-
Disinfectant effectiveness of chlorhexidine gel compared to sodium hypochlorite: a systematic review with meta-analysis
-
Theodoro Weissheimer, Karem Paula Pinto, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Lina Naomi Hashizume, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(4):e37. Published online October 26, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
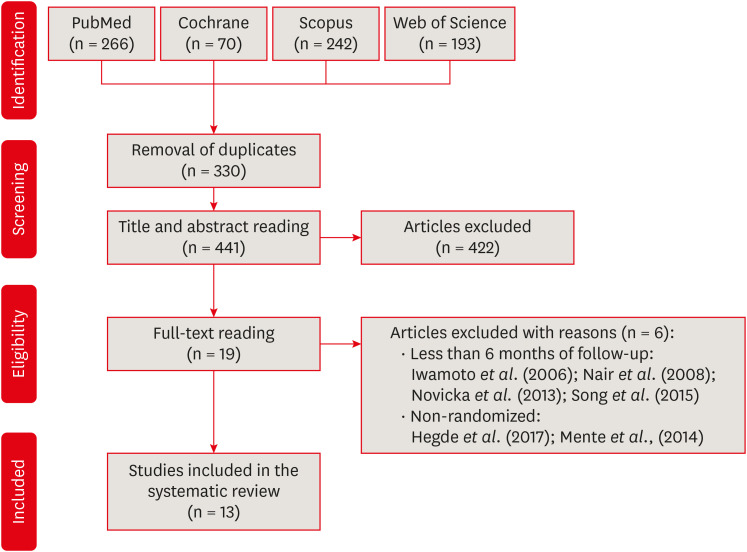
This study aimed to compare the disinfectant ability of chlorhexidine (CHX) gel and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Systematic searches were conducted from inception until December 8th, 2022 (MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and Grey Literature databases). Only randomized clinical trials were included. The revised Cochrane risk of bias tools for randomized trials were used to assess the quality of studies. Meta-analyses were performed. The overall quality of evidence was assessed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation tool. Six studies were included. Five had a low risk of bias and 1 had some concerns. Three studies assessed bacterial reduction. Two were included in the meta-analysis for bacterial reduction (mean difference, 75.03 [confidence interval, CI, −271.15, 421.22], p = 0.67; I2 = 74%); and 3 in the meta-analysis for cultivable bacteria after chemomechanical preparation (odds ratio, 1.03 [CI, 0.20, 5.31], P = 0.98; I2 = 49%). Five studies assessed endotoxin reduction. Three were included in a meta-analysis (mean difference, 20.59 [CI, −36.41, 77.59], p = 0.48; I2 = 74%). There seems to be no difference in the disinfectant ability of CHX gel and NaOCl, but further research is necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Preparing porcine lens to mimic human lens capsule
Yajing Pei, Shaofeng Han, Mingfeng Lu, Yang Yang, Ke Ma
Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery.2024; 50(9): 963. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Disinfection Protocols for Dental Impressions in Prosthodontics
Subhash Sonkesriya, Ghanshyam Gaur, Akanksha Maheshwari, Arun Kumar Ashahiya, Simran Kaur Aulakh, Amit Kumar, Bhumika Kamal Badiyani
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
-
393
View
-
18
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Shaping ability and apical debris extrusion after root canal preparation with rotary or reciprocating instruments: a micro-CT study
-
Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Sara Gomes de Moura, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Waleska Florentino Misael, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Luciana Moura Sassone
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e16. Published online February 25, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e16
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
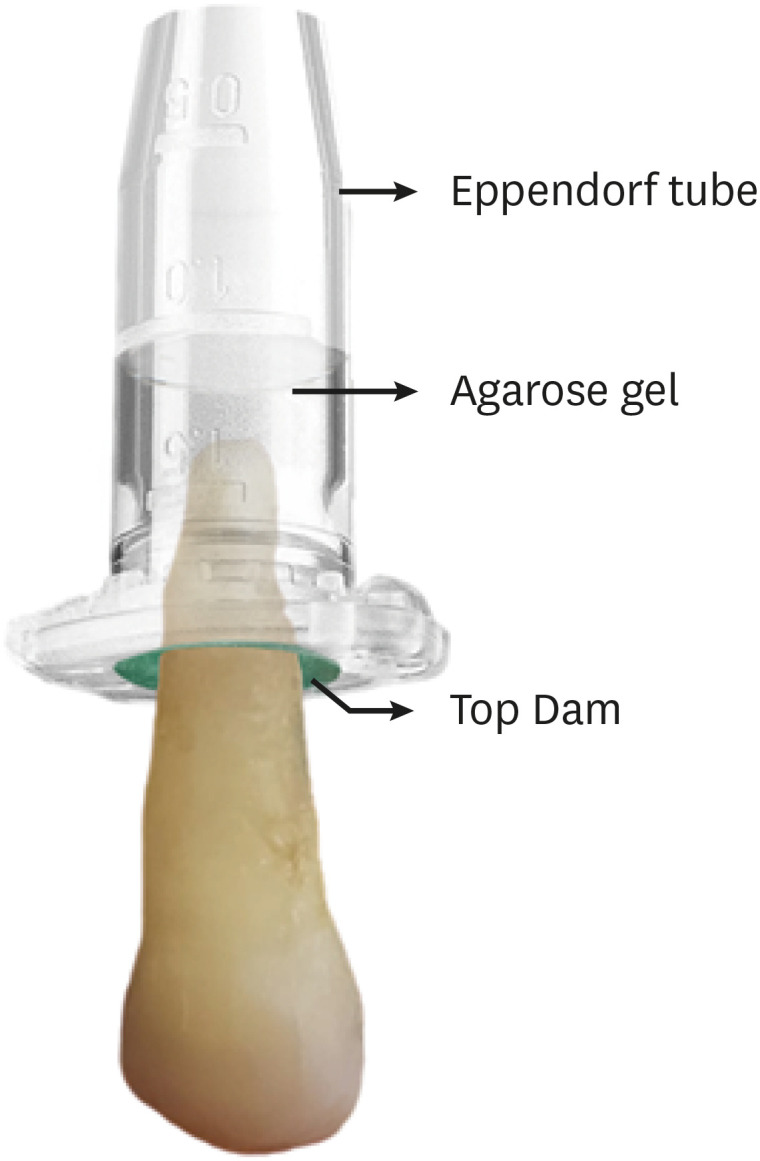
The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems and the apical extrusion of debris after root canal instrumentation. The ProTaper Universal system was used as a reference for comparison. Materials and MethodsThirty-three mandibular premolars with a single canal were scanned using micro-computed tomography and were matched into 3 groups (n = 11) according to the instrumentation system: TruShape, Reciproc Blue and ProTaper Universal. The teeth were accessed and mounted in an apparatus with agarose gel, which simulated apical resistance provided by the periapical tissue and enabled the collection of apically extruded debris. During root canal preparation, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite was used as an irrigant. The samples were scanned again after instrumentation. The percentage of unprepared area, removed dentin, and volume of apically extruded debris were analyzed. The data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test for multiple comparisons at a 5% significance level. ResultsNo significant differences in the percentage of unprepared area were observed among the systems (p > 0.05). ProTaper Universal presented a higher percentage of dentin removal than the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems (p < 0.05). The systems produced similar volumes of apically extruded debris (p > 0.05). ConclusionsAll systems caused apically extruded debris, without any significant differences among them. TruShape, Reciproc Blue, and ProTaper Universal presented similar percentages of unprepared area after root canal instrumentation; however, ProTaper Universal was associated with higher dentin removal than the other systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A quantitative comparison of apically extruded debris during root canal preparation using NiTi full-sequence rotary and single-file rotary systems: An in vitro study
Pallavi Goel, R. Vikram, R. Anithakumari, M. S. Adarsha, M. E. Sudhanva
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 235. CrossRef - Extrusion of Sodium Hypochlorite in Oval-Shaped Canals: A Comparative Study of the Potential of Four Final Agitation Approaches Employing Agarose-Embedded Mandibular First Premolars
Aalisha Parkar, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Alexander Maniangat Luke
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(10): 2748. CrossRef - Shaping Efficiency of Rotary and Reciprocating Kinematics of Engine-driven Nickel-Titanium Instruments in Moderate and Severely curved Root Canals Using Microcomputed Tomography: A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Claudiu Călin, Ana-Maria Focșăneanu, Friedrich Paulsen, Andreea C. Didilescu, Tiberiu Niță
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 907. CrossRef - Intracanal removal and apical extrusion of filling material after retreatment using rotary or reciprocating instruments: A new approach using human cadavers
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Victor O. Cortes‐Cid, Marilia F. V. Marceliano‐Alves, Andrea F. Campello, Luan F. Bastos, Ricardo T. Lopes, José F. Siqueira, Flávio R. F. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(1): 100. CrossRef - Assessment of debris extrusion on using automated irrigation device with conventional needle irrigation – An ex vivo study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Raja Kumar, Sindhu Ramesh
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 263. CrossRef - Postoperative pain perception and associated risk factors in children after continuous rotation versus reciprocating kinematics: A randomised prospective clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Dania Ibrahem Sermani, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 345. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of new reciprocating or rotary instruments with two cross‐sectional designs: An ex vivo study
Isabela G. Guedes, Renata C. V. Rodrigues, Marília F. Marceliano‐Alves, Flávio R. F. Alves, Isabela N. Rôças, José F. Siqueira
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(12): 1385. CrossRef
-
250
View
-
12
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
9
Crossref
-
Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
-
