-
The push-out bond strength of BIOfactor mineral trioxide aggregate, a novel root repair material
-
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Durmus Alperen Bozkurt, Arslan Terlemez, Melek Akman
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e5. Published online January 28, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e5
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
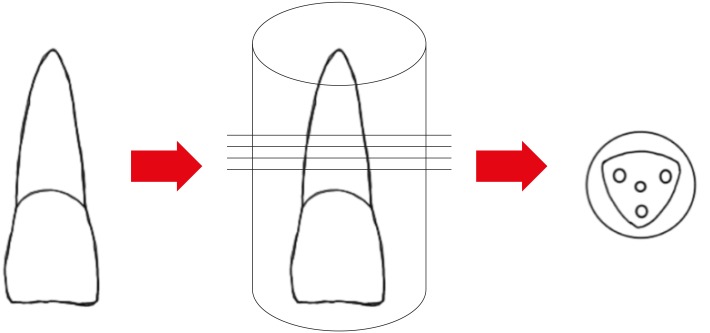
The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the push-out bond strength of a novel calcium silicate-based root repair material-BIOfactor MTA to root canal dentin in comparison with white MTA-Angelus (Angelus) and Biodentine (Septodont). Materials and MethodsThe coronal parts of 12 central incisors were removed and the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. Midroot dentin of each sample was horizontally sectioned into 1.1 mm slices and 3 slices were obtained from each root. Three canal-like standardized holes having 1 mm in diameter were created parallel to the root canal on each dentin slice with a diamond bur. The holes were filled with MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, or BIOfactor MTA. Wet gauze was placed over the specimens and samples were stored in an incubator at 37°C for 7 days to allow complete setting. Then samples were subjected to the push-out test method using a universal test machine with the loading speed of 1 mm/min. Data was statistically analyzed using Friedman test and post hoc Wilcoxon signed rank test with Bonferroni correction. ResultsThere were no significant differences among the push-out bond strength values of MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA (p > 0.017). Most of the specimens exhibited cohesive failure in all groups, with the highest rate found in Biodentine group. ConclusionsBased on the results of this study, MTA-Angelus, Biodentine, and BIOfactor MTA showed similar resistances to the push-out testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Examination of the Bond Strength of Retrograde Filling in Teeth with Failed Apical Resection After Retreatment
Sevda Tok, Leyla Benan Ayranci
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(7): 3441. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Push-out Bond Strength of Conventional Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, Biodentine, and Two Novel Antibacterial-enhanced Mineral Trioxide Aggregates
Sanjeev Khanagar, Suman Panda, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Satish Vishwanathaiah, Ather A Syed, Sara Kalagi, Arokia RS Merlin, Vignesh Ravindran, Aram AlShehri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(2): 168. CrossRef - Influence of Phase Composition and Morphology on the Calcium Ion Release of Several Classical and Hybrid Endodontic Cements
Ivanka Dimitrova, Galia Gentscheva, Ivanka Spassova, Daniela Kovacheva
Materials.2024; 17(22): 5568. CrossRef - The Effect of Two Different MTA (Mineral Trioxide Aggregate) On Thermal Insulation
Gizem Akkus, Ecem Salmaz, Didem Oner Ozdas
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of push‐out bond strength and apical microleakage of different calcium silicate‐based cements after using EDTA, chitosan and phytic acid irrigations
Tutku Koçak Şahin, Murat Ünal
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(9): 2072. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of the physical characteristics and push-out bond strength of new experimental nano-MTA
Nada Omar, Yousra Aly, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interfacial characteristics of BIOfactor MTA and Biodentine with dentin
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Şeref Nur Mutlu, Mehmet Ali Soylu, Emine Şimşek
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(2): 258. CrossRef - Systemic effect of calcium silicate-based cements with different radiopacifiers-histopathological analysis in rats
Osman Ataş, Kubra Bılge, Semsettin Yıldız, Serkan Dundar, Ilknur Calik, Asime Gezer Ataş, Alihan Bozoglan
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15376. CrossRef - The push-out bond strength of three root canal materials used in primary teeth: in vitro study
Hazal Özer, Merve Abaklı İnci, Sevcihan Açar Tuzluca
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different irrigation protocols on push-out bond strength of pre-mixed calcium silicate-based cements
Sabiha Ceren İlisulu, Aliye Tugce Gürcan, Soner Sismanoglu
Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society.2023; 59(5): 1381. CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Sealing Quality and Bond Strength of Different MTA Apical Plugs
Taibe Tokgöz Kaplan, Murat Selim Botsalı
European Journal of Therapeutics.2023; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Kan kontaminasyonunun farklı kök ucu dolgu materyallerinin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Şeyma Nur GERÇEKCİOĞLU, Melike BAYRAM, Emre BAYRAM
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2023; 40(1): 9. CrossRef - Tooth Discoloration Effect of BIOfactor Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A 6-Month In Vitro Study
Şeref Nur Mutlu, Makbule Bilge Akbulut
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(15): 8914. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Push-Out Bond Strength of Root-End Filling Materials by Using Different Condensation Methods
Pelin Tüfenkçi, Sevinç Sevgi, Ayşenur Öncü, Fatma Semra Sevimay, Berkan Çelikten
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Different Adhesive Strategies on the Microshear Bond Strength of Calcium-Silicate-Based Materials
Aliye Tuğçe Gürcan, Soner Şişmanoğlu, Görkem Sengez
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2022; 13(2): 191. CrossRef - BIOfactor MTA’nın Radyoopasitesinin Dijital Radyografi ile Değerlendirilmesi
Şeref Nur MUTLU, Makbule Bilge AKBULUT
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 520. CrossRef - Morphological and Chemical Analysis of Different Types of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements
Okba Mahmoud, Nashwan Abdullah Al-Afifi, Mohideen Salihu Farook, Maysara Adnan Ibrahim, Saaid Al Shehadat, Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, Sandrine Bittencourt Berger
