and the distance from root apex to the inferior alveolar nerve in Saudi Sub-population: Three-dimensional radiographic evaluation
Tariq Mohammed Aqili, Esam Sami Almuzaini, Abdulbari Saleh Aljohani, Ahmed Khaled Al Saeedi, Hassan Abdulmuti Hammudah, Muath Alassaf, Muhannad M. Hakeem, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(2): e0317053. CrossRef - Prevalence of radix molaris in mandibular molars of a subpopulation of Brazil’s Northeast region: a cross-sectional CBCT study
Yasmym Martins Araújo de Oliveira, Maria Clara Mendes Gomes, Maria Fernanda da Silva Nascimento, Ricardo Machado, Danna Mota Moreira, Hermano Camelo Paiva, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris and distolingual canals and their association with the incidence of middle mesial canals in mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Afaf Al-Haddad, Ebtsam A. Aledaili
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the root and canal morphology in the permanent dentition of Saudi Arabian population using cone beam computed and micro-computed tomography – a systematic review
Mohammed Mustafa, Rumesa Batul, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Hadi Mohammed Alamri, Abdulaziz Abdulwahed, Ahmed A. Almokhatieb, Qamar Hashem, Abdullah Alsakaker, Mohammad Khursheed Alam, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of radix accesoria dentis in a northern Peruvian population evaluated by cone-beam tomography
Karla Renata León-Almanza, Anthony Adrián Jaramillo-Nuñez, Catherin Angélica Ruiz-Cisneros, Paul Martín Herrera-Plasencia
Heliyon.2024; 10(16): e35919. CrossRef - Radix molaris is a hidden truth of mandibular first permanent molars: A descriptive- analytic study using cone beam computed tomography
Mohammed A. Alobaid, Saurabh Chaturvedi, Ebtihal Mobarak S. Alshahrani, Ebtsam M. Alshehri, Amal S. Shaiban, Mohamed Khaled Addas, Giuseppe Minervini
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1957. CrossRef - Prevalence of Radix Entomolaris in Mandibular Permanent Molars Analyzed by Cone-Beam CT in the Saudi Population of Ha'il Province
Moazzy I Almansour, Ahmed A Madfa, Adhwaa F Algharbi, Reem Almuslumani, Noeer K Alshammari, Ghufran M Al Hussain
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of radix entomolaris in India and its comparison with the rest of the world
Sumit MOHAN, Jyoti THAKUR
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Radix Paramolaris an Endodontic Challenge: A Case Report
Ashwini B Prasad, Deepak Raisingani, Ridhima Gupta, Rimjhim Jain
Journal of Mahatma Gandhi University of Medical Sciences and Technology.2022; 7(1): 32. CrossRef - Evaluation of Radix Entomolaris and Middle Mesial Canal in Mandibular Permanent First Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography
Ranjdar Mahmood Talabani, Kazhan Omer Abdalrahman, Rawa Jamal Abdul, Dlsoz Omer Babarasul, Sara Hilmi Kazzaz, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Maxillary and Mandibular First Molar by CBCT: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
Rakan Rafdan Alhujhuj, Rizwan Jouhar, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Abdullatif Abdulrahman Almujhim, Mohammed Tariq Albutayh, Necdet Adanir
Diagnostics.2022; 12(9): 2121. CrossRef - Ethnical Anatomical Differences in Mandibular First Permanent Molars between Indian and Saudi Arabian Subpopulations: A Retrospective Cross-sectional Study
Abdulwahab Alamir, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Apathsakayan Renugalakshmi, Thilla S Vinothkumar, Anandhi S Arthisri, Ahmed Juraybi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(5): 484. CrossRef
-
2,581
View
-
37
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls. In vitro SEM study
-
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):258-264. Published online July 22, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.258
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This in vitro study aimed to investigate the ability of Candida albicans (C. albicans) and Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) to penetrate dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal surface of split human teeth. Materials and MethodsSixty intact extracted human single-rooted teeth were divided into 4 groups, negative control, positive control without canal instrumentation, instrumented, and retreated. Root canals in the instrumented group were enlarged with endodontic instruments, while root canals in the retreated group were enlarged, filled, and then removed the canal filling materials. The teeth were split longitudinally after canal preparation in 3 groups except the negative control group. The teeth were