-
Effects of CTHRC1 on odontogenic differentiation and angiogenesis in human dental pulp stem cells
-
Jong-soon Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e18. Published online April 28, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e18
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
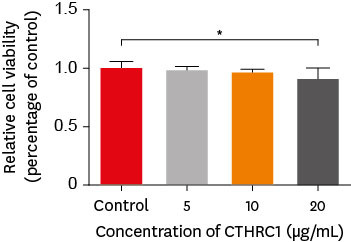
This study aimed to determine whether collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 (CTHRC1), which is involved in vascular remodeling and bone formation, can stimulate odontogenic differentiation and angiogenesis when administered to human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs). Materials and MethodsThe viability of hDPSCs upon exposure to CTHRC1 was assessed with the WST-1 assay. CTHRC1 doses of 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL were administered to hDPSCs. Reverse-transcription polymerase reaction was used to detect dentin sialophosphoprotein, dentin matrix protein 1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor 2. The formation of mineralization nodules was evaluated using Alizarin red. A scratch wound assay was conducted to evaluate the effect of CTHRC1 on cell migration. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance followed by the Tukey post hoc test. The threshold for statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. ResultsCTHRC1 doses of 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL had no significant effect on the viability of hDPSCs. Mineralized nodules were formed and odontogenic markers were upregulated, indicating that CTHRC1 promoted odontogenic differentiation. Scratch wound assays demonstrated that CTHRC1 significantly enhanced the migration of hDPSCs. ConclusionsCTHRC1 promoted odontogenic differentiation and mineralization in hDPSCs.
-
THE EFFECT OF PRIMING ETCHED DENTIN WITH SOLVENT ON THE MICROTENSILE BOND STRENGTH OF HYDROPHOBIC DENTIN ADHESIVE
-
Eun-Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Bae, Jong-Soon Kim, Jae-Hoon Kim, In-Bog Lee, Chang-Keun Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(1):42-50. Published online January 14, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.1.042
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Abstract
Deterioration of long-term dentin adhesion durability is thought to occur by hydrolytic degradation within hydrophilic domains of the adhesive and hybrid layers. This study investigated the hypothesis that priming the collagen network with an organic solvent displace water without collapse and thereby obtain good bond strength with an adhesive made of hydrophobic monomers and organic solvents. Three experimental adhesives were prepared by dissolving two hydrophobic monomers, bisphenol-A-glycidylmethacrylate (Bis-GMA) and triethylenegly-col dimethacrylate (TEGDMA), into acetone, ethanol or methanol. After an etching and rinsing procedure, the adhesives were applied onto either wet dentin surfaces (wet bonding) or dentin surfaces primed with the same solvent (solvent-primed bonding). Microtensile bond strength (MTBS) was measured at 48 hrs, 1 month and after 10,000 times of thermocycles. The bonded interfaces were evaluated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Regardless of bonding protocols, well-developed hybrid layers were observed at the bonded interface in most specimens. The highest mean MTBS was observed in the adhesive containing ethanol at 48 hrs. With solvent-primed bonding, increased MTBS tendencies were seen with thermocycling in the adhesives containing ethanol or methanol. However, in the case of wet bonding, no increase in MTBS was observed with aging.
-
Effect of cavity shape, bond quality and volume on dentin bond strength
-
Hyo-Jin Lee, Jong-Soon Kim, Shin-Jae Lee, Bum-Soon Lim, Seung-Ho Baek, Byeong-Hoon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(6):450-460. Published online November 30, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.6.450
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of cavity shape, bond quality of bonding agent and volume of resin composite on shrinkage stress developed at the cavity floor. This was done by measuring the shear bond strength with respect to iris materials (cavity shape; adhesive-coated dentin as a high C-factor and Teflon-coated metal as a low C-factor), bonding agents (bond quality; Scotchbond™ Multi-purpose and Xeno®III) and iris hole diameters (volume; 1 mm or 3 mm in diameter × 1.5 mm in thickness). Ninety-six molars were randomly divided into 8 groups (2 × 2 × 2 experimental setup). In order to simulate a Class I cavity, shear bond strength was measured on the flat occlusal dentin surface with irises. The iris hole was filled with Z250 restorative resin composite in a bulk-filling manner. The data was analyzed using three-way ANOVA and the Tukey test. Fracture mode analysis was also done. When the cavity had high C-factor, good bond quality and large volume, the bond strength decreased significantly. The volume of resin composite restricted within the well-bonded cavity walls is also be suggested to be included in the concept of C-factor, as well as the cavity shape and bond quality. Since the bond quality and volume can exaggerate the effect of cavity shape on the shrinkage stress developed at the resin-dentin bond, resin composites must be filled in a method, which minimizes the volume that can increase the C-factor.
|