-
Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
-
Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e54. Published online October 20, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e54
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
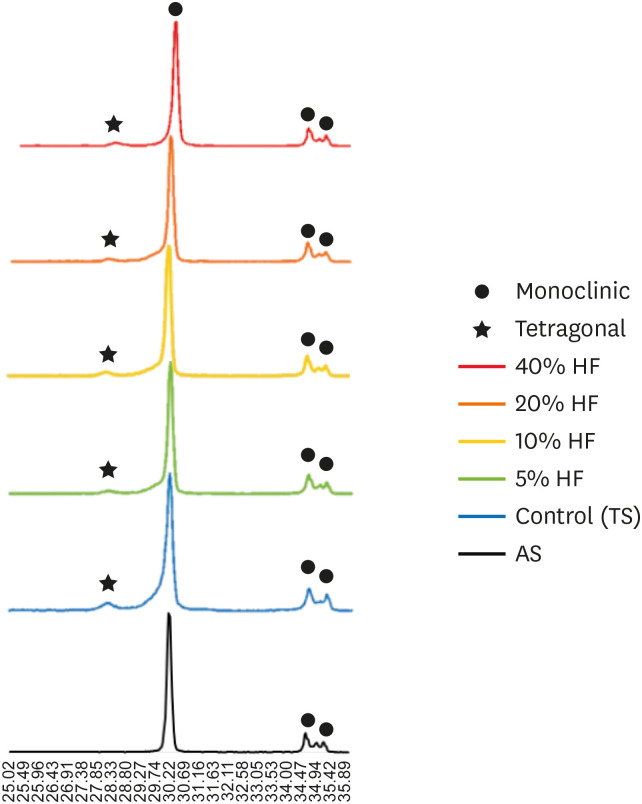
The purpose of this study was to quantify phase transformation after hydrofluoric acid (HF) etching at various concentrations on the surface of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), and to evaluate changes in bonding strength before and after thermal cycling. Materials and MethodsA group whose Y-TZP surface was treated with tribochemical silica abrasion (TS) was used as the control. Y-TZP specimens from each experimental group were etched with 5%, 10%, 20%, and 40% HF solutions at room temperature for 10 minutes. First, to quantify the phase transformation, Y-TZP specimens (n = 5) treated with TS, 5%, 10%, 20% and 40% HF solutions were subjected to X-ray diffraction. Second, to evaluate the change in bond strength before and after thermal cycling, zirconia primer and MDP-containing resin cement were sequentially applied to the Y-TZP specimen. After 5,000 thermal cycles for half of the Y-TZP specimens, shear bond strength was measured for all experimental groups (n = 10). ResultsThe monoclinic phase content in the 40% HF-treated group was higher than that of the 5%, 10%, and 20% HF-treated groups, but lower than that of TS-treated group (p < 0.05). The 40% HF-treated group showed significantly higher bonding strength than the TS, 5%, and 10% HF-treated groups, even after thermal cycling (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThrough this experiment, the group treated with SiO2 containing air-borne abrasion on the Y-TZP surface showed higher phase transformation and higher reduction in bonding strength after thermal cycling compared to the group treated with high concentration HF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Phase transition regulation and enhancement of optical properties in YPO4:Eu3+ through the influence of alkali metal ions
Junwei Zhan, Liusai Yang, Yaoxian Zhu, Yifan Zhu, Jianlei Liu, Siyan Peng, Jianping Zou
Journal of Molecular Structure.2026; 1352: 144420. CrossRef - Improving the Clinical Performance of Dental Implants Through Advanced Surface Treatments: The Case of Ti and ZrO2 Coatings
Mohamed Aissi, Qanita Tayyaba, Azzedine Er-Ramly, Hendra Hermawan, Nadia Merzouk
Metals.2025; 15(3): 320. CrossRef - Enhancing the bonding of zirconia to resin by constructing a graded zirconia-glass composite surface
Zhiqi Yan, Jiale Li, Jing Chen, Zhe Zhao, Fan Li, Ling Zhang, Jihua Chen, Fu Wang
Surfaces and Interfaces.2025; 64: 106374. CrossRef - Surface property changes observed in zirconia during etching with high-concentration hydrofluoric acid over various immersion times
Ga-Eul YOU, Myung-Jin LIM, Kyung-San MIN, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(1): 52. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength for different generation of zirconia CAD/CAM blocks
Man-Jong Cho, Sunwoong Song, Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park, Bum-Soon Lim
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(3): 157. CrossRef - Is zirconia surface etching a viable alternative to airborne particle abrasion? A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Carlo D'Alessandro, Uros Josic, Claudia Mazzitelli, Tatjana Maravic, Laurel Graham, Carlo Barausse, Annalisa Mazzoni, Lorenzo Breschi, Markus B. Blatz