International Journal of Dentistry.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Influence of Blood Contamination on Push-Out Bond Strength of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Materials to Root Dentin
Cristina Rodrigues Paulo, Joana A. Marques, Diana B. Sequeira, Patrícia Diogo, Rui Paiva, Paulo J. Palma, João Miguel Santos
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6849. CrossRef - An In vitro comparative evaluation of effect of novel irrigant Qmix and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the push-out bond strength of biodentine and endosequence bioceramic root repair material
VandanaJ Gade, Aparajita Gangrade, JaykumarR Gade, Neelam Rahul
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2021; 13(2): 124. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
-
202
View
-
3
Download
-
21
Crossref
-
Effects of four novel root-end filling materials on the viability of periodontal ligament fibroblasts
-
Makbule Bilge Akbulut, Pembegul Uyar Arpaci, Ayce Unverdi Eldeniz
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e24. Published online May 25, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e24
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the biocompatibility of newly proposed root-end filling materials, Biodentine, Micro-Mega mineral trioxide aggregate (MM-MTA), polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement, and Smart Dentin Replacement (SDR), in comparison with contemporary root-end filling materials, intermediate restorative material (IRM), Dyract compomer, ProRoot MTA (PMTA), and Vitrebond, using human periodontal ligament (hPDL) fibroblasts. Materials and MethodsTen discs from each material were fabricated in sterile Teflon molds and 24-hour eluates were obtained from each root-end filling material in cell culture media after 1- or 3-day setting. hPDL fibroblasts were plated at a density of 5 × 103/well, and were incubated for 24 hours with 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, and 1:8 dilutions of eluates. Cell viability was evaluated by XTT assay. Data was statistically analysed. Apoptotic/necrotic activity of PDL cells exposed to material eluates was established by flow cytometry. ResultsThe Vitrebond and IRM were significantly more cytotoxic than the other root-end filling materials (p < 0.05). Those cells exposed to the Biodentine and Dyract compomer eluates showed the highest survival rates (p < 0.05), while the PMTA, MM-MTA, SDR, and PMMA groups exhibited similar cell viabilities. Three-day samples were more cytotoxic than 1-day samples (p < 0.05). Eluates from the cements at 1:1 dilution were significantly more cytotoxic (p < 0.05). Vitrebond induced cell necrosis as indicated by flow cytometry. ConclusionsThis in vitro study demonstrated that Biodentine and Compomer were more biocompatible than the other root-end filling materials. Vitrebond eluate caused necrotic cell death.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
Samaneh Arab, Marjan Bahraminasab, Masoumeh Motamedi, Jamshid Hadjati, Alaviye Vahid
Journal of Microbiota.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Apoptotic effects of biodentine, calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement, ferric sulfate, and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the human pulp of exfoliated deciduous teeth
Bahareh NAZEMI SALMAN, Mahshid MOHEBBI RAD, Ehsan SABURI
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Mechanical/Chemical Properties and Cytotoxicity of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements Containing Sr/F-Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles and Methacrylate Functionalized Polyacids
Wisitsin Potiprapanpong, Parichart Naruphontjirakul, Chutikarn Khamsuk, Somruethai Channasanon, Arnit Toneluck, Siriporn Tanodekaew, Naruporn Monmaturapoj, Anne M. Young, Piyaphong Panpisut
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 10231. CrossRef - Comparative biological properties of resin-free and resin-based calcium silicate-based endodontic repair materials on human periodontal ligament stem cells
Shehabeldin M. Saber, Shaimaa M. Gomaa, Mohamed M. Elashiry, Ahmed El-Banna, Edgar Schäfer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(11): 6757. CrossRef - Comparison of root end sealing ability of three retrograde filling materials in teeth with root apices resected at 900 using dye penetration method under fluorescent microscope
Dr. Payal Chaudhari, Manoj Chandak, Dr. Aditya Patel
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1049. CrossRef - The Effects of Tricalcium-Silicate-Nanoparticle-Containing Cement: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Naho Ezawa, Yoshihiko Akashi, Kei Nakajima, Katsutoshi Kokubun, Masahiro Furusawa, Kenichi Matsuzaka
Materials.2023; 16(12): 4451. CrossRef - Evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of a new Harvard MTA compared to MTA Flow and ProRoot MTA on human gingival fibroblasts
Abdel-Rahman Youssef, Samia Elsherief
The Saudi Dental Journal.2021; 33(7): 679. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Bioactivity of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Bioactive Endodontic Type Cements: A Systematic Review
Uma Dixit, Rucha Shivajirao Bhise Patil, Rupanshi Parekh
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - MTT versus other cell viability assays to evaluate the biocompatibility of root canal filling materials: a systematic review
A. V. B. Pintor, L. D. Queiroz, R. Barcelos, L. S. G. Primo, L. C. Maia, G. G. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(10): 1348. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Follow-up for Apical Microsurgery of Teeth with Core and Post Restorations
Astrid Truschnegg, Petra Rugani, Barbara Kirnbauer, Lumnije Kqiku, Norbert Jakse, Robert Kirmeier
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 178. CrossRef - Comparison of Cytotoxic Effects of Calcium Silicate-based Materials on Human Pulp Fibroblasts
Mehmet Adıgüzel, Fuat Ahmetoğlu, Ayçe Ünverdi Eldeniz, Mehmet Gökhan Tekin, Bülent Göğebakan
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(4): 241. CrossRef
-
270
View
-
2
Download
-
12
Crossref
|