-
Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
-
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e13. Published online March 18, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e13
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
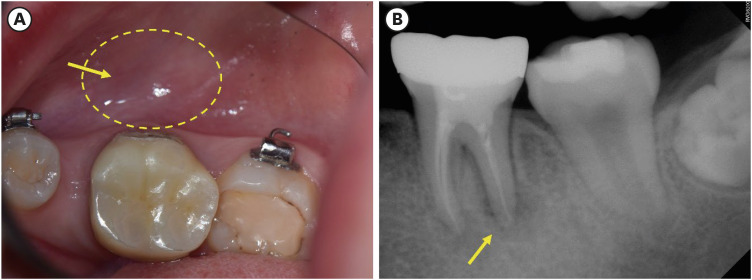
Chronic osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis, known as Garre’s osteomyelitis, is a type of osteomyelitis characterized by a distinctive gross thickening of the periosteum of bones. Peripheral reactive bone formation can be caused by mild irritation or infection. Garre’s osteomyelitis is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and the mandible is more affected than the maxilla. The following is a case report of a 12-year-old female patient with Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible due to an infection of a root canal-treated tooth. Without surgical intervention, the patient’s symptoms were relieved through nonsurgical root canal re-treatment with long-term calcium hydroxide placement. A cone-beam computed tomography image obtained 6 months after treatment completion displayed complete healing of the periapical lesion and resolution of the peripheral reactive buccal bone. Due to the clinical features of Garre's osteomyelitis, which is characterized by thickening of the periosteum, it can be mistaken for other diseases such as fibrous dysplasia. It is important to correctly diagnose Garre's osteomyelitis based on its distinctive clinical features to avoid unnecessary surgical intervention, and it can lead to minimally invasive treatment options. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Focal osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis
Zarah Yakoob
South African Dental Journal.2025; 79(09): 508. CrossRef - Garré’s osteomyelitis of the mandible in an adolescent: a case report
Wiem Feki, Imen Haddar, Marwa Bahloul, Zeineb Mnif, Thouraya Kammoun, Ines Maaloul
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Garré’s Chronic Sclerosing Osteomyelitis: An Overview of Clinical and Radiologic Features
Mohamed Fadil, Ayman Farouki, Rachida Saouab, Hassan En-nouali, Jamal El Fenni, Zakariya Toufga
Oxford Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
7,198
View
-
183
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Oral manifestation and root canal therapy of the patient with mucopolysaccharidosis
-
Ji-Hye Yoon, Hyo-Il Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e14. Published online April 4, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e14
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency in enzymes that participate in the degradation of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) such as heparin sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Left untreated, patients show progressive mental and physical deterioration due to deposition of GAGs in organs. Death often occurs due to cardiac or respiratory failure before patients reach their early twenties. MPS has several oral and dental manifestations. An enlarged head, short neck, and open mouth associated with a large tongue are major characteristics of MPS patients. Dental complications can be severe, including unerupted dentition, dentigerous cyst-like follicles, malocclusions, condylar defects, and gingival hyperplasia. A 21-year-old female patient with MPS was described in this article, with special emphasis on oral manifestations and dental treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pediatric Interventions in a Sanfilippo Syndrome Patient Under General Anesthesia: A Case Report
Ahmad Al Malak, Hassan Issawi, Mohammad Hassoun, Mohammad Al Halabi, Darko Macan
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioural disorders and sleep problems in Sanfilippo syndrome: overlaps with some other conditions and importance indications
Karolina Wiśniewska, Jakub Wolski, Paulina Anikiej-Wiczenbach, Magdalena Żabińska, Grzegorz Węgrzyn, Karolina Pierzynowska
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.2025; 34(6): 1795. CrossRef - Hurler syndrome: Oral and radiographic findings of a rare clinical case
W. Kabbassi, H. Hessissen, J. Hammouti
Medical Reports.2025; 14: 100325. CrossRef - Sanfilippo syndrome: consensus guidelines for clinical care
Nicole Muschol, Roberto Giugliani, Simon A. Jones, Joseph Muenzer, Nicholas J. C. Smith, Chester B. Whitley, Megan Donnell, Elise Drake, Kristina Elvidge, Lisa Melton, Cara O’Neill
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Manifestaciones bucales de pacientes con mucopolisacaridosis. Serie de casos
Andrea Verónica Ríos, Mariana Llorensi
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,433
View
-
7
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
In vitro characterization of human dental pulp stem cells isolated by three different methods
-
Ji-Hyun Jang, Hyeon-Woo Lee, Kyu Min Cho, Hee-Woong Shin, Mo Kwan Kang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):283-295. Published online October 12, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.283