inoculated with both microorganisms separately and in combination. Teeth specimens were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the depth of penetration into the dentinal tubules was assessed using the SMILE view software (JEOL Ltd). ResultsPenetration of C. albicans and E. faecalis into the dentinal tubules was observed in all 3 groups, although penetration was partially restricted by dentin debris of tubules in the instrumented group and remnants of canal filling materials in the retreated group. In all 3 groups, E. faecalis penetrated deeper into the dentinal tubules by way of cell division than C. albicans which built colonies and penetrated by means of hyphae. ConclusionsMicroorganisms can easily penetrate dentinal tubules of root canals with different appearance based on the microorganism size and status of dentinal tubules.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Capped silver nanoparticle penetration in primary dentition: an in vitro SEM-EDS analysis
Amjad Almuqrin, Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne, Jayanti Mendhi, Laurence J. Walsh, Sobia Zafar
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of photobiomodulation therapy on regenerative potential of non-vital mature permanent teeth in healthy canine dogs
S. F. Khattab, Y. F. Gomaa, E. A. E. Abdelaziz, N. M. A. Khattab
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2025; 26(3): 493. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A 12-month randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy of revitalization of retreated mature incisors with periapical radiolucency in adolescents
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Osama Seif-Elnasr Hussien, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb, Yassmin Mohamed ElMakawi, Norhan Khaled Omar Wahba
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Failed Regenerative Endodontic Case Treated by Modified Aspiration-irrigation Technique and Apexification
Loai Alsofi, Sara Almarzouki
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(1): 92. CrossRef - Effectiveness of EndoActivator, PATS Vario system, and XP-endo Finisher files on smear layer removal under scanning electron microscope: A comparative study
Rishabh Patel, Gaurav Shinde, Prashant Bondarde, Aruna Vishwakarma, Madhuri Bhandare, Vaibhavi Pharne
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry.2024; 42(3): 195. CrossRef - Influence of root canal moisture on the penetration of TotalFill bioceramic sealer into the dentinal tubules: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Archika M Singh, Tarek M Elsewify, Walid S El-Sayed, Husam H Nuawafleh, Ranya F Elemam, Bassem M Eid
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Fungi and bacteria occupy distinct spatial niches within carious dentin
Rosalyn M. Sulyanto, Clifford J. Beall, Kasey Ha, Joseph Montesano, Jason Juang, John R. Dickson, Shahr B. Hashmi, Seth Bradbury, Eugene J. Leys, Mira Edgerton, Sunita P. Ho, Ann L. Griffen, Alex Andrianopoulos
PLOS Pathogens.2024; 20(5): e1011865. CrossRef - The advancement in irrigation solution within the field of endodontics, A Review
Fatima Fahad , Raghad A Al-Hashimi , Munther J Hussain
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 54. CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Fabrication of Rapidly Soluble Zn2+-Releasing Phosphate-Based Glass and Its Incorporation into Dental Resin
Fan Deng, Haruaki Kitagawa, Tomoki Kohno, Tingyi Wu, Naoya Funayama, Pasiree Thongthai, Hefei Li, Gabriela L. Abe, Ranna Kitagawa, Jun-Ichi Sasaki, Satoshi Imazato
Molecules.2024; 29(21): 5098. CrossRef - Combined effect of electrical energy and graphene oxide on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Myung-Jin LEE, Mi-Ah KIM, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 844. CrossRef - Effect of Different Irrigant Activation Techniques on the Penetration of Calcium Hydroxide, an Intracanal Medicament: An In Vitro Study
Radha Kalyani Narla, Ravi kumar J, Tejosmita Chowdary Pavuluri, Krishna Chaitanya P, Ramesh Penumaka, Ratna Kamal Nagelli
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative assessment of antibacterial effect of two types of laser and their effect on morphology and mineral content of dentin
Soha Adel Abdou, Haythem S Moharrum, Elsayed Abdallah Eltayeb
Journal of The Arab Society for Medical Research.2023; 18(2): 117. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endodontic Disinfection Protocols in an E. faecalis Biofilm Model—Using DAPI Staining and SEM
Maria Dede, Sabine Basche, Jörg Neunzehn, Martin Dannemann, Christian Hannig, Marie-Theres Kühne
