-
Retrospective study of fracture survival in endodontically treated molars: the effect of single-unit crowns versus direct-resin composite restorations
-
Kanet Chotvorrarak, Warattama Suksaphar, Danuchit Banomyong
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e29. Published online May 6, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e29
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
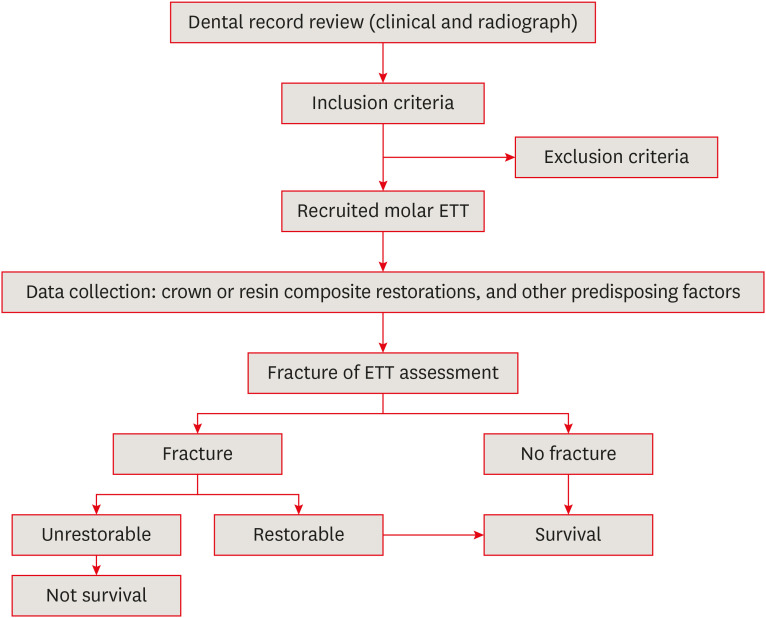
This study was conducted to compare the post-fracture survival rate of endodontically treated molar endodontically treated teeth (molar ETT) restored with resin composites or crowns and to identify potential risk factors, using a retrospective cohort design. Materials and MethodsDental records of molar ETT with crowns or composite restorations (recall period, 2015–2019) were collected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. The incidence of unrestorable fractures was identified, and molar ETT were classified according to survival. Information on potential risk factors was collected. Survival rates and potential risk factors were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier log-rank test and Cox regression model. ResultsThe overall survival rate of molar ETT was 87% (mean recall period, 31.73 ± 17.56 months). The survival rates of molar ETT restored with composites and crowns were 81.6% and 92.7%, reflecting a significant difference (p < 0.05). However, ETT restored with composites showed a 100% survival rate if only 1 surface was lost, which was comparable to the survival rate of ETT with crowns. The survival rates of ETT with composites and crowns were significantly different (97.6% vs. 83.7%) in the short-term (12–24 months), but not in the long-term (> 24 months) (87.8% vs. 79.5%). ConclusionsThe survival rate from fracture was higher for molar ETT restored with crowns was higher than for ETT restored with composites, especially in the first 2 years after restoration. Molar ETT with limited tooth structure loss only on the occlusal surface could be successfully restored with composite restorations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Risk factors for the appearance of cracks and fractures of teeth according to a survey of dentists
Emilia A. Olesova, Alexander A. Ilyin, Sergey D. Arutyunov, Elena V. Glazkova, Arsen A. Popov, Svetlana P. Iarilkina
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2024; 28(6): 562. CrossRef - Performance of Bonded Lithium Disilicate Partial-coverage Crowns in the Restoration of Endodontically Treated Posterior Teeth: An Up to Seven-Year Retrospective Study
Q Jiang, Z Wang, S Zhang, X Liu, B Fu
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 365. CrossRef - In Vitro Bond Strength of Dentin Treated with Sodium Hypochlorite: Effects of Antioxidant Solutions
Guillermo Grazioli, Elisa de León Cáceres, Romina Tessore, Rafael Lund, Ana Monjarás-Ávila, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Carlos Cuevas-Suárez
Antioxidants.2024; 13(9): 1116. CrossRef - Stress Analysis on Mesiolingual Cavity of Endodontically Treated Molar Restored Using Bidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Composite (Wallpapering Technique)
Harnia Neri, Dudi Aripin, Anna Muryani, Hendra Dharsono, Yolanda Yolanda, Andi Mahyuddin
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2024; Volume 16: 75. CrossRef - Effect of Luting Cement Film Thickness on the Pull-Out Bond Strength of Endodontic Post Systems
Khalil Aleisa, Syed Rashid Habib, Abdul Sadekh Ansari, Ragad Altayyar, Shahad Alharbi, Sultan Ali S. Alanazi, Khalid Tawfik Alduaiji
