-
Efficacy of reciprocating instruments and final irrigant activation protocols on retreatment of mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: a micro-CT analysis
-
Lilian Tietz, Renan Diego Furlan, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Theodoro Weissheimer, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e13. Published online February 15, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e13
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
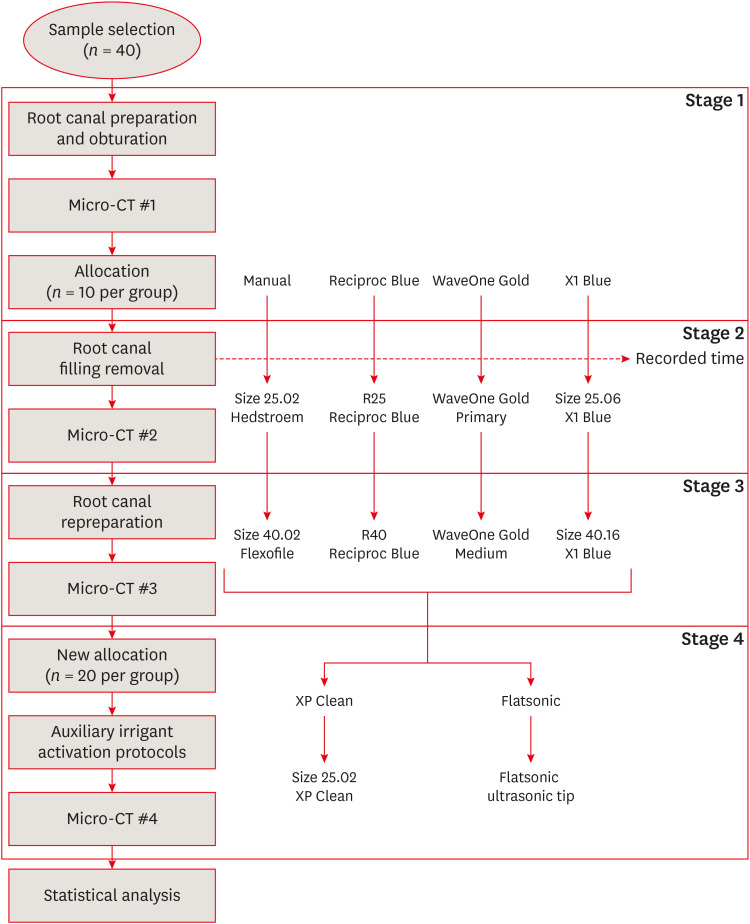
This study evaluated the efficacy of 3 reciprocating systems and the effects of 2 instruments for irrigant activation on filling material removal. Materials and MethodsForty mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared up to size 25.06 and obturated. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) examination #1 was performed. Teeth were then divided into 4 groups (n = 10), according to the retreatment protocol: (1) manual, (2) Reciproc Blue, (3) WaveOne Gold, and (4) X1 Blue. Micro-CT examinations #2 and #3 were performed after filling removal and repreparation, respectively. Next, all teeth were divided into 2 new groups (n = 20) according to the irrigant activation protocol: XP Clean (XP Clean size 25.02) and Flatsonic (Flatsonic ultrasonic tip). Micro-CT examination #4 was performed after irrigant activation. Statistical analysis was performed with a significance level set at 5%. ResultsWaveOne Gold removed a significantly greater amount of filling material than the manual group (p < 0.05). The time to reach the WL was similar for all reciprocating systems (p > 0.05). X1 Blue was faster than the manual group (p < 0.05). Only manual group improved the filling material removal after the repreparation stage (p < 0.05). Both activation protocols significantly improved the filling material removal (p < 0.05), without differences between them (p > 0.05). ConclusionsNone of the tested instruments completely removed the filling material. X1 Blue size 25.06 reached the working length in the shortest time. XP Clean and Flatsonic improved the filling material removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Ability of 3 Reciprocating Instruments to Remove Obturation Material: A Micro–Computed Tomography Study
Fábio Luiz Cecagno, Alexandre Sigrist De Martin, Carlos Eduardo Fontana, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Wayne Martins Nascimento, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 376. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of cleaning efficiency of single file NiTi rotary system during root canal treatment procedure - A scanning electron microscope study
Ruchi Vashisht, Umesh Kumar, Swaty Jhamb, Ruchi Singla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 316. CrossRef - Influence of rotary and reciprocating kinematics on the accuracy of an integrated apex locator
Verônica de Almeida Gardelin, Júlia Itzel Acosta Moreno Vinholes, Renata Grazziotin‐Soares, Fernanda Geraldo Pappen, Fernando Branco Barletta
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 202. CrossRef
-
243
View
-
10
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
|