-
Success rate of direct pulp capping on permanent teeth using bioactive materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
-
Karem Paula Pinto, Gabriela Ribeiro da Silva, Cláudio Malizia Alves Ferreira, Luciana Moura Sassone, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e34. Published online September 6, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e34
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
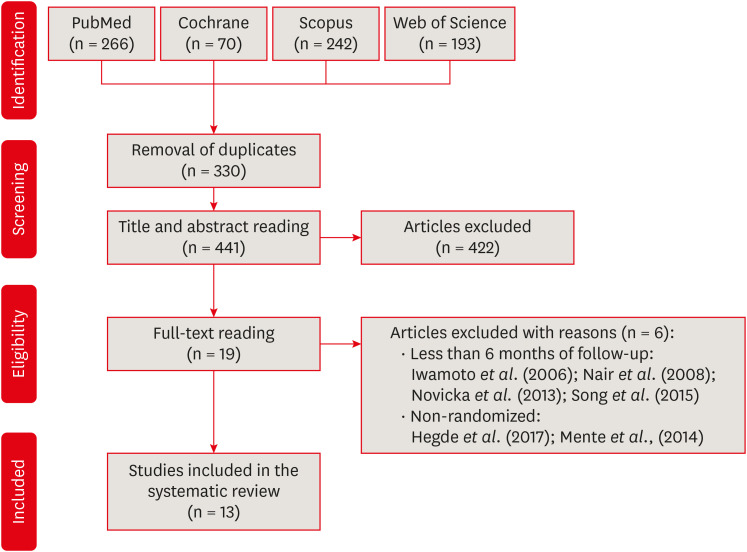
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the success rate of direct pulp capping (DPC) on permanent teeth, comparing the use of MTA with calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate-based cements. A systematic search was carried out in 4 databases until July 2023. The selection was based on PICOS criteria and only randomized clinical trials were included. The risk of bias was assessed using RoB-2 tool, and meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The overall quality of evidence was determined using the GRADE tool. Thirteen studies were included. Meta-analyses indicated significantly higher success rate for DPC using MTA compared to calcium hydroxide, while no significant difference was observed between MTA and Biodentine, showing a success rate from 80% to 100% even after 3 years of follow-up. Five studies were classified as having high risk of bias and the GRADE assessment revealed low certainty of evidence. DPC is highly effective for permanent teeth when using MTA or Biodentine. There is a need for future well-designed randomized clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of DPC using newer bioceramic materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
Njwan Fadhel SHEHAB
Dental Materials Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Photobiomodulation-assisted pulp capping using nano-hydroxyapatite and mineral trioxide aggregate: Report of two cases
Priya Pal, Rhythm Bains, Promila Verma, Vivek Kumar Bains
Journal of Healthcare Research and Education.2026; 2: 2. CrossRef - Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics consensus statement on deep caries management
Deepak Kumar Sharma, R. S. Mohan Kumar, Shishir Singh, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Meenal Nithin Gulve, Dipali Y. Shah, Sathish Abraham, Shruthi Nagaraja, Raksha Bhat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 714. CrossRef
-
17,885
View
-
524
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Disinfectant effectiveness of chlorhexidine gel compared to sodium hypochlorite: a systematic review with meta-analysis
-
Theodoro Weissheimer, Karem Paula Pinto, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e37. Published online October 26, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
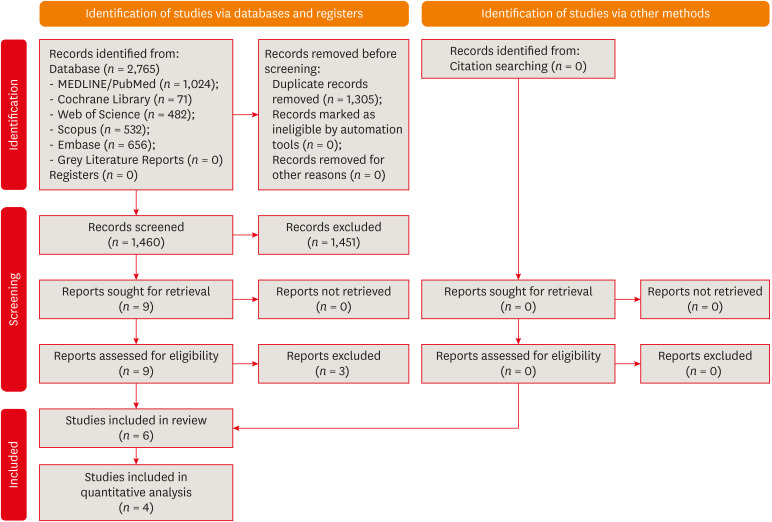
This study aimed to compare the disinfectant ability of chlorhexidine (CHX) gel and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Systematic searches were conducted from inception until December 8th, 2022 (MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and Grey Literature databases). Only randomized clinical trials were included. The revised Cochrane risk of bias tools for randomized trials were used to assess the quality of studies. Meta-analyses were performed. The overall quality of evidence was assessed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation tool. Six studies were included. Five had a low risk of bias and 1 had some concerns. Three studies assessed