-
Calcium silicate-based sealers remnants in isthmuses of mesial roots of mandibular molars: an in vitro evaluation
-
David Saldanha de Brito Alencar, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Marina Angélica Marciano
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e25. Published online July 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e25
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
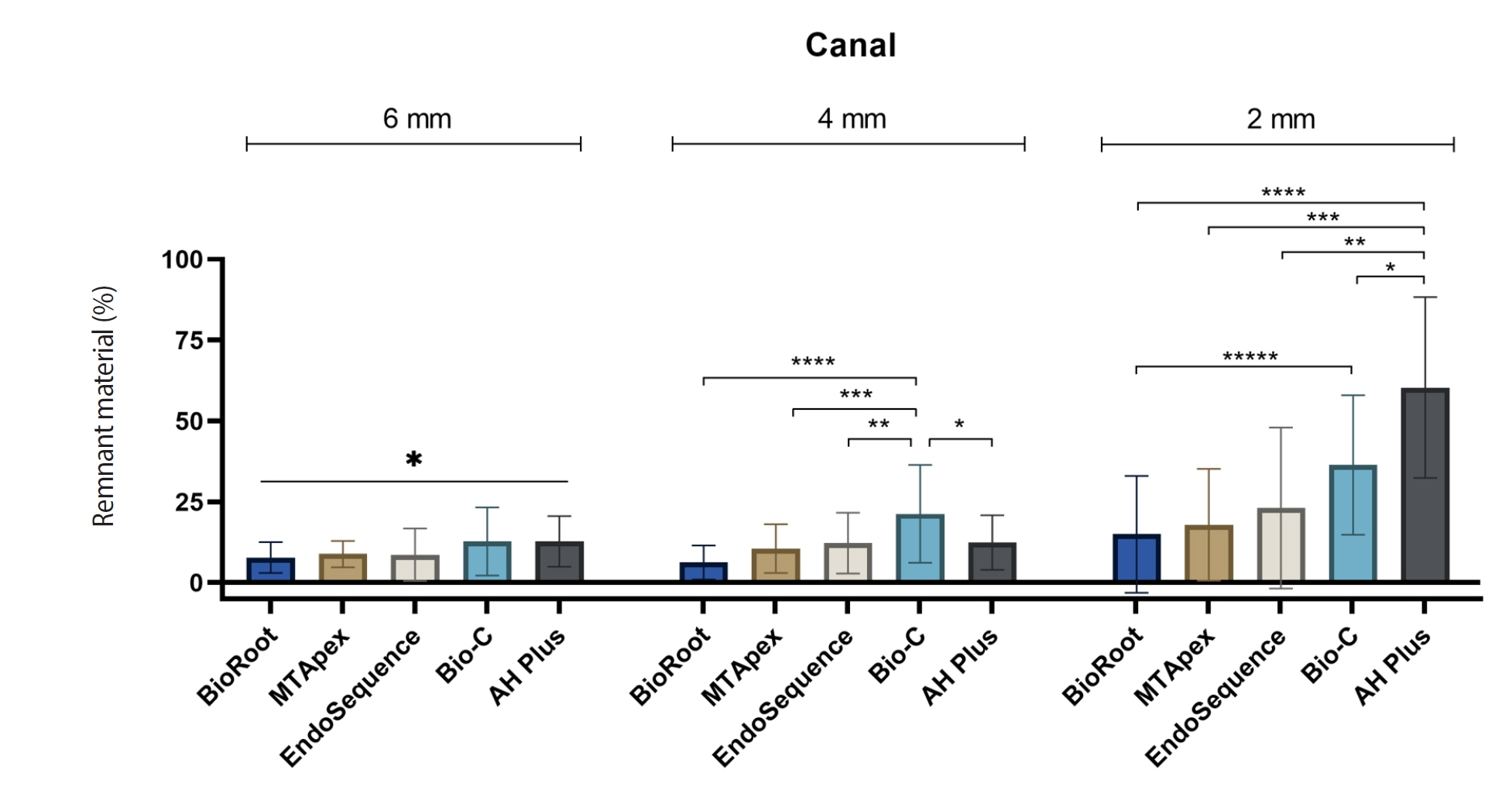
Endodontic retreatment aims to address treatment failure through the removal of root canal filling materials. This in vitro study evaluated the presence of filling material remnants in the mesial root canals, specifically focusing on the isthmuses, of mandibular molars after retreatment.