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
In this study, we characterized human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) obtained by different culture methods to establish the most suitable methodology for dental tissue engineering and regenerative endodontic applications. Materials and MethodsHDPCs were isolated by the outgrowth method (HDPCs-OG), the enzymatic digestion method (collagenase/dispase/trypsin, HDPCs-ED), or the combination of both methods (HDPCs-Combined). The expression of mesenchymal stem cell markers (CD105, CD90, and CD73) was investigated. In vitro differentiation capacities of HDPCs into adipogenic, osteogenic, and chondrogenic lineages were compared. Differentiation markers were analyzed by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blotting. ResultsOur data indicated that whole HDPCs-ED, HPDCs-OG, and HDPCs-Combined could be differentiated into adipogenic, chrondrogenic, and osteogenic cell types. However, we found that the methods for isolating and culturing HDPCs influence the differentiation capacities of cells. HDPCs-OG and HDPCs-ED were preferably differentiated into adipogenic and osteogenic cells, respectively. Differentiation markers shown by RT-PCR and western blotting analysis were mostly upregulated in the treated groups compared with the control groups. ConclusionsOur findings confirmed that cell populations formed by two different culture methods and the combined culture method exhibited different properties. The results of this study could provide an insight into regenerative endodontic treatment using HDPCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of simulated microgravity on dental pulp stem cell stemness
Huailong Hou, Zhengjun Qiu, Jingyi Che, Yanping Li, Jingxuan Sun, Weiwei Zhang, Jinjie Ma, Shuang Zhang, Mengdi Li, Yumei Niu, Lina He
Journal of Molecular Histology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validated methods for isolation and qualification of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells from different sources
Vincenzo Mattei, Francesca Santilli, Fanny Pulcini, Jessica Fabrizi, Loreto Lancia, Costantino Santacroce, Francesca Megiorni, Simona Ceccarelli, Emanuela Paldino, Roberto Gramignoli, Maria G. Roubelakis, Sadri Bahareh, Massoud Vosough, Sveva Bollini, Umb
Journal of Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ISOLATION OF HUMAN ADULT DENTAL PULP STEM CELLS USING ENZYMATIC DIGESTION
Sehrish Khan, Saima Butt, Shumaila Usman, Sana Mirza
JOURNAL OF KHYBER COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY.2024; 14(4): 9. CrossRef - Diş Hekimliğinde Oromaksillofasiyal Bölgeden Alınabilen Mezenkimal Kök Hücreler
Sefer MAHMUTOĞLU, Ayşegül MENDİ, Derviş YILMAZ
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 11(2): 184. CrossRef - Sinking Our Teeth in Getting Dental Stem Cells to Clinics for Bone Regeneration
Sarah Hani Shoushrah, Janis Lisa Transfeld, Christian Horst Tonk, Dominik Büchner, Steffen Witzleben, Martin A. Sieber, Margit Schulze, Edda Tobiasch
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(12): 6387. CrossRef - Isolation, Characterization, and Differentiation of Stem Cells From Various Dental Sources: An In Vitro Study
Sandeep S. Katti, Kishore Bhat, Chetana Bogar
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2021; 12(2): 254. CrossRef - Intra-Individual Variability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cell Features Isolated from the Same Donor
Nela Pilbauerova, Jan Schmidt, Tomas Soukup, Jan Duska, Jakub Suchanek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13515. CrossRef - Comparison of Osteogenic Potentials of Dental Pulp and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using the New Cell Transplantation Platform, CellSaic, in a Rat Congenital Cleft-Jaw Model
Jinzhao Lyu, Yoshiya Hashimoto, Yoshitomo Honda, Naoyuki Matsumoto
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(17): 9478. CrossRef - In Vitro Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Cultured in Two Microsphere-Forming Culture Plates
Nam-Ung Bu, Hyo-Seol Lee, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Young Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 242. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Enzymatic Isolation, Amplification and Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Nela Pilbauerova, T. Soukup, T. Suchánková Kleplová, J. Suchánek
Folia Biologica.2019; 65(3): 124. CrossRef - Metabolism as an early predictor of DPSCs aging
Dannie Macrin, Ammar Alghadeer, Yan Ting Zhao, Jason W. Miklas, Abdiasis M. Hussein, Damien Detraux, Aaron M. Robitaille, Anup Madan, Randall T. Moon, Yuliang Wang, Arikketh Devi, Julie Mathieu, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of platelet lysate in culture of PDLSCs: anin vitrocomparative study
Duaa A. Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Raghda B. Barham, Nidaa A. Ababneh, Diana A. Shahin, Abdallah A. Al-oweidi, Hanan D. Jafar, Mazin A. Al-Salihi, Abdalla S. Awidi
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7465. CrossRef - Progress in the use of dental pulp stem cells in regenerative medicine