bacterial reduction. Two were included in the meta-analysis for bacterial reduction (mean difference, 75.03 [confidence interval, CI, −271.15, 421.22], p = 0.67; I2 = 74%); and 3 in the meta-analysis for cultivable bacteria after chemomechanical preparation (odds ratio, 1.03 [CI, 0.20, 5.31], P = 0.98; I2 = 49%). Five studies assessed endotoxin reduction. Three were included in a meta-analysis (mean difference, 20.59 [CI, −36.41, 77.59], p = 0.48; I2 = 74%). There seems to be no difference in the disinfectant ability of CHX gel and NaOCl, but further research is necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Bactericidal Effects of Ultraviolet-C Light-Emitting Diode Prototype Device Through Thin Optical Fiber
Mi-Jeong Jeon, Yu-Sung Choi, Deog-Gyu Seo
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4504. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Irrigation Protocols in Endodontic Therapy: An Umbrella Review
Manuel J. Orozco-Gallego, Eliana L. Pineda-Vélez, Wilder J. Rojas-Gutiérrez, Martha L. Rincón-Rodríguez, Andrés A. Agudelo-Suárez
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 273. CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of Disinfectants on Gutta-Percha Cones: Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans
Tringa Kelmendi, Donika Bajrami Shabani, Aida Meto, Hani Ounsi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(19): 6846. CrossRef - Preparing porcine lens to mimic human lens capsule
Yajing Pei, Shaofeng Han, Mingfeng Lu, Yang Yang, Ke Ma
Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery.2024; 50(9): 963. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Disinfection Protocols for Dental Impressions in Prosthodontics
Subhash Sonkesriya, Ghanshyam Gaur, Akanksha Maheshwari, Arun Kumar Ashahiya, Simran Kaur Aulakh, Amit Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
-
6,047
View
-
119
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
-
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e42. Published online July 21, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
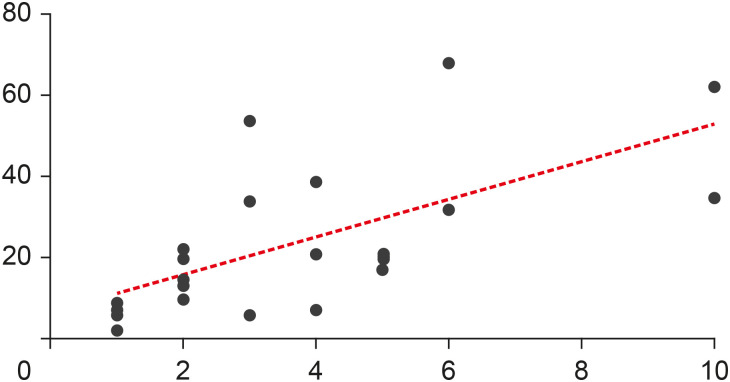
This study aimed to analyze the main features of the 25 most-cited articles in minimally invasive access cavities. Materials and MethodsAn electronic search was conducted on the Clarivate Analytics' Web of Science ‘All Databases’ to identify the most-cited articles related to this topic. Citation counts were cross-matched with data from Elsevier's Scopus and Google Scholar. Information about authors, contributing institutions and countries, year and journal of publication, study design and topic, access cavity, and keywords were analyzed. ResultsThe top 25 most-cited articles received a total of 572 (Web of Science), 1,160 (Google Scholar) and 631 (Scopus) citations. It was observed a positive significant association between the number of citations and age of publication (r = 0.6907, p < 0.0001); however, there was no significant association regarding citation density and age of publication (r = −0.2631, p = 0.2038). The Journal of Endodontics made the highest contribution (n = 15, 60%). The United States had the largest number of publications (n = 7) followed by Brazil (n = 4), with the most contributions from the University of Tennessee and Grande Rio University (n = 3), respectively. The highest number of most-cited articles were ex vivo studies (n = 16), and ‘fracture resistance’ was the major topic studied (n = 10). ConclusionsThis study revealed a growing interest for researchers in the field of minimally invasive access cavities. Future trends are focused on the expansion of collaborative networks and the conduction of laboratory studies on under-investigated parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Research Trends in Internal Root Resorption from 1947 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis of the 50 Most-cited Articles
