-
Isthmuses, accessory canals, and the direction of root curvature in permanent mandibular first molars: an in vivo computed tomography study
-
Aria Chuppani Dastgerdi, Manizheh Navabi, Vahid Rakhshan
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e7. Published online December 12, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e7
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
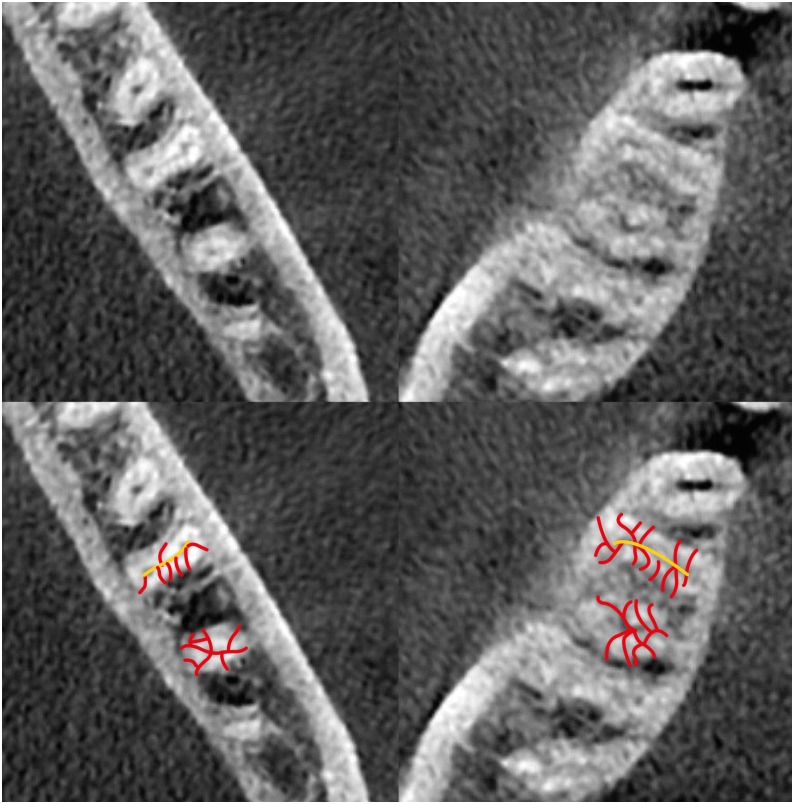
This study was performed to assess the anatomy of mandibular first molars. Materials and MethodsIn this in vivo study, cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) volumes of 312 bilateral intact first mandibular molars from 156 patients (79 men and 77 women; average age, 35.6 ± 11.2 years) were investigated in terms of the direction of each canal's curvature in the buccolingual and mesiodistal dimensions (direction of the position of the apex in relation to the longitudinal axis of the root), the presence of an isthmus (a narrow, ribbon-shaped communication between 2 root canals) in 3 segments (0–2, 2–4, and 4–6 mm) from the apex), and the presence and number of accessory canals (smaller canals besides the main root canals, connecting the pulp to the periodontium). Data were analyzed statistically (α = 0.05). ResultsMesiolingual canals were mostly buccally and distally inclined, while mesiobuccal and distolingual canals were mostly distally curved. Isthmuses were more common in younger patients (χ2 test, p < 0.05). The average numbers of accessory canals in the apical, middle, and coronal segments were 9.9 ± 4.2, 6.9 ± 2.9, and 9.3 ± 3.0 canals per segment, respectively (analysis of variance, p < 0.001). Age and sex were not associated with the number of accessory canals (p > 0.05). ConclusionsThe complex anatomy of these teeth deserves attention during non-surgical or surgical endodontic treatment. Around the apex, isthmuses might be more prevalent in younger and female individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Micro-CT and histological examination of accessory canals in 34 equine cheek teeth
Szabolcs A. Korsós, Carsten Staszyk, Matthieu Boone, Iván Josipovic, Jörg Vogelsberg, Lieven Vlaminck
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic value of cone beam computed tomography for root canal morphology assessment – a micro-CT based comparison
Mariana Pires, Jorge N.R. Martins, Mário Rito Pereira, Isabel Vasconcelos, Rui Pereira da Costa, Isabel Duarte, António Ginjeira
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring age and gender variations in root canal morphology of maxillary premolars in Saudi sub population: a cross-sectional CBCT study
Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Azhar Iqbal, Rumesa Batul, Abdul Habeeb Adil, Jamaluddin Syed, Hmoud Ali Algarni, Meshal Aber Alonazi, Tahir Yusuf Noorani
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of root canal morphology in maxillary premolars among the Pakistani subpopulation: a CBCT-based study
Hmoud Ali Algarni, Meshal Aber Alonazi, Hamza Arshad, Fatima Zahra, Fahad Umer, Irfan Maqbool, Azhar Iqbal, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
European Journal of Medical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficacy of a novel SWEEPS laser-activated irrigation compared to ultrasonic activation in the removal of pulp tissue from an isthmus area in the apical third of the root canal
Ivona Bago, Adriana Đurin, Debora Kanižaj, Lovorka Batelja Vuletić, Ivana Vidović Zdrilić, Ivica Anić
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of passive ultrasonic irrigation on hard tissue debris removal: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Luciana Moura Sassone, Raissa Dias Fares, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,978
View
-
21
Download
-
6
Crossref
|