-
Biological assessment of a new ready-to-use hydraulic sealer
-
Francine Benetti, João Eduardo Gomes-Filho, India Olinta de Azevedo-Queiroz, Marina Carminatti, Letícia Citelli Conti, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Sandra Helena Penha de Oliveira, Edilson Ervolino, Elói Dezan-Júnior, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e21. Published online March 24, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
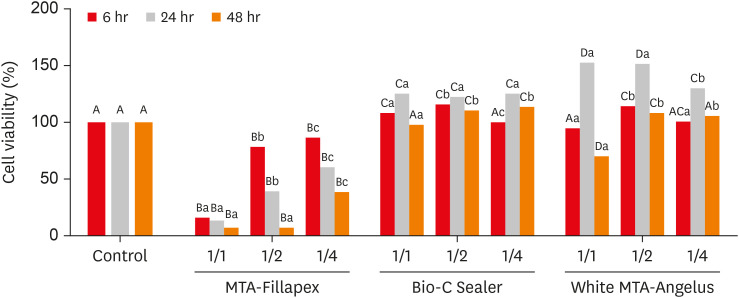
This study compared the cytotoxicity, biocompatibility, and tenascin immunolabeling of a new ready-to-use hydraulic sealer (Bio-C Sealer) with MTA-Fillapex and white MTA-Angelus. Materials and MethodsL929 fibroblasts were cultivated and exposed to undiluted and diluted material extracts. Polyethylene tubes with or without (the control) the materials were implanted into the dorsa of rats. At 7 days and 30 days, the rats were euthanized, and the specimens were prepared for analysis; inflammation and immunolabeling were measured, and statistical analysis was performed (p < 0.05). ResultsMTA-Fillapex exhibited greater cytotoxicity than the other materials at all time points (p < 0.05). The undiluted Bio-C Sealer exhibited greater cytocompatibility at 6 and 48 hours than white MTA-Angelus, with higher cell viability than in the control (p < 0.05). White MTA-Angelus displayed higher cell viability than the control at 24 hours, and the one-half dilution displayed similar results at both 6 and 48 hours (p < 0.05). At 7 days and 30 days, the groups exhibited moderate inflammation with thick fibrous capsules and mild inflammation with thin fibrous capsules, respectively (p > 0.05). At 7 days, moderate to strong immunolabeling was observed (p > 0.05). After 30 days, the control and MTA-Fillapex groups exhibited strong immunolabeling, the white MTA-Angelus group exhibited moderate immunolabeling (p > 0.05), and the Bio-C Sealer group exhibited low-to-moderate immunolabeling, differing significantly from the control (p < 0.05). ConclusionsBio-C Sealer and white MTA-Angelus exhibited greater cytocompatibility than MTA-Fillapex; all materials displayed adequate biocompatibility and induced tenascin immunolabeling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical and radiographic assessment of mineral trioxide aggregate with platelet rich fibrin as pulp capping biomaterials: a 12-month randomized trial
Rahma Ahmed Ibrahem Hafiz Abuhashema, Mona El Saied Essa, Shereen Hafez Ibrahim, Omaima Mohamed Safwat
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and bioactivity of bioceramic endodontic sealer: NeoSealer Flo
Evelin Carine Alves SILVA, Jéssica Arielli PRADELLI, Guilherme Ferreira da SILVA, Paulo Sérgio CERRI, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of photoactivation on tissue response to different dyes used in photodynamic therapy and laser ablation therapy
Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Cristiane Cantiga-Silva, Henrique Augusto Banci, Flávio Duarte Faria, Nathália Evelyn da Silva Machado, Carolina de Barros Morais Cardoso, Pedro Henrique Chaves de Oliveira, Lucas Rodrigues de Araújo Estrela, Gustavo Sivieri
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology.2024; 251: 112843. CrossRef - Bleaching effectiveness and cytotoxicity of new experimental formulation of niobium-based bleaching gel
Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Francine Benetti, Luiz Carlos Alves de Oliveira, Jadson Cláudio Belchior, Raquel Conceição Ferreira, Allyson Nogueira Moreira, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(4): 1613. CrossRef - Biological investigation of resinous endodontic sealers containing calcium hydroxide
Carlos Roberto Emerenciano Bueno, Francine Benetti, Marina Tolomei Sandoval Cury, Ana Maria Veiga Vasques, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Índia Olinta de Azevedo Queiroz, Ana Cláudia Rodrigues da Silva, Rogério de Castilho Jacinto, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, E
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0287890. CrossRef - Tricalcium silicate cement sealers
Anita Aminoshariae, Carolyn Primus, James C. Kulild
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2022; 153(8): 750. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of push-out bond strength of bioceramic and epoxy sealers after using various final irrigants: An in vitro study
Chandrasekhar Veeramachaneni, Swathi Aravelli, Sreeja Dundigalla
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(2): 145. CrossRef
-
2,367
View
-
18
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
Influence of pain-relieving therapies on inflammation and the expression of proinflammatory neuropeptides after dental bleaching treatment
-
Livia Maria Alves Valentim da Silva, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, Marjorie de Oliveira Gallinari, Francine Benetti, Vanessa Rahal, Edilson Ervolino, Sibele de Alcântara, André Luiz Fraga Briso
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e20. Published online February 28, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e20
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
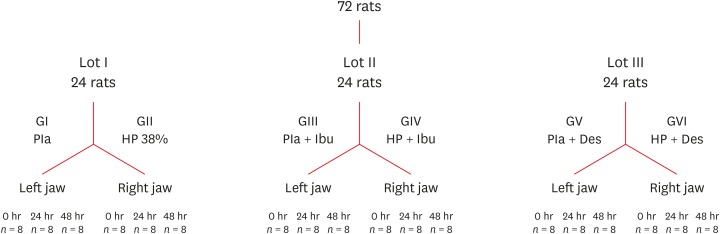
