-
Influence of CBCT parameters on image quality and the diagnosis of vertical root fractures in teeth with metallic posts: an ex vivo study
-
Larissa Pereira Lagos de Melo, Polyane Mazucatto Queiroz, Larissa Moreira-Souza, Mariana Rocha Nadaes, Gustavo Machado Santaella, Matheus Lima Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e16. Published online April 27, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e16
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
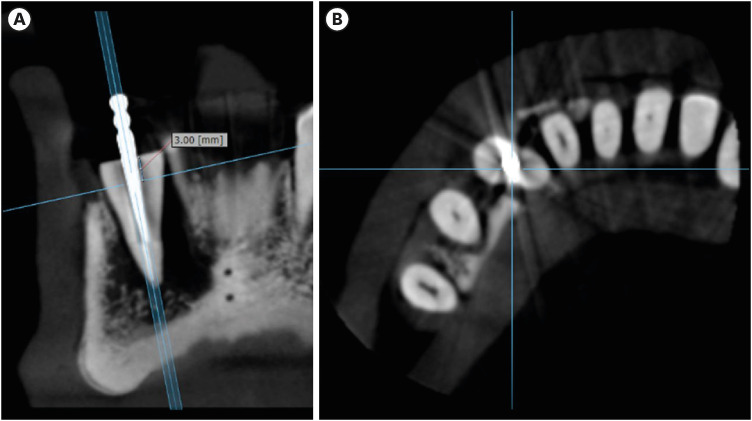
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of peak kilovoltage (kVp) and a metal artifact reduction (MAR) tool on image quality and the diagnosis of vertical root fracture (VRF) in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Materials and MethodsTwenty single-rooted human teeth filled with an intracanal metal post were divided into 2 groups: control (n = 10) and VRF (n = 10). Each tooth was placed into the socket of a dry mandible, and CBCT scans were acquired using a Picasso Trio varying the kVp (70, 80, 90, or 99), and the use of MAR (with or without). The examinations were assessed by 5 examiners for the diagnosis of VRF using a 5-point scale. A subjective evaluation of the expression of artifacts was done by comparing random axial images of the studied protocols. The results of the diagnoses were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and the Tukey post hoc test, the subjective evaluations were compared using the Friedman test, and intra-examiner reproducibility was evaluated using the weighted kappa test (α = 5%). ResultsThe kVp and MAR did not influence the diagnosis of VRF (p > 0.05). According to the subjective classification, the 99 kVp protocol with MAR demonstrated the least expression of artifacts, while the 70 kVp protocol without MAR led to the most artifacts. ConclusionsProtocols with higher kVp combined with MAR improved the image quality of CBCT examinations. However, those factors did not lead to an improvement in the diagnosis of VRF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Diagnostic Performance of Iterative Reconstruction of Cone-beam Computed Tomography for Detecting Vertical Root Fractures in the Presence of Metal Artifacts
Matheus Barros-Costa, Gustavo Santaella, Christiano Oliveira-Santos, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, William C. Scarfe, Francisco Carlos Groppo
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(6): 715. CrossRef - Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Laser-Enhanced Disinfection in Endodontic Therapy
Janos Kantor, Sorana Maria Bucur, Eugen Silviu Bud, Victor Nimigean, Ioana Maria Crișan, Mariana Păcurar
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4055. CrossRef - Exploring Diagnostic Reliability of CBCT for Vertical Root Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analytical Approach
Luiz Carlos de Lima Dias-Junior, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Adriana Pinto Bezerra, Marcio Correa, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Stefano Corbella
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning for dentomaxillofacial cone-beam computed tomography image quality enhancement: A pilot study
Ali Nazari, Seyed Mohammad Yousef Najafi, Reza Abbasi, Hossein Mohammad-Rahimi, Parisa Motie, Mina Iranparvar Alamdari, Mehdi Hosseinzadeh, Ruben Pauwels, Falk Schwendicke
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2025; 55(3): 271. CrossRef - Diagnostic Accuracy of Intraoral, Extraoral and Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)-Generated Bitewings for Detecting Approximal Caries and Periodontal Bone Loss
Jyoti Mago, Alan G Lurie, Aadarsh Gopalakrishna, Aditya Tadinada
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vertical root fracture diagnosis in teeth with metallic posts: Impact of metal artifact reduction and sharpening filters