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105394. CrossRef - Exploring Zirconia Adhesion: Pre and Postsintering Physical Surface Treatment, Chemical Treatment, and Cement Interactions
Flávia Gonçalves, Mirko Dennys Ayala-Perez, Francisco Carlos dos Santos Reis, Walter Gomes Miranda-Júnior, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 3Y-TZP electrostatic painting to increase bond strength to dentin and dental prostheses
Alessandro Brito Thomaz, Carlos Nelson Elias, Heraldo Elias Salomão dos Santos, Celso Renato de Souza Resende, Claudinei dos Santos
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 26: 9063. CrossRef - Effect of surface topography and wettability on shear bond strength of Y-TZP ceramic
Suriyakul Wongsue, Ornnicha Thanatvarakorn, Taweesak Prasansuttiporn, Piyarat Nimmanpipug, Thanapat Sastraruji, Keiichi Hosaka, Richard M. Foxton, Masatoshi Nakajima
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adhesive Cementation of Zirconia Based Ceramics-Surface Modification Methods Literature Review
Magdalena Szawioła-Kirejczyk, Karolina Chmura, Krzysztof Gronkiewicz, Andrzej Gala, Jolanta E. Loster, Wojciech Ryniewicz
Coatings.2022; 12(8): 1067. CrossRef - Y-TZP Physicochemical Properties Conditioned with ZrO2 and SiO2 Nanofilms and Bond Strength to Dual Resin Cement
Ricardo Faria Ribeiro, Danilo Flamini Oliveira, Camila Bussola Tovani, Ana Paula Ramos, Ana Flavia Sanches Borges, Adriana Claudia Lapria Faria, Rossana Pereira de Almeida, Renata Cristina Silveira Rodrigues
Materials.2022; 15(22): 7905. CrossRef - Enhanced osteogenic activity of titania-modified zirconia implant by ultraviolet irradiation
Shuang Tang, Yan Wang, Zhenyu Zong, Ning Ding, Zutai Zhang
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,933
View
-
21
Download
-
13
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
Effect of hydrofluoric acid-based etchant at an elevated temperature on the bond strength and surface topography of Y-TZP ceramics
-
Mi-Kyung Yu, Myung-Jin Lim, Noo-Ri Na, Kwang-Won Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e6. Published online December 3, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e6
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
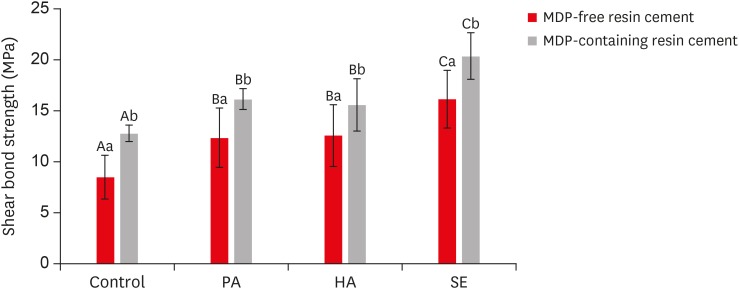
This study investigated the effects of a hydrofluoric acid (HA; solution of hydrogen fluoride [HF] in water)-based smart etching (SE) solution at an elevated temperature on yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) ceramics in terms of bond strength and morphological changes. Materials and MethodsEighty sintered Y-TZP specimens were prepared for shear bond strength (SBS) testing. The bonding surface of the Y-TZP specimens was treated with 37% phosphoric acid etching at 20°C–25°C, 4% HA etching at 20°C–25°C, or HA-based SE at 70°C–80°C. In all groups, zirconia primers were applied to the bonding surface of Y-TZP. For each group, 2 types of resin cement (with or without methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate [MDP]) were used. SBS testing was performed. Topographic changes of the etched Y-TZP surface were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The results were analyzed and compared using 2-way analysis of variance. ResultsRegardless