Methods
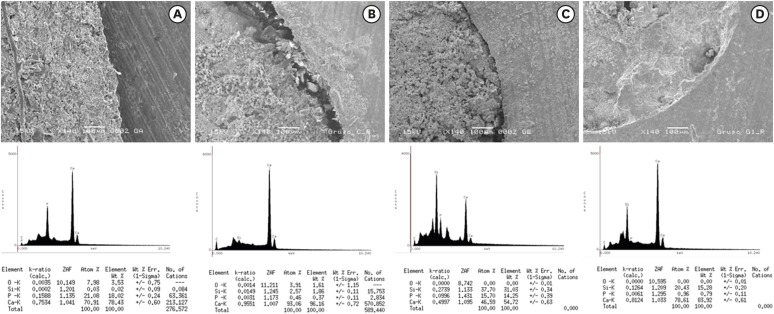
One hundred extracted mandibular molar mesial roots with isthmuses were prepared with an R25 file, obturated with one of five calcium silicate-based sealers (BioRoot RCS [Septodont], MTApex [Ultradent Products Inc.], EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow [Brasseler USA], Bio-C Sealer [Angelus]) or an epoxy resin-based sealer (AH Plus Jet [Dentsply Maillefer]), all stained with rhodamine B, and stored at 37ºC for 30 days to allow for setting. Retreatment was subsequently performed using R40 and XP-endo Finisher R instruments (FKG Dentaire) with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite irrigation. The presence of remaining filling material was then assessed using confocal microscopy, and setting times were tested per ISO 6876:2012.
Results
AH Plus Jet showed the most remnants at 2 mm and the longest retreatment time. Calcium silicate-based sealers exhibited prolonged setting times under dry conditions, with EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow showing a particularly extended setting period.
Conclusions
Despite retreatment, residues remained in all canals and isthmus regions, particularly Bio-C Sealer and AH Plus Jet in apical areas, emphasizing the difficulty of complete removal and the persistence of filling material.
-
Effect of intracanal medications on the interfacial properties of reparative cements
-
Andrea Cardoso Pereira, Mariana Valerio Pallone, Marina Angélica Marciano, Karine Laura Cortellazzi, Marcos Frozoni, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Adriana de Jesus Soares
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e21. Published online May 9, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effect of calcium hydroxide with 2% chlorhexidine gel (HCX) or distilled water (HCA) compared to triple antibiotic paste (TAP) on push-out bond strength and the cement/dentin interface in canals sealed with White MTA Angelus (WMTA) or Biodentine (BD). Materials and MethodsA total of 70 extracted human lower premolars were endodontically prepared and randomly divided into 4 groups according to the intracanal medication, as follows: group 1, HCX; group 2, TAP; group 3, HCA; and group 4, control (without intracanal medication). After 7 days, the medications were removed and the cervical third of the specimens was sectioned into five 1-mm sections. The sections were then sealed with WMTA or BD as a reparative material. After 7 days in 100% humidity, a push-out bond strength test was performed. Elemental analysis was performed at the interface, using energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The data were statistically analyzed using analysis of variance and the Tukey test (p < 0.05). ResultsBD presented a higher bond strength than WMTA (p < 0.05). BD or WMTA in canals treated with calcium hydroxide intracanal medications had the highest bond strength values, with a statistically significant difference compared to TAP in the WMTA group (p < 0.05). There were small amounts of phosphorus in samples exposed to triple antibiotic paste, regardless of the coronal sealing. ConclusionsThe use of intracanal medications did not affect the bond strength of WMTA and BD, except when TAP was used with WMTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Endodontic treatment of teeth with a wide apical opening – a clinical case
V. A. Popov, E. S. Pestova, S. A. Anisimova
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(2): 282. CrossRef - Effects of calcium hydroxide intracanal medicament on push‐out bond strength of endodontic sealers: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Mohammed Nasser Alhajj, Fadhilah Daud, Sadeq Ali Al‐Maweri, Yanti Johari, Zuryati Ab‐Ghani, Mariatti Jaafar, Yoshihito Naito, Widyasri Prananingrum, Zaihan Ariffin
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(8): 1166. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Novel Tool for Apical Plug Formation during Apexification of Immature Teeth
Yasser Alsayed Tolibah, Line Droubi, Saleh Alkurdi, Mohammad Tamer Abbara, Nada Bshara, Thuraya Lazkani, Chaza Kouchaji, Ibrahim Ali Ahmad, Ziad D. Baghdadi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5304. CrossRef - Spectrophotometric analysis of internal bleaching of traumatized teeth with coronal discoloration following regenerative endodontic procedures
Jaqueline Lazzari, Walbert Vieira, Vanessa Pecorari, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Adriana De-Jesus-Soares
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Do intracanal medications used in regenerative endodontics affect the bond strength of powder-to-liquid and ready-to-use cervical sealing materials?
