-
Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
-
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e18. Published online March 27, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e18
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
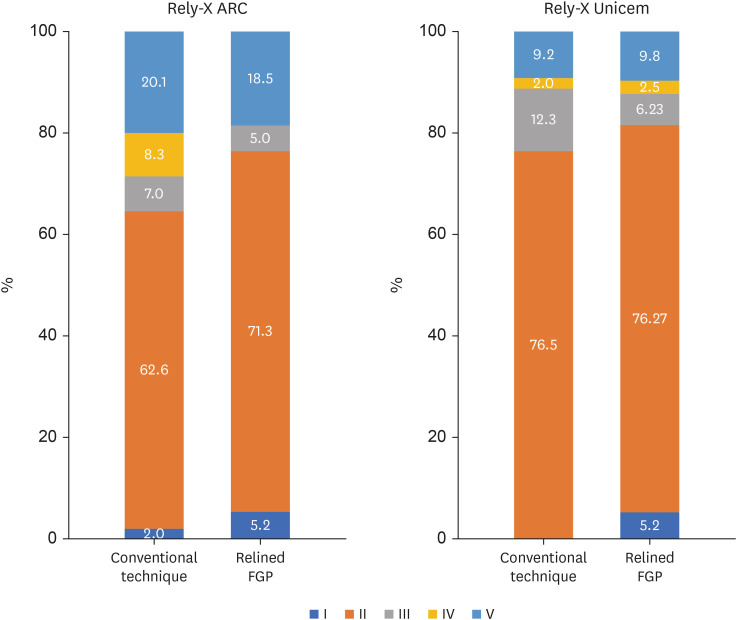
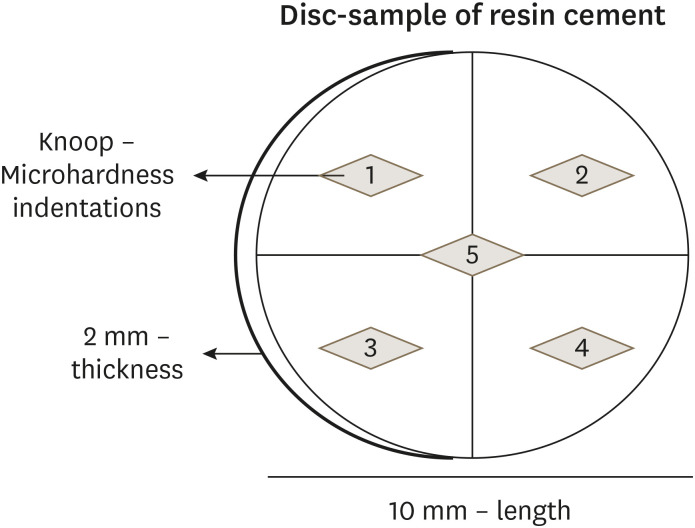
This study was conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of relined and non-relined fiberglass posts when cemented to root canal dentin using a conventional dual-cure resin cement or a self-adhesive resin cement. Materials and MethodsTwo types of resin cements were utilized: conventional and self-adhesive. Additionally, 2 cementation protocols were employed, involving relined and non-relined fiberglass posts. In total, 72 bovine incisors were cemented and subjected to push-out bond strength testing (n = 10) followed by failure mode analysis. The cross-sectional microhardness (n = 5) was assessed along the root canal, and interface analyses (n = 3) were conducted using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data from the push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness tests were analyzed via 3-way analysis of variance and the Bonferroni post-hoc test (α = 0.05). ResultsFor non-relined fiberglass posts, conventional resin cement exhibited higher push-out bond strength than self-adhesive cement. Relined fiberglass posts yielded comparable results between the resin cements. Type II failure was the most common failure mode for both resin cements, regardless of cementation protocol. The use of relined fiberglass posts improved the cross-sectional microhardness values for both cements. SEM images revealed voids and bubbles in the incisors with non-relined fiberglass posts. ConclusionsMechanical properties were impacted by the cementation protocol. Relined fiberglass posts presented the highest push-out bond strength and cross-sectional microhardness values, regardless of the resin cement used (conventional dual-cure or self-adhesive). Conversely, for non-relined fiberglass posts, the conventional dual-cure resin cement yielded superior results to the self-adhesive resin cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef
-
4,304
View
-
121
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of self-adhesive resin cements
-
Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Giovanna Corrêa Denucci, Gabriela Soffner, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e32. Published online July 14, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e32
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of inorganic composition and filler particle morphology on the mechanical properties of different self-adhesive resin cements (SARCs). Materials and MethodsThree SARCs including RelyX Unicem-2 (RUN), Maxcem Elite (MAX), and Calibra Universal (CAL) were tested. Rectangular bar-shaped specimens were prepared for flexural strength (FS) and flexural modulus (FM) and determined by a 3-point bending test. The Knoop microhardness (KHN) and top/bottom microhardness ratio (%KHN) were conducted on the top and bottom faces of disc-shaped samples. Sorption (Wsp) and solubility (Wsl) were evaluated after 24 hours of water immersion. Filler morphology was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). FS, FM, %KHN, Wsp, Wsl, and EDS results were submitted to 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s post-hoc test, and KHN also to paired t-test (α = 0.05). ResultsSARC-CAL presented the highest FS value, and SARC-RUN presented the highest FM. SARC-MAX and RUN showed the lowest Wsp and Wsl values. KHN values decreased from top to bottom and the SARCs did not differ statistically. Also, all resin cements presented carbon, aluminum, and silica in their composition. SARC-MAX and RUN showed irregular and splintered particles while CAL presented small and regular size particles. ConclusionsA higher mechanical strength can be achieved by a reduced spread in grit size and the filler morphology can influence the KHN, as well as photoinitiators in the composition. Wsp and Wsl can be correlated with ions diffusion of inorganic particles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability in Bioactive and Conventional Resin Cements Under Thermal Stress Conditions
Alaa Turkistani, Hanin E. Yeslam
Biomimetics.2025; 10(7): 432. CrossRef - Assessment of fit accuracy and retentive strength of additively manufactured zirconia crowns luted to Ti‐base abutments with different resin cements: An in vitro study