of the type of resin cement, the highest bond strength was measured in the SE group, with significant differences compared to the other groups (p < 0.05). In all groups, MDP-containing resin cement yielded significantly higher bond strength values than MDP-free resin cement (p < 0.05). It was also shown that the Y-TZP surface was etched by the SE solution, causing a large change in the surface topography. ConclusionsBond strength significantly improved when a heated HA-based SE solution was applied to the Y-TZP surface, and the etched Y-TZP surface was more irregular and had higher surface roughness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Different Surface Roughening Techniques on Clear Aligner Attachments Bonded to Monolithic Zirconia: In Vitro Study
Nehal F Albelasy, Ahmad M Hafez, Abdullah S Alhunayni
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 25(12): 1104. CrossRef - Effect of Acid Surface Treatments on the Shear Bond Strength of Metal Bracket to Zirconia Ceramics
Punchanit Wongrachit, Bancha Samruajbenjakun, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon, Tanapat Jearanai, Supontep Teerakanok, Pannapat Chanmanee
Ceramics.2024; 7(2): 689. CrossRef - Exploring Zirconia Adhesion: Pre and Postsintering Physical Surface Treatment, Chemical Treatment, and Cement Interactions
Flávia Gonçalves, Mirko Dennys Ayala-Perez, Francisco Carlos dos Santos Reis, Walter Gomes Miranda-Júnior, Letícia Cristina Cidreira Boaro, Heng Bo Jiang
BioMed Research International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of zirconia surfaces and shear bond strength after acid–etching with ultrasonic vibration
Xiaozhen Zhang, Hepeng Nie, Jiaxin Lv, Shanshan Yuan, Juan Wang, Kunzhan Cai, Jin Wu, Qingqing Zhang, Chunbo Tang
Materials Research Express.2024; 11(2): 025401. CrossRef - Effects of Surface-Etching Systems on the Shear Bond Strength of Dual-Polymerized Resin Cement and Zirconia
Sang-Hyun Kim, Kyung Chul Oh, Hong-Seok Moon
Materials.2024; 17(13): 3096. CrossRef - Zirconia bond strength durability following artificial aging: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Athanasios E. Rigos, Katia Sarafidou, Eleana Kontonasaki
Japanese Dental Science Review.2023; 59: 138. CrossRef - Y-TZP Physicochemical Properties Conditioned with ZrO2 and SiO2 Nanofilms and Bond Strength to Dual Resin Cement
Ricardo Faria Ribeiro, Danilo Flamini Oliveira, Camila Bussola Tovani, Ana Paula Ramos, Ana Flavia Sanches Borges, Adriana Claudia Lapria Faria, Rossana Pereira de Almeida, Renata Cristina Silveira Rodrigues
Materials.2022; 15(22): 7905. CrossRef - Effect of the nanofilm-coated zirconia ceramic on resin cement bond strength
Viviane Maria Gonçalves de Figueiredo, Alecsandro de Moura Silva, Marcos Massi, Argemiro Soares da Silva Sobrinho, José Renato Cavalcanti de Queiroz, João Paulo Barros Machado, Renata Falchete do Prado, Lafayette Nogueira Junior
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2022; 16(3): 170. CrossRef - Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Bond Strength and Topography for Y-TZP Etched with Hydrofluoric Acid Depending on Concentration and Temperature Conditions
Hyo-Eun Kim, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
Medicina.2020; 56(11): 568. CrossRef - Do different sintering conditions influence bond strength between the resin cements and a currently used esthetic zirconia?