To minimize the tooth sensitivity caused by in-office bleaching, many dentists use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and topical desensitizing gels containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of these substances on inflammation and the expression of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in pulp nerve fibers. Materials and MethodsSeventy-two rats were divided into 6 groups as follows: GI, control; GII, only dental bleaching; GIII, only ibuprofen; GIV, ibuprofen administered 30 minutes before and after the bleaching treatment and every 12 hours until the analysis; GV, only topical application of a desensitizing agent; and GVI, topical application of a desensitizing agent before dental bleaching. Placebo gel was applied to the upper left jaw and the bleaching agent was applied to the upper right jaw in all groups. Subsequently, the groups were divided into 3 subgroups based on the time of analysis: 0, 24, and 48 hours after bleaching (n = 8). The rats were euthanized and the maxillae were processed and evaluated by histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses. The data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by the Dunn test (p < 0.05). ResultsIn the bleaching groups, the inflammatory process and expression of neuropeptides decreased over time. The animals in which a desensitizing agent was applied showed better results within 24 hours. ConclusionsThe use of a desensitizing agent had positive effects on inflammation and pain-related neuropeptide expression, minimizing the painful effects of dental bleaching treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effectiveness of Analgesics in Dental Whitening Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gabriella Alves Julião Costa, Caio Ferreira Freire Caetano, Ravy Jucá Farias, Diana Araújo Cunha, Dayrine Silveira de Paula, Edson Luiz Cetira Filho, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2025; 26(5): 639. CrossRef - The Use of Ozone Therapy in Combination with a Desensitizing Agent for Dentinal Tubules Occlusion: An In Vitro Study
Banna Alnufaiy
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of neurogenic inflammation in pulp repair and the techniques used for its assessment (narrative review)
Muna Sh. Ahmed, Anas F. Mahdee
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of dental bleaching on the pulp tissue: A systematic review of in vivo studies
Mariana Viana Donato, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Juliana Goto, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Francine Ben
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(6): 630. CrossRef - Role of induced nitric oxide synthases in orofacial nociception/discomfort after dental tooth bleaching with hydrogen peroxide
Marcílio Rodrigues Pinto, Kirlya Isabel da Silva Medeiros, Letícia Menezes Maia, Antonio Alexandre Coelho, Ana Paula Negreiros Nunes Alves, Caio Ferreira Freire Caetano, Karine Cestaro Mesquita, Paulo Goberlânio de Barros Silva, Fabricio Bitu Sousa
Archives of Oral Biology.2024; 161: 105937. CrossRef - Can different agents reduce the damage caused by bleaching gel to pulp tissue? A systematic review of basic research
Letícia Aparecida Silva Batista, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Luís Fernando Santos Alves Morgan, Carolina Bosso André, Thaís Yumi Suzuki, Francine Benetti
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Different Drugs with Anti-Inflamatory Potential in Prevention of Pulp Damage During the Teeth Bleaching
Miona Glisic, Andjela Milojevic, Milica Milinkovic, Marina Rankovic
Experimental and Applied Biomedical Research (EABR).2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bleaching gel volume influences hydrogen peroxide diffusion, inflammation, and the presence of nitric oxide in the pulp tissue: in vitro and in vivo model
Sibele de ALCÂNTARA, Francine BENETTI, Lívia Maria Alves Valentim da SILVA, Nathália Evelyn da Silva MACHADO, Isabela Joane Prado SILVA, Lara Maria Bueno ESTEVES, Edilson ERVOLINO, Luciano Tavares Angelo CINTRA, André Luiz Fraga BRISO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of a thermosensitive ibuprofen-loaded nanogel as smart material applied as anti-inflammatory in tooth bleaching: An in vivo study
Samara K.S.C.F. Moura, Milena L.V. dos Santos, Lucas A. do Nascimento, Mariana F.A. da Silva, Glória M. de França, Lucas M. da Costa, Aldo C. Medeiros, Raimundo F. Araújo-Júnior, Aurigena A. de Araújo, Cláudia N. Oliveira, André L. Dorini, Rejane A. de Ca
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2022; 68: 103123. CrossRef - Topical application of Otosporin® before in-office bleaching: a split mouth, triple-blind, multicenter randomized clinical trial
Michael Willian Favoreto, Laína Vochikovski, Renata Maria Oleniki Terra, Veridiana Silva Campos, Mariana Evangelista Santos, Sônia Saeger Meireles, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(3): 2555. CrossRef - A novel tooth bleaching gel based on peroxymonosulfate/polyphosphates advanced oxidation process: Effective whitening avoiding pulp damage and sensitivity
Su Yang, Baiyan Sui, Xin Liu, Jiao Sun, Jun Wang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2022; 429: 132525. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Violet LED alone or in association with bleaching gel during dental photobleaching: A Systematic Review
Bianca Rossi, Susana Morimoto, Tamara Kerber Tedesco, Sandra Ribeiro Cunha, Anna Carolina Ratto Tempestini Horliana, Karen Müller Ramalho
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 38: 102813. CrossRef
-
1,905
View
-
13
Download
-
12
Crossref
|