-
Biomineralization of three calcium silicate-based cements after implantation in rat subcutaneous tissue
-
Ranjdar Mahmood Talabani, Balkees Taha Garib, Reza Masaeli, Kavosh Zandsalimi, Farinaz Ketabat
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e1. Published online December 2, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
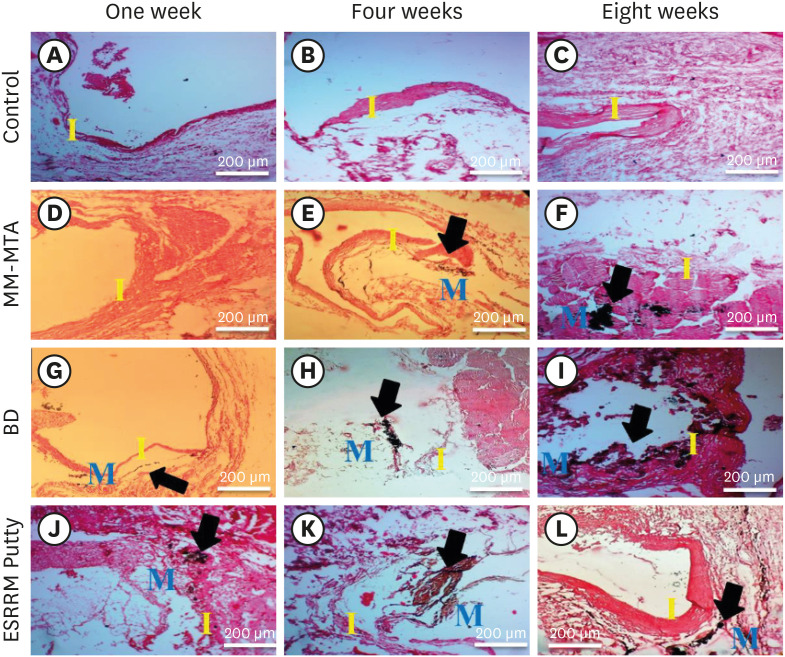
The aim of this study was to evaluate the dystrophic mineralization deposits from 3 calcium silicate-based cements (Micro-Mega mineral trioxide aggregate [MM-MTA], Biodentine [BD], and EndoSequence Root Repair Material [ESRRM] putty) over time after subcutaneous implantation into rats. Materials and MethodsForty-five silicon tubes containing the tested materials and 15 empty tubes (serving as a control group) were subcutaneously implanted into the backs of 15 Wistar rats. At 1, 4, and 8 weeks after implantation, the animals were euthanized (n = 5 animals/group), and the silicon tubes were removed with the surrounding tissues. Histopathological tissue sections were stained with von Kossa stain to assess mineralization. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDX) were also used to assess the chemical components of the surface precipitates deposited on the implant and the pattern of calcium and phosphorus distribution at the material-tissue interface. The calcium-to-phosphorus ratios were compared using the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test at a significance level of 5%. ResultsThe von Kossa staining showed that both BD and ESRRM putty induced mineralization starting at week 1; this mineralization increased further until the end of the study. In contrast, MM-MTA induced dystrophic calcification later, from 4 weeks onward. SEM/EDX showed no statistically significant differences in the calcium- and phosphorus-rich areas among the 3 materials at any time point (p > 0.05). ConclusionsAfter subcutaneous implantation, biomineralization of the 3-calcium silicate-based cements started early and increased over time, and all 3 tested cements generated calcium- and phosphorus-containing surface precipitates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Antibacterial, biocompatible, and mineralization‐inducing properties of calcium silicate‐based cements
Taimy Cruz Hondares, Xiaoxiao Hao, Yanfang Zhao, Yuyin Lin, Dobrawa Napierala, Janice G. Jackson, Ping Zhang
International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry.2024; 34(6): 843. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef
-
241
View
-
11
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
|