Fatma Ayse Sanal, Hamiyet Kilinc
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(16): 1809. CrossRef
-
2,040
View
-
11
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
The effect of continuous application of MDP-containing primer and luting resin cement on bond strength to tribochemical silica-coated Y-TZP
-
Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e19. Published online April 3, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e19
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
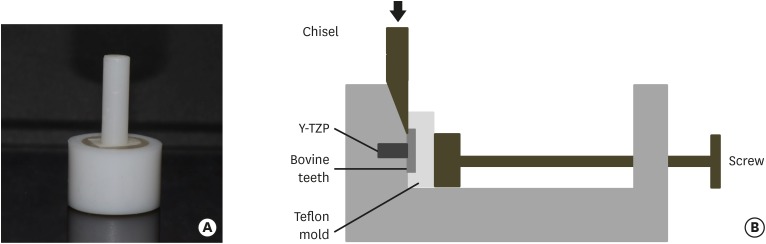
This study investigated the effect of continuous application of 10-methacryloyloxydecyldihydrogen phosphate (MDP)-containing primer and luting resin cement on bond strength to tribochemical silica-coated yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP). Materials and MethodsForty bovine teeth and Y-TZP specimens were prepared. The dentin specimens were embedded in molds, with one side of the dentin exposed for cementation with the zirconia specimen. The Y-TZP specimen was prepared in the form of a cylinder with a diameter of 3 mm and a height of 10 mm. The bonding surface of the Y-TZP specimen was sandblasted with silica-coated aluminium oxide particles. The forty tribochemical silica-coated Y-TZP specimens were cemented to the bovine dentin (4 groups; n = 10) with either an MDP-free primer or an MDP-containing primer and either an MDP-free resin cement or an MDP-containing resin cement. After a shear bond strength (SBS) test, the data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test (α = 0.05). ResultsThe group with MDP-free primer and resin cement showed significantly lower SBS values than the MDP-containing groups (p < 0.05). Among the MDP-containing groups, the group with MDP-containing primer and resin cement showed significantly higher SBS values than the other groups (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe combination of MDP-containing primer and luting cement following tribochemical silica coating to Y-TZP was the best choice among the alternatives tested in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Improving Zirconia–Resin Cement Bonding Through Laser Surface Texturing: A Comparative Study
Ji-Young Yoon
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 19. CrossRef - Challenges faced when masking a single discoloured tooth - Part 2: indirect restoration procedures
May Aljanahi, Argwan Alhussin, Haitham Elbishari
British Dental Journal.2025; 239(1): 25. CrossRef - Enhancing dental porcelain repair strength: the impact of chairside plasma surface treatment—an in vitro study
Mehmet Köse, Özlem Çölgeçen
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Laser Surface Texturing Using a Surface Transition Machine on Bonding Strength to Zirconia Ceramic
YongWoo Choi, Jongbin Kim, Mi Ran Han, Jisun Shin, Joonhaeng Lee, Jongsoo Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2025; 52(3): 302. CrossRef - The effect of restorative material selection and cementation procedures on the durability of endocrowns in the anterior teeth: an in-vitro study
Nehal Samra, Manal M Madina, Salwa Abd El-Raof El-Negoly, Lamia Dawood
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of primer components of silane and 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate on resin bonding to tribochemical silica-coated highly translucent zirconia
Fumika Tsuda, Keiichi Yoshida, Takashi Sawase
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Zirconia Crowns with Porcelain Veneers for Optimal Esthetics in Children Using CAD/CAM Technology:
A Case Report
P Bakhtiary, P Aref
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2022; 7(3): 168. CrossRef - A novel porous silica-zirconia coating for improving bond performance of dental zirconia
Zhiwei Su, Mingxing Li, Ling Zhang, Chaoyang Wang, Leiqing Zhang, Jingqiu Xu, Baiping Fu
Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B.2021; 22(3): 214. CrossRef - Change of phase transformation and bond strength of Y-TZP with various hydrofluoric acid etching
Mi-Kyung Yu, Eun-Jin Oh, Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of hydrofluoric acid-based etchant at an elevated temperature on the bond strength and surface topography of Y-TZP ceramics
Mi-Kyung Yu, Myung-Jin Lim, Noo-Ri Na, Kwang-Won Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Computer-aided Design and Computer-aided Manufacturing Restorations with Minimal Invasive Approaches
Emine Mustafaoğlu, Özge Ünal, Bora Bağış
International Journal of Prosthodontics and Restorative Dentistry.2020; 10(1): 39. CrossRef - Changes in Bond Strength and Topography for Y-TZP Etched with Hydrofluoric Acid Depending on Concentration and Temperature Conditions