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(4): 176. CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Matricaria chamomilla L. Extract Against Enterococcus faecalis
Ariana Kameri, Arben Haziri, Zeqir Hashani, Agime Dragidella, Kemajl Kurteshi, Arsim Kurti
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 13. CrossRef - Efficacy of Smear Layer Removal at the Apical One-Third of the Root Using Different Protocols of Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminium Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser
Amel Yousif Habshi, Nausheen Aga, Khadija Yousif Habshi, Muna Eisa Mohamed Hassan, Ziaullah Choudhry, Muhammad Adeel Ahmed, Azeem Ul Yaqin Syed, Rizwan Jouhar
Medicina.2023; 59(3): 433. CrossRef - Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
E. Karatas, M. Hadis, W. M. Palin, M. R. Milward, S. A. Kuehne, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Functionalized surface of PLGA nanoparticles in thermosensitive gel to enhance the efficacy of antibiotics against antibiotic resistant infections in endodontics: A randomized clinical trial
Mona G. Arafa, Hadeel A. Mousa, Mohamed Medhat Kataia, Shehabeldin M., Nagia N. Afifi
International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X.2023; 6: 100219. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - TREATMENT OF PERIODONTITIS WITH INCLUSIVE ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS
Lyudmila Tatintsyan, Janna Khachatryan, Sona Ambartsumyan, Arsen Mikaelyan, Valery Tatintsyan, Minas Pogosyan, Anna Hakobyan, Arsen Kupelyan, Armen Shahinyan
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2022; : 15. CrossRef - Antimicrobial action of photodynamic therapy on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm using curing light, curcumin and riboflavin
Mahsa Moradi, Mahta Fazlyab, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Nasim Chiniforush
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 274. CrossRef - Candida albicans and Enterococcus faecalis biofilm frenemies: When the relationship sours
Om Alkhir Alshanta, Khawlah Albashaireh, Emily McKloud, Christopher Delaney, Ryan Kean, William McLean, Gordon Ramage
Biofilm.2022; 4: 100072. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide/iodoform nanoparticles as an intracanal filling medication: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro study using a bovine primary tooth model
Arturo Garrocho-Rangel, Diana María Escobar-García, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Denisse Herrera-Badillo, Fernanda Carranco-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Flores-Arriaga, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 687. CrossRef - Dentin Disinfection Efficacy Using Four Different Irrigation Protocols
David Jaramillo, Jose L Ibarrola, Ana Arias, Phillipe Sleiman, Ali Naji, David E Jaramillo
Dental Research and Management.2021; : 33. CrossRef - Histologic, Radiographic, and Micro-Computed Tomography Evaluation of Experimentally Enlarged Root Apices in Dog Teeth with Apical Periodontitis after Regenerative Treatment
Mohammed S. Alenazy, Saad Al-Nazhan, Hezekiah A Mosadomi
Current Therapeutic Research.2021; 94: 100620. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of dentin volume removal and centralization of the root canal after shaping with the ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and One-Curve instruments using micro-CT
Hatice Yalniz, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Aysenur Oncu, Berkan Celikten, Ayse Isil Orhan, Kaan Orhan
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - The influence of centrifugation and inoculation time on the number, distribution, and viability of intratubular bacteria and surface biofilm in deciduous and permanent bovine dentin
Viktoria A. Dezhurko-Korol, Nina E. Novozhilova, Irina M. Makeeva, Anastasia Yu. Arkhipova, Mihail M. Moisenovich, Ludmila V. Akhmadishina, Alexander N. Lukashev, Alexander M. Semenov, Maria R. Leontieva, Svetlana F. Byakova
Archives of Oral Biology.2020; 114: 104716. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of synthetic and natural-derived novel endodontic irrigating solution – An In vitro study
Thangi Sowjanya, Sudhakar Naidu, MahendraVarma Nadimpalli, GowtamDev Dondapati, TB V G Raju, ParvathaneniKrishna Prasad
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Three Different Intracanal Medicaments against Candida albicans: An In Vitro Study
Ravi Vaiyapuri, Jambai S Sivakumar, Chittrarasu Mathimaraiselvan, Andamuthu Sivakumar, Anjaneya Shiva Prasad, Sasmitha Chandrasekaran
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020; 5(2): 79. CrossRef - Assessment of Nitrofurantoin as an Experimental Intracanal Medicament in Endodontics