Evaldo Rodrigues, Antônio Henrique Braitt, Bruno Ferraz Galvão, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(1):60-64. Published online August 29, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.60
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Root canal anatomy is complex, and the recognition of anatomic variations could be a challenge for clinicians. This case report describes the importance of cone beam computed tomographyic (CBCT) imaging during endodontic treatment. A 23 year old woman was referred by her general dental practitioner with the chief complaint of spontaneous pain in her right posterior maxilla. From the clinical and radiographic findings, a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis was made and endodontic treatment was suggested to the patient. The patient underwent CBCT examination, and CBCT scan slices revealed seven canals: three mesiobuccal (MB1, MB2, and MB3), two distobuccal (DB1 and DB2), and two palatal (P1 and P2). Canals were successfully treated with reciprocating files and filled using single-cone filling technique. Precise knowledge of root canal morphology and its variation is important during root canal treatment. CBCT examination is an excellent tool for identifying and managing these complex root canal systems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - KONİK IŞINLI BİLGİSAYARLI TOMOGRAFİ İLE DOĞRULANMIŞ OLAĞANDIŞI ÜST BİRİNCİ BÜYÜK AZI DİŞİN ENDODONTİK TEDAVİSİ
Didem Seda Gültekin, Funda Kont Çobankara
Journal of International Dental Sciences.2025; 11(1): 46. CrossRef - An Unusual Case of Maxillary First Molar: A Case Report
Reetu Shrestha
International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT).2024; : 1330. CrossRef - Root canal therapy of maxillary first molar with seven canals diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography – a case report
Saini Rashmi, Saini V. Kumar
Tanta Dental Journal.2022; 19(3): 169. CrossRef - Four-Rooted Maxillary First Molars: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gabriel Magnucki, Sven V. K. Mietling, Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Endodontic treatment of various palatal roots in maxillary molars
Chengshi Wei, Keyi Li, Lili Shen, Guangliang Bai, Xiufen Tian
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2021; 152(12): 1044. CrossRef - Diversity of root canal morphology of maxillary first molars
Juhász Kincső-Réka, Kovács Mónika, Pop Mihai, Pop Silvia, Kerekes-Máthé Bernadette
Bulletin of Medical Sciences.2021; 94(1): 63. CrossRef - Endodontic Management of Maxillary First Molar with Seven Root Canals Diagnosed Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
Ravindranath Megha, Venkatachalam Prakash
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(1): 89. CrossRef - Endodontic management of the maxillary first molar with special root canals: A case report and review of the literature
Zhi-Hui Zhang, Hai-Lin Yao, Yan Zhang, Xiao Wang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(12): 2590. CrossRef - Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report
Prateeksha Chowdhry, Pallavi Reddy, Mamta Kaushik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of cone beam computed tomography in perplexing endodontic cases
Amandeep Kaur, Ajay Logani
Endodontology.2018; 30(2): 187. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with seven root canal systems evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography scanning
VijayReddy Venumuddala, Sridhar Moturi, SV Satish, BKalyan Chakravarthy, Sudhakar Malapati
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2017; 7(5): 297. CrossRef
