-
Influence of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on debris extrusion and sealer penetration
-
Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Hakan Karaaslan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Bahar Özçelik
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e2. Published online December 22, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e2
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
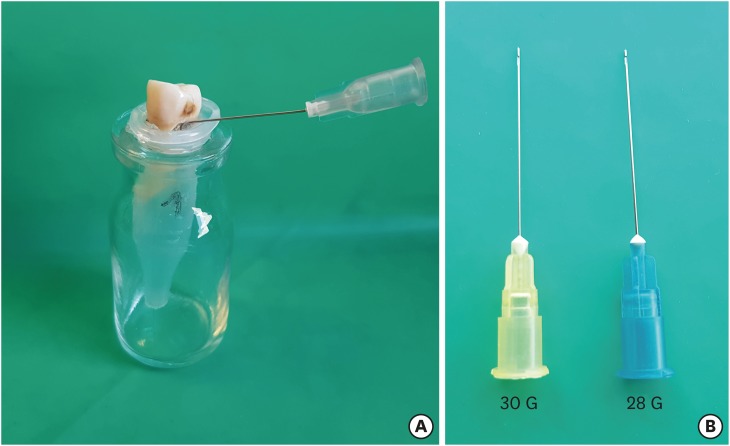
To determine the effect of size and insertion depth of irrigation needle on the amount of apical extruded debris and the amount of penetration depth of sealer using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Materials and MethodsTwenty maxillary premolars were assigned to 2 groups (n = 10), according to the size of needle tip, 28 G or 30 G. Buccal roots of samples were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 1 mm short of the working length (WL), while palatal roots were irrigated with respective needle type inserted 3 mm short of the WL. Prepared teeth were removed from the pre-weighed Eppendorf tubes. Canals were filled with F3 gutta-percha cone and rhodamine B dye-labeled AH 26 sealer. Teeth were transversally sectioned at 1 and 3 mm levels from the apex and observed under a CLSM. Eppendorf tubes were incubated to evaporate the irrigant and were weighed again. The difference between pre- and post-weights was calculated, and statistical evaluation was performed. ResultsInserting needles closer to the apex and using needles with wider diameters were associated with significantly more debris extrusion (p < 0.05). The position of needles and level of sections had statistically significant effects on sealer penetration depth (p < 0.05 for both). ConclusionsFollowing preparation, inserting narrower needles compatible with the final apical diameter of the prepared root canal at 3 mm short of WL during final irrigation might prevent debris extrusion and improve sealer penetration in the apical third.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Preliminary insights: exploring irrigation practices during endodontic treatment among general dental practitioners in Malaysia
Kai Qi Chiew, Xin Ni Lim, Shekhar Bhatia, Naveen Chhabra
British Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency of diode laser in control of post-endodontic pain: a randomized controlled trial
Hend H. Ismail, Maram Obeid, Ehab Hassanien
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2797. CrossRef - Endodontic management of an aberrant germinated composite odontome: A case report
Ankit Arora, Kavina Desai, Sonali Kapoor, Seema Gajera
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 684. CrossRef - Potentials of 3D-Modeling in the Preclinical Stage of Root Needle Research
Aleksandr V. Kuligin, Larisa N. Kazakova, Oksana S. Tereshchuk, Vadim V. Bokov
I.P. Pavlov Russian Medical Biological Herald.2022; 30(1): 95. CrossRef - Effect of root canal geometry and needle type on apical extrusion of irrigant: an ex vivo study
Büşra SERÇE FİKİRLİ, Bülent ALTUNKAYNAK, Güven KAYAOĞLU
Acta Odontologica Turcica.2022; 39(3): 58. CrossRef - An in vitro radiological evaluation of irrigant penetration in the root canals using three different irrigation systems: Waterpik WP-100 device, passive irrigation, and manual dynamic irrigation systems
Suragani Hemalatha, Archana Srinivasan, A Srirekha, Lekha Santhosh, C Champa, Ashwija Shetty
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 403. CrossRef - Preparation Ability of ProTaper Next and XP-endo Shaper Instruments in Isthmus-containing Root Canal System
Mustafa Sarıkahya, Tayfun Alaçam
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2021; 5(2): 28. CrossRef - Penetration depth of irrigants into root dentine after sonic, ultrasonic and photoacoustic activation
K. M. Galler, V. Grubmüller, R. Schlichting, M. Widbiller, A. Eidt, C. Schuller, M. Wölflick, K.‐A. Hiller, W. Buchalla
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(8): 1210. CrossRef
-
199
View
-
6
Download
-
8
Crossref
|