Hyo-Eun Kim, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
Medicina.2020; 56(11): 568. CrossRef - Effects of MDP‑based primers on shear bond strength between resin cement and zirconia
Xin Yue, Xiaoyan Hou, Jing Gao, Pingping Bao, Jing Shen
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,218
View
-
10
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a calcium hydroxide paste using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone as a vehicle
-
Myung-Jin Lim, Hyun-Jin Jang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):290-300. Published online October 20, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.290
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study investigated the removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a newly developed calcium hydroxide paste (cleaniCal, Maruchi) using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone (NMP) as a vehicle in comparison with ApexCal (Ivoclar Vivadent) and Calcipex II (Nishika), which use different vehicles such as polyethylene glycol and propylene glycol, respectively. Materials and MethodsThirty maxillary premolars with oval-shaped canals were divided into 3 groups and the teeth were filled with one of the pastes. After removal of the paste, micro-computed tomographic (μ-CT) imaging was obtained to assess the volume of residual paste in the root canal of each tooth. The teeth were then split longitudinally and the area of the paste-coated surface was evaluated by stereomicroscopy. The cytotoxicity of each product was assessed using an agar overlay assay. The effect of each vehicle on cell viability was evaluated using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's tests to detect any significance (p < 0.05). ResultsIn the μ-CT and stereomicroscopic analysis, cleaniCal exhibited less remnants of medicament than ApexCal and Calcipex. cleaniCal showed a higher cytotoxicity than the other pastes in the agar overlay assay. Furthermore, NMP exhibited lower cell viability compared to the other vehicles. ConclusionscleaniCal showed better removal efficacy compared to the other products. However, clinicians should be aware of the higher cytotoxicity of the NMP-based material and consider its possible adverse effects on periradicular tissue when it is overfilled.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
Dohee Kim, Young Kim, Jeong Joon Han
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic effects of reduced graphene oxide on the antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments containing different vehicles
Mi-Ah Kim, Min-Kyeong Kim, Eun-Sook Kang, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - Lipoteichoic Acid from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG as a Novel Intracanal Medicament Targeting Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm Formation
Ji-Young Yoon, Somin Park, Dongwook Lee, Ok-Jin Park, WooCheol Lee, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2024; 62(10): 897. CrossRef - Rheological properties and handling characteristics of four injectable calcium hydroxide pastes
Min-Jung KIM, In-Bog LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 796. CrossRef - Role of vehicles on antimicrobial efficacy of calcium hydroxide
Dikshya Purohit, Shronika, Pradyumna Misra, Gaurav Jain, Preeti Shukla
Asian Journal of Oral Health and Allied Sciences.2023; 13: 9. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Using Biomimetic Material in a 9-Year-Old Boy
Sahili Mungekar-Markandey, Ashwin Jawdekar
Journal of Dental Research and Review.2022; 9(4): 320. CrossRef - Sonic irrigation for removal of calcium hydroxide in the apical root canal: A micro-CT and light-coupled tracking analysis
Wonjoon Moon, Shin Hye Chung, Juhea Chang, Zhaoqiang Zhang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0268791. CrossRef - Effect of N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone on Enterococcus faecalis biofilms
Mi-Ah KIM, Prasanna NEELAKANTAN, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 774. CrossRef - Characterization, Antimicrobial Effects, and Cytocompatibility of a Root Canal Sealer Produced by Pozzolan Reaction between Calcium Hydroxide and Silica
Mi-Ah Kim, Vinicius Rosa, Prasanna Neelakantan, Yun-Chan Hwang, Kyung-San Min
Materials.2021; 14(11): 2863. CrossRef - Synthesis, structure, and theoretical studies of a calcium complex of a unique dianion derived from 1-methylpyrrolidin-2-one
Ray J. Butcher, Andrew P. Purdy, Paul A. Brown, Daniel Gunlycke