-
275
View
-
2
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Push-out bond strength of a self-adhesive resin cement used as endodontic sealer
-
Eduardo Diogo Gurgel-Filho, Felipe Coelho Lima, Vicente de Paula Aragão Saboia, Tauby de Souza Coutinho-Filho, Aline de Almeida Neves, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):282-287. Published online August 20, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.282
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of the present study was to investigate the bond strength of RelyX Unicem (3M) to root canal dentin when used as an endodontic sealer. Materials and MethodsSamples of 24 single-rooted teeth were prepared with Gates Glidden drills and K3 files. After that, the roots were randomly assigned to three experimental groups (n = 8) according to the filling material, (1) AH Plus (Dentsply De Trey GmbH)/Gutta-Percha cone; (2) Epiphany SE (Pentron)/Resilon cone; (3) RelyX Unicem/Gutta-Percha cone. All roots were filled using a single cone technique associated to vertical condensation. After the filling procedures, each tooth was prepared for a push-out bond strenght test by cutting 1 mm-thick root slices. Loading was performed on a universal testing machine at a speed of 0.5 mm/min. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey test for multiple comparisons were used to compare the results among the experimental groups. ResultsEpiphany SE/Resilon showed significantly lower push-out bond strength than both AH Plus/Gutta-Percha and RelyX Unicem/Gutta-Percha (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in bond strength between AH Plus/Gutta-Percha and RelyX Unicem/Gutta-Percha (p > 0.05). ConclusionsUnder the present in vitro conditions, bond strength to root dentin promoted by RelyX Unicem was similar to AH Plus. Epiphany SE/Resilon resulted in lower bond strength values when compared to both materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In-Vitro Comparative Adhesion Evaluation of Bioceramic and Dual-Cure Resin Endodontic Sealers Using SEM, AFM, Push-Out and FTIR
Radu Marcel Chisnoiu, Marioara Moldovan, Doina Prodan, Andrea Maria Chisnoiu, Dana Hrab, Ada Gabriela Delean, Alexandrina Muntean, Doina Iulia Rotaru, Ovidiu Pastrav, Mihaela Pastrav
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(10): 4454. CrossRef - Push-out Bond Strength of Fiber Posts Cemented Using New Universal Adhesives on Etched and Nonetched Intraradicular Dentin
Hani F Ounsi, Simone Grandini, Marco Ferrari, Valentina Spicciarelli, Giacomo Corsentino, Crystal Marruganti
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2020; 21(1): 91. CrossRef - Comparison of push-out bond strength of three different obturating systems to intraradicular dentin: An In vitro study
MohammedKhwaja Moinuddin, LKarthik Prasad, Nimeshika Ramachandruni, Shekar Kamishetty, RaviChandra Cherkupalli
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(4): 631. CrossRef - The influence of methodological variables on the push‐out resistance to dislodgement of root filling materials: a meta‐regression analysis
F. M. Collares, F. F. Portella, S. B. Rodrigues, R. K. Celeste, V. C. B. Leitune, S. M. W. Samuel
International Endodontic Journal.2016; 49(9): 836. CrossRef - Effect of photon induced photoacoustic streaming (PIPS) on bond strength to dentine of two root canal filling materials
Ivana Miletić, Nicoletta Chieffi, Carlo Rengo, Marco Ferrari, Dan Nathanson, Anja Baraba
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.2016; 48(10): 951. CrossRef
-
248
View
-
2
Download
-
5
Crossref
|