-
Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA in vivo
-
Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e17. Published online February 25, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
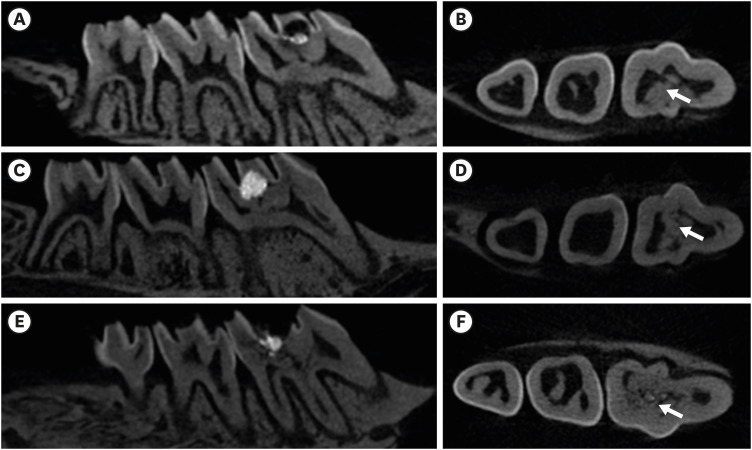
In recent in vitro study, it was reported that osteostatin (OST) has an odontogenic effect and synergistic effect with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) in human dental pulp cells. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate whether OST has a synergistic effect with MTA on hard tissue formation in vivo. Materials and MethodsThirty-two maxillary molars of Spraque-Dawley rats were used in this study. An occlusal cavity was prepared and the exposed pulps were randomly divided into 3 groups: group 1 (control; ProRoot MTA), group 2 (OST 100 μM + ProRoot MTA), group 3 (OST 10 mM + ProRoot MTA). Exposed pulps were capped with each material and cavities were restored with resin modified glass ionomer. The animals were sacrificed after 4 weeks. All harvested teeth were scanned with micro-computed tomography (CT). The samples were prepared and hard tissue formation was evaluated histologically. For immunohistochemical analysis, the specimens were sectioned and incubated with primary antibodies against dentin sialoprotein (DSP). ResultsIn the micro-CT analysis, it is revealed that OST with ProRoot MTA groups showed more mineralized bridge than the control (p < 0.05). In the H&E staining, it is showed that more quantity of the mineralized dentin bridge was formed in the OST with ProRoot MTA group compared to the control (p < 0.05). In all groups, DSP was expressed in newly formed reparative dentin area. ConclusionsOST can be a supplementary pulp capping material when used with MTA to make synergistic effect in hard tissue formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Biocompatibility and pro-mineralization effects of premixed calcium silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro and in vivo study
Nyein Chan KO, Sonoko NODA, Yamato OKADA, Kento TAZAWA, Nobuyuki KAWASHIMA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 729. CrossRef - Osteostatin, a peptide for the future treatment of musculoskeletal diseases
Daniel Lozano, Arancha R. Gortazar, Sergio Portal-Núñez
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 223: 116177. CrossRef - Comparison of bioactive material failure rates in vital pulp treatment of permanent matured teeth – a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Péter Komora, Orsolya Vámos, Noémi Gede, Péter Hegyi, Kata Kelemen, Adél Galvács, Gábor Varga, Beáta Kerémi, János Vág
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hard tissue formation in pulpotomized primary teeth in dogs with nanomaterials MCM-48 and MCM-48/hydroxyapatite: an in vivo animal study
Sahar Talebi, Nosrat Nourbakhsh, Ardeshir Talebi, Amir Abbas Nourbakhsh, Abbas Haghighat, Maziar Manshayi, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi, Razieh Karimi, Rahman Nazeri, Kenneth J.D. Mackenzie
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reparative Mineralized Tissue Characterization by Different Bioactive Direct Pulp-capping Agents
Mrunal Shinde, Varsha Pandit, Sarita Singh, Aniket Jadhav, Sarah Marium, Smita Patil
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Effects of barium titanate on the dielectric constant, radiopacity, and biological properties of tricalcium silicate-based bioceramics
Yoorina CHOI, Yun-Chan HWANG, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 55. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - A Breakthrough in the Era of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements: A Critical Review
Payal S Chaudhari, Manoj G Chandak, Akshay A Jaiswal, Nikhil P Mankar, Priyanka Paul
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef
-
251
View
-
8
Download
-
9
Web of Science
-
11
Crossref
-
Oral manifestation and root canal therapy of the patient with mucopolysaccharidosis
-
Ji-Hye Yoon, Hyo-Il Lee, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Bin-Na Lee, Won-Mann Oh
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e14. Published online April 4, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e14
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency in enzymes that participate in the degradation of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) such as heparin sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Left untreated, patients show progressive mental and physical deterioration due to deposition of GAGs in organs. Death often occurs due to cardiac or respiratory failure before patients reach their early twenties. MPS has several oral and dental manifestations. An enlarged head, short neck, and open mouth associated with a large tongue are major characteristics of MPS patients. Dental complications can be severe, including unerupted dentition, dentigerous cyst-like follicles, malocclusions, condylar defects, and gingival hyperplasia. A 21-year-old female patient with MPS was described in this article, with special emphasis on oral manifestations and dental treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pediatric Interventions in a Sanfilippo Syndrome Patient Under General Anesthesia: A Case Report
Ahmad Al Malak, Hassan Issawi, Mohammad Hassoun, Mohammad Al Halabi, Darko Macan
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioural disorders and sleep problems in Sanfilippo syndrome: overlaps with some other conditions and importance indications
Karolina Wiśniewska, Jakub Wolski, Paulina Anikiej-Wiczenbach, Magdalena Żabińska, Grzegorz Węgrzyn, Karolina Pierzynowska
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sanfilippo syndrome: consensus guidelines for clinical care
Nicole Muschol, Roberto Giugliani, Simon A. Jones, Joseph Muenzer, Nicholas J. C. Smith, Chester B. Whitley, Megan Donnell, Elise Drake, Kristina Elvidge, Lisa Melton, Cara O’Neill
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Manifestaciones bucales de pacientes con mucopolisacaridosis. Serie de casos
Andrea Verónica Ríos, Mariana Llorensi
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
237
View
-
3
Download
-
4
Crossref
|