Acta Crystallographica Section E Crystallographic Communications.2021; 77(1): 70. CrossRef - Effect of a calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicament containing N-2-methyl pyrrolidone as a vehicle against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm
Taegun KIM, Mi-Ah KIM, Yun-Chan HWANG, Vinicius ROSA, Massimo DEL FABBRO, Kyung-San MIN
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,033
View
-
11
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Effect of adhesive luting on the fracture resistance of zirconia compared to that of composite resin and lithium disilicate glass ceramic
-
Myung-Jin Lim, Kwang-Won Lee
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):1-8. Published online October 14, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of adhesive luting on the fracture resistance of zirconia compared to that of a composite resin and a lithium disilicate glass ceramic. Materials and MethodsThe specimens (dimension: 2 mm × 2 mm × 25 mm) of the composite resin, lithium disilicate glass ceramic, and yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) were prepared. These were then divided into nine groups: three non-luting groups, three non-adhesive luting groups, and three adhesive luting groups, for each restorative material. In the non-luting groups, specimens were placed on the bovine tooth without any luting agents. In the non-adhesive luting groups, only zinc phosphate cement was used for luting the specimen to the bovine tooth. In the adhesive luting groups, specimens were pretreated, and the adhesive luting procedure was performed using a self-adhesive resin cement. For all the groups, a flexural test was performed using universal testing machine, in which the fracture resistance was measured by recording the force at which the specimen was fractured. ResultsThe fracture resistance after adhesive luting increased by approximately 29% in the case of the composite resin, 26% in the case of the lithium disilicate glass ceramic, and only 2% in the case of Y-TZP as compared to non-adhesive luting. ConclusionsThe fracture resistance of Y-TZP did not increased significantly after adhesive luting as compared to that of the composite resin and the lithium disilicate glass ceramic.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The influence of endodontic access preparation on the mechanical strength of zirconia crowns: A literature review
Abdulrahman Almalki
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 20. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue of a repaired 4 YSZ ceramic: Effect of the repair protocol on the adhesive and mechanical behavior
Pablo Machado Soares, Lucas Saldanha da Rosa, Rafaela Oliveira Pilecco, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Luiz Felipe Valandro, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan, Marilia Pivetta Rippe
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23709. CrossRef - Effect of wall thickness on shape accuracy of hollow zirconia artificial teeth fabricated by a 3D printer
Hiro Kobayashi, Franz Sebastian Schwindling, Akinori Tasaka, Peter Rammelsberg, Shuichiro Yamashita, Stefan Rues
Journal of Prosthodontic Research.2024; 69(2): 233. CrossRef - Effect of powder air polishing and ultrasonic scaling on the marginal and internal interface (tooth-veneer) of ceramic veneers: an in vitro study
Florian Fuchs, Laura Antonia Mayer, Lena Unterschütz, Dirk Ziebolz, Nadia Oberueck, Ellen Schulz‑Kornas, Sebastian Hahnel, Andreas Koenig
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical performance of two onlay designs for molars after root canal treatment
Shujiang Chen, Meng Lu, Zhimin Zhu, Wenchuan Chen
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 171. CrossRef - Tooth‐cusp preservation with lithium disilicate onlay restorations: A fatigue resistance study
Elizabeth Griffis, Islam Abd Alraheam, Lee Boushell, Terrence Donovan, Dennis Fasbinder, Taiseer A. Sulaiman
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(3): 512. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue vs static loading for shear bond strength test of lithium disilicate and dentin substrates: A comparison of resin cement viscosities
Kiara Serafini Dapieve, Renan Vaz Machry, Ana Carolina Cadore-Rodrigues, Jessica Klöckner Knorst, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Niek De Jager, Luiz Felipe Valandro, Cornelis Johannes Kleverlaan
Dental Materials.2022; 38(12): 1910. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and 3D finite element analysis of machined ceramic crowns bonded to endodontically treated molars with two planes versus flat occlusal preparation designs: an in vitro study
Omnia Nabil, Carl Hany Halim, Ashraf Hassan Mokhtar