Polymers.2021; 13(18): 3082. CrossRef
-
270
View
-
14
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
Bacterial leakage and micro-computed tomography evaluation in round-shaped canals obturated with bioceramic cone and sealer using matched single cone technique
-
Kallaya Yanpiset, Danuchit Banomyong, Kanet Chotvorrarak, Ratchapin Laovanitch Srisatjaluk
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e30. Published online July 5, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e30
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
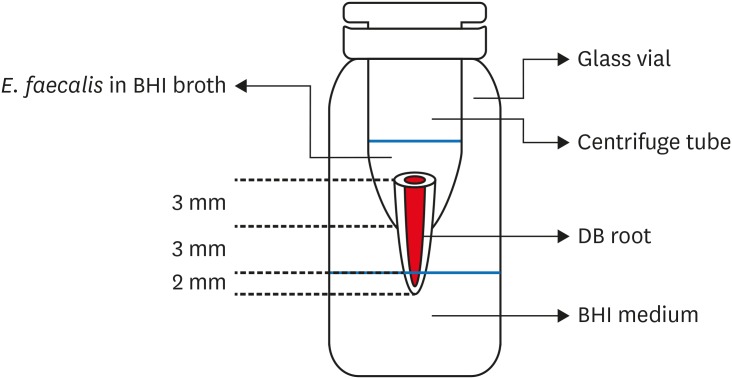
To evaluate sealing ability of root canals obturated with bioceramic-impregnated gutta percha cone (BCC) or gutta percha (GP), with bioceramic sealer (BCS) or AH Plus (AH; Dentsply-Maillefer), in roundly-prepared canals using matched single-cone technique, based on bacterial leakage test, and to analyze obturation quality using micro-computed tomography (CT) analysis. Materials and MethodsNinety-two distobuccal roots of maxillary molars were prepared using nickel-titanium files to apical size 40/0.06. The roots were divided into 4 groups (n = 20) that were obturated with a master cone and sealer: GP/AH, BCC/AH, GP/BCS, and BCC/BCS. Bacterial leakage model using Enterococcus faecalis was used to evaluate sealing ability for 60-day period. Obturated samples from each group (n = 4) were analyzed using micro-CT. ResultsAll groups showed bacterial leakage at 20%–45% of samples with mean leakage times of 42–52 days. There were no significant differences in bacterial leakage among the groups. Micro-CT showed minimal gaps and voids in all groups at less than 1%. ConclusionsIn roundly-prepared canals, the single cone obturation with BCC/BCS was comparable to GP/AH for bacterial leakage at 60 days.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In vitro comparative evaluation of apical leakage using a bioceramic sealer with three different obturating techniques: A glucose leakage model
Tanvi S Agrawal, Shishir Singh, Rajesh S Podar, Gaurav Kulkarni, Anuprita Gadkari, Navin Agarwal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 76. CrossRef - In Vitro Microscopical and Microbiological Assessment of the Sealing Ability of Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers
Karin Christine Huth, Sabina Noreen Wuersching, Leander Benz, Stefan Kist, Maximilian Kollmuss
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(11): 341. CrossRef - Comparison between AH plus sealer and total fill bioceramic sealer performance in previously untreated and retreatment cases of maxillary incisors with large-sized periapical lesion: a randomized controlled trial
Eisa Wahbi, Hassan Achour, Yasser Alsayed Tolibah
BDJ Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial sealing ability of calcium silicate-based sealer for endodontic surgery: an in-vitro study
Mai M. Mansour, Sybel M. Moussa, Marwa A. Meheissen, Mahmoud R. Aboelseoud
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Assessment of Bacterial Sealing Ability of Two Different Bio-Ceramic Sealers in Single-Rooted Teeth Using Single Cone Obturation Technique: An In Vitro Study
Doaa M. AlEraky, Ahmed M. Rahoma, Hatem M. Abuohashish, Abdullh AlQasser, Abbas AlHamali, Hussain M. AlHussain, Hussain M. AlShoalah, Zakrya AlSaghah, Abdulrahman Khattar, Shimaa Rifaat
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(5): 2906. CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of Morse taper implant design on microleakage at implant-healing abutment interface
Soyeon KIM, Joo Won LEE, Jae-Heon KIM, Van Mai TRUONG, Young-Seok PARK