MarinaCarvalho Prado, Kevillin Martiniano, AndreaCardoso Pereira, KarineL Cortellazzi, MarinaA Marciano, Gabriel Abuna, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(5): 464. CrossRef
-
1,382
View
-
15
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Effect of ultrasonic agitation on push-out bond strength and adaptation of root-end filling materials
-
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marina Angélica Marciano, Jussaro Alves Duque, Samuel Lucas Fernandes, Mariana Bailo Rosseto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e23. Published online April 27, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e23
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the effect of ultrasonic agitation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), calcium silicate-based cement (CSC), and Sealer 26 (S26) on adaptation at the cement/dentin interface and push-out bond strength. Materials and MethodsSixty maxillary canines were divided into 6 groups (n = 10): MTA, S26, and CSC, with or without ultrasonic activation (US). After obturation, the apical portions of the teeth were sectioned, and retrograde cavities were prepared and filled with cement by hand condensation. In the US groups, the cement was activated for 60 seconds: 30 seconds in the mesio-distal direction and 30 seconds in the buccal-lingual direction, using a mini Irrisonic insert coupled with the ultrasound transducer. After the materials set, 1.5-mm thick sections were obtained from the apexes. The presence of gaps and the bond between cement and dentin were analyzed using low-vacuum scanning electron microscopy. Push-out bond strength was measured using a universal testing machine. ResultsUltrasonic agitation increased the interfacial adaptation of the cements. The S26 US group showed a higher adaptation value than MTA (p < 0.05). US improved the push-out bond strength for all the cements (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe US of retrograde filling cements enhanced the bond to the dentin wall of the root-end filling materials tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of ultrasonic activation on setting time, pH and calcium ion release, solubility, and chemical structure of calcium silicate sealers
Simone Argenta Scalabrin, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Milton Carlos Kuga, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of different disinfection protocols on the bond strength of NeoMTA 2 bioceramic sealer used as a root canal apical plug (in vitro study)
Nada Omar, Nihal Refaat Kabel, Muhammad Abbass Masoud, Tamer M. Hamdy
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Endo-Z bur or Bladesonic ultrasonic tip on the adaptation of filling material. A micro-CT study
Pedro Henrique Fiorin de Souza, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(5): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Different Mixing Methods on Physicochemical Properties of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Systematic Review
Amin Salem Milani, Faraz Radmand, Behrad Rahbani, Mahdi Hadilou, Farnaz Haji Abbas Oghli, Fatemeh Salehnia, Milad Baseri, Stefano Pagano
International Journal of Dentistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Micro-CT comparative evaluation of porosity and dentin adaptation of root end filling materials applied with incremental, bulk, and ultrasonic activation techniques
Berkan Celikten, Aysenur Oncu, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Mert Ocak, Kaan Orhan
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2022; 236(8): 1209. CrossRef - Effect of ultrasonic activation of the adhesive system on dentin tubule penetration and the pushout bond strength of fiber posts
Isabel Verdum, Igor Abreu de Bem, Pedro Henrique Marks Duarte, Lucas Silveira Machado, Jefferson Ricardo Pereira, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 127(2): 295. CrossRef - Influence of Ultrasonic Activation on the Physicochemical Properties of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Fredson Márcio Acris De Carvalho, Yara Teresinha Corrêa Silva-Sousa, Carlos Eduardo Saraiva Miranda, Paulo Henrique Miller Calderon, Ana Flávia Simões Barbosa, Luciana Martins Domingues De Macedo, Fuad Jacob Abi Rached-Junior, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental discoloration caused by Grey-MTAFlow cement: analysis of its physicochemical, biological and antimicrobial properties
Lauter Eston PELEPENKO, Flávia SAAVEDRA, Gabriela Fernanda BOMBARDA, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida GOMES, Adriana DE-JESUS-SOARES, Alexandre Augusto ZAIA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Marina Angélica MARCIANO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers on Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength to Root Dentin
Igor Abreu De Bem, Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1302. CrossRef
-
1,535
View
-
9
Download
-
10
Crossref
|