Rafat Sasany, Sultan Merve Uçar, Burak Yilmaz
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Resin Cement Color Stability and Restoration Thickness as Determinants of the Final Shade in a Glass–Ceramic CAD/CAM Material
Hanin E. Yeslam, Alaa Turkistani
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(9): 319. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Resin-Based Luting Materials—Review
Aleksandra Maletin, Milica Jeremić Knežević, Daniela Đurović Koprivica, Tanja Veljović, Tatjana Puškar, Bojana Milekić, Ivan Ristić
Polymers.2023; 15(20): 4156. CrossRef - A Scoping Review on the Polymerization of Resin-Matrix Cements Used in Restorative Dentistry
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Orlanda Torres, Óscar Carvalho, Filipe S. Silva, Susana O. Catarino, Mutlu Özcan, Júlio C. M. Souza
Materials.2023; 16(4): 1560. CrossRef
-
1,681
View
-
19
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
The effect of individualization of fiberglass posts using bulk-fill resin-based composites on cementation: an in vitro study
-
Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Jairo Matozinho Cordeiro, Carolina Perez Rangel, Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(4):e37. Published online October 18, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
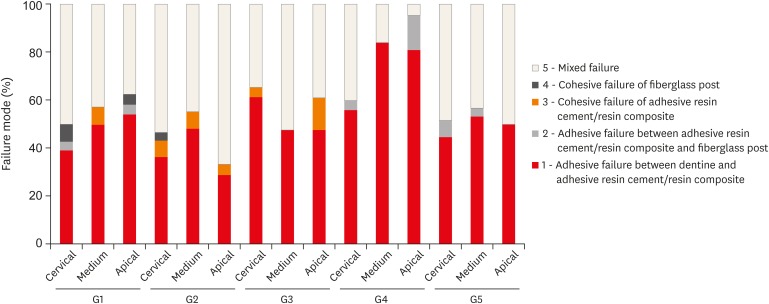
This study evaluated the bond strength of various fiberglass post cementation techniques using different resin-based composites. Materials and MethodsThe roots from a total of 100 bovine incisors were randomly assigned to 5 treatment groups: G1, post + Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (SBMP) + RelyX ARC luting agent; G2, relined post (Filtek Z250) + SBMP + RelyX ARC; G3, individualized post (Filtek Z250) + SBMP; G4, individualized post (Filtek Bulk-Fill) + SBMP; G5, individualized post (Filtek Bulk-Fill Flow) + SBMP. The samples were subjected to the push-out (n = 10) and pull-out (n = 10) bond strength tests. Data from the push-out bond strength test were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Bonferroni post hoc test, and data from the pull-out bond strength test were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA. ResultsThe data for push-out bond strength presented higher values for G2 and G5, mainly in the cervical and middle thirds, and the data from the apical third showed a lower mean push-out bond strength in all groups. No significant difference was noted for pull-out bond strength among all groups. The most frequent failure modes observed were adhesive failure between dentine and resin and mixed failure. ConclusionsFiberglass post cementation using restorative and flowable bulk-fill composites with the individualization technique may be a promising alternative to existing methods of post cementation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - EVALUATION OF PUSH-OUT BOND STRENGTH OF GLASS FIBER POSTS USING DIFFERENT LUTING CEMENTS
Jannah Mohammed, Maha Agha
BULLETIN OF STOMATOLOGY AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY.2025; : 274. CrossRef - Effects of a relined fiberglass post with conventional and self-adhesive resin cement
Wilton Lima dos Santos Junior, Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance of weakened roots restored with relined or milled CAD-CAM glass fiber posts
Belizane das Graças Oliveira MAIA, Thais da Silva Alves SANTOS, Cláudio Antonio Talge CARVALHO, Francielle Silvestre VERNER, Rafael Binato JUNQUEIRA
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 92. CrossRef - Evaluation of pretreatments on intra‐radicular dentin bond strength of self‐adhesive resin cements
Marina Rodrigues Santi, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Beatriz Ometto Sahadi, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins, Jorge Rodrigo Soto‐Montero
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(7): 1051. CrossRef - Comparison of the Mechanical Properties and Push-out Bond Strength of Self-adhesive and Conventional Resin Cements on Fiber Post Cementation
MR Santi, RBE Lins, BO Sahadi, JR Soto-Montero, LRM Martins
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(3): 346. CrossRef - Glass fiber posts
Renata Pereira, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Victória Castelan Rodrigues, Débora Alves Nunes Leite Lima, Luís Roberto Marcondes Martins, Flávio Henrique Baggio Aguiar
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 19: e207508. CrossRef
-
1,146
View
-
10
Download
-
6
Crossref
|