-
Physicochemical properties, cytotoxicity and penetration into dentinal tubules of sodium hypochlorite with and without surfactants
-
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Isadora Barbieri, Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Ana Paula Ramos, Gisele Faria
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e47. Published online September 10, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e47
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
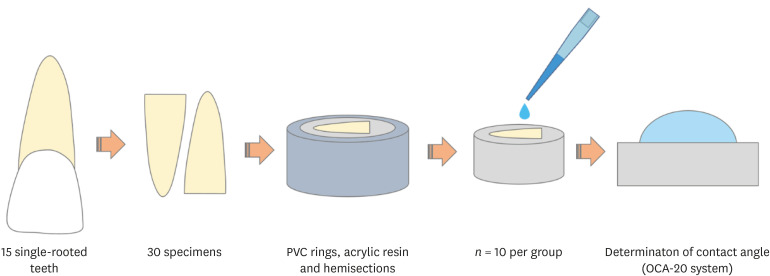
The aim of this study was to assess the physicochemical properties, cytotoxicity and penetration into dentinal tubules of ChlorCid™ Surf (3% sodium hypochlorite [NaOCl] with surfactant) in comparison to ChlorCid™ (3% NaOCl without surfactant). Materials and MethodsThe physicochemical properties evaluated were pH, surface tension, free available chlorine (FAC) and contact angle. Cytotoxicity was evaluated in L929 fibroblasts exposed to the solutions by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide and neutral red assays. Assessment of penetration into dentinal tubules was performed by staining single-rooted permanent human teeth with crystal violet (n = 9), which were irrigated with the solutions and analyzed in cervical, middle and apical segments. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's post-test, 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post-test or t-test (α = 0.05). ResultsChlorCid™ Surf and ChlorCid™ FAC values were close to those indicated by the manufacturer. ChlorCid™ Surf showed lower surface tension and contact angle on dentin, and higher pH than ChlorCid™ (p < 0.05). The penetration of ChlorCid™ Surf was higher in cervical and middle segments, compared with ChlorCid™ (p < 0.05). There was no difference in irrigant cytotoxicity (p > 0.05). ConclusionsChlorCid™ Surf showed lower surface tension, lower contact angle on root canal dentin, higher penetration into dentinal tubules and more alkaline pH, compared with ChlorCid™. However, both solutions showed similar cytotoxicity and FAC content.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of penetration enhancers on the performance of irrigants for root canal disinfection
Yi Luo, Runze Liu, Pei Liu, Mengting Duan, Wei Fan, Bing Fan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical and Biological Properties of the “All-In-One” Endodontic Irrigant Triton
Jesus Aranda, Elda Olivia Nobre de Souza, Arturo Javier Aranda Garcia, Renato de Toledo Leonardo, Ana Paula Ramos, Giampiero Rossi-Fedele, Gisele Faria
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of post space disinfection protocols on the push-out bond strength of fiber posts luted with self-adhesive cement
Satheesh B. Haralur, Salem Ali Alqahtani, Khalid Salem Alqahtani, Mohammed A. Al-Qarni, Saeed M. AlQahtani
AIP Advances.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research methods assessing sodium hypochlorite cytotoxicity: A scoping review
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Luana Raphael da Silva, Gisele Faria
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23060. CrossRef - Amelioration in the sodium hypochlorite as root canal irrigant – A review
Preety Sehrawat
International Dental Journal of Student's Research.2024; 12(2): 65. CrossRef - Sonic-assisted antibacterial photodynamic therapy: a strategy for enhancing lateral canal disinfection
Yanhuang Wang, Lishan Lei, Jing Huang, Zhiyu Cai, Xiaojing Huang
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Contact Angle and Depth of Penetration of Sodium Hypochlorite With Various Surfactants: An In Vitro Study
Shubhashini N, Krithika D, Akhilesh Gowda , Shruthi Nagaraja , Rhea S Mathew, Nivaskumar G A, Vinaychandra R
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, and hypochlorous acid on dentinal surfaces infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Aysenur Oncu, Berkan Celikten, Betül Aydın, Gulin Amasya, Erkan Tuncay, Gamze Guney Eskiler, Leyla Açık, Fatma Semra Sevimay
Microscopy Research and Technique.2024; 87(9): 2094. CrossRef - Advances in the Role of Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigant in Chemical Preparation of Root Canal Treatment
Chen Cai, Xuan Chen, Yang Li, Qianzhou Jiang, Yeliz Guven
BioMed Research International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of sodium hypochlorite-based formulations on the adhesion interface after fiber post cementation
Joatan Lucas de Sousa Gomes COSTA, Tatiane Miranda MANZOLI, João Felipe BESEGATO, Joissi Ferrari ZANIBONI, Eliane Cristina Gulin DE OLIVEIRA, Lucas David GALVANI, Andréa Abi Rached DANTAS, Luis Geraldo VAZ, Milton Carlos KUGA
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 878. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and penetration into dentinal tubules of calcium hypochlorite with surfactants
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Julia da Silva Toledo, Ana Paula Ramos, Gisele Faria
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 1. CrossRef
-
2,465
View
-
32
Download
-
11
Crossref
|