Mewan Salahalddin A. Alrahman, Bestoon Muhammed Faraj, Kawa F. Dizaye, Abdelwahab Omri
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Conjugate of chitosan nanoparticles with chloroaluminium phthalocyanine: Synthesis, characterization and photoinactivation of Streptococcus mutans biofilm
Leonardo Lobo Ribeiro Cavalcante, Antonio Claudio Tedesco, Luandra Aparecida Unten Takahashi, Fabiana Almeida Curylofo-Zotti, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2020; 30: 101709. CrossRef - Effect of triple antibiotic loaded apatitic nanocarriers on Enterococcus faecalis biofilm – An In vitro study
S. Nagarathinam, V. Sujatha, K. Madhumathi, S. Mahalaxmi, P.Pranav Vanajassun, T.S.Sampath Kumar
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2019; 51: 499. CrossRef - Wear profile of canal wall surfaces and bond strength of endodontic sealers after in situ acid challenge
R. D. Silva‐Neto, M. D. Sousa‐Neto, J. D. Pécora, R. G. Palma‐Dibb, A. E. Souza‐Gabriel
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 364. CrossRef - Bacterial invasion of dentinal tubules from the external root surface with and without an intact cemental layer- a confocal laser scanning microscopic study
Jovita D’souza, Sneha Gokhale, Vikram Padbidri, Lovely M
Advances in Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine: Open Access.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - AgCa-PLGA submicron particles inhibit the growth and colonization of E. Faecalis and P. Gingivalis on dentin through infiltration into dentinal tubules
Wei Fan, Danfeng Liu, Yanyun Li, Qing Sun, Bing Fan
International Journal of Pharmaceutics.2018; 552(1-2): 206. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy Associated with Conventional Endodontic Treatment: A Clinical and Molecular Microbiological Study
Caroline C. da Silva, Sérgio P. Chaves Júnior, Gabriela L. D. Pereira, Karla B. F. da C. Fontes, Lívia A. A. Antunes, Helvécio C. C. Póvoa, Leonardo S. Antunes, Natalia L. P. P. Iorio
Photochemistry and Photobiology.2018; 94(2): 351. CrossRef - Human teeth biobank: Microbiological analysis of the teeth storage solution
Fabiana Almeida Curylofo‐Zotti, Francine Lorencetti‐Silva, Jéssica de Almeida Coelho, Rachel Maciel Monteiro, Evandro Watanabe, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Microscopy Research and Technique.2018; 81(3): 332. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics by Cell Homing
Ling He, Juan Zhong, Qimei Gong, Bin Cheng, Sahng G. Kim, Junqi Ling, Jeremy J. Mao
Dental Clinics of North America.2017; 61(1): 143. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontics for Adult Patients
Ling He, Sahng G. Kim, Qimei Gong, Juan Zhong, Sainan Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Ling Ye, Junqi Ling, Jeremy J. Mao
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(9): S57. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Sealing Ability of Three Obturation Techniques Using a Glucose Leakage Test
Katarzyna Olczak, Halina Pawlicka
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis in endodontic infections: antibiotic resistance profile and susceptibility to photodynamic therapy
Ana Carolina Chipoletti Prado, Patrícia Pimentel De Barros, Jéssica Diane Dos Santos, Luciane Dias De Oliveira, Claudio Antônio Talge Carvalho, Marcia Carneiro Valera, Antonio Olavo Cardoso Jorge, Juliana Campos Junqueira
Lasers in Dental Science.2017; 1(2-4): 91. CrossRef - Study of invasion and colonization of E. faecalis in microtubes by a novel device
Xiaoqiang Sun, Shujing Wang, Yue Yang, Chunxiong Luo, Benxiang Hou
Biomedical Microdevices.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Nail Damage (Severe Onychodystrophy) Induced by Acrylate Glue: Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-Ray Investigations
Tudor Pinteala, Anca Eduard Chiriac, Irina Rosca, Francesca Larese Filon, Mariana Pinteala, Anca Chiriac, Cristian Podoleanu, Simona Stolnicu, Marius Florin Coros, Adina Coroaba
Skin Appendage Disorders.2016; 2(3-4): 137. CrossRef -
Phage therapy against
Enterococcus faecalis
in dental root canals
Leron Khalifa, Mor Shlezinger, Shaul Beyth, Yael Houri-Haddad, Shunit Coppenhagen-Glazer, Nurit Beyth, Ronen Hazan
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Approach of High Technology Techniques for Control and Elimination of Endodontic Microbiota
Nasim Chiniforush, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Sima Shahabi, Abbas Bahador
Journal of lasers in medical sciences.2015; 6(4): 139. CrossRef - Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 149. CrossRef
-
2,365
View
-
29
Download
-
48
Crossref
|