F1000Research.2021; 8: 1020. CrossRef - Establishment of optimal variable elastic modulus distribution in the design of full-crown restorations by finite element analysis
Jianghai CHEN, Yutao JIAN, Shumin CHEN, Xiaodong WANG, Li DAO, Ke ZHAO
Dental Materials Journal.2021; 40(6): 1403. CrossRef - Load-bearing capacity of CAD/CAM 3D-printed zirconia, CAD/CAM milled zirconia, and heat-pressed lithium disilicate ultra-thin occlusal veneers on molars
A. Ioannidis, D. Bomze, C.H.F. Hämmerle, J. Hüsler, O. Birrer, S. Mühlemann
Dental Materials.2020; 36(4): e109. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and 3D finite element analysis of machined ceramic crowns bonded to endodontically treated molars with two planes versus flat occlusal preparation designs: an in vitro study
Omnia Nabil, Carl Hany Halim, Ashraf Hassan Mokhtar
F1000Research.2019; 8: 1020. CrossRef - The effect of adhesive failure and defects on the stress distribution in all-ceramic crowns
Yonggang Liu, Yuanzhi Xu, Bo Su, Dwayne Arola, Dongsheng Zhang
Journal of Dentistry.2018; 75: 74. CrossRef
-
1,449
View
-
8
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
In vitro evaluation of a newly produced resin-based endodontic sealer
-
Yoo-Seok Song, Yoorina Choi, Myung-Jin Lim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Chan-Ui Hong, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):189-195. Published online July 26, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.189
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
A variety of root canal sealers were recently launched to the market. This study evaluated physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability of a newly launched resin-based sealer (Dia-Proseal, Diadent) compared to the existing root canal sealers (AHplus, Dentsply DeTrey and ADseal, Metabiomed). Materials and MethodsThe physicochemical properties of the tested sealers including pH, solubility, dimensional change, and radiopacity were evaluated. Biocompatibility was measured using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For microleakage test, single-rooted teeth were instrumented, and obturated with gutta-percha and one of the sealers (n = 10). After immersion in 1% methylene blue solution for 2 weeks, the specimens were split longitudinally. Then, the maximum length of staining was measured. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey test (p = 0.05). ResultsDia-Proseal showed the highest pH value among the tested sealers (p < 0.05). ADseal showed higher dimensional change compared to AHplus and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The solubility values of AHplus and Dia-Proseal were similar, whereas ADseal had the lowest solubility value (p < 0.05). The flow values of sealer in increasing order were AHplus, DiaProseal, and ADseal (p < 0.05). The radiopacity of AHplus was higher than those of ADseal and Dia-Proseal (p < 0.05). The cell viability of the tested materials was statistically similar throughout the experimental period. There were no significant differences in microleakage values among the tested samples. ConclusionsThe present study indicates that Dia-Proseal has acceptable physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and sealing ability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of Apical Sealing Ability of Different Endodontic Sealers – An In Vitro Study
Supriya Patil, Rahul Singh, B Jyothi Lekshmi, Sameer Ahmed Khan, H Shalini, Prashanth Kumar Katta
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 1): S513. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of ICON resin infiltration and bioactive glass adhesive for managing initial caries lesions using quantitative light-induced fluorescence: a randomized clinical trial
Zakereyya S.M. Albashaireh, Susan N. Al-Khateeb, Malak K. Altallaq
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 159: 105853. CrossRef - An In Vitro Comparison of Epoxy Resin Sealer Removal During Endodontic Retreatment
Prashant A Bondarde, Aditi S Patkar, Aishwarya R Pawar, Rukmini Pande, Akshata Deshpande, Rachana S Agrawal, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereomicroscopic evaluation of sealing ability of four different root canal sealers: an in-vitro study
Sonam Sah, Panna Mangat, Ajay Kumar, Neha Sah, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Marco Di Blasio, Gabriele Cervino, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Biological investigation of resinous endodontic sealers containing calcium hydroxide
Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Francine Benetti, Marina Tolomei Sandoval Cury, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Ana Cláudia Rodrigues da Silva, Rogério de Castilho Jacinto, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, E