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(5): 767. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - Comparison of Sealing Ability of Bioceramic Sealer, AH Plus, and GuttaFlow in Conservatively Prepared Curved Root Canals Obturated with Single-Cone Technique: An In vitro Study
Shalan Kaul, Ajay Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani, Laxmi Sukhtankar, M. Madhumitha, Amit Kumar
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S857. CrossRef - Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Root Canal Obturation Techniques
Mahmood Reza Kalantar Motamedi, Amin Mortaheb, Maryam Zare Jahromi, Brett E. Gilbert, Marilena Vivona
Scanning.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Both Fiber Post/Core Resin Construction System and Root Canal Sealer on the Material Interface in Deep Areas of Root Canal
Hiroki Miura, Shinji Yoshii, Masataka Fujimoto, Ayako Washio, Takahiko Morotomi, Hiroshi Ikeda, Chiaki Kitamura
Materials.2021; 14(4): 982. CrossRef - Sealing ability and microbial leakage of root-end filling materials: MTA versus epoxy resin: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mario Dioguardi, Mario Alovisi, Diego Sovereto, Giuseppe Troiano, Giancarlo Malagnino, Michele Di Cosola, Angela Pia Cazzolla, Luigi Laino, Lorenzo Lo Muzio
Heliyon.2021; 7(7): e07494. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef - BIOCERAMIC-BASED ROOT CANAL SEALERS
L Somolová, Z Zapletalová, M Rosa, B Novotná, I Voborná, Y Morozova
Česká stomatologie a praktické zubní lékařství.2021; 121(4): 116. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Narrative Review and Clinical Perspectives
Germain Sfeir, Carla Zogheib, Shanon Patel, Thomas Giraud, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frédéric Bukiet
Materials.2021; 14(14): 3965. CrossRef - Physico-Chemical Properties of Calcium-Silicate vs. Resin Based Sealers—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory-Based Studies
Viresh Chopra, Graham Davis, Aylin Baysan
Materials.2021; 15(1): 229. CrossRef - Comparison of apical sealing ability of bioceramic sealer and epoxy resin-based sealer using the fluid filtration technique and scanning electron microscopy
Widcha Asawaworarit, Thitapa Pinyosopon, Kanittha Kijsamanmith
Journal of Dental Sciences.2020; 15(2): 186. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic evaluation of root canal filling with a single gutta-percha cone and calcium silicate sealer
Jong Cheon Kim, Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of sealing ability of gutta percha and resilon as root canal filling materials- a systematic review
Pragya Pandey, Himanshi Aggarwal, A.P. Tikku, Arpit Singh, Rhythm Bains, Shambhavi Mishra
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(2): 220. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Root fillings with a matched-taper single cone and two calcium silicate–based sealers: an analysis of voids using micro-computed tomography
Eugenio Pedullà, Roula S. Abiad, Gianluca Conte, Giusy R. M. La Rosa, Ernesto Rapisarda, Prasanna Neelakantan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(12): 4487. CrossRef - Influence of different disinfection protocols on gutta-percha cones surface roughness assessed by two different methods
A.M. Nunes, J.P. Gouvea, L. da Silva
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2019; 8(6): 5464. CrossRef - Endodontic sealers based on calcium silicates: a systematic review
David Donnermeyer, Sebastian Bürklein, Till Dammaschke, Edgar Schäfer
Odontology.2019; 107(4): 421. CrossRef
-
271
View
-
7
Download
-
26
Crossref
|