Eduardo Anitua, María Troya, Mar Zalduendo
Cytotherapy.2018; 20(4): 479. CrossRef - Identification of a novel heterozygous mutation of ACAN in a Korean family with proportionate short stature
Yoo-Mi Kim, Chong Kun Cheon, Han Hyuk Lim, Han-Wook Yoo
Journal of Genetic Medicine.2018; 15(2): 102. CrossRef - Conditioned medium from relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients reduces the expression and release of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS-gingivalis in THP-1 and MO3.13 cell lines
Patrizia Ballerini, Francesca Diomede, Nicola Petragnani, Simona Cicchitti, Ilaria Merciaro, Marcos F.X.B. Cavalcanti, Oriana Trubiani
Cytokine.2017; 96: 261. CrossRef
-
2,237
View
-
19
Download
-
16
Crossref
-
Surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canals of maxillary incisors
-
Ji-Hyun Jang, Jung-Min Lee, Jin-Kyu Yi, Sung-Baik Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):79-84. Published online October 10, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.79
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This case report presents surgical endodontic management outcomes of maxillary incisors that were infected via the lateral canals. Two cases are presented in which endodontically-treated maxillary central incisors had sustained lateral canal infections. A surgical endodontic treatment was performed on both teeth. Flap elevation revealed vertical bone destruction along the root surface and infected lateral canals, and microscopy revealed that the lateral canals were the origin of the lesions. After the infected lateral canals were surgically managed, both teeth were asymptomatic and labial fistulas were resolved. There were no clinical or radiographic signs of surgical endodontic management failure at follow-up visits. This case report highlights the clinical significance and surgical endodontic management of infected lateral canal of maxillary incisor. It is important to be aware of root canal anatomy variability in maxillary incisors. Maxillary central incisors infected via the lateral canal can be successfully managed by surgical endodontic treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Surgical Management of Radicular Cyst with Platelet-rich Fibrin Placement followed by Nonvital Bleaching of a Discolored Maxillary Left Central Incisor (21)
Sagarika Sortey, Gautam Badole, Pratima Shenoi, Rajesh Kubde, Shriya Shahu, Ankita Ramteke, Varsha Uttarwar
Bharati Vidyapeeth Journal of Dentistry and Allied Sciences.2025; 2(1): 31. CrossRef - Apical Surgery of a Maxillary Left Central Tooth Using NeoPutty After Retreatment Failure: A Case Report
Sajedeh Namaei Ghasemi, Zakieh Kheradmand, Siavash Moushekhian, Zeinab Ghasemi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cone Beam Computed Tomography as a Diagnostic Tool in the Diagnosis of an Iatrogenic Root Defect of a Root Canal Treated Maxillary Central Incisor with Periapical Lesion and Its Management by Re-apicectomy
Swathi Aravelli, Uday Kumar, Gunnam Sai Nishitha, K. Mallika Yadav, P. Sivaram, Nimeshika Ramachandruni
Bharati Vidyapeeth Journal of Dentistry and Allied Sciences.2025; 2(4): 155. CrossRef - On the Causes of Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Findings From Endodontic Microsurgery: A Case Report
Mateo José Pesántez-Ibarra, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco, Jeimmy Katherine Molina-Barrera, Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Rafael Fernández-Grisales
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert consensus on difficulty assessment of endodontic therapy
Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Jingping Liang, Junqi Ling, Zhuan Bian, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Xinmei Chen, Jiyao Li, Ling Ye, Lei Cheng, Xin Xu, Tao Hu, Hongkun Wu, Bin Guo, Qin Su, Zhi Chen, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Zhen
International Journal of Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical endodontic treatment of maxillary incisors: Case report
Moazzy I. Almansour
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resective and Regenerative Approach for an Unresolved Periapical Lesion: A Surgical Case Report With 24-Month Follow-Up
Anchu R Thomas, Melwin Mathew, Sunil K Nettemu, Anoop Mayya
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An in vitro endodontic model to quantify the accessory canal filling potential of the vertical and lateral condensation techniques
Thomas Gerhard Wolf, Louisa Willems, Benjamín Briseño‐Marroquín
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(2): 245. CrossRef - Application of a new system for classifying root and canal anatomy in studies involving micro‐computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography: Explanation and elaboration
H. M. A. Ahmed, N. Ibrahim, N. S. Mohamad, P. Nambiar, R. F. Muhammad, M. Yusoff, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1056. CrossRef - German Dentists’ Preferences for the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jonas Conrad, Jan Retelsdorf, Sameh Attia, Christof Dörfer, Mohamed Mekhemar
