-
Effects of the cathepsin K inhibitor with mineral trioxide aggregate cements on osteoclastic activity
-
Hee-Sun Kim, Soojung Kim, Hyunjung Ko, Minju Song, Miri Kim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e17. Published online April 23, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
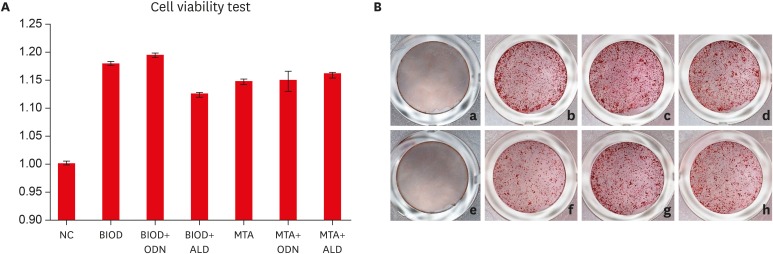
Root resorption is an unexpected complication after replantation procedures. Combining anti-osteoclastic medicaments with retrograde root filling materials may avert this resorptive activity. The purpose of this study was to assess effects of a cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cements on osteoclastic activity. MethodsMC3T3-E1 cells were cultured for biocompatibility analyses. RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in the presence of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B and lipopolysaccharide, followed by treatment with Biodentine (BIOD) or ProRoot MTA with or without medicaments (Odanacatib [ODN], a cathepsin inhibitor and alendronate, a bisphosphonate). After drug treatment, the cell counting kit-8 assay and Alizarin red staining were performed to evaluate biocompatibility in MC3T3-E1 cells. Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed in RAW 264.7 cells to determine the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's post hoc test (p < 0.05). ResultsBiocompatibility results showed that there were no significant differences among any of the groups. RAW 264.7 cells treated with BIOD and ODN showed the lowest levels of TNF-α and PGE2. Treatments with BIOD + ODN were more potent suppressors of inflammatory cytokine expression (p < 0.05). ConclusionThe cathepsin K inhibitor with calcium silicate-based cement inhibits osteoclastic activity. This may have clinical application in preventing inflammatory root resorption in replanted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Root-filling materials for endodontic surgery: biological and clinical aspects
Andreas Koutroulis, Vasileios Kapralos, Dag Ørstavik, Pia Titterud Sunde
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2024; 11: 115. CrossRef - Effect of intra‐alveolar delivery of Frondoside A on inflammatory response of delayed tooth replantation
Lan Herr, Ju Ri Ye, Sang Wook Kang, Sang Tae Ro, Yong Kwon Chae, Ko Eun Lee, Mi Sun Kim, Myeong Kwan Jih, Chunui Lee, Sung Chul Choi, Ok Hyung Nam
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(2): 178. CrossRef - Bone-targeting PLGA derived lipid drug delivery system ameliorates bone loss in osteoporotic ovariectomized rats
Youyun Zeng, Yiding Shen, Shuyi Wu, Lei Cai, Zhen Wang, Kexin Cai, Jiating Shen, Kendrick Hii Ru Yie, Hualin Zhang, Lihua Xu, Jinsong Liu
Materials & Design.2022; 221: 110967. CrossRef
-
1,177
View
-
8
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
C-shaped root canals of mandibular second molars in a Korean population: a CBCT analysis
-
Hee-Sun Kim, Daun Jung, Ho Lee, Yoon-Sic Han, Sohee Oh, Hye-Young Sim
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
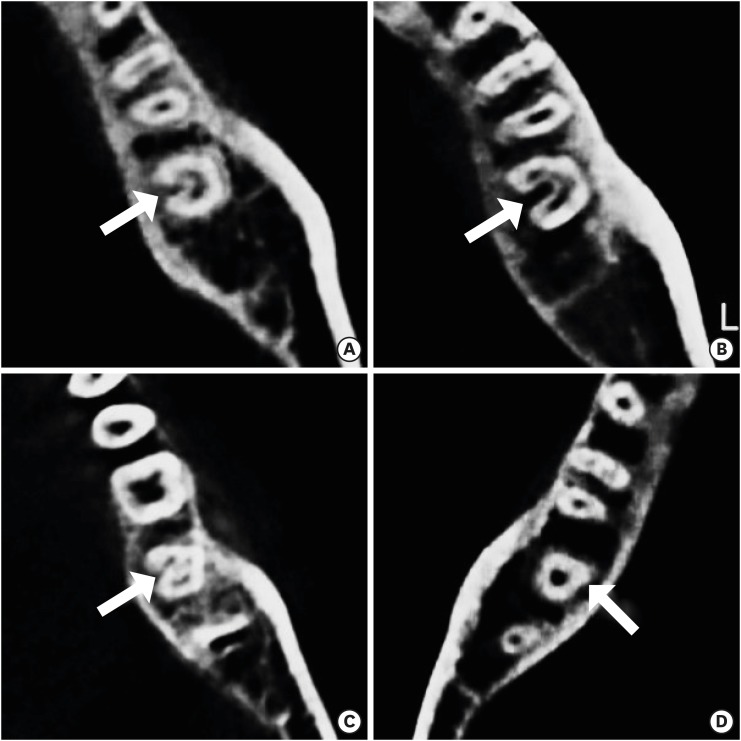
The purpose of this study was to investigate the C-shaped root canal anatomy of mandibular second molars in a Korean population. Materials and MethodsA total of 542 teeth were evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The canal shapes were classified according to a modified version of Melton's method at the level where the pulp chamber floor became discernible. ResultsOf the 542 mandibular second molars, 215 (39.8%) had C-shaped canals, 330 (53%) had 3 canals, 17 (3.3%) had 2 canals, 12 (2.2%) had 4 canals, and 8 (1.7%) had 1 canal. The prevalence of C-shaped canals was 47.8% in females and 28.4% in males. Seventy-seven percent of the C-shaped canals showed a bilateral appearance. The prevalence of C-shaped canals showed no difference according to age or tooth position. Most teeth with a C-shaped canal system presented Melton's type II (45.6%) and type III (32.1%) configurations. ConclusionsThere was a high prevalence of C-shaped canals in the mandibular second molars of the Korean population studied. CBCT is expected to be useful for endodontic diagnosis and treatment planning of mandibular second molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of mandibular and maxillary second molar root canal anatomy in a Turkish subpopulation using CBCT: comparison of Briseno-Marroquin and Vertucci classifications
Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, İpek Öreroğlu, Kemal Çağlar, Kader Cesur Aydin
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e18. CrossRef - A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
Jacob John, Wei Cheong Ngeow, Ting-Chun Shen, Lih-Jyh Fuh, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Yen-Wen Shen, Jui-Ting Hsu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of c-shaped canal morphology in premolar and molar teeth assessed by cone-beam computed tomography: systematic review and meta-analysis
Faezeh Yousefi, Younes Mohammadi, Elham Shokri
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frequency of C-Shaped Root Canals in Permanent Mandibular Second Molars in a Sample of Pakistani Population using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Syed Nabeel Ahmed, Muhammad Mansoor Majeed, Sakina Kazmi, Muhammad Omar Ansari
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2024; : 109. CrossRef - ANÁLISE DAS VARIAÇÕES ANATÔMICAS DE CANAIS C-SHAPED NOS MOLARES INFERIORES: UMA REVISÃO INTEGRATIVA DA LITERATURA
Larissa Eulália Pereira, Thayana Karla Guerra Lira dos Santos
Revista Contemporânea.2024; 4(5): e4264. CrossRef - External Validation of the Effect of the Combined Use of Object Detection for the Classification of the C-Shaped Canal Configuration of the Mandibular Second Molar in Panoramic Radiographs: A Multicenter Study
Sujin Yang, Kee-Deog Kim, Yoshitaka Kise, Michihito Nozawa, Mizuho Mori, Natsuho Takata, Akitoshi Katsumata, Yoshiko Ariji, Wonse Park, Eiichiro Ariji
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 627. CrossRef - A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of C‐Shaped Canal Configuration in Maxillary Molars Among an Iranian Population
Nafiseh Nikkerdar, Mohammad Moslehi, Amin Golshah, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Egyptian subpopulation: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Mohammed abou El Seoud, Shaimaa Mohamed Abu el Sadat, Nawar Naguib Nawar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al‑Zubaidi, Abdulmjeed S. Enizy, Ahmed A. Madfa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in kuwaiti sub-population
AbdullahJassim Alenezi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, MazenA Aldosimani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 283. CrossRef - Prevalence and morphology of C‐shaped and non‐C‐shaped root canal systems in mandibular second molars
T Fenelon, P Parashos
Australian Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars of a selected patient group using cone beam computed tomography: prevalence, configuration and radicular groove types
Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan, Güzide Pelin Sezgin
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 949. CrossRef - Prevalência estimada de canais “C- Shaped”: Uma revisão sistemática e meta-análise
Natália Pereira da Silva Falcão, Sandro Junio de Oliveira Tavares, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Katherine Azevedo Batistela Rodrigues Thuller, Leonardo dos Santos Antunes, Estefano Borgo Sarmento, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azevedo, Cinthya Cristina Gomes, Ca
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 91. CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Clinical and radiological assessment of the anatomical and topographic structure of the root canals of teeth in patients of different age groups
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, O.A. Boriskina, I.S. Berkutova, V.A. Venediktova, R.R. Saltovets
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(5): 32. CrossRef
-
1,848
View
-
13
Download
-
18
Crossref
|