Débora Costa Ruiz, Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Amanda Farias-Gomes, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2024; 54(2): 139. CrossRef - Comparing standard- and low-dose CBCT in diagnosis and treatment decisions for impacted mandibular third molars: a non-inferiority randomised clinical study
Kuo Feng Hung, Andy Wai Kan Yeung, May Chun Mei Wong, Michael M. Bornstein, Yiu Yan Leung
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,459
View
-
46
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
Morphological characteristics of the mesiobuccal root in the presence of a second mesiobuccal canal: a micro-CT study
-
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Matheus Lima Oliveira, Karla Rovaris, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, Frederico Sampaio Neves
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e6. Published online January 18, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e6
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
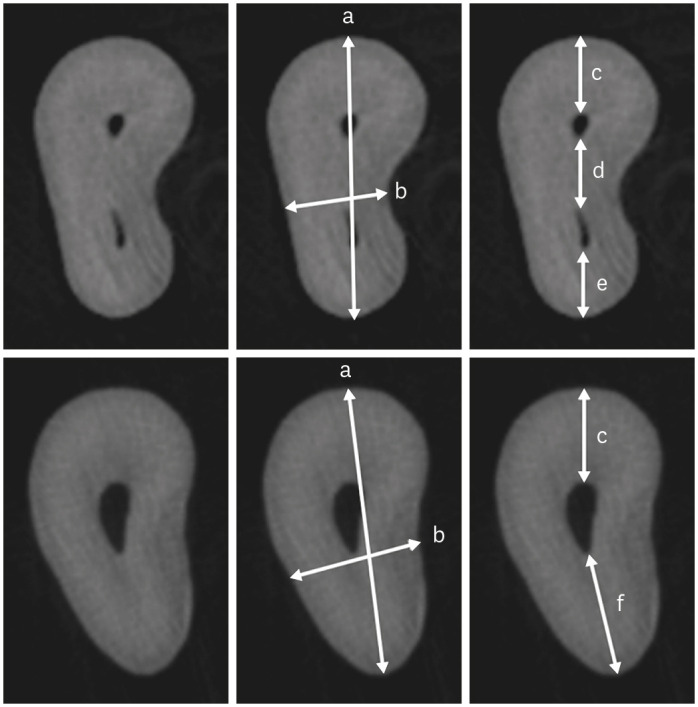
This study investigated the internal morphology of mesiobuccal (MB) roots of maxillary molars with a second mesiobuccal (MB2) canal. Materials and MethodsForty-seven maxillary first or second molars from Brazilians were scanned using micro-computed tomography. The following measurements were obtained from the MB roots: root thickness, root width, and dentin thickness of the buccal aspect of the first mesiobuccal (MB1) canal, between the MB1 and MB2 canals, and the palatal aspect of the MB2 and MB1 canals at 3 mm from the root apex and in the furcation region. For statistical analysis, the Student’s t-test and analysis of variance with the post-hoc Tukey test were used (α = 0.05). ResultsIn maxillary molars with an MB2 canal, MB roots were significantly thicker (p = 0.0014) and narrower (p = 0.0016) than in maxillary molars without an MB2 canal. The dentin thickness of the palatal aspect of the MB1 canal was also significantly greater than that of MB roots without an MB2 canal at 3 mm from the root apex (p = 0.0007) and in the furcation region (p < 0.0001). In the furcation region of maxillary molars with an MB2 canal, the dentin thickness between the MB1 and MB2 canals was significantly smaller than that in the buccal and palatal aspects (p < 0.0001). ConclusionsThe internal morphology of MB roots of maxillary molars with an MB2 canal revealed differences in dentin thickness, root diameter, and distance between the canals when compared with maxillary molars without an MB2 canal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness and safety of three NiTi systems in endodontic retreatment of MB1 and MB2 root canals: a micro-CT and CBCT combined analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Pedro Luis Busto Rosim, Andréa Gonçalves, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of root and canal morphology of maxillary molars in a Chinese kazakh population
Shuchun Yang, Chenye Li, Hui Shi, Ming Liu, Xu Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Can maxillary molar dimensions predict the presence of the second mesiobuccal canal?
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Deborah Queiroz Freitas, Karla Rovaris, Matheus L. Oliveira, Frederico Sampaio Neves
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(3): 482. CrossRef - Can the detection of second mesiobuccal canals be enhanced based on the volume of adjacent canals?
Lucas P. Lopes Rosado, Deborah Q. Freitas, Karla Rovaris, Matheus L. Oliveira, Frederico S. Neves
Archives of Oral Biology.2023; 146: 105604. CrossRef - Assessment of the coronal root canal morphology of permanent maxillary first molars using digital 3D-reconstruction technology based on micro-computed tomography data
Mudan Wang, Yuxuan Gao, Qi Deng, Yuan Gao, Dongzhe Song, Dingming Huang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(2): 586. CrossRef
-
1,397
View
-
33
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
|