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7447. CrossRef - Surgical management of an accessory canal in a maxillary premolar: a case report
Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A new system for classifying accessory canal morphology
H. M. A. Ahmed, P. Neelakantan, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 164. CrossRef - Effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and surgical endodontic treatment on the bacterial load reduction and periapical lesion healing. Three years follow up
Aguinaldo S. Garcez, Julio G. Arantes-Neto, Debora P. Sellera, Eduardo Rodrigues Fregnani
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2015; 12(4): 575. CrossRef
-
1,735
View
-
14
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Clinical management of a fused upper premolar with supernumerary tooth: a case report
-
Kyu-Min Cho, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang-Hyuk Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):319-323. Published online July 17, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.319
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
In dentistry, the term 'fusion' is used to describe a developmental disorder of dental hard tissues. In the permanent dentition, fusion of a normal tooth and a supernumerary tooth usually involves the incisors or canines. However, a few cases of fusion involving premolars have also been reported to date. We present a rare case in which fusion of the maxillary left second premolar and a supernumerary tooth in a 13-year-old girl was diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT, Alphard-3030, Asahi Roentgen Ind. Co., Ltd.). The tooth was bicuspidized after routine nonsurgical root canal treatment, and the separated teeth underwent appropriate restoration procedures. The second premolar and supernumerary tooth remained asymptomatic without any signs of inflammation after a follow-up period of 9 years. Identification of anatomical anomalies is important for treatment in cases involving fusion with supernumerary tooth, and therefore the microscopic examinations and CBCT are essential for the diagnosis. Fused teeth can be effectively managed by the comprehensive treatment which includes both endodontic and periodontal procedures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
Tatsuya Akitomo, Satoru Kusaka, Momoko Usuda, Mariko Kametani, Ami Kaneki, Taku Nishimura, Masashi Ogawa, Chieko Mitsuhata, Ryota Nomura
Children.2023; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Malformed Teeth and Their Endodontic Implications
Annapoorna Annapoorna, Manjunatha M, Shubhashini N, Swetha H. B.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(04): 245. CrossRef - Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
Gautam P. Badole, Pratima R. Shenoi, Ameya Parlikar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Common dental diseases in children and malocclusion
Jing Zou, Mingmei Meng, Clarice S Law, Yale Rao, Xuedong Zhou
International Journal of Oral Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Dilacerated Maxillary Central Incisor fused to a Supernumerary Tooth using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An Unusual Clinical Presentation
Thilla S Vinothkumar, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy, Ganesh Arathi, Sathishkumar Ramkumar, Gnanasekaran Felsypremila
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2017; 18(6): 522. CrossRef - Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report
Miguel Agostinho Beco Pinto Cardoso, Rita Brandão Noites, Miguel André Duarte Martins, Manuel Pedro da Fonseca Paulo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 148. CrossRef
-
1,844
View
-
20
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Colorimetric comparison of single layered dental composite with double layered dental composite
-
Young-Sang Song, Ja-Hyun Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):84-89. Published online May 18, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.84
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study analyzed the difference in color caused by different thickness in enamel layer of composite resins when applied with single and layering placement technique, and evaluated if the results agreed with the shade guide from the manufacturers to verify reliability of the color matching process of the manufacturers.
Materials and Methods
For single composite resin samples, 6 mm diameter and 4 mm thickness cylindrical samples were fabricated using Ceram-X mono (DENTSPLY DeTrey) and CIE L*a*b* values were measured with spectrophotometer. Same process was done for layering composite resin samples, making 3 dentinal shade samples, 4 mm thickness, for each shade using Ceram-X duo (DENTSPLY DeTrey) and enamel shade resins were layered in 2 mm thickness and CIE L*a*b* values were measured. These samples were ground to 0.2 mm thickness each time, and CIE L*a*b* values were measured to 1 mm thickness of enamel shade resin.
