-
Microtensile bond strength of CAD/CAM-fabricated polymer-ceramics to different adhesive resin cements
-
Leyla Sadighpour, Farideh Geramipanah, Zahra Ghasri, Mehrnoosh Neshatian
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e40. Published online September 3, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e40
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
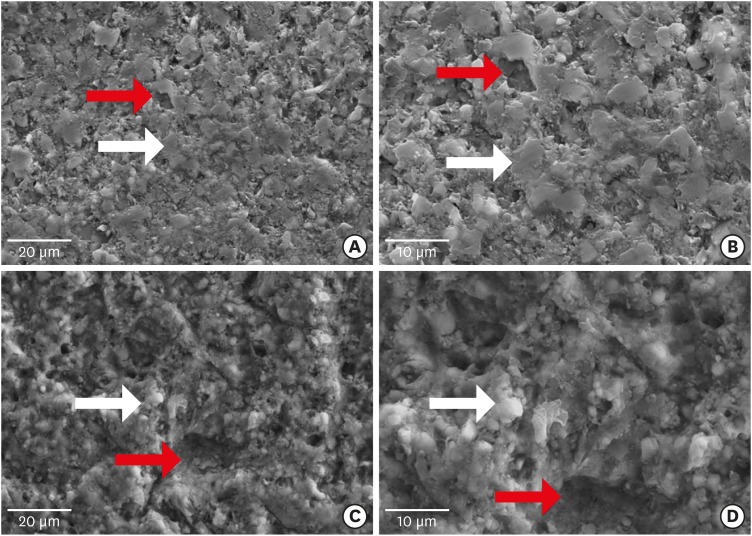
This study evaluated the microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of polymer-ceramic and indirect composite resin with 3 classes of resin cements. Materials and MethodsTwo computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated polymer-ceramics (Enamic [ENA; Vita] and Lava Ultimate [LAV; 3M ESPE]) and a laboratory indirect composite resin (Gradia [GRA; GC Corp.]) were equally divided into 6 groups (n = 18) with 3 classes of resin cements: Variolink N (VAR; Vivadent), RelyX U200 (RXU; 3M ESPE), and Panavia F2 (PAN; Kuraray). The μTBS values were compared between groups by 2-way analysis of variance and the post hoc Tamhane test (α = 0.05). ResultsRestorative materials and resin cements significantly influenced µTBS (p < 0.05). In the GRA group, the highest μTBS was found with RXU (27.40 ± 5.39 N) and the lowest with VAR (13.54 ± 6.04 N) (p < 0.05). Similar trends were observed in the ENA group. In the LAV group, the highest μTBS was observed with VAR (27.45 ± 5.84 N) and the lowest with PAN (10.67 ± 4.37 N) (p < 0.05). PAN had comparable results to those of ENA and GRA, whereas the μTBS values were significantly lower with LAV (p = 0.001). The highest bond strength of RXU was found with GRA (27.40 ± 5.39 N, p = 0.001). PAN showed the lowest µTBS with LAV (10.67 ± 4.37 N; p < 0.001). ConclusionsWhen applied according to the manufacturers' recommendations, the µTBS of polymer-ceramic CAD/CAM materials and indirect composites is influenced by the luting cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of hydrofluoric acid and self-etch ceramic primers on the flexural strength and fatigue resistance of glass ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Paulo Matias Moreira, Gabriela Luiza Moreira Carvalho, Rodrigo de Castro Albuquerque, Carolina Bosso André
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 198. CrossRef - Light transmittance through resin-matrix composite onlays adhered to resin-matrix cements or flowable composites
Rita Fidalgo-Pereira, Susana O. Catarino, Óscar Carvalho, Nélio Veiga, Orlanda Torres, Annabel Braem, Júlio C.M. Souza
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 151: 106353. CrossRef - Effect of thermocycling on the mechanical properties of permanent composite-based CAD-CAM restorative materials produced by additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques
Tuğba Temizci, Hatice Nalan Bozoğulları
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of different surface treatments on resin-matrix CAD/CAM ceramics bonding to dentin: in vitro study
Hanan Fathy, Hamdi H. Hamama, Noha El-Wassefy, Salah H. Mahmoud
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital image analysis of fluorescence of ceramic veneers with different ceramic materials and resin cements
Jiao ZHANG, Qing YU
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(6): 868. CrossRef - Fatigue Behavior of Monolithic Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Ceramic Restorations: Effects of Conditionings of the Intaglio Surface and the Resin Cements
F Dalla-Nora, LF Guilardi, CP Zucuni, LF Valandro, MP Rippe
Operative Dentistry.2021; 46(3): 316. CrossRef
-
201
View
-
2
Download
-
6
Crossref
|