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0287890. CrossRef - Comparison of the apical seal obtained by Adseal, Proseal, and AH26 sealers in root canal obturation with lateral compaction technique
Akam Saeidi, Romina Hajipour, Elham Mahmoudi, Farideh Feizi, Soraya Khafri
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Calcium Silicate-based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Sealers: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Nezar Boreak, Mazen Ahmed Qadi, Faisal Hadi Khormi, Luay Mutaen Faqiri, Sadeem Omar Zaylai, Yaser Ali Jad, Bassam Ali Hamdi, Asayil Juraybi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 24(8): 610. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength of bioceramic and epoxy sealers after using various final irrigants: An in vitro study
Chandrasekhar Veeramachaneni, Swathi Aravelli, Sreeja Dundigalla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(2): 145. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Reinforcement Using MTA-based, Epoxy Resin-based, and Silicone-based Endodontic Sealers in Canals Instrumented with Single-file Rotary System: An In Vitro Study
Reshma Rajasekhar, Varsha Maria Sebastian, Farhat Nasreen, Pramod Junjanna, Azeem Hassan, Venkidesh Hari Maratt
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1098. CrossRef - The Short-Term Antibacterial Activity of Three Selected Endodontic Sealers against Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Culture
Matej Rosa, Yuliya Morozova, Roman Moštěk, Pavel Holík, Lucia Somolová, Barbora Novotná, Soňa Zábojníková, Kateřina Bogdanová, Kateřina Langová, Iva Voborná, Lenka Pospíšilová, Josef Paul Kovařík
Life.2022; 12(2): 158. CrossRef - Antimicrobial potential of AH Plus supplemented with bismuth lipophilic nanoparticles on E. faecalis isolated from clinical isolates
Jesús Alejandro Torres-Betancourt, Rene Hernandez-Delgadillo, Jorge Jaime Flores-Treviño, Juan Manuel Solís-Soto, Nayely Pineda-Aguilar, Maria Argelia Akemi Nakagoshi-Cepeda, Rosa Isela Sánchez-Nájera, Shankararaman Chellam, Claudio Cabral-Romero
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry Analysis and Radiopacity of Five Different Root Canal Sealers
Gözde Kandemir Demirci, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Miçooğulları Kurt, Burcu Serefoglu, Pelin Güneri, Michael Hülsmann, Mehmet Kemal Caliskan
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(5): 1. CrossRef - Ultrasonic vibration and thermo‐hydrodynamic technique for filling root canals: Technical overview and a case series
Yong‐Sik Cho
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1668. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Two Generations of MTA-Based Root Canal Sealers
Sawsan Abu Zeid, Hadeel Yaseen Edrees, Abeer Abdulaziz Mokeem Saleh, Osama S. Alothmani
Materials.2021; 14(20): 5911. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiopacity of endodontic materials using two models for conversion to millimeters of aluminum
Victor Manuel OCHOA-RODRÍGUEZ, Jorge Homero WILCHES-VISBAL, Barbara ROMA, Hernán COAGUILA-LLERENA, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO, Andréa GONÇALVES, Rubens SPIN-NETO, Gisele FARIA
Brazilian Oral Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - SELECTED PROPERTIES OF CONTEMPORARY ENDODONTIC SEALERS: PART 1
M Rosa, Y Morozova, R Moštěk, A Jusku, V Kováčová, L Somolová, I Voborná, T Kovalský
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2020; 120(4): 107. CrossRef - Calcium phosphates as fillers for methacrylate-based sealer
Flávia Veronezi Rostirolla, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Fabio Rocha Bohns, Fernando Freitas Portella, Susana Maria Werner Samuel, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(12): 4417. CrossRef - Do in vitro solubility studies on endodontic sealers demonstrate a high level of evidence? A systematic review
Ankur Razdan, Ana Raquel Benetti, Lars Bjørndal
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(4): 253. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties of two epoxy resin-based sealants: Topseal® and Adseal™. a comparative study
Julio César Cardona-Hidalgo, José Manuel González-Carreño, Julio César Avendaño-Rueda
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Biocompatibility of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Materials.2019; 12(15): 2411. CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties of Epoxy Resin-Based and Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers
Ju Kyung Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
-
1,867
View
-
19
Download
-
26
Crossref
|