Results
Color difference (ΔE*) between single and layering composite resin was 1.37 minimum and 10.53 maximum when layering thicknesses were between 1 mm and 2 mm and 6 out of 10 same shade groups suggested by manufacturer showed remarkable color difference at any thickness (ΔE* > 3.3).
Conclusion
When using Ceram-X mono and duo for composite resin restoration, following the manufacturer's instructions for choosing the shade is not appropriate, and more accurate information for Ceram-X duo is needed on the variation and expression of the shades depending on the thickness of the enamel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Improvement of mechanical strength and water repellency of Hanji (traditional Korean paper) through acetylation in supercritical CO2
Seungmok Shin, Hwi-Sung Lee, Hee Suk Woo, Mulugeta G. Aregay, Tae Jun Yoon, Youn-Woo Lee
The Journal of Supercritical Fluids.2022; 190: 105735. CrossRef - Color Change in Tooth Induced by Various Calcium Silicate-Based Pulp-Capping Materials
Jiyoon Jeon, Namki Choi, Seonmi Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(3): 280. CrossRef
-
961
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Bonding efficacy of cured or uncured dentin adhesives in indirect resin
-
Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):490-497. Published online November 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.490
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This study examined the effect of the uncured dentin adhesives on the bond interface between the resin inlay and dentin.
Materials and Methods
Dentin surface was exposed in 24 extracted human molars and the teeth were assigned to indirect and direct resin restoration group. For indirect resin groups, exposed dentin surfaces were temporized with provisional resin. The provisional restoration was removed after 1 wk and the teeth were divided further into 4 groups which used dentin adhesives (OptiBond FL, Kerr; One-Step, Bisco) with or without light-curing, respectively (Group OB-C, OB-NC, OS-C and OS-NC). Pre-fabricated resin blocks were cemented on the entire surfaces with resin cement. For the direct resin restoration groups, the dentin surfaces were treated with dentin adhesives (Group OB-D and OS-D), followed by restoring composite resin. After 24 hr, the teeth were assigned to microtensile bond strength (µTBS) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), respectively.
Results
The indirect resin restoration groups showed a lower µTBS than the direct resin restoration groups. The µTBS values of the light cured dentin adhesive groups were higher than those of the uncured dentin adhesive groups (p < 0.05). CLSM analysis of the light cured dentin adhesive groups revealed definite and homogenous hybrid layers. However, the uncured dentin adhesive groups showed uncertain or even no hybrid layer.
Conclusions
Light-curing of the dentin adhesive prior to the application of the cementing material in luting a resin inlay to dentin resulted in definite, homogenous hybrid layer formation, which may improve the bond strength.
-
The effects of short-term application of calcium hydroxide on dentin fracture strength
-
Eun-Jung Shin, Yeong-Joon Park, Bin-Na Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):425-430. Published online September 30, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.425
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
-
Objectives
This in vitro study investigated whether short-term application of calcium hydroxide in the root canal system for 1 and 4 wk affects the fracture strength of human permanent teeth.
Materials and Methods
Thirty two mature human single rooted mandibular premolars in similar size and dentin thickness without decay or restorations were hand and rotary instrumented and 16 teeth vertically packed with calcium hydroxide paste and sealed coronally with caviton to imitate the endodontic procedure and the other 16 teeth was left empty as a control group. The apicies of all the samples were sealed with resin, submerged in normal saline and put in a storage box at 37℃ to mimic the oral environment. After 1 and 4 wk, 8 samples out of 16 samples from each group were removed from the storage box and fracture strength test was performed. The maximum load required to fracture the samples was recorded and data were analysed statistically by the two way ANOVA test at 5% significance level.
Results
The mean fracture strengths of two groups after 1 wk and 4 wk were similar. The intracanal placement of calcium hydroxide weakened the fracture strength of teeth by 8.2% after 4 wk: an average of 39.23 MPa for no treatment group and 36.01 MPa for CH group. However there was no statistically significant difference between experimental groups and between time intervals.
Conclusions
These results suggest that short term calcium hydroxide application is available during endodontic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of niobium pentoxide incorporated calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament on fracture resistance of root canal dentin
Nadimpalli Teja Varma, Venkatappan Sujatha, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(12): 1211. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide as an Intracanal Medication on Dentine Fracture Resistance: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Chayanit Sunlakawit, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Natchalee Srimaneekarn, Sittichoke Osiri
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(12): 1714. CrossRef
-
3,077
View
-
23
Download
-
2
Crossref
|