Laise Pena Braga Monteiro, Larissa Pillar Gomes Martel, Roberta Fonseca de Castro, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Juliana Melo da Silva Brandão
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(2): 196. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Sixty Years of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Use in Endodontics: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Study
Camila Segatto Hartmann, Luiz Fernando Monteiro Czornobay, Julia Menezes Savaris, Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Mariane Cardoso, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Cleonice da Silveira Teixe
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the forces applied by rubber dam clamps on mandibular first molar teeth with different endodontic access cavities: a 3D FEA study
Mehmet Eskibağlar, Serkan Erdem, Büşra Karaağaç Eskibağlar, Mete Onur Kaman
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17921. CrossRef - A Global Overview of Guided Endodontics: A Bibliometric Analysis
Thaine Oliveira Lima, Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Nailson Silva Meneses Júnior, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Mariane Cardoso, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(1): 10. CrossRef - Novel method for augmented reality guided endodontics: An in vitro study
Marco Farronato, Andres Torres, Mariano S. Pedano, Reinhilde Jacobs
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 132: 104476. CrossRef - Contribution of Türkiye to the Field of Endodontology: A Visualized Bibliometric Analysis Based on Web of Science
Olcay ÖZDEMİR, Yağız ÖZBAY, Neslihan YILMAZ ÇIRAKOĞLU
Medical Records.2023; 5(1): 91. CrossRef - Effect of access cavities on the biomechanics of mandibular molars: a finite element analysis
Xiao Wang, Dan Wang, Yi-rong Wang, Xiao-gang Cheng, Long-xing Ni, Wei Wang, Yu Tian
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Contemporary research trends on nanoparticles in endodontics: a bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles
Sıla Nur Usta, Zeliha Uğur-Aydın, Kadriye Demirkaya, Cumhur Aydın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evolving trend of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in endodontics: A bibliometric study
GalvinSim Siang Lin, JiaZheng Leong, WenXin Chong, MikoChong Kha Chee, ChinSheng Lee, Manahil Maqbool, TahirYusuf Noorani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 236. CrossRef - Global research trends on photodynamic therapy in endodontics: A bibliometric analysis
Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Leandro Bueno Gobbo, Tamares Andrade da Silva, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Caio Cezar Randi Ferraz
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 40: 103039. CrossRef - Minimal Invasive Endodontics: A Comprehensive Narrative Review
Jaydip Marvaniya, Kishan Agarwal, Dhaval N Mehta, Nirav Parmar, Ritwik Shyamal , Jenee Patel
